-
 @ 3bf0c63f:aefa459d
2025-04-25 18:55:52
@ 3bf0c63f:aefa459d
2025-04-25 18:55:52Report of how the money Jack donated to the cause in December 2022 has been misused so far.
Bounties given
March 2025
- Dhalsim: 1,110,540 - Work on Nostr wiki data processing
February 2025
- BOUNTY* NullKotlinDev: 950,480 - Twine RSS reader Nostr integration
- Dhalsim: 2,094,584 - Work on Hypothes.is Nostr fork
- Constant, Biz and J: 11,700,588 - Nostr Special Forces
January 2025
- Constant, Biz and J: 11,610,987 - Nostr Special Forces
- BOUNTY* NullKotlinDev: 843,840 - Feeder RSS reader Nostr integration
- BOUNTY* NullKotlinDev: 797,500 - ReadYou RSS reader Nostr integration
December 2024
- BOUNTY* tijl: 1,679,500 - Nostr integration into RSS readers yarr and miniflux
- Constant, Biz and J: 10,736,166 - Nostr Special Forces
- Thereza: 1,020,000 - Podcast outreach initiative
November 2024
- Constant, Biz and J: 5,422,464 - Nostr Special Forces
October 2024
- Nostrdam: 300,000 - hackathon prize
- Svetski: 5,000,000 - Latin America Nostr events contribution
- Quentin: 5,000,000 - nostrcheck.me
June 2024
- Darashi: 5,000,000 - maintaining nos.today, searchnos, search.nos.today and other experiments
- Toshiya: 5,000,000 - keeping the NIPs repo clean and other stuff
May 2024
- James: 3,500,000 - https://github.com/jamesmagoo/nostr-writer
- Yakihonne: 5,000,000 - spreading the word in Asia
- Dashu: 9,000,000 - https://github.com/haorendashu/nostrmo
February 2024
- Viktor: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/viktorvsk/saltivka and https://github.com/viktorvsk/knowstr
- Eric T: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/tcheeric/nostr-java
- Semisol: 5,000,000 - https://relay.noswhere.com/ and https://hist.nostr.land relays
- Sebastian: 5,000,000 - Drupal stuff and nostr-php work
- tijl: 5,000,000 - Cloudron, Yunohost and Fraidycat attempts
- Null Kotlin Dev: 5,000,000 - AntennaPod attempt
December 2023
- hzrd: 5,000,000 - Nostrudel
- awayuki: 5,000,000 - NOSTOPUS illustrations
- bera: 5,000,000 - getwired.app
- Chris: 5,000,000 - resolvr.io
- NoGood: 10,000,000 - nostrexplained.com stories
October 2023
- SnowCait: 5,000,000 - https://nostter.vercel.app/ and other tools
- Shaun: 10,000,000 - https://yakihonne.com/, events and work on Nostr awareness
- Derek Ross: 10,000,000 - spreading the word around the world
- fmar: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/frnandu/yana
- The Nostr Report: 2,500,000 - curating stuff
- james magoo: 2,500,000 - the Obsidian plugin: https://github.com/jamesmagoo/nostr-writer
August 2023
- Paul Miller: 5,000,000 - JS libraries and cryptography-related work
- BOUNTY tijl: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/github-tijlxyz/wikinostr
- gzuus: 5,000,000 - https://nostree.me/
July 2023
- syusui-s: 5,000,000 - rabbit, a tweetdeck-like Nostr client: https://syusui-s.github.io/rabbit/
- kojira: 5,000,000 - Nostr fanzine, Nostr discussion groups in Japan, hardware experiments
- darashi: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/darashi/nos.today, https://github.com/darashi/searchnos, https://github.com/darashi/murasaki
- jeff g: 5,000,000 - https://nostr.how and https://listr.lol, plus other contributions
- cloud fodder: 5,000,000 - https://nostr1.com (open-source)
- utxo.one: 5,000,000 - https://relaying.io (open-source)
- Max DeMarco: 10,269,507 - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aA-jiiepOrE
- BOUNTY optout21: 1,000,000 - https://github.com/optout21/nip41-proto0 (proposed nip41 CLI)
- BOUNTY Leo: 1,000,000 - https://github.com/leo-lox/camelus (an old relay thing I forgot exactly)
June 2023
- BOUNTY: Sepher: 2,000,000 - a webapp for making lists of anything: https://pinstr.app/
- BOUNTY: Kieran: 10,000,000 - implement gossip algorithm on Snort, implement all the other nice things: manual relay selection, following hints etc.
- Mattn: 5,000,000 - a myriad of projects and contributions to Nostr projects: https://github.com/search?q=owner%3Amattn+nostr&type=code
- BOUNTY: lynn: 2,000,000 - a simple and clean git nostr CLI written in Go, compatible with William's original git-nostr-tools; and implement threaded comments on https://github.com/fiatjaf/nocomment.
- Jack Chakany: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/jacany/nblog
- BOUNTY: Dan: 2,000,000 - https://metadata.nostr.com/
April 2023
- BOUNTY: Blake Jakopovic: 590,000 - event deleter tool, NIP dependency organization
- BOUNTY: koalasat: 1,000,000 - display relays
- BOUNTY: Mike Dilger: 4,000,000 - display relays, follow event hints (Gossip)
- BOUNTY: kaiwolfram: 5,000,000 - display relays, follow event hints, choose relays to publish (Nozzle)
- Daniele Tonon: 3,000,000 - Gossip
- bu5hm4nn: 3,000,000 - Gossip
- BOUNTY: hodlbod: 4,000,000 - display relays, follow event hints
March 2023
- Doug Hoyte: 5,000,000 sats - https://github.com/hoytech/strfry
- Alex Gleason: 5,000,000 sats - https://gitlab.com/soapbox-pub/mostr
- verbiricha: 5,000,000 sats - https://badges.page/, https://habla.news/
- talvasconcelos: 5,000,000 sats - https://migrate.nostr.com, https://read.nostr.com, https://write.nostr.com/
- BOUNTY: Gossip model: 5,000,000 - https://camelus.app/
- BOUNTY: Gossip model: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/kaiwolfram/Nozzle
- BOUNTY: Bounty Manager: 5,000,000 - https://nostrbounties.com/
February 2023
- styppo: 5,000,000 sats - https://hamstr.to/
- sandwich: 5,000,000 sats - https://nostr.watch/
- BOUNTY: Relay-centric client designs: 5,000,000 sats https://bountsr.org/design/2023/01/26/relay-based-design.html
- BOUNTY: Gossip model on https://coracle.social/: 5,000,000 sats
- Nostrovia Podcast: 3,000,000 sats - https://nostrovia.org/
- BOUNTY: Nostr-Desk / Monstr: 5,000,000 sats - https://github.com/alemmens/monstr
- Mike Dilger: 5,000,000 sats - https://github.com/mikedilger/gossip
January 2023
- ismyhc: 5,000,000 sats - https://github.com/Galaxoid-Labs/Seer
- Martti Malmi: 5,000,000 sats - https://iris.to/
- Carlos Autonomous: 5,000,000 sats - https://github.com/BrightonBTC/bija
- Koala Sat: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/KoalaSat/nostros
- Vitor Pamplona: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/vitorpamplona/amethyst
- Cameri: 5,000,000 - https://github.com/Cameri/nostream
December 2022
- William Casarin: 7 BTC - splitting the fund
- pseudozach: 5,000,000 sats - https://nostr.directory/
- Sondre Bjellas: 5,000,000 sats - https://notes.blockcore.net/
- Null Dev: 5,000,000 sats - https://github.com/KotlinGeekDev/Nosky
- Blake Jakopovic: 5,000,000 sats - https://github.com/blakejakopovic/nostcat, https://github.com/blakejakopovic/nostreq and https://github.com/blakejakopovic/NostrEventPlayground
-
 @ 91bea5cd:1df4451c
2025-04-15 06:27:28
@ 91bea5cd:1df4451c
2025-04-15 06:27:28Básico
bash lsblk # Lista todos os diretorios montados.Para criar o sistema de arquivos:
bash mkfs.btrfs -L "ThePool" -f /dev/sdxCriando um subvolume:
bash btrfs subvolume create SubVolMontando Sistema de Arquivos:
bash mount -o compress=zlib,subvol=SubVol,autodefrag /dev/sdx /mntLista os discos formatados no diretório:
bash btrfs filesystem show /mntAdiciona novo disco ao subvolume:
bash btrfs device add -f /dev/sdy /mntLista novamente os discos do subvolume:
bash btrfs filesystem show /mntExibe uso dos discos do subvolume:
bash btrfs filesystem df /mntBalancea os dados entre os discos sobre raid1:
bash btrfs filesystem balance start -dconvert=raid1 -mconvert=raid1 /mntScrub é uma passagem por todos os dados e metadados do sistema de arquivos e verifica as somas de verificação. Se uma cópia válida estiver disponível (perfis de grupo de blocos replicados), a danificada será reparada. Todas as cópias dos perfis replicados são validadas.
iniciar o processo de depuração :
bash btrfs scrub start /mntver o status do processo de depuração Btrfs em execução:
bash btrfs scrub status /mntver o status do scrub Btrfs para cada um dos dispositivos
bash btrfs scrub status -d / data btrfs scrub cancel / dataPara retomar o processo de depuração do Btrfs que você cancelou ou pausou:
btrfs scrub resume / data
Listando os subvolumes:
bash btrfs subvolume list /ReportsCriando um instantâneo dos subvolumes:
Aqui, estamos criando um instantâneo de leitura e gravação chamado snap de marketing do subvolume de marketing.
bash btrfs subvolume snapshot /Reports/marketing /Reports/marketing-snapAlém disso, você pode criar um instantâneo somente leitura usando o sinalizador -r conforme mostrado. O marketing-rosnap é um instantâneo somente leitura do subvolume de marketing
bash btrfs subvolume snapshot -r /Reports/marketing /Reports/marketing-rosnapForçar a sincronização do sistema de arquivos usando o utilitário 'sync'
Para forçar a sincronização do sistema de arquivos, invoque a opção de sincronização conforme mostrado. Observe que o sistema de arquivos já deve estar montado para que o processo de sincronização continue com sucesso.
bash btrfs filsystem sync /ReportsPara excluir o dispositivo do sistema de arquivos, use o comando device delete conforme mostrado.
bash btrfs device delete /dev/sdc /ReportsPara sondar o status de um scrub, use o comando scrub status com a opção -dR .
bash btrfs scrub status -dR / RelatóriosPara cancelar a execução do scrub, use o comando scrub cancel .
bash $ sudo btrfs scrub cancel / ReportsPara retomar ou continuar com uma depuração interrompida anteriormente, execute o comando de cancelamento de depuração
bash sudo btrfs scrub resume /Reportsmostra o uso do dispositivo de armazenamento:
btrfs filesystem usage /data
Para distribuir os dados, metadados e dados do sistema em todos os dispositivos de armazenamento do RAID (incluindo o dispositivo de armazenamento recém-adicionado) montados no diretório /data , execute o seguinte comando:
sudo btrfs balance start --full-balance /data
Pode demorar um pouco para espalhar os dados, metadados e dados do sistema em todos os dispositivos de armazenamento do RAID se ele contiver muitos dados.
Opções importantes de montagem Btrfs
Nesta seção, vou explicar algumas das importantes opções de montagem do Btrfs. Então vamos começar.
As opções de montagem Btrfs mais importantes são:
**1. acl e noacl
**ACL gerencia permissões de usuários e grupos para os arquivos/diretórios do sistema de arquivos Btrfs.
A opção de montagem acl Btrfs habilita ACL. Para desabilitar a ACL, você pode usar a opção de montagem noacl .
Por padrão, a ACL está habilitada. Portanto, o sistema de arquivos Btrfs usa a opção de montagem acl por padrão.
**2. autodefrag e noautodefrag
**Desfragmentar um sistema de arquivos Btrfs melhorará o desempenho do sistema de arquivos reduzindo a fragmentação de dados.
A opção de montagem autodefrag permite a desfragmentação automática do sistema de arquivos Btrfs.
A opção de montagem noautodefrag desativa a desfragmentação automática do sistema de arquivos Btrfs.
Por padrão, a desfragmentação automática está desabilitada. Portanto, o sistema de arquivos Btrfs usa a opção de montagem noautodefrag por padrão.
**3. compactar e compactar-forçar
**Controla a compactação de dados no nível do sistema de arquivos do sistema de arquivos Btrfs.
A opção compactar compacta apenas os arquivos que valem a pena compactar (se compactar o arquivo economizar espaço em disco).
A opção compress-force compacta todos os arquivos do sistema de arquivos Btrfs, mesmo que a compactação do arquivo aumente seu tamanho.
O sistema de arquivos Btrfs suporta muitos algoritmos de compactação e cada um dos algoritmos de compactação possui diferentes níveis de compactação.
Os algoritmos de compactação suportados pelo Btrfs são: lzo , zlib (nível 1 a 9) e zstd (nível 1 a 15).
Você pode especificar qual algoritmo de compactação usar para o sistema de arquivos Btrfs com uma das seguintes opções de montagem:
- compress=algoritmo:nível
- compress-force=algoritmo:nível
Para obter mais informações, consulte meu artigo Como habilitar a compactação do sistema de arquivos Btrfs .
**4. subvol e subvolid
**Estas opções de montagem são usadas para montar separadamente um subvolume específico de um sistema de arquivos Btrfs.
A opção de montagem subvol é usada para montar o subvolume de um sistema de arquivos Btrfs usando seu caminho relativo.
A opção de montagem subvolid é usada para montar o subvolume de um sistema de arquivos Btrfs usando o ID do subvolume.
Para obter mais informações, consulte meu artigo Como criar e montar subvolumes Btrfs .
**5. dispositivo
A opção de montagem de dispositivo** é usada no sistema de arquivos Btrfs de vários dispositivos ou RAID Btrfs.
Em alguns casos, o sistema operacional pode falhar ao detectar os dispositivos de armazenamento usados em um sistema de arquivos Btrfs de vários dispositivos ou RAID Btrfs. Nesses casos, você pode usar a opção de montagem do dispositivo para especificar os dispositivos que deseja usar para o sistema de arquivos de vários dispositivos Btrfs ou RAID.
Você pode usar a opção de montagem de dispositivo várias vezes para carregar diferentes dispositivos de armazenamento para o sistema de arquivos de vários dispositivos Btrfs ou RAID.
Você pode usar o nome do dispositivo (ou seja, sdb , sdc ) ou UUID , UUID_SUB ou PARTUUID do dispositivo de armazenamento com a opção de montagem do dispositivo para identificar o dispositivo de armazenamento.
Por exemplo,
- dispositivo=/dev/sdb
- dispositivo=/dev/sdb,dispositivo=/dev/sdc
- dispositivo=UUID_SUB=490a263d-eb9a-4558-931e-998d4d080c5d
- device=UUID_SUB=490a263d-eb9a-4558-931e-998d4d080c5d,device=UUID_SUB=f7ce4875-0874-436a-b47d-3edef66d3424
**6. degraded
A opção de montagem degradada** permite que um RAID Btrfs seja montado com menos dispositivos de armazenamento do que o perfil RAID requer.
Por exemplo, o perfil raid1 requer a presença de 2 dispositivos de armazenamento. Se um dos dispositivos de armazenamento não estiver disponível em qualquer caso, você usa a opção de montagem degradada para montar o RAID mesmo que 1 de 2 dispositivos de armazenamento esteja disponível.
**7. commit
A opção commit** mount é usada para definir o intervalo (em segundos) dentro do qual os dados serão gravados no dispositivo de armazenamento.
O padrão é definido como 30 segundos.
Para definir o intervalo de confirmação para 15 segundos, você pode usar a opção de montagem commit=15 (digamos).
**8. ssd e nossd
A opção de montagem ssd** informa ao sistema de arquivos Btrfs que o sistema de arquivos está usando um dispositivo de armazenamento SSD, e o sistema de arquivos Btrfs faz a otimização SSD necessária.
A opção de montagem nossd desativa a otimização do SSD.
O sistema de arquivos Btrfs detecta automaticamente se um SSD é usado para o sistema de arquivos Btrfs. Se um SSD for usado, a opção de montagem de SSD será habilitada. Caso contrário, a opção de montagem nossd é habilitada.
**9. ssd_spread e nossd_spread
A opção de montagem ssd_spread** tenta alocar grandes blocos contínuos de espaço não utilizado do SSD. Esse recurso melhora o desempenho de SSDs de baixo custo (baratos).
A opção de montagem nossd_spread desativa o recurso ssd_spread .
O sistema de arquivos Btrfs detecta automaticamente se um SSD é usado para o sistema de arquivos Btrfs. Se um SSD for usado, a opção de montagem ssd_spread será habilitada. Caso contrário, a opção de montagem nossd_spread é habilitada.
**10. descarte e nodiscard
Se você estiver usando um SSD que suporte TRIM enfileirado assíncrono (SATA rev3.1), a opção de montagem de descarte** permitirá o descarte de blocos de arquivos liberados. Isso melhorará o desempenho do SSD.
Se o SSD não suportar TRIM enfileirado assíncrono, a opção de montagem de descarte prejudicará o desempenho do SSD. Nesse caso, a opção de montagem nodiscard deve ser usada.
Por padrão, a opção de montagem nodiscard é usada.
**11. norecovery
Se a opção de montagem norecovery** for usada, o sistema de arquivos Btrfs não tentará executar a operação de recuperação de dados no momento da montagem.
**12. usebackuproot e nousebackuproot
Se a opção de montagem usebackuproot for usada, o sistema de arquivos Btrfs tentará recuperar qualquer raiz de árvore ruim/corrompida no momento da montagem. O sistema de arquivos Btrfs pode armazenar várias raízes de árvore no sistema de arquivos. A opção de montagem usebackuproot** procurará uma boa raiz de árvore e usará a primeira boa que encontrar.
A opção de montagem nousebackuproot não verificará ou recuperará raízes de árvore inválidas/corrompidas no momento da montagem. Este é o comportamento padrão do sistema de arquivos Btrfs.
**13. space_cache, space_cache=version, nospace_cache e clear_cache
A opção de montagem space_cache** é usada para controlar o cache de espaço livre. O cache de espaço livre é usado para melhorar o desempenho da leitura do espaço livre do grupo de blocos do sistema de arquivos Btrfs na memória (RAM).
O sistema de arquivos Btrfs suporta 2 versões do cache de espaço livre: v1 (padrão) e v2
O mecanismo de cache de espaço livre v2 melhora o desempenho de sistemas de arquivos grandes (tamanho de vários terabytes).
Você pode usar a opção de montagem space_cache=v1 para definir a v1 do cache de espaço livre e a opção de montagem space_cache=v2 para definir a v2 do cache de espaço livre.
A opção de montagem clear_cache é usada para limpar o cache de espaço livre.
Quando o cache de espaço livre v2 é criado, o cache deve ser limpo para criar um cache de espaço livre v1 .
Portanto, para usar o cache de espaço livre v1 após a criação do cache de espaço livre v2 , as opções de montagem clear_cache e space_cache=v1 devem ser combinadas: clear_cache,space_cache=v1
A opção de montagem nospace_cache é usada para desabilitar o cache de espaço livre.
Para desabilitar o cache de espaço livre após a criação do cache v1 ou v2 , as opções de montagem nospace_cache e clear_cache devem ser combinadas: clear_cache,nosapce_cache
**14. skip_balance
Por padrão, a operação de balanceamento interrompida/pausada de um sistema de arquivos Btrfs de vários dispositivos ou RAID Btrfs será retomada automaticamente assim que o sistema de arquivos Btrfs for montado. Para desabilitar a retomada automática da operação de equilíbrio interrompido/pausado em um sistema de arquivos Btrfs de vários dispositivos ou RAID Btrfs, você pode usar a opção de montagem skip_balance .**
**15. datacow e nodatacow
A opção datacow** mount habilita o recurso Copy-on-Write (CoW) do sistema de arquivos Btrfs. É o comportamento padrão.
Se você deseja desabilitar o recurso Copy-on-Write (CoW) do sistema de arquivos Btrfs para os arquivos recém-criados, monte o sistema de arquivos Btrfs com a opção de montagem nodatacow .
**16. datasum e nodatasum
A opção datasum** mount habilita a soma de verificação de dados para arquivos recém-criados do sistema de arquivos Btrfs. Este é o comportamento padrão.
Se você não quiser que o sistema de arquivos Btrfs faça a soma de verificação dos dados dos arquivos recém-criados, monte o sistema de arquivos Btrfs com a opção de montagem nodatasum .
Perfis Btrfs
Um perfil Btrfs é usado para informar ao sistema de arquivos Btrfs quantas cópias dos dados/metadados devem ser mantidas e quais níveis de RAID devem ser usados para os dados/metadados. O sistema de arquivos Btrfs contém muitos perfis. Entendê-los o ajudará a configurar um RAID Btrfs da maneira que você deseja.
Os perfis Btrfs disponíveis são os seguintes:
single : Se o perfil único for usado para os dados/metadados, apenas uma cópia dos dados/metadados será armazenada no sistema de arquivos, mesmo se você adicionar vários dispositivos de armazenamento ao sistema de arquivos. Assim, 100% do espaço em disco de cada um dos dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos pode ser utilizado.
dup : Se o perfil dup for usado para os dados/metadados, cada um dos dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos manterá duas cópias dos dados/metadados. Assim, 50% do espaço em disco de cada um dos dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos pode ser utilizado.
raid0 : No perfil raid0 , os dados/metadados serão divididos igualmente em todos os dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos. Nesta configuração, não haverá dados/metadados redundantes (duplicados). Assim, 100% do espaço em disco de cada um dos dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos pode ser usado. Se, em qualquer caso, um dos dispositivos de armazenamento falhar, todo o sistema de arquivos será corrompido. Você precisará de pelo menos dois dispositivos de armazenamento para configurar o sistema de arquivos Btrfs no perfil raid0 .
raid1 : No perfil raid1 , duas cópias dos dados/metadados serão armazenadas nos dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos. Nesta configuração, a matriz RAID pode sobreviver a uma falha de unidade. Mas você pode usar apenas 50% do espaço total em disco. Você precisará de pelo menos dois dispositivos de armazenamento para configurar o sistema de arquivos Btrfs no perfil raid1 .
raid1c3 : No perfil raid1c3 , três cópias dos dados/metadados serão armazenadas nos dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos. Nesta configuração, a matriz RAID pode sobreviver a duas falhas de unidade, mas você pode usar apenas 33% do espaço total em disco. Você precisará de pelo menos três dispositivos de armazenamento para configurar o sistema de arquivos Btrfs no perfil raid1c3 .
raid1c4 : No perfil raid1c4 , quatro cópias dos dados/metadados serão armazenadas nos dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos. Nesta configuração, a matriz RAID pode sobreviver a três falhas de unidade, mas você pode usar apenas 25% do espaço total em disco. Você precisará de pelo menos quatro dispositivos de armazenamento para configurar o sistema de arquivos Btrfs no perfil raid1c4 .
raid10 : No perfil raid10 , duas cópias dos dados/metadados serão armazenadas nos dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos, como no perfil raid1 . Além disso, os dados/metadados serão divididos entre os dispositivos de armazenamento, como no perfil raid0 .
O perfil raid10 é um híbrido dos perfis raid1 e raid0 . Alguns dos dispositivos de armazenamento formam arrays raid1 e alguns desses arrays raid1 são usados para formar um array raid0 . Em uma configuração raid10 , o sistema de arquivos pode sobreviver a uma única falha de unidade em cada uma das matrizes raid1 .
Você pode usar 50% do espaço total em disco na configuração raid10 . Você precisará de pelo menos quatro dispositivos de armazenamento para configurar o sistema de arquivos Btrfs no perfil raid10 .
raid5 : No perfil raid5 , uma cópia dos dados/metadados será dividida entre os dispositivos de armazenamento. Uma única paridade será calculada e distribuída entre os dispositivos de armazenamento do array RAID.
Em uma configuração raid5 , o sistema de arquivos pode sobreviver a uma única falha de unidade. Se uma unidade falhar, você pode adicionar uma nova unidade ao sistema de arquivos e os dados perdidos serão calculados a partir da paridade distribuída das unidades em execução.
Você pode usar 1 00x(N-1)/N % do total de espaços em disco na configuração raid5 . Aqui, N é o número de dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos. Você precisará de pelo menos três dispositivos de armazenamento para configurar o sistema de arquivos Btrfs no perfil raid5 .
raid6 : No perfil raid6 , uma cópia dos dados/metadados será dividida entre os dispositivos de armazenamento. Duas paridades serão calculadas e distribuídas entre os dispositivos de armazenamento do array RAID.
Em uma configuração raid6 , o sistema de arquivos pode sobreviver a duas falhas de unidade ao mesmo tempo. Se uma unidade falhar, você poderá adicionar uma nova unidade ao sistema de arquivos e os dados perdidos serão calculados a partir das duas paridades distribuídas das unidades em execução.
Você pode usar 100x(N-2)/N % do espaço total em disco na configuração raid6 . Aqui, N é o número de dispositivos de armazenamento adicionados ao sistema de arquivos. Você precisará de pelo menos quatro dispositivos de armazenamento para configurar o sistema de arquivos Btrfs no perfil raid6 .
-
 @ c066aac5:6a41a034
2025-04-05 16:58:58
@ c066aac5:6a41a034
2025-04-05 16:58:58I’m drawn to extremities in art. The louder, the bolder, the more outrageous, the better. Bold art takes me out of the mundane into a whole new world where anything and everything is possible. Having grown up in the safety of the suburban midwest, I was a bit of a rebellious soul in search of the satiation that only came from the consumption of the outrageous. My inclination to find bold art draws me to NOSTR, because I believe NOSTR can be the place where the next generation of artistic pioneers go to express themselves. I also believe that as much as we are able, were should invite them to come create here.
My Background: A Small Side Story
My father was a professional gamer in the 80s, back when there was no money or glory in the avocation. He did get a bit of spotlight though after the fact: in the mid 2000’s there were a few parties making documentaries about that era of gaming as well as current arcade events (namely 2007’sChasing GhostsandThe King of Kong: A Fistful of Quarters). As a result of these documentaries, there was a revival in the arcade gaming scene. My family attended events related to the documentaries or arcade gaming and I became exposed to a lot of things I wouldn’t have been able to find. The producer ofThe King of Kong: A Fistful of Quarters had previously made a documentary calledNew York Dollwhich was centered around the life of bassist Arthur Kane. My 12 year old mind was blown: The New York Dolls were a glam-punk sensation dressed in drag. The music was from another planet. Johnny Thunders’ guitar playing was like Chuck Berry with more distortion and less filter. Later on I got to meet the Galaga record holder at the time, Phil Day, in Ottumwa Iowa. Phil is an Australian man of high intellect and good taste. He exposed me to great creators such as Nick Cave & The Bad Seeds, Shakespeare, Lou Reed, artists who created things that I had previously found inconceivable.
I believe this time period informed my current tastes and interests, but regrettably I think it also put coals on the fire of rebellion within. I stopped taking my parents and siblings seriously, the Christian faith of my family (which I now hold dearly to) seemed like a mundane sham, and I felt I couldn’t fit in with most people because of my avant-garde tastes. So I write this with the caveat that there should be a way to encourage these tastes in children without letting them walk down the wrong path. There is nothing inherently wrong with bold art, but I’d advise parents to carefully find ways to cultivate their children’s tastes without completely shutting them down and pushing them away as a result. My parents were very loving and patient during this time; I thank God for that.
With that out of the way, lets dive in to some bold artists:
Nicolas Cage: Actor
There is an excellent video by Wisecrack on Nicolas Cage that explains him better than I will, which I will linkhere. Nicolas Cage rejects the idea that good acting is tied to mere realism; all of his larger than life acting decisions are deliberate choices. When that clicked for me, I immediately realized the man is a genius. He borrows from Kabuki and German Expressionism, art forms that rely on exaggeration to get the message across. He has even created his own acting style, which he calls Nouveau Shamanic. He augments his imagination to go from acting to being. Rather than using the old hat of method acting, he transports himself to a new world mentally. The projects he chooses to partake in are based on his own interests or what he considers would be a challenge (making a bad script good for example). Thus it doesn’t matter how the end result comes out; he has already achieved his goal as an artist. Because of this and because certain directors don’t know how to use his talents, he has a noticeable amount of duds in his filmography. Dig around the duds, you’ll find some pure gold. I’d personally recommend the filmsPig, Joe, Renfield, and his Christmas film The Family Man.
Nick Cave: Songwriter
What a wild career this man has had! From the apocalyptic mayhem of his band The Birthday Party to the pensive atmosphere of his albumGhosteen, it seems like Nick Cave has tried everything. I think his secret sauce is that he’s always working. He maintains an excellent newsletter calledThe Red Hand Files, he has written screenplays such asLawless, he has written books, he has made great film scores such asThe Assassination of Jesse James by the Coward Robert Ford, the man is religiously prolific. I believe that one of the reasons he is prolific is that he’s not afraid to experiment. If he has an idea, he follows it through to completion. From the albumMurder Ballads(which is comprised of what the title suggests) to his rejected sequel toGladiator(Gladiator: Christ Killer), he doesn’t seem to be afraid to take anything on. This has led to some over the top works as well as some deeply personal works. Albums likeSkeleton TreeandGhosteenwere journeys through the grief of his son’s death. The Boatman’s Callis arguably a better break-up album than anything Taylor Swift has put out. He’s not afraid to be outrageous, he’s not afraid to offend, but most importantly he’s not afraid to be himself. Works I’d recommend include The Birthday Party’sLive 1981-82, Nick Cave & The Bad Seeds’The Boatman’s Call, and the filmLawless.
Jim Jarmusch: Director
I consider Jim’s films to be bold almost in an ironic sense: his works are bold in that they are, for the most part, anti-sensational. He has a rule that if his screenplays are criticized for a lack of action, he makes them even less eventful. Even with sensational settings his films feel very close to reality, and they demonstrate the beauty of everyday life. That's what is bold about his art to me: making the sensational grounded in reality while making everyday reality all the more special. Ghost Dog: The Way of the Samurai is about a modern-day African-American hitman who strictly follows the rules of the ancient Samurai, yet one can resonate with the humanity of a seemingly absurd character. Only Lovers Left Aliveis a vampire love story, but in the middle of a vampire romance one can see their their own relationships in a new deeply human light. Jim’s work reminds me that art reflects life, and that there is sacred beauty in seemingly mundane everyday life. I personally recommend his filmsPaterson,Down by Law, andCoffee and Cigarettes.
NOSTR: We Need Bold Art
NOSTR is in my opinion a path to a better future. In a world creeping slowly towards everything apps, I hope that the protocol where the individual owns their data wins over everything else. I love freedom and sovereignty. If NOSTR is going to win the race of everything apps, we need more than Bitcoin content. We need more than shirtless bros paying for bananas in foreign countries and exercising with girls who have seductive accents. Common people cannot see themselves in such a world. NOSTR needs to catch the attention of everyday people. I don’t believe that this can be accomplished merely by introducing more broadly relevant content; people are searching for content that speaks to them. I believe that NOSTR can and should attract artists of all kinds because NOSTR is one of the few places on the internet where artists can express themselves fearlessly. Getting zaps from NOSTR’s value-for-value ecosystem has far less friction than crowdfunding a creative project or pitching investors that will irreversibly modify an artist’s vision. Having a place where one can post their works without fear of censorship should be extremely enticing. Having a place where one can connect with fellow humans directly as opposed to a sea of bots should seem like the obvious solution. If NOSTR can become a safe haven for artists to express themselves and spread their work, I believe that everyday people will follow. The banker whose stressful job weighs on them will suddenly find joy with an original meme made by a great visual comedian. The programmer for a healthcare company who is drowning in hopeless mundanity could suddenly find a new lust for life by hearing the song of a musician who isn’t afraid to crowdfund their their next project by putting their lighting address on the streets of the internet. The excel guru who loves independent film may find that NOSTR is the best way to support non corporate movies. My closing statement: continue to encourage the artists in your life as I’m sure you have been, but while you’re at it give them the purple pill. You may very well be a part of building a better future.
-
 @ 3104fbbf:ac623068
2025-04-04 06:58:30
@ 3104fbbf:ac623068
2025-04-04 06:58:30
Introduction
If you have a functioning brain, it’s impossible to fully stand for any politician or align completely with any political party. The solutions we need are not found in the broken systems of power but in individual actions and local initiatives. Voting for someone may be your choice, but relying solely on elections every few years as a form of political activism is a losing strategy. People around the world have fallen into the trap of thinking that casting a ballot once every four years is enough, only to return to complacency as conditions worsen. Voting for the "lesser of two evils" has been the norm for decades, yet expecting different results from the same flawed system is naive at best.
The truth is, governments are too corrupt to save us. In times of crisis, they won’t come to your aid—instead, they will tighten their grip, imposing more surveillance, control, and wealth extraction to benefit the oligarch class. To break free from this cycle, we must first protect ourselves individually—financially, geographically, and digitally—alongside our families.
Then, we must organize and build resilient local communities. These are the only ways forward. History has shown us time and again that the masses are easily deceived by the political circus, falling for the illusion of a "savior" who will fix everything. But whether right, center, or left, the story remains the same: corruption, lies, and broken promises. If you possess a critical and investigative mind, you know better than to place your trust in politicians, parties, or self-proclaimed heroes. The real solution lies in free and sovereign individuals who reject the herd mentality and take responsibility for their own lives.
From the beginning of time, true progress has come from individuals who think for themselves and act independently. The nauseating web of politicians, billionaires, and oligarchs fighting for power and resources has never been—and will never be—the answer to our problems. In a world increasingly dominated by corrupted governments, NGOs, and elites, ordinary people must take proactive steps to protect themselves and their families.
1. Financial Protection: Reclaiming Sovereignty Through Bitcoin
Governments and central banks have long manipulated fiat currencies, eroding wealth through inflation and bailouts that transfer resources to the oligarch class. Bitcoin, as a decentralized, censorship-resistant, and finite currency, offers a way out. Here’s what individuals can do:
-
Adopt Bitcoin as a Savings Tool: Shift a portion of your savings into Bitcoin to protect against inflation and currency devaluation. Bitcoin’s fixed supply (21 million coins) ensures it cannot be debased like fiat money.
-
Learn Self-Custody: Store your Bitcoin in a hardware wallet or use open-source software wallets. Avoid centralized exchanges, which are vulnerable to government seizure or collapse.
-
Diversify Geographically: Hold assets in multiple jurisdictions to reduce the risk of confiscation or capital controls. Consider offshore accounts or trusts if feasible.
-
Barter and Local Economies: In times of crisis, local barter systems and community currencies can bypass failing national systems. Bitcoin can serve as a global medium of exchange in such scenarios.
2. Geographical Flexibility: Reducing Dependence on Oppressive Systems
Authoritarian regimes thrive on controlling populations within fixed borders. By increasing geographical flexibility, individuals can reduce their vulnerability:
-
Obtain Second Passports or Residencies: Invest in citizenship-by-investment programs or residency permits in countries with greater freedoms and lower surveillance.
-
Relocate to Freer Jurisdictions: Research and consider moving to regions with stronger property rights, lower taxes, and less government overreach.
-
Decentralize Your Life: Avoid keeping all your assets, family, or business operations in one location. Spread them across multiple regions to mitigate risks.
3. Digital Privacy: Fighting Surveillance with Advanced Tools
The rise of mass surveillance and data harvesting by governments and corporations threatens individual freedom. Here’s how to protect yourself:
-
Use Encryption: Encrypt all communications using tools like Signal or ProtonMail. Ensure your devices are secured with strong passwords and biometric locks.
-
Adopt Privacy-Focused Technologies: Use Tor for anonymous browsing, VPNs to mask your IP address, and open-source operating systems like Linux to avoid backdoors.
-
Reject Surveillance Tech: Avoid smart devices that spy on you (e.g., Alexa, Google Home). Opt for decentralized alternatives like Mastodon instead of Twitter, or PeerTube instead of YouTube.
-
Educate Yourself on Digital Privacy: Learn about tools and practices that enhance your online privacy and security.
4. Building Resilient Local Communities: The Foundation of a Free Future
While individual actions are crucial, collective resilience is equally important. Governments are too corrupt to save populations in times of crisis—history shows they will instead impose more control and transfer wealth to the elite.
To counter this, communities must organize locally:
-
Form Mutual Aid Networks: Create local groups that share resources, skills, and knowledge. These networks can provide food, medical supplies, and security during crises.
-
Promote Local Economies: Support local businesses, farmers, and artisans. Use local currencies or barter systems to reduce dependence on centralized financial systems.
-
Develop Off-Grid Infrastructure: Invest in renewable energy, water filtration, and food production to ensure self-sufficiency. Community gardens, solar panels, and rainwater harvesting are excellent starting points.
-
Educate and Empower: Host workshops on financial literacy, digital privacy, and sustainable living. Knowledge is the most powerful tool against authoritarianism.
5. The Bigger Picture: Rejecting the Illusion of Saviors
The deep corruption within governments, NGOs, and the billionaire class is evident. These entities will never act in the interest of ordinary people. Instead, they will exploit crises to expand surveillance, control, and wealth extraction. The idea of a political “savior” is a dangerous illusion. True freedom comes from individuals taking responsibility for their own lives and working together to build decentralized, resilient systems.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The path to a genuinely free humanity begins with individual action. By adopting Bitcoin, securing digital privacy, increasing geographical flexibility, and building resilient local communities, ordinary people can protect themselves against authoritarianism. Governments will not save us—they are the problem. It is up to us to create a better future, free from the control of corrupt elites.
-
The tools for liberation already exist.
-
The question is: will we use them?
For those interested, I share ideas and solutions in my book « THE GATEWAY TO FREEDOM » https://blisshodlenglish.substack.com/p/the-gateway-to-freedom
⚡ The time to act is now. Freedom is not given—it is taken. ⚡
If you enjoyed this article, consider supporting it with a Zap!
My Substack ENGLISH = https://blisshodlenglish.substack.com/ My substack FRENCH = https://blisshodl.substack.com/
Get my Book « THE GATEWAY TO FREEDOM » here 🙏 => https://coinos.io/blisshodl
-
-
 @ 7bdef7be:784a5805
2025-04-02 12:02:45
@ 7bdef7be:784a5805
2025-04-02 12:02:45We value sovereignty, privacy and security when accessing online content, using several tools to achieve this, like open protocols, open OSes, open software products, Tor and VPNs. ## The problem Talking about our social presence, we can manually build up our follower list (social graph), pick a Nostr client that is respectful of our preferences on what to show and how, but with the standard following mechanism, our main feed is public, **so everyone can actually snoop** what we are interested in, and what is supposable that we read daily. ## The solution Nostr has a simple solution for this necessity: encrypted lists. Lists are what they appear, a collection of people or interests (but they can also group much other stuff, see [NIP-51](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/blob/master/51.md)). So we can create lists with contacts that we don't have in our main social graph; these lists can be used primarily to create **dedicated feeds**, but they could have other uses, for example, related to monitoring. The interesting thing about lists is that they can also be **encrypted**, so unlike the basic following list, which is always public, we can hide the lists' content from others. The implications are obvious: we can not only have a more organized way to browse content, but it is also **really private one**. One might wonder what use can really be made of private lists; here are some examples: - Browse “can't miss” content from users I consider a priority; - Supervise competitors or adversarial parts; - Monitor sensible topics (tags); - Following someone without being publicly associated with them, as this may be undesirable; The benefits in terms of privacy as usual are not only related to the casual, or programmatic, observer, but are also evident when we think of **how many bots scan our actions to profile us**. ## The current state Unfortunately, lists are not widely supported by Nostr clients, and encrypted support is a rarity. Often the excuse to not implement them is that they are harder to develop, since they require managing the encryption stuff ([NIP-44](https://github.com/nostr-protocol/nips/blob/master/51.md)). Nevertheless, developers have an easier option to start offering private lists: give the user the possibility to simply **mark them as local-only**, and never push them to the relays. Even if the user misses the sync feature, this is sufficient to create a private environment. To date, as far as I know, the best client with list management is Gossip, which permits to manage **both encrypted and local-only lists**. Beg your Nostr client to implement private lists!
-
 @ 79008e78:dfac9395
2025-03-22 11:22:07
@ 79008e78:dfac9395
2025-03-22 11:22:07Keys and Addresses
อลิซต้องการจ่ายเงินให้กับบ๊อบแต่โหนดของบิตคอยน์ในระบบหลายพันโหนดจะตรวจสอบธุรกรรมของเธอ โดยไม่รู้ว่าอลิซหรือบ๊อบเป็นใคร ละเราต้องการรักษาความเป็นส่วนตัวของพวกเขาไว้เช่นนี้ อลิซจำเป็นต้องสื่อสารว่าบ๊อบควรได้รับบิตคอยน์บางส่วนของเธอโดยไม่เชื่อมโยงแง่มุมใด ๆ ของธุรกรรมนั้นกับตัวตนในโลกจริงของบ๊อบ หรือกับการชำระเงินด้วยบิตคอยน์ครั้งอื่น ๆ ที่บ๊อบได้รับ อลิซใช้ต้องทำให้มั่นใจว่ามีเพียแค่บ๊อบเท่านั้นที่สามารถใช้จ่ายบิตคอยน์ที่เขาได้รับต่อไปได้
ในบิตคอยน์ไวท์เปเปอร์ได้อธิบายถึงแผนการที่เรียบง่ายมากสำหรับการบรรลุเป้าหมายเหล่านั้น ดังที่แสดงในรูปด้านล่างนี้

ตัวของผู้รับอย่างบ๊อบเองจะได้รับบิตคอยน์ไปยัง public key ของเขาที่ถูกลงนามโดยผู้จ่ายอย่างอลิซ โดยบิตคอยน์ที่อลิซนำมาจ่ายนั้นก็ได้รับมาจากที่ใครสักคนส่งมาที่ public key ของเธอ และเธอก็ใช้ private key ของเธอในการลงนามเพื่อสร้างลายเซ็นของเธอและโหนดต่าง ๆ ของบิตคอยน์จะทำการตรวจสอบว่าลายเซ็นของอลิซผูกมัดกับเอาต์พุตของฟังก์ชันแฮชซึ่งตัวมันเองผูกมัดกับ public key ของบ๊อบและรายละเอียดธุรกรรมอื่นๆ
ในบทนี้เราจะพิจารณาpublic key private key Digital signatrue และ hash function จากนั้นใช้ทั้งหมดนี้ร่วมกันเพื่ออธิบาย address ที่ใช้โดยซอฟต์แวร์บิตคอยน์สมัยใหม่
Public Key Cryptography (การเข้ารหัสของ public key)
ระบบเข้ารหัสของ public key ถูกคิดค้นขึ้นในทศวรรษ 1970 มาจากรากฐานทางคณิตศาสตร์สำหรับความปลอดภัยของคอมพิวเตอร์และข้อมูลสมัยใหม่
นับตั้งแต่การคิดค้นระบบเข้ารหัส public key ได้มีการค้นพบฟังก์ชันทางคณิตศาสตร์ที่เหมาะสมหลายอย่าง เช่น การยกกำลังของจำนวนเฉพาะและการคูณของเส้นโค้งวงรี โดยฟังก์ชันทางคณิตศาสตร์เหล่านี้สามารถคำนวณได้ง่ายในทิศทางหนึ่ง แต่เป็นไปไม่ได้ที่จะคำนวณในทิศทางตรงกันข้ามโดยใช้คอมพิวเตอร์และอัลกอริทึมที่มีอยู่ในปัจจุบัน จากฟังก์ชันทางคณิตศาสตร์เหล่านี้ การเข้ารหัสลับช่วยให้สามารถสร้างลายเซ็นดิจิทัลที่ไม่สามารถปลอมแปลงได้และบิตคอยน์ได้ใช้การบวกและการคูณของเส้นโค้งวงรีเป็นพื้นฐานสำหรับการเข้ารหัสลับของมัน
ในบิตคอยน์ เราสามารถใช้ระบบเข้ารหัส public key เพื่อสร้างคู่กุญแจที่ควบคุมการเข้าถึงบิตคอยน์ คู่กุญแจประกอบด้วย private key และ public key ที่ได้มาจาก private key public keyใช้สำหรับรับเงิน และ private key ใช้สำหรับลงนามในธุรกรรมเพื่อใช้จ่ายเงิน
ความสัมพันธ์ทางคณิตศาสตร์ระหว่าง public key และ private key ที่ช่วยให้ private key สามารถใช้สร้างลายเซ็นบนข้อความได้ ลายเซ็นเหล่านี้สามารถตรวจสอบความถูกต้องกับ public key ได้โดยไม่เปิดเผย private key
TIP: ในการใช้งานซอฟแวร์กระเป๋าเงินบิตคอยน์บสงอัน จะทำการเก็บ private key และ public key ถูกเก็บไว้ด้วยกันในรูปแบบคู่กุญแจเพื่อความสะดวก แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม public key สามารถคำนวณได้จาก private key ดังนั้นการเก็บเพียง private key เท่านั้นก็เป็นไปได้เช่นกัน
bitcoin wallet มักจะทำการรวบรวมคู่กุญแต่ละคู่ ซึ่งจะประกอบไปด้วย private key และ public key โดย private key จะเป็นตัวเลขที่ถูกสุ่มเลือกขึ้นมา และเราขะใช้เส้นโค้งวงรี ซึ่งเป็นฟังก์ชันการเข้ารหัสทางเดียว เพื่อสร้าง public key ขึ้นมา
ทำไมจึงใช้การเข้ารหัสแบบอสมมาตร
ทำไมการเข้ารหัสแบบอสมมาตรจึงถูกใช้บิตคอยน์? มันไม่ได้ถูกใช้เพื่อ "เข้ารหัส" (ทำให้เป็นความลับ) ธุรกรรม แต่คุณสมบัติที่มีประโยชน์ของการเข้ารหัสแบบอสมมาตรคือความสามารถในการสร้าง ลายเซ็นดิจิทัล private key สามารถนำไปใช้กับธุรกรรมเพื่อสร้างลายเซ็นเชิงตัวเลข ลายเซ็นนี้สามารถสร้างได้เฉพาะโดยผู้ที่มีความเกี่ยวข้องกับ private key เท่านั้น แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม ทุกคนที่สามารถเข้าถึง public key และธุรกรรมสามารถใช้สิ่งเหล่านี้เพื่อ ตรวจสอบ ลายเซ็นได้ คุณสมบัติที่มีประโยชน์นี้ของการเข้ารหัสแบบอสมมาตรทำให้ทุกคนสามารถตรวจสอบลายเซ็นทุกรายการในทุกธุรกรรมได้ ในขณะที่มั่นใจว่าเฉพาะเจ้าของ private key เท่านั้นที่สามารถสร้างลายเซ็นที่ถูกต้องได้
Private keys
private key เป็นเพียงตัวเลขที่ถูกสุ่มขึ้น และการควบคุม private key ก็เป็นรากฐานสำคัญที่ทำให้เจ้าชองกุญแจดอกนี้สามารถควบคุมบิตคอยน์ทั้งหมดที่มีความเกี่ยวข้องกับ public key ที่คู่กัน private key นั้นใช้ในการสร้างลายเซ็นดิจิทัลที่ใช้ในการเคลื่อนย้ายบิตคอยน์ เราจำเป็นต้องเก็บ private key ให้เป็นความลับตลอดเวลา เพราะการเปิดเผยมันให้กับบุคคลอื่นนั้นก็เปรียบเสมือนกับการนำอำนาจในการควบคุมบิตคอยน์ไปให้แก่เขา นอกจากนี้ private key ยังจำเป็นต้องได้รับการสำรองข้อมูลและป้องกันจากการสูญหายโดยไม่ตั้งใจ เพราะหากเราได้ทำมันสูญหายไป จะไม่สามารถกู้คืนได้ และบิตคอยน์เหล่านั้นจะถูกปกป้องโดยกุญแจที่หายไปนั้นตลอดกาลเช่นกัน
TIP: private key ของบิตคอยน์นั้นเป็นเพียงแค่ตัวเลข คุณสามารถสร้างมันได้โดยใช้เพียงเหรียญ ดินสอ และกระดาษ โดยการโยนเหรียญเพียง 256 ครั้งจะทำให้คุณได้เลขฐานสองที่สามารถใช้เป็น private key ของบิตคอยน์ จากนั้นคุณสามารถใช้มันในการคำนวณหา public key แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม โปรดระมัดระวังเกี่ยวกับการเลือใช้วิธีการสุ่มที่ไม่สมบูรณ์ เพราะนั่นอาจลดความปลอดภัยของ private key และบิตคอยน์ที่มัมปกป้องอยู่อย่างมีนัยสำคัญ
ขั้นตอนแรกและสำคัญที่สุดในการสร้างกุญแจคือการหาแหล่งที่มาของความสุ่มที่ปลอดภัย (ซึ่งเรียกว่า เอนโทรปี) การสร้างกุญแจของบิตคอยน์นั้นเกือบเหมือนกับ "เลือกตัวเลขระหว่าง 1 และ 2^256" ซึ่งวิธีที่แน่นอนที่คุณใช้ในการเลือกตัวเลขนั้นไม่สำคัญตราบใดที่มันไม่สามารถคาดเดาหรือทำซ้ำได้ โดยปกติแล้วซอฟต์แวร์ของบิตคอยน์มักจะใช้ตัวสร้างตัวเลขสุ่มที่มีความปลอดภัยทางการเข้ารหัสเพื่อสร้างเอนโทรปี 256 บิต
สิ่งที่สำคัญในเรื่องนี้คือ private key สามารถเป็นตัวเลขใดๆ ระหว่าง 0 และ n - 1 (รวมทั้งสองค่า) โดยที่ n เป็นค่าคงที่ (n = 1.1578 × 10^77 ซึ่งน้อยกว่า 2^256 เล็กน้อย) ซึ่งกำหนดอยู่ใน elliptic curve ที่ใช้ใน Bitcoin ในการสร้างกุญแจดังกล่าว เราสุ่มเลือกเลขขนาด 256 บิตและตรวจสอบว่ามันน้อยกว่า n ในแง่ของการเขียนโปรแกรม โดยปกติแล้วสิ่งนี้ทำได้โดยการป้อนสตริงของบิตสุ่มที่ใหญ่กว่า ซึ่งรวบรวมจากแหล่งที่มาของความสุ่มที่มีความปลอดภัยทางการเข้ารหัส เข้าไปในอัลกอริทึมแฮช SHA256 ซึ่งจะสร้างค่าขนาด 256 บิตที่สามารถตีความเป็นตัวเลขได้อย่างสะดวก หากผลลัพธ์น้อยกว่า n เราจะได้กุญแจส่วนตัวที่เหมาะสม มิฉะนั้น เราก็เพียงแค่ลองอีกครั้งด้วยตัวเลขสุ่มอื่น
คำเตือน: อย่าเขียนโค้ดของคุณเองเพื่อสร้างตัวเลขสุ่ม หรือใช้ตัวสร้างตัวเลขสุ่ม "แบบง่าย" ที่มีให้ในภาษาโปรแกรมของคุณ ใช้ตัวสร้างตัวเลขสุ่มเทียมที่มีความปลอดภัยทางการเข้ารหัส (CSPRNG) จากแหล่งที่มีเอนโทรปีเพียงพอ ศึกษาเอกสารของไลบรารีตัวสร้างตัวเลขสุ่มที่คุณเลือกเพื่อให้มั่นใจว่ามีความปลอดภัยทางการเข้ารหัส การใช้งาน CSPRNG ที่ถูกต้องมีความสำคัญอย่างยิ่งต่อความปลอดภัยของกุญแจ
ต่อไปนี้คือกุญแจส่วนตัว (k) ที่สร้างขึ้นแบบสุ่มซึ่งแสดงในรูปแบบเลขฐานสิบหก (256 บิตแสดงเป็น 64 หลักเลขฐานสิบหก โดยแต่ละหลักคือ 4 บิต):
1E99423A4ED27608A15A2616A2B0E9E52CED330AC530EDCC32C8FFC6A526AEDDTIP: จำนวนที่เป็นไปได้ของ private key ทั้งหมดนั้นมีอยู่ 2^256 เป็นตัวเลขที่ใหญ่มากจนยากจะจินตนาการได้ มันมีค่าประมาณ 10^77 (เลข 1 ตามด้วยเลข 0 อีก 77 ตัว) ในระบบเลขฐานสิบ เพื่อให้เข้าใจง่ายขึ้น ลองเปรียบเทียบกับจักรวาลที่เรามองเห็นได้ซึ่งนักวิทยาศาสตร์ประมาณการว่ามีอะตอมทั้งหมดประมาณ 10^80 อะตอม นั่นหมายความว่าช่วงค่าของกุญแจส่วนตัว Bitcoin มีขนาดใกล้เคียงกับจำนวนอะตอมทั้งหมดในจักรวาลที่เรามองเห็นได้
การอธิบายเกี่ยวกับวิทยาการเข้ารหัสแบบเส้นโค้งวงรี (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
วิทยาการเข้ารหัสแบบเส้นโค้งวงรี (ECC) เป็นประเภทหนึ่งของการเข้ารหัสแบบอสมมาตรหรือ public key ซึ่งอาศัยหลักการของปัญหาลอการิทึมแบบไม่ต่อเนื่อง โดยแสดงออกผ่านการบวกและการคูณบนจุดต่างๆ ของเส้นโค้งวงรี

บิตคอยน์ใช้เส้นโค้งวงรีเฉพาะและชุดค่าคงที่ทางคณิตศาสตร์ ตามที่กำหนดไว้ในมาตรฐานที่เรียกว่า secp256k1 ซึ่งกำหนดโดยสถาบันมาตรฐานและเทคโนโลยีแห่งชาติ (NIST) เส้นโค้ง secp256k1 ถูกกำหนดโดยฟังก์ชันต่อไปนี้ ซึ่งสร้างเส้นโค้งวงรี: y² = (x³ + 7) บนฟิลด์จำกัด (F_p) หรือ y² mod p = (x³ + 7) mod p
โดยที่ mod p (มอดูโลจำนวนเฉพาะ p) แสดงว่าเส้นโค้งนี้อยู่บนฟิลด์จำกัดของอันดับจำนวนเฉพาะ p ซึ่งเขียนได้เป็น F_p โดย p = 2^256 – 2^32 – 2^9 – 2^8 – 2^7 – 2^6 – 2^4 – 1 ซึ่งเป็นจำนวนเฉพาะที่มีค่ามหาศาล
บิตคอยน์ใช้เส้นโค้งวงรีที่ถูกนิยามบนฟิลด์จำกัดของอันดับจำนวนเฉพาะแทนที่จะอยู่บนจำนวนจริง ทำให้มันมีลักษณะเหมือนรูปแบบของจุดที่กระจัดกระจายในสองมิติ ซึ่งทำให้ยากต่อการจินตนาการภาพ อย่างไรก็ตาม คณิตศาสตร์ที่ใช้นั้นเหมือนกับเส้นโค้งวงรีบนจำนวนจริง
ตัวอย่างเช่น การเข้ารหัสลับด้วยเส้นโค้งวงรี: การแสดงภาพเส้นโค้งวงรีบน F(p) โดยที่ p=17 แสดงเส้นโค้งวงรีเดียวกันบนฟิลด์จำกัดของอันดับจำนวนเฉพาะ 17 ที่มีขนาดเล็กกว่ามาก ซึ่งแสดงรูปแบบของจุดบนตาราง
เส้นโค้งวงรี secp256k1 ที่ใช้ในบิตคอยน์สามารถนึกถึงได้ว่าเป็นรูปแบบของจุดที่ซับซ้อนมากกว่าบนตารางที่มีขนาดใหญ่มหาศาลจนยากจะเข้าใจได้

ตัวอย่างเช่น จุด P ที่มีพิกัด (x, y) ต่อไปนี้เป็นจุดที่อยู่บนเส้นโค้ง secp256k1:
P = (55066263022277343669578718895168534326250603453777594175500187360389116729240, 32670510020758816978083085130507043184471273380659243275938904335757337482424)เราสามารถใช้ Python เพื่อยืนยันว่าจุดนี้อยู่บนเส้นโค้งวงรีได้ตามตัวอย่างนี้: ตัวอย่างที่ 1: การใช้ Python เพื่อยืนยันว่าจุดนี้อยู่บนเส้นโค้งวงรี ``` Python 3.10.6 (main, Nov 14 2022, 16:10:14) [GCC 11.3.0] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.p = 115792089237316195423570985008687907853269984665640564039457584007908834671663 x = 55066263022277343669578718895168534326250603453777594175500187360389116729240 y = 32670510020758816978083085130507043184471273380659243275938904335757337482424 (x ** 3 + 7 - y**2) % p 0 ``` ผลลัพธ์เป็น 0 ซึ่งแสดงว่าจุดนี้อยู่บนเส้นโค้งวงรีจริง เพราะเมื่อแทนค่า x และ y ลงในสมการ y² = (x³ + 7) mod p แล้ว ทั้งสองด้านของสมการมีค่าเท่ากัน
ในคณิตศาสตร์ของเส้นโค้งวงรี มีจุดที่เรียกว่า "จุดที่อนันต์" (point at infinity) ซึ่งมีบทบาทคล้ายกับศูนย์ในการบวก บนคอมพิวเตอร์ บางครั้งจุดนี้แทนด้วย x = y = 0 (ซึ่งไม่เป็นไปตามสมการเส้นโค้งวงรี แต่เป็นกรณีพิเศษที่สามารถตรวจสอบได้ง่าย)
มีตัวดำเนินการ + ที่เรียกว่า "การบวก" ซึ่งมีคุณสมบัติคล้ายกับการบวกแบบดั้งเดิมของจำนวนจริงที่เด็กๆ เรียนในโรงเรียน เมื่อมีจุดสองจุด P1 และ P2 บนเส้นโค้งวงรี จะมีจุดที่สาม P3 = P1 + P2 ซึ่งอยู่บนเส้นโค้งวงรีเช่นกัน
ในเชิงเรขาคณิต จุดที่สาม P3 นี้คำนวณได้โดยการลากเส้นระหว่าง P1 และ P2 เส้นนี้จะตัดกับเส้นโค้งวงรีที่จุดเพิ่มเติมอีกหนึ่งจุดพอดี เรียกจุดนี้ว่า P3' = (x, y) จากนั้นให้สะท้อนกับแกน x เพื่อได้ P3 = (x, -y)
มีกรณีพิเศษบางกรณีที่อธิบายความจำเป็นของ "จุดที่อนันต์":
- ถ้า P1 และ P2 เป็นจุดเดียวกัน เส้น "ระหว่าง" P1 และ P2 ควรขยายเป็นเส้นสัมผัสกับเส้นโค้ง ณ จุด P1 นี้ เส้นสัมผัสนี้จะตัดกับเส้นโค้งที่จุดใหม่อีกหนึ่งจุดพอดี คุณสามารถใช้เทคนิคจากแคลคูลัสเพื่อหาความชันของเส้นสัมผัส เทคนิคเหล่านี้ใช้ได้อย่างน่าแปลกใจ แม้ว่าเราจะจำกัดความสนใจไว้ที่จุดบนเส้นโค้งที่มีพิกัดเป็นจำนวนเต็มเท่านั้น!
- ในบางกรณี (เช่น ถ้า P1 และ P2 มีค่า x เดียวกันแต่ค่า y ต่างกัน) เส้นสัมผัสจะตั้งฉากพอดี ซึ่งในกรณีนี้ P3 = "จุดที่อนันต์"
- ถ้า P1 เป็น "จุดที่อนันต์" แล้ว P1 + P2 = P2 ในทำนองเดียวกัน ถ้า P2 เป็นจุดที่อนันต์ แล้ว P1 + P2 = P1 นี่แสดงให้เห็นว่าจุดที่อนันต์มีบทบาทเป็นศูนย์
การบวกนี้มีคุณสมบัติเชิงสมาคม (associative) ซึ่งหมายความว่า (A + B) + C = A + (B + C) นั่นหมายความว่าเราสามารถเขียน A + B + C โดยไม่ต้องมีวงเล็บและไม่มีความกำกวม
เมื่อเรานิยามการบวกแล้ว เราสามารถนิยามการคูณในแบบมาตรฐานที่ต่อยอดจากการบวก สำหรับจุด P บนเส้นโค้งวงรี ถ้า k เป็นจำนวนเต็มบวก แล้ว kP = P + P + P + … + P (k ครั้ง) โปรดทราบว่า k บางครั้งถูกเรียกว่า "เลขชี้กำลัง"
Public Keys
ในระบบคริปโตกราฟีแบบเส้นโค้งวงรี (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) public key ถูกคำนวณจาก private key โดยใช้การคูณเส้นโค้งวงรี ซึ่งเป็นกระบวนการที่ไม่สามารถย้อนกลับได้:
K = k × G
โดยที่:
- k คือ private key
- G คือจุดคงที่ที่เรียกว่า จุดกำเนิด (generator point)
- K คือ public key
การดำเนินการย้อนกลับ ที่เรียกว่า "การหาลอการิทึมแบบไม่ต่อเนื่อง" (finding the discrete logarithm) - คือการคำนวณหา k เมื่อรู้ค่า K - เป็นสิ่งที่ยากมากเทียบเท่ากับการลองค่า k ทุกค่าที่เป็นไปได้ (วิธีการแบบ brute-force)
ความยากของการย้อนกลับนี้คือหลักการความปลอดภัยหลักของระบบ ECC ที่ใช้ในบิตคอยน์ ซึ่งทำให้สามารถเผยแพร่ public key ได้อย่างปลอดภัย โดยที่ไม่ต้องกังวลว่าจะมีใครสามารถคำนวณย้อนกลับเพื่อหา private key ได้
TIP:การคูณเส้นโค้งวงรีเป็นฟังก์ชันประเภทที่นักเข้ารหัสลับเรียกว่า “ trap door function ”:
- เป็นสิ่งที่ทำได้ง่ายในทิศทางหนึ่ง
- แต่เป็นไปไม่ได้ที่จะทำในทิศทางตรงกันข้าม
คนที่มี private key สามารถสร้าง public key ได้อย่างง่ายดาย และสามารถแบ่งปันกับโลกได้โดยรู้ว่าไม่มีใครสามารถย้อนกลับฟังก์ชันและคำนวณ private key จาก public key ได้ กลวิธีทางคณิตศาสตร์นี้กลายเป็นพื้นฐานสำหรับลายเซ็นดิจิทัลที่ปลอมแปลงไม่ได้และมีความปลอดภัย ซึ่งใช้พิสูจน์การควบคุมเงินบิตคอยน์
เริ่มต้นด้วยการใช้ private key ในรูปแบบของตัวเลขสุ่ม เราคูณมันด้วยจุดที่กำหนดไว้ล่วงหน้าบนเส้นโค้งที่เรียกว่า จุดกำเนิด (generator point) เพื่อสร้างจุดอื่นที่อยู่บนเส้นโค้งเดียวกัน ซึ่งคำตอบจะเป็น public key ที่สอดคล้องกัน จุดกำเนิดถูกกำหนดไว้เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของมาตรฐาน secp256k1 และเป็นค่าเดียวกันสำหรับกุญแจทั้งหมดในระบบบิตคอยน์
เนื่องจากจุดกำเนิด G เป็นค่าเดียวกันสำหรับผู้ใช้บิตคอยน์ทุกคน private key (k) ที่คูณกับ G จะได้ public key (K) เดียวกันเสมอ ความสัมพันธ์ระหว่าง k และ K เป็นแบบตายตัวแต่สามารถคำนวณได้ในทิศทางเดียวเท่านั้น คือจาก k ไปยัง K นี่คือเหตุผลที่ public key ของบิตคอยน์ (K) สามารถแบ่งปันกับทุกคนได้โดยไม่เปิดเผย private key (k) ของผู้ใช้
TIP: private key สามารถแปลงเป็น public key ได้ แต่ public key ไม่สามารถแปลงกลับเป็น private key ได้ เพราะคณิตศาสตร์ที่ใช้ทำงานได้เพียงทิศทางเดียวเท่านั้น
เมื่อนำการคูณเส้นโค้งวงรีมาใช้งาน เราจะนำ private key (k) ที่สร้างขึ้นก่อนหน้านี้มาคูณกับจุดกำเนิด G เพื่อหา public key (K):
K = 1E99423A4ED27608A15A2616A2B0E9E52CED330AC530EDCC32C8FFC6A526AEDD × Gpublic key (K) จะถูกกำหนดเป็นจุด K = (x, y) โดยที่:x = F028892BAD7ED57D2FB57BF33081D5CFCF6F9ED3D3D7F159C2E2FFF579DC341A y = 07CF33DA18BD734C600B96A72BBC4749D5141C90EC8AC328AE52DDFE2E505BDBเพื่อจะให้เห็นภาพของการคูณจุดด้วยจำนวนเต็มมากขึ้น เราจะใช้เส้นโค้งวงรีที่ง่ายกว่าบนจำนวนจริง (โดยหลักการทางคณิตศาสตร์ยังคงเหมือนกัน) เป้าหมายของเราคือการหาผลคูณ kG ของจุดกำเนิด G ซึ่งเทียบเท่ากับการบวก G เข้ากับตัวเอง k ครั้งติดต่อกันในเส้นโค้งวงรี การบวกจุดเข้ากับตัวเองเทียบเท่ากับการลากเส้นสัมผัสที่จุดนั้นและหาว่าเส้นนั้นตัดกับเส้นโค้งอีกครั้งที่จุดใด จากนั้นจึงสะท้อนจุดนั้นบนแกน x
การเข้ารหัสลับด้วยเส้นโค้งวงรี: การแสดงภาพการคูณจุด G ด้วยจำนวนเต็ม k บนเส้นโค้งวงรี แสดงกระบวนการในการหา G, 2G, 4G เป็นการดำเนินการทางเรขาคณิตบนเส้นโค้งได้ดังนี้
TIP: ในซอฟแวร์ของบิตคอยน์ส่วนใหญ่ใช้ไลบรารีเข้ารหัสลับ libsecp256k1 เพื่อทำการคำนวณทางคณิตศาสตร์เส้นโค้งวงรี

Output and Input Scripts
แม้ว่าภาพประกอบจาก Bitcoin whitepaper ที่แสดงเรื่อง "Transaction chain" จะแสดงให้เห็นว่ามีการใช้ public key และ digital signature โดยตรง แต่ในความเป็นจริงบิตคอยน์เวอร์ชันแรกนั้นมีการส่งการชำระเงินไปยังฟิลด์ที่เรียกว่า output script และมีการใช้จ่ายบิตคอยน์เหล่านั้นโดยได้รับอนุญาตจากฟิลด์ที่เรียกว่า input script ฟิลด์เหล่านี้อนุญาตให้มีการดำเนินการเพิ่มเติมนอกเหนือจาก (หรือแทนที่) การตรวจสอบว่าลายเซ็นสอดคล้องกับ public key หรือไม่ ตัวอย่างเช่น output script สามารถมี public key สองดอกและต้องการลายเซ็นสองลายเซ็นที่สอดคล้องกันในฟิลด์ input script ที่ใช้จ่าย
ในภายหลัง ในหัวข้อ [tx_script] เราจะได้เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับสคริปต์อย่างละเอียด สำหรับตอนนี้ สิ่งที่เราต้องเข้าใจคือ บิตคอยน์จะถูกรับเข้า output script ที่ทำหน้าที่เหมือน public key และการใช้จ่ายบิตคอยน์จะได้รับอนุญาตโดย input script ที่ทำหน้าที่เหมือนลายเซ็น
IP Addresses: The Original Address for Bitcoin (P2PK)
เราได้เห็นแล้วว่าอลิซสามารถจ่ายเงินให้บ็อบโดยการมอบบิตคอยน์บางส่วนของเธอให้กับกุญแจสาธารณะของบ็อบ แต่อลิซจะได้กุญแจสาธารณะของบ็อบมาได้อย่างไร? บ็อบอาจจะให้สำเนากุญแจแก่เธอ แต่ลองดูกุญแจสาธารณะที่เราใช้งานในตัวอย่างที่ผ่านมาอีกครั้ง:
x = F028892BAD7ED57D2FB57BF33081D5CFCF6F9ED3D3D7F159C2E2FFF579DC341A y = 07CF33DA18BD734C600B96A72BBC4749D5141C90EC8AC328AE52DDFE2E505BDBTIP จากหลาม: :สังเกตได้ว่า public key มีความยาวมาก ลองจินตนาการว่าบ็อบพยายามอ่านกุญแจนี้ให้อลิซฟังทางโทรศัพท์ คงจะยากมากที่จะอ่านและบันทึกโดยไม่มีข้อผิดพลาด
แทนที่จะป้อนกุญแจสาธารณะโดยตรง เวอร์ชันแรกของซอฟต์แวร์บิตคอยน์อนุญาตให้ผู้จ่ายเงินป้อนที่อยู่ IP ของผู้รับได้ ตามที่แสดงในหน้าจอการส่งเงินรุ่นแรกของบิตคอยน์ผ่าน The Internet Archive
คุณสมบัตินี้ถูกลบออกในภายหลัง เนื่องจากมีปัญหามากมายในการใช้ที่อยู่ IP แต่คำอธิบายสั้นๆ จะช่วยให้เราเข้าใจได้ดีขึ้นว่าทำไมคุณสมบัติบางอย่างอาจถูกเพิ่มเข้าไปในโปรโตคอลบิตคอยน์

เมื่ออลิซป้อนที่อยู่ IP ของบ็อบในบิตคอยน์เวอร์ชัน 0.1 Full node ของเธอจะทำการเชื่อมต่อกับ full node ของเขาและได้รับ public key ใหม่จากกระเป๋าสตางค์ของบ็อบที่โหนดของเขาไม่เคยให้กับใครมาก่อน การที่เป็น public key ใหม่นี้มีความสำคัญเพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าธุรกรรมต่าง ๆ ที่จ่ายให้บ็อบจะไม่สามารถถูกเชื่อมโยงเข้าด้วยกันโดยคนที่กำลังดูบล็อกเชนและสังเกตเห็นว่าธุรกรรมทั้งหมดจ่ายไปยัง public key เดียวกัน
เมื่อใช้ public key จากโหนดของอลิซซึ่งได้รับมาจากโหนดของบ็อบ กระเป๋าสตางค์ของอลิซจะสร้างเอาต์พุตธุรกรรมที่จ่ายให้กับสคริปต์เอาต์พุตดังนี้
<Bob's public key> OP_CHECKSIGต่อมาบ็อบจะสามารถใช้จ่ายเอาต์พุตนั้นด้วยสคริปต์อินพุตที่ประกอบด้วยลายเซ็นของเขาเท่านั้น:<Bob's signature>เพื่อให้เข้าใจว่าสคริปต์อินพุตและเอาต์พุตกำลังทำอะไร คุณสามารถรวมพวกมันเข้าด้วยกัน (สคริปต์อินพุตก่อน) แล้วสังเกตว่าข้อมูลแต่ละชิ้น (แสดงในเครื่องหมาย < >) จะถูกวางไว้ที่ด้านบนสุดของรายการที่เรียกว่าสแตก (stack) เมื่อพบรหัสคำสั่ง (opcode) มันจะใช้รายการจากสแตก โดยเริ่มจากรายการบนสุด มาดูว่ามันทำงานอย่างไรโดยเริ่มจากสคริปต์ที่รวมกัน:<Bob's signature> <Bob's public key> OP_CHECKSIGสำหรับสคริปต์นี้ ลายเซ็นของบ็อบจะถูกนำไปไว้บนสแตก จากนั้น public key ของบ็อบจะถูกวางไว้ด้านบนของลายเซ็น และบนสุดจะเป็นคำสั่ง OP_CHECKSIG ที่จะใช้องค์ประกอบสองอย่าง เริ่มจาก public key ตามด้วยลายเซ็น โดยลบพวกมันออกจากสแตก มันจะตรวจสอบว่าลายเซ็นตรงกับ public key และยืนยันฟิลด์ต่าง ๆ ในธุรกรรม ถ้าลายเซ็นถูกต้อง OP_CHECKSIG จะแทนที่ตัวเองบนสแตกด้วยค่า 1 ถ้าลายเซ็นไม่ถูกต้อง มันจะแทนที่ตัวเองด้วย 0 ถ้ามีรายการที่ไม่ใช่ศูนย์อยู่บนสุดของสแตกเมื่อสิ้นสุดการประเมิน สคริปต์ก็จะผ่าน ถ้าสคริปต์ทั้งหมดในธุรกรรมผ่าน และรายละเอียดอื่น ๆ ทั้งหมดเกี่ยวกับธุรกรรมนั้นต้องถูกต้องจึงจะถือว่าธุรกรรมนั้นถูกต้อง
โดยสรุป สคริปต์ข้างต้นใช้ public key และลายเซ็นเดียวกันกับที่อธิบายใน whitepaper แต่เพิ่มความซับซ้อนของฟิลด์สคริปต์สองฟิลด์และรหัสคำสั่งหนึ่งตัว ซึ่งเราจะเริ่มเห็นประโยชน์เมื่อเรามองที่ส่วนต่อไป
TIP:จากหลาม agian: เอาต์พุตประเภทนี้เป็นที่รู้จักในปัจจุบันว่า P2PK ซึ่งมันไม่เคยถูกใช้อย่างแพร่หลายสำหรับการชำระเงิน และไม่มีโปรแกรมที่ใช้กันอย่างแพร่หลายที่รองรับการชำระเงินผ่านที่อยู่ IP เป็นเวลาเกือบทศวรรษแล้ว
Legacy addresses for P2PKH
แน่นอนว่าการป้อนที่อยู่ IP ของคนที่คุณต้องการจ่ายเงินให้นั้นมีข้อดีหลายประการ แต่ก็มีข้อเสียหลายประการเช่นกัน หนึ่งในข้อเสียที่สำคัญคือผู้รับจำเป็นต้องให้กระเป๋าสตางค์ของพวกเขาออนไลน์ที่ที่อยู่ IP ของพวกเขา และต้องสามารถเข้าถึงได้จากโลกภายนอก
ซึ่งสำหรับคนจำนวนมากนั่นไม่ใช่ตัวเลือกที่เป็นไปได้เพราะหากพวกเขา:
- ปิดคอมพิวเตอร์ในเวลากลางคืน
- แล็ปท็อปของพวกเขาเข้าสู่โหมดสลีป
- อยู่หลังไฟร์วอลล์
- หรือกำลังใช้การแปลงที่อยู่เครือข่าย (NAT)
ปัญหานี้นำเรากลับมาสู่ความท้าทายเดิมที่ผู้รับเงินอย่างบ็อบต้องให้ public key ที่มีความยาวมากแก่ผู้จ่ายเงินอย่างอลิซ public key ของบิตคอยน์ที่สั้นที่สุดที่นักพัฒนาบิตคอยน์รุ่นแรกรู้จักมีขนาด 65 ไบต์ เทียบเท่ากับ 130 ตัวอักษรเมื่อเขียนในรูปแบบเลขฐานสิบหก (เฮกซาเดซิมอล) แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม บิตคอยน์มีโครงสร้างข้อมูลหลายอย่างที่มีขนาดใหญ่กว่า 65 ไบต์มาก ซึ่งจำเป็นต้องถูกอ้างอิงอย่างปลอดภัยในส่วนอื่น ๆ ของบิตคอยน์โดยใช้ข้อมูลขนาดเล็กที่สุดเท่าที่จะปลอดภัยได้
โดยบิตคอยน์แก้ปัญหานี้ด้วย ฟังก์ชันแฮช (hash function) ซึ่งเป็นฟังก์ชันที่รับข้อมูลที่อาจมีขนาดใหญ่ นำมาแฮช และให้ผลลัพธ์เป็นข้อมูลขนาดคงที่ ฟังก์ชันแฮชจะผลิตผลลัพธ์เดียวกันเสมอเมื่อได้รับข้อมูลนำเข้าแบบเดียวกัน และฟังก์ชันที่ปลอดภัยจะทำให้เป็นไปไม่ได้ในทางปฏิบัติสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเลือกข้อมูลนำเข้าอื่นที่ให้ผลลัพธ์เหมือนกันได้ นั่นทำให้ผลลัพธ์เป็น คำมั่นสัญญา (commitment) ต่อข้อมูลนำเข้า เป็นสัญญาว่าในทางปฏิบัติ มีเพียงข้อมูลนำเข้า x เท่านั้นที่จะให้ผลลัพธ์ X
สมมติว่าผมต้องการถามคำถามคุณและให้คำตอบของผมในรูปแบบที่คุณไม่สามารถอ่านได้ทันที สมมติว่าคำถามคือ "ในปีไหนที่ซาโตชิ นาคาโมโตะเริ่มทำงานบนบิทคอยน์?" ผมจะให้การยืนยันคำตอบของผมในรูปแบบของผลลัพธ์จากฟังก์ชันแฮช SHA256 ซึ่งเป็นฟังก์ชันที่ใช้บ่อยที่สุดในบิทคอยน์:
94d7a772612c8f2f2ec609d41f5bd3d04a5aa1dfe3582f04af517d396a302e4eต่อมา หลังจากคุณบอกคำตอบที่คุณเดาสำหรับคำถามนั้น ผมสามารถเปิดเผยคำตอบของผมและพิสูจน์ให้คุณเห็นว่าคำตอบของผม เมื่อใช้เป็นข้อมูลสำหรับฟังก์ชันแฮช จะให้ผลลัพธ์เดียวกันกับที่ผมให้คุณก่อนหน้านี้$ echo "2007. He said about a year and a half before Oct 2008" | sha256sum 94d7a772612c8f2f2ec609d41f5bd3d04a5aa1dfe3582f04af517d396a302e4eทีนี้ให้สมมติว่าเราถามบ็อบว่า " public key ของคุณคืออะไร?" บ็อบสามารถใช้ฟังก์ชันแฮชเพื่อให้การยืนยันที่ปลอดภัยทางการเข้ารหัสต่อ public key ของเขา หากเขาเปิดเผยกุญแจในภายหลัง และเราตรวจสอบว่ามันให้ผลการยืนยันเดียวกันกับที่เขาให้เราก่อนหน้านี้ เราสามารถมั่นใจได้ว่ามันเป็นกุญแจเดียวกันที่ใช้สร้างการยืนยันก่อนหน้านี้ฟังก์ชันแฮช SHA256 ถือว่าปลอดภัยมากและให้ผลลัพธ์ 256 บิต (32 ไบต์) น้อยกว่าครึ่งหนึ่งของขนาด public key ของบิทคอยน์ดั้งเดิม แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม มีฟังก์ชันแฮชอื่นๆ ที่ปลอดภัยน้อยกว่าเล็กน้อยที่ให้ผลลัพธ์ขนาดเล็กกว่า เช่น ฟังก์ชันแฮช RIPEMD-160 ซึ่งให้ผลลัพธ์ 160 บิต (20 ไบต์) ด้วยเหตุผลที่ซาโตชิ นาคาโมโตะไม่เคยระบุ เวอร์ชันดั้งเดิมของบิทคอยน์สร้างการยืนยันต่อ public key โดยการแฮชกุญแจด้วย SHA256 ก่อน แล้วแฮชผลลัพธ์นั้นด้วย RIPEMD-160 ซึ่งให้การยืนยันขนาด 20 ไบต์ต่อ public key
เราสามารถดูสิ่งนี้ตามอัลกอริทึม เริ่มจากกุญแจสาธารณะ K เราคำนวณแฮช SHA256 และคำนวณแฮช RIPEMD-160 ของผลลัพธ์ ซึ่งให้ตัวเลข 160 บิต (20 ไบต์): A = RIPEMD160(SHA256(K))
ทีนี้เราคงเข้าใจวิธีสร้างการยืนยันต่อ public key แล้ว ต่อไปเราจะมาดูวิธีการใช้งานโดยพิจารณาสคริปต์เอาต์พุตต่อไปนี้:
OP_DUP OP_HASH160 <Bob's commitment> OP_EQUAL OP_CHECKSIGและสคริปต์อินพุตต่อไปนี้:<Bob's signature> <Bob's public key>และเมื่อเรารวมมันเข้าด้วยกันเราจะได้ผลลัพธ์ดังนี้:<Bob's signature> <Bob's public key> OP_DUP OP_HASH160 <Bob's commitment> OP_EQUAL OP_CHECKSIGเหมือนที่เราทำใน IP Addresses: The Original Address for Bitcoin (P2PK) เราเริ่มวางรายการลงในสแต็ก ลายเซ็นของบ็อบถูกวางก่อน จากนั้น public key ของเขาถูกวางไว้ด้านบน จากนั้นดำเนินการ OP_DUP เพื่อทำสำเนารายการบนสุด ดังนั้นรายการบนสุดและรายการที่สองจากบนในสแต็กตอนนี้เป็น public key ของบ็อบทั้งคู่ การดำเนินการ OP_HASH160 ใช้ (ลบ) public key บนสุดและแทนที่ด้วยผลลัพธ์ของการแฮชด้วย RIPEMD160(SHA256(K)) ดังนั้นตอนนี้บนสุดของสแต็กคือแฮชของ public key ของบ็อบ ต่อไป commitment ถูกเพิ่มไว้บนสุดของสแต็ก การดำเนินการ OP_EQUALVERIFY ใช้รายการสองรายการบนสุดและตรวจสอบว่าพวกมันเท่ากัน ซึ่งควรเป็นเช่นนั้นหาก public key ที่บ็อบให้ในสคริปต์อินพุตเป็น public key เดียวกันกับที่ใช้สร้างการยืนยันในสคริปต์เอาต์พุตที่อลิซจ่าย หาก OP_EQUALVERIFY ล้มเหลว ทั้งสคริปต์จะล้มเหลว สุดท้าย เราเหลือสแต็กที่มีเพียงลายเซ็นของบ็อบและ public key ของเขา รหัสปฏิบัติการ OP_CHECKSIG ตรวจสอบว่าพวกมันสอดคล้องกัน
TIP: จากหลาม ถ้าอ่านตรงนี้และงง ๆ ผมไปทำรูปมาให้ดูง่ายขึ้นครับ
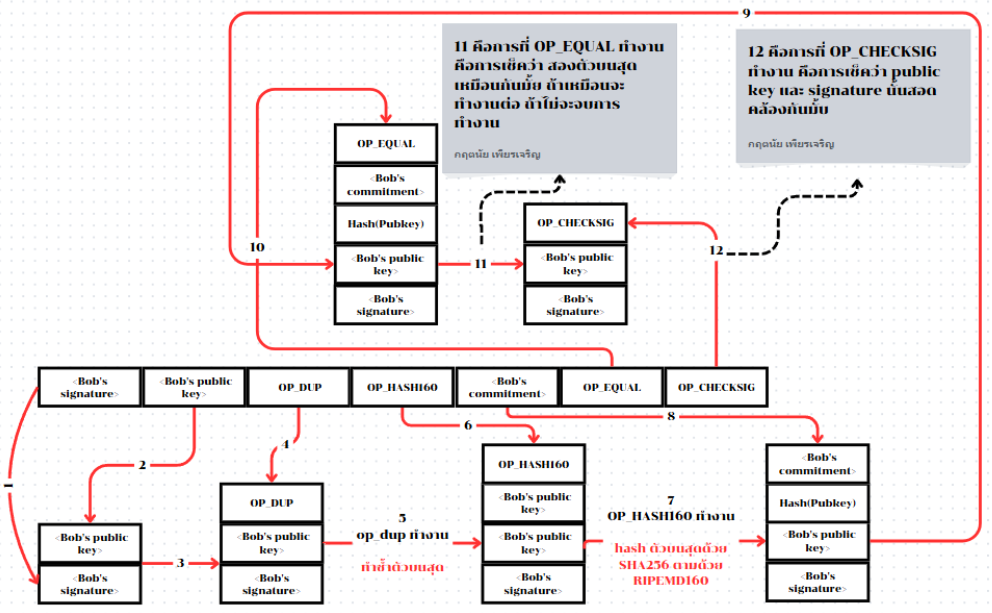
แม้กระบวนการของการ pay-to-publickey-hash(P2PKH) อาจดูซับซ้อน แต่มันทำให้การที่อลิซจ่ายเงินให้บ็อบมีเพียงการยืนยันเพียง 20 ไบต์ต่อ public key ของเขาแทนที่จะเป็นตัวกุญแจเอง ซึ่งจะมีขนาด 65 ไบต์ในเวอร์ชันดั้งเดิมของบิทคอยน์ นั่นเป็นข้อมูลที่น้อยกว่ามากที่บ็อบต้องสื่อสารกับอลิซ
แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม เรายังไม่ได้พูดถึงวิธีที่บ็อบรับ 20 ไบต์เหล่านั้นจากกระเป๋าเงินบิทคอยน์ของเขาไปยังกระเป๋าเงินของอลิซ มีการเข้ารหัสค่าไบต์ที่ใช้กันอย่างแพร่หลาย เช่น เลขฐานสิบหก แต่ข้อผิดพลาดใด ๆ ในการคัดลอกการยืนยันจะทำให้บิทคอยน์ถูกส่งไปยังเอาต์พุตที่ไม่สามารถใช้จ่ายได้ ทำให้พวกมันสูญหายไปตลอดกาล โดยในส่วนถัดไป เราจะดูที่การเข้ารหัสแบบกะทัดรัดและการตรวจสอบความถูกต้อง
Base58check Encoding
ระบบคอมพิวเตอร์มีวิธีเขียนตัวเลขยาวๆ ให้สั้นลงโดยใช้ทั้งตัวเลขและตัวอักษรผสมกัน เพื่อใช้พื้นที่น้อยลงอย่างเช่น
- ระบบเลขฐานสิบ (ปกติที่เราใช้) - ใช้เลข 0-9 เท่านั้น
- ระบบเลขฐานสิบหก - ใช้เลข 0-9 และตัวอักษร A-F ตัวอย่าง: เลข 255 ในระบบปกติ เขียนเป็น FF ในระบบเลขฐานสิบหก (สั้นกว่า)
- ระบบเลขฐานหกสิบสี่ (Base64) - ใช้สัญลักษณ์ถึง 64 ตัว: ตัวอักษรเล็ก (a-z) 26 ตัว, ตัวอักษรใหญ่ (A-Z) 26 ตัว, ตัวเลข (0-9) 10 ตัว, สัญลักษณ์พิเศษอีก 2 ตัว ("+" และ "/")
โดยระบบ Base64 นี้ช่วยให้เราส่งไฟล์คอมพิวเตอร์ผ่านข้อความธรรมดาได้ เช่น การส่งรูปภาพผ่านอีเมล โดยใช้พื้นที่น้อยกว่าการเขียนเป็นเลขฐานสิบแบบปกติมาก
การเข้ารหัสแบบ Base58 คล้ายกับ Base64 โดยใช้ตัวอักษรพิมพ์ใหญ่ พิมพ์เล็ก และตัวเลข แต่ได้ตัดตัวอักษรบางตัวที่มักถูกเข้าใจผิดว่าเป็นตัวอื่นและอาจดูเหมือนกันเมื่อแสดงในฟอนต์บางประเภทออกไป
Base58 คือ Base64 ที่ตัดตัวอักษรต่อไปนี้ออก:
- เลข 0 (ศูนย์)
- ตัวอักษร O (ตัว O พิมพ์ใหญ่)
- ตัวอักษร l (ตัว L พิมพ์เล็ก)
- ตัวอักษร I (ตัว I พิมพ์ใหญ่)
- และสัญลักษณ์ "+" และ "/"
หรือพูดให้ง่ายขึ้น Base58 คือกลุ่มตัวอักษรพิมพ์เล็ก พิมพ์ใหญ่ และตัวเลข แต่ไม่มีตัวอักษรทั้งสี่ตัว (0, O, l, I) ที่กล่าวถึงข้างต้น ตัวอักษรทั้งหมดที่ใช้ใน Base58 จะแสดงให้เห็นในตัวอักษร Base58 ของบิทคอยน์
Example 2. Bitcoin’s base58 alphabet
123456789ABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxyzการเพิ่มความปลอดภัยพิเศษเพื่อป้องกันการพิมพ์ผิดหรือข้อผิดพลาดในการคัดลอก base58check ได้รวม รหัสตรวจสอบ (checksum) ที่เข้ารหัสในตัวอักษร base58 เข้าไปด้วย รหัสตรวจสอบนี้คือข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมอีก 4 ไบต์ที่เพิ่มเข้าไปที่ท้ายของข้อมูลที่กำลังถูกเข้ารหัสรหัสตรวจสอบนี้ได้มาจากการแฮชข้อมูลที่ถูกเข้ารหัส และจึงสามารถใช้เพื่อตรวจจับข้อผิดพลาดจากการคัดลอกและการพิมพ์ได้ เมื่อโปรแกรมได้รับรหัส base58check ซอฟต์แวร์ถอดรหัสจะคำนวณรหัสตรวจสอบของข้อมูลและเปรียบเทียบกับรหัสตรวจสอบที่รวมอยู่ในรหัสนั้น
หากทั้งสองไม่ตรงกัน แสดงว่ามีข้อผิดพลาดเกิดขึ้น และข้อมูล base58check นั้นไม่ถูกต้อง กระบวนการนี้ช่วยป้องกันไม่ให้ address บิทคอยน์ที่พิมพ์ผิดถูกยอมรับโดยซอฟต์แวร์กระเป๋าเงินว่าเป็น address ที่ถูกต้อง ซึ่งเป็นข้อผิดพลาดที่อาจส่งผลให้สูญเสียเงินได้
การแปลงข้อมูล (ตัวเลข) เป็นรูปแบบ base58check มีขั้นตอนดังนี้:
- เราเริ่มโดยการเพิ่ม prefix เข้าไปในข้อมูล เรียกว่า "version byte" ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบุประเภทของข้อมูลที่ถูกเข้ารหัสได้ง่าย ตัวอย่างเช่น: prefix ศูนย์ (0x00 ในระบบเลขฐานสิบหก) แสดงว่าข้อมูลควรถูกใช้เป็นการยืนยัน (hash) ในสคริปต์เอาต์พุต legacy P2PKH
- จากนั้น เราคำนวณ "double-SHA" checksum ซึ่งหมายถึงการใช้อัลกอริทึมแฮช SHA256 สองครั้งกับผลลัพธ์ก่อนหน้า (prefix ต่อกับข้อมูล):
checksum = SHA256(SHA256(prefix||data)) - จากแฮช 32 ไบต์ที่ได้ (การแฮชซ้อนแฮช) เราเลือกเฉพาะ 4 ไบต์แรก ไบต์ทั้งสี่นี้ทำหน้าที่เป็นรหัสตรวจสอบข้อผิดพลาดหรือ checksum
- นำ checksum นี้ไปต่อที่ท้ายข้อมูล
การเข้ารหัสแบบ base58check คือรูปแบบการเข้ารหัสที่ใช้ base58 พร้อมกับการระบุเวอร์ชันและการตรวจสอบความถูกต้อง เพื่อการเข้ารหัสข้อมูลบิทคอยน์ โดยคุณสามารถดูภาพประกอบด้านล่างเพื่อความเข้าใจเพิ่มเติม

ในบิตคอยน์นั้น นอกจากจะใช้ base58check ในการยืนยัน public key แล้ว ก็ยังมีการใช้ในข้อมูลอื่น ๆ ด้วย เพื่อทำให้ข้อมูลนั้นกะทัดรัด อ่านง่าย และตรวจจับข้อผิดพลาดได้ง่ายด้วยรหัสนำหน้า (version prefix) ในการเข้ารหัสแบบ base58check ถูกใช้เพื่อสร้างรูปแบบที่แยกแยะได้ง่าย ซึ่งเมื่อเข้ารหัสด้วย base58 โดยจะมีตัวอักษรเฉพาะที่จุดเริ่มต้นของข้อมูลที่เข้ารหัส base58check ตัวอักษรเหล่านี้ช่วยให้เราระบุประเภทของข้อมูลที่ถูกเข้ารหัสและวิธีการใช้งานได้ง่าย นี่คือสิ่งที่แยกความแตกต่าง ตัวอย่างเช่น ระหว่าง address บิทคอยน์ที่เข้ารหัส base58check ซึ่งขึ้นต้นด้วยเลข 1 กับรูปแบบการนำเข้า private key (WIF - Wallet Import Format) ที่เข้ารหัส base58check ซึ่งขึ้นต้นด้วยเลข 5 ตัวอย่างของ version prefix สามารถดูได้ตามตารางด้านล่างนี้

ภาพต่อไปนี้จะทำให้คุณเห็นภาพของกระบวนการแปลง public key ให้เป็น bitcoin address

Compressed Public Keys
ในยุคแรก ๆ ของบิตคอยน์นั้น มีเพียงการสร้าง public key แบบ 65 Bytes เท่านั้น แต่ในเวลาต่อมา เหล่านักพัฒนาในยุคหลังได้พบวิธีการสร้าง public key แบบใหม่ที่มีเพียง 33 Bytes และสามารถทำงานร่วมกันกับโหนดทั้งหมดในขณะนั้นได้ จีงไม่จะเป็นต้องเปลี่ยนแปลงกฎหรือโครงสร้างภายในโปรโตคอลของบิตคอยน์ โดย poublic key แบบใหม่ที่มีขนาด 33 Bytes นี้เรียกว่า compressed public key (public key ที่ถูกบีบอัด) และมีการเรียก public key ที่มีขนาด 65 Bytes ว่า uncompressed public key (public key ที่ไม่ถูกบีบอัด) ซึ่งประโยชน์ของ public key ที่เล็กลงนั้น นอกจากจะช่วยให้การส่ง public key ให้ผู้อื่นทำได้ง่ายขึ้นแล้ว ยังช่วยให้ธุรกรรมมีขนาดเล็กลง และช่วยให้สามารถทำการชำระเงินได้มากขึ้นในบล็อกเดียวกัน
อย่างที่เราได้เรียนรู้จากเนื้อหาในส่วนของ public key เราได้ทราบว่า public key คือจุด (x, y) บนเส้นโค้งวงรี เนื่องจากเส้นโค้งแสดงฟังก์ชันทางคณิตศาสตร์ จุดบนเส้นโค้งจึงเป็นคำตอบของสมการ ดังนั้นหากเรารู้พิกัด x เราก็สามารถคำนวณพิกัด y ได้โดยแก้สมการ y² mod p = (x³ + 7) mod p นั่นหมายความว่าเราสามารถเก็บเพียงพิกัด x ของ public key โดยละพิกัด y ไว้ ซึ่งช่วยลดขนาดของกุญแจและพื้นที่ที่ต้องใช้เก็บข้อมูลลง 256 บิต การลดขนาดลงเกือบ 50% ในทุกธุรกรรมรวมกันแล้วช่วยประหยัดข้อมูลได้มากมายในระยะยาว!
นี่คือ public key ที่ได้ยกเป็นตัวอย่างไว้ก่อนหน้า
x = F028892BAD7ED57D2FB57BF33081D5CFCF6F9ED3D3D7F159C2E2FFF579DC341A y = 07CF33DA18BD734C600B96A72BBC4749D5141C90EC8AC328AE52DDFE2E505BDBและนี่คือ public key ที่มีตัวนำหน้า 04 ตามด้วยพิกัด x และ y ในรูปแบบ 04 x y:
K = 04F028892BAD7ED57D2FB57BF33081D5CFCF6F9ED3D3D7F159C2E2FFF579DC341A07CF33DA18BD734C600B96A72BBC4749D5141C90EC8AC328AE52DDFE2E505BDBuncompressed public key นั้นจะมีตัวนำหน้าเป็น 04 แต่ compressed public key จะมีตัวนำหน้าเป็น 02 หรือ 03 โดยเหตุผลนั้นมาจากสมการ y² mod p = (x³ + 7) mod p เนื่องจากด้านซ้ายของสมการคือ y² คำตอบสำหรับ y จึงเป็นรากที่สอง ซึ่งอาจมีค่าเป็นบวกหรือลบก็ได้ หากมองเชิงภาพ นี่หมายความว่าพิกัด y ที่ได้อาจอยู่เหนือหรือใต้แกน x เราต้องไม่ลืมว่าเส้นโค้งมีความสมมาตร ซึ่งหมายความว่ามันจะสะท้อนเหมือนกระจกโดยแกน x ดังนั้น แม้เราจะละพิกัด y ได้ แต่เราต้องเก็บ เครื่องหมาย ของ y (บวกหรือลบ) หรืออีกนัยหนึ่งคือเราต้องจำว่ามันอยู่เหนือหรือใต้แกน x เพราะแต่ละตำแหน่งแทนจุดที่แตกต่างกันและเป็น public key ที่แตกต่างกัน
เมื่อคำนวณเส้นโค้งวงรีในระบบเลขฐานสองบนสนามจำกัดของเลขจำนวนเฉพาะ p พิกัด y จะเป็นเลขคู่หรือเลขคี่ ซึ่งสอดคล้องกับเครื่องหมายบวก/ลบตามที่อธิบายก่อนหน้านี้ ดังนั้น เพื่อแยกความแตกต่างระหว่างค่าที่เป็นไปได้สองค่าของ y เราจึงเก็บ compressed public key ด้วยตัวนำหน้า 02 ถ้า y เป็นเลขคู่ และ 03 ถ้า y เป็นเลขคี่ ซึ่งช่วยให้ซอฟต์แวร์สามารถอนุมานพิกัด y จากพิกัด x และคลายการบีบอัดของ public key ไปยังพิกัดเต็มของจุดได้อย่างถูกต้อง ดังภาพประกอบต่อไปนี้

นี่คือ public key เดียวกันกับที่ยกตัวอย่างไว้ข้างต้นซึ่งแสดงให้เห็นในรูป compressed public key ที่เก็บใน 264 บิต (66 ตัวอักษรเลขฐานสิบหก) โดยมีตัวนำหน้า 03 ซึ่งบ่งชี้ว่าพิกัด y เป็นเลขคี่:
K = 03F028892BAD7ED57D2FB57BF33081D5CFCF6F9ED3D3D7F159C2E2FFF579DC341Acompressed public key สอดคล้องกับ private key เดียวกันกับ uncompressed public key หมายความว่ามันถูกสร้างจาก private key เดียวกัน แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม มันก็มีส่วนที่แตกต่างจาก uncompressed public key นั้นคือ หากเราแปลง compressed public key เป็น commitment โดยใช้ฟังก์ชัน HASH160 (RIPEMD160(SHA256(K))) มันจะสร้าง commitment ที่แตกต่างจาก uncompressed public key และจะนำไปสู่ bitcoin address ที่แตกต่างกันในที่สุด สิ่งนี้อาจทำให้สับสนเพราะหมายความว่า private key เดียวสามารถสร้าง public key ในสองรูปแบบที่แตกต่างกัน (แบบบีบอัดและแบบไม่บีบอัด) ซึ่งสร้าง bitcoin address ที่แตกต่างกันcompressed public key เป็นค่าเริ่มต้นในซอฟต์แวร์บิตคอยน์เกือบทั้งหมดในปัจจุบัน และถูกกำหนดให้ใช้กับคุณสมบัติใหม่บางอย่างที่เพิ่มในการอัปเกรดโปรโตคอลในภายหลัง
อย่างไรก็ตาม ซอฟต์แวร์บางตัวยังคงต้องรองรับ uncompressed public key เช่น แอปพลิเคชันกระเป๋าเงินที่นำเข้า private key จากกระเป๋าเงินเก่า เมื่อกระเป๋าเงินใหม่สแกนบล็อกเชนสำหรับผลลัพธ์และอินพุต P2PKH เก่า มันจำเป็นต้องรู้ว่าควรสแกนกุญแจขนาด 65 ไบต์ (และ commitment ของกุญแจเหล่านั้น) หรือกุญแจขนาด 33 ไบต์ (และ commitment ของกุญแจเหล่านั้น) หากไม่สแกนหาประเภทที่ถูกต้อง อาจทำให้ผู้ใช้ไม่สามารถใช้ยอดคงเหลือทั้งหมดได้ เพื่อแก้ไขปัญหานี้ เมื่อส่งออก private key จากกระเป๋าเงิน WIF ที่ใช้แสดง private key ในกระเป๋าเงินบิตคอยน์รุ่นใหม่จะถูกนำไปใช้แตกต่างกันเล็กน้อยเพื่อบ่งชี้ว่า private key เหล่านี้ถูกใช้ในการสร้าง compressed public key
Legacy: Pay to Script Hash (P2SH)
ตามที่เราได้เห็นในส่วนก่อนหน้านี้ ผู้รับบิตคอยน์ สามารถกำหนดให้การชำระเงินที่ส่งมาให้เขานั้นมีเงื่อนไขบางอย่างในสคริปต์เอาต์พุตได้โดยจะต้องปฏิบัติตามเงื่อนไขเหล่านั้นโดยใช้สคริปต์อินพุตเมื่อเขาใช้จ่ายบิตคอยน์เหล่านั้น ในส่วน IP Addresses: The Original Address for Bitcoin (P2PK) เงื่อนไขก็คือสคริปต์อินพุตต้องให้ลายเซ็นที่เหมาะสม ในส่วน Legacy Addresses for P2PKH นั้นจำเป็นต้องมี public key ที่เหมาะสมด้วย
ส่วนสำหรับผู้ส่งก็จะวางเงื่อนไขที่ผู้รับต้องการในสคริปต์เอาต์พุตที่ใช้จ่ายให้กับผู้รับ โดยผู้รับจะต้องสื่อสารเงื่อนไขเหล่านั้นให้ผู้ส่งทราบ ซึ่งคล้ายกับปัญหาที่บ๊อบต้องสื่อสาร public key ของเขาให้อลิซทราบ และเช่นเดียวกับปัญหานั้นที่ public key อาจมีขนาดค่อนข้างใหญ่ เงื่อนไขที่บ๊อบใช้ก็อาจมีขนาดใหญ่มากเช่นกัน—อาจมีขนาดหลายพันไบต์ นั่นไม่เพียงแต่เป็นข้อมูลหลายพันไบต์ที่ต้องสื่อสารให้อลิซทราบ แต่ยังเป็นข้อมูลหลายพันไบต์ที่เธอต้องจ่ายค่าธรรมเนียมธุรกรรมทุกครั้งที่ต้องการใช้จ่ายเงินให้บ๊อบ อย่างไรก็ตาม การใช้ฟังก์ชันแฮชเพื่อสร้าง commitment ขนาดเล็กสำหรับข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่ก็สามารถนำมาใช้ได้ในกรณีนี้เช่นกัน
ในเวลาต่อมานั้น การอัปเกรด BIP16 สำหรับโปรโตคอลบิตคอยน์ในปี 2012 ได้อนุญาตให้สคริปต์เอาต์พุตสร้าง commitment กับ redemption script (redeem script) ได้ แปลว่าเมื่อบ๊อบใช้จ่ายบิตคอยน์ของเขา ภายในสคริปต์อินพุตของเขานั้นจะต้องให้ redeem script ที่ตรงกับ commitment และข้อมูลที่จำเป็นเพื่อให้เป็นไปตาม redeem script (เช่น ลายเซ็น) เริ่มต้นด้วยการจินตนาการว่าบ๊อบต้องการให้มีลายเซ็นสองอันเพื่อใช้จ่ายบิตคอยน์ของเขา หนึ่งลายเซ็นจากกระเป๋าเงินบนเดสก์ท็อปและอีกหนึ่งจากอุปกรณ์เซ็นแบบฮาร์ดแวร์ เขาใส่เงื่อนไขเหล่านั้นลงใน redeem script:
<public key 1> OP_CHECKSIGVERIFY <public key 2> OP_CHECKSIGจากนั้นเขาสร้าง commitment กับ redeem script โดยใช้กลไก HASH160 เดียวกับที่ใช้สำหรับ commitment แบบ P2PKH, RIPEMD160(SHA256(script)) commitment นั้นถูกวางไว้ในสคริปต์เอาต์พุตโดยใช้เทมเพลตพิเศษ:OP_HASH160 <commitment> OP_EQUALคำเตือน: เมื่อใช้ pay to script hash (P2SH) คุณต้องใช้เทมเพลต P2SH โดยเฉพาะ ซึ่งจะไม่มีข้อมูลหรือเงื่อนไขเพิ่มเติมในสคริปต์เอาต์พุต หากสคริปต์เอาต์พุตไม่ได้เป็น OP_HASH160 <20 ไบต์> OP_EQUAL แน่นอนว่า redeem script จะไม่ถูกใช้และบิตคอยน์ใด ๆ อาจไม่สามารถใช้จ่ายได้หรืออาจถูกใช้จ่ายได้โดยทุกคน (หมายความว่าใครก็สามารถนำไปใช้ได้)
เมื่อบ๊อบต้องการจ่ายเงินที่เขาได้รับผ่าน commitment สำหรับสคริปต์ของเขา เขาจะใช้สคริปต์อินพุตที่รวมถึง redeem script ซึ่งถูกแปลงให้เป็นข้อมูลอีลิเมนต์เดียว นอกจากนี้เขายังให้ลายเซ็นที่จำเป็นเพื่อให้เป็นไปตาม redeem script โดยเรียงลำดับตามที่จะถูกใช้โดย opcodes:
<signature2> <signature1> <redeem script>เมื่อโหนดของบิตคอยน์ได้รับการใช้จ่ายของบ๊อบพวกมันจะตรวจสอบว่า redeem script ที่ถูกแปลงเป็นค่าแฮชแล้วมีค่าเดียวกันกับ commitment มั้ย หลังจากนั้นพวกมันจะแทนที่มันบนสแต็คด้วยค่าที่ถอดรหัสแล้ว:<signature2> <signature1> <pubkey1> OP_CHECKSIGVERIFY <pubkey2> OP_CHECKSIGสคริปต์จะถูกประมวลผล และหากผ่านการตรวจสอบและรายละเอียดธุรกรรมอื่น ๆ ทั้งหมดถูกต้อง ธุรกรรมก็จะถือว่าใช้ได้address สำหรับ P2SH ก็ถูกสร้างด้วย base58check เช่นกัน คำนำหน้าเวอร์ชันถูกตั้งเป็น 5 ซึ่งทำให้ที่อยู่ที่เข้ารหัสแล้วขึ้นต้นด้วยเลข 3 ตัวอย่างของที่อยู่ P2SH คือ 3F6i6kwkevjR7AsAd4te2YB2zZyASEm1HM
TIP: P2SH ไม่จำเป็นต้องเหมือนกับธุรกรรมแบบหลายลายเซ็น (multisignature) เสมอไป ถึง address P2SH ส่วนใหญ่ แทนสคริปต์แบบหลายลายเซ็นก็ตาม แต่อาจแทนสคริปต์ที่เข้ารหัสธุรกรรมประเภทอื่น ๆ ได้ด้วย
P2PKH และ P2SH เป็นสองเทมเพลตสคริปต์เท่านั้นที่ใช้กับการเข้ารหัสแบบ base58check พวกมันเป็นที่รู้จักในปัจจุบันว่าเป็น address แบบ legacy และกลายเป็นรูปแบบที่พบน้อยลงเรื่อยๆ address แบบ legacy ถูกแทนที่ด้วยaddress ตระกูล bech32
การโจมตี P2SH แบบ Collision
address ทั้งหมดที่อิงกับฟังก์ชันแฮชมีความเสี่ยงในทางทฤษฎีต่อผู้โจมตีที่อาจค้นพบอินพุตเดียวกันที่สร้างเอาต์พุตฟังก์ชันแฮช (commitment) โดยอิสระ ในกรณีของบิตคอยน์ หากพวกเขาค้นพบอินพุตในวิธีเดียวกับที่ผู้ใช้ดั้งเดิมทำ พวกเขาจะรู้ private key ของผู้ใช้และสามารถใช้จ่ายบิตคอยน์ของผู้ใช้นั้นได้ โอกาสที่ผู้โจมตีจะสร้างอินพุตสำหรับ commitment ที่มีอยู่แล้วโดยอิสระนั้นขึ้นอยู่กับความแข็งแกร่งของอัลกอริทึมแฮช สำหรับอัลกอริทึมที่ปลอดภัย 160 บิตอย่าง HASH160 ความน่าจะเป็นอยู่ที่ 1 ใน 2^160 นี่เรียกว่าการโจมตีแบบ preimage attack
ผู้โจมตีสามารถพยายามสร้างข้อมูลนำเข้าสองชุดที่แตกต่างกัน (เช่น redeem scripts) ที่สร้างการเข้ารหัสแบบเดียวกันได้ สำหรับ address ที่สร้างโดยฝ่ายเดียวทั้งหมด โอกาสที่ผู้โจมตีจะสร้างข้อมูลนำเข้าที่แตกต่างสำหรับการเข้ารหัสที่มีอยู่แล้วมีประมาณ 1 ใน 2^160 สำหรับอัลกอริทึม HASH160 นี่คือการโจมตีแบบ second preimage attack
อย่างไรก็ตาม สถานการณ์จะเปลี่ยนไปเมื่อผู้โจมตีสามารถมีอิทธิพลต่อค่าข้อมูลนำเข้าดั้งเดิมได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น ผู้โจมตีมีส่วนร่วมในการสร้างสคริปต์แบบหลายลายเซ็น (multisignature script) ซึ่งพวกเขาไม่จำเป็นต้องส่ง public key ของตนจนกว่าจะทราบ public key ของฝ่ายอื่นทั้งหมด ในกรณีนั้น ความแข็งแกร่งของอัลกอริทึมการแฮชจะลดลงเหลือรากที่สองของมัน สำหรับ HASH160 ความน่าจะเป็นจะกลายเป็น 1 ใน 2^80 นี่คือการโจมตีแบบ collision attack
เพื่อให้เข้าใจตัวเลขเหล่านี้ในบริบทที่ชัดเจน ข้อมูล ณ ต้นปี 2023 นักขุดบิตคอยน์ทั้งหมดรวมกันสามารถประมวลผลฟังก์ชันแฮชประมาณ 2^80 ทุกชั่วโมง พวกเขาใช้ฟังก์ชันแฮชที่แตกต่างจาก HASH160 ดังนั้นฮาร์ดแวร์ที่มีอยู่จึงไม่สามารถสร้างการโจมตีแบบ collision attack สำหรับมันได้ แต่การมีอยู่ของเครือข่ายบิตคอยน์พิสูจน์ว่าการโจมตีแบบชนกันต่อฟังก์ชัน 160 บิตอย่าง HASH160 สามารถทำได้จริงในทางปฏิบัติ นักขุดบิตคอยน์ได้ลงทุนเทียบเท่ากับหลายพันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐในฮาร์ดแวร์พิเศษ ดังนั้นการสร้างการโจมตีแบบ collision attack จึงไม่ใช่เรื่องถูก แต่มีองค์กรที่คาดหวังว่าจะได้รับบิตคอยน์มูลค่าหลายพันล้านดอลลาร์ไปยัง address ที่สร้างโดยกระบวนการที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหลายฝ่าย ซึ่งอาจทำให้การโจมตีนี้มีกำไร
มีโปรโตคอลการเข้ารหัสที่เป็นที่ยอมรับอย่างดีในการป้องกันการโจมตีแบบ collision attack แต่วิธีแก้ปัญหาที่ง่ายโดยไม่ต้องใช้ความรู้พิเศษจากผู้พัฒนากระเป๋าเงินคือการใช้ฟังก์ชันแฮชที่แข็งแกร่งกว่า การอัปเกรดบิตคอยน์ในภายหลังทำให้เป็นไปได้ และ address บิตคอยน์ใหม่ให้ความต้านทานการชนกันอย่างน้อย 128 บิต การดำเนินการแฮช 2^128 ครั้งจะใช้เวลานักขุดบิตคอยน์ปัจจุบันทั้งหมดประมาณ 32 พันล้านปี
แม้ว่าเราไม่เชื่อว่ามีภัยคุกคามเร่งด่วนต่อผู้ที่สร้าง address P2SH ใหม่ แต่เราแนะนำให้กระเป๋าเงินใหม่ทั้งหมดใช้ที่อยู่ประเภทใหม่เพื่อขจัดความกังวลเกี่ยวกับการโจมตีแบบ collision attack ของ P2SH address
Bech32 Addresses
ในปี 2017 โปรโตคอลบิตคอยน์ได้รับการอัปเกรด เพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้ตัวระบุธุรกรรม (txids) ไม่สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงได้ โดยไม่ได้รับความยินยอมจากผู้ใช้ที่ทำการใช้จ่าย (หรือองค์ประชุมของผู้ลงนามเมื่อต้องมีลายเซ็นหลายรายการ) การอัปเกรดนี้เรียกว่า segregated witness (หรือเรียกสั้นๆ ว่า segwit) ซึ่งยังให้ความสามารถเพิ่มเติมสำหรับข้อมูลธุรกรรมในบล็อกและประโยชน์อื่น ๆ อีกหลายประการ แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม หากมีผู้ใช้เก่าที่ต้องการเข้าถึงประโยชน์ของ segwit โดยตรงต้องยอมรับการชำระเงินไปยังสคริปต์เอาต์พุตใหม่
ตามที่ได้กล่าวไว้ใน p2sh หนึ่งในข้อดีของเอาต์พุตประเภท P2SH คือผู้จ่ายไม่จำเป็นต้องรู้รายละเอียดของสคริปต์ที่ผู้รับใช้ การอัปเกรด segwit ถูกออกแบบมาให้ใช้กลไกนี้ได้ดังเดิม จึง ทำให้ผู้จ่ายสามารถเริ่มเข้าถึงประโยชน์ใหม่ ๆ หลายอย่างได้ทันทีโดยใช้ที่อยู่ P2SH แต่เพื่อให้ผู้รับสามารถเข้าถึงประโยชน์เหล่านั้นได้ พวกเขาจำเป็นจะต้องให้กระเป๋าเงินของผู้จ่ายจ่ายเงินให้เขาโดยใช้สคริปต์ประเภทอื่นแทน ซึ่งจะต้องอาศัยการอัปเกรดกระเป๋าเงินของผู้จ่ายเพื่อรองรับสคริปต์ใหม่เหล่านี้
ในช่วงแรก เหล่านักพัฒนาบิตคอยน์ได้นำเสนอ BIP142 ซึ่งจะยังคงใช้ base58check ร่วมกับไบต์เวอร์ชันใหม่ คล้ายกับการอัปเกรด P2SH แต่การให้กระเป๋าเงินทั้งหมดอัปเกรดไปใช้สคริปต์ใหม่ที่มีเวอร์ชัน base58check ใหม่นั้น คาดว่าจะต้องใช้ความพยายามเกือบเท่ากับการให้พวกเขาอัปเกรดไปใช้รูปแบบ address ที่เป็นแบบใหม่ทั้งหมด ด้วยเหตุนี้้เอง ผู้สนับสนุนบิตคอยน์หลายคนจึงเริ่มออกแบบรูปแบบ address ที่ดีที่สุดเท่าที่เป็นไปได้ พวกเขาระบุปัญหาหลายอย่างกับ base58check ไว้ดังนี้:
- การที่ base58check ใช้อักษรที่มีทั้งตัวพิมพ์ใหญ่และตัวพิมพ์เล็กทำให้ไม่สะดวกในการอ่านออกเสียงหรือคัดลอก ลองอ่าน address แบบเก่าในบทนี้ให้เพื่อนฟังและให้พวกเขาคัดลอก คุณจะสังเกตว่าคุณต้องระบุคำนำหน้าทุกตัวอักษรด้วยคำว่า "ตัวพิมพ์ใหญ่" และ "ตัวพิมพ์เล็ก" และเมื่อคุณตรวจสอบสิ่งที่พวกเขาเขียน คุณจะพบว่าตัวพิมพ์ใหญ่และตัวพิมพ์เล็กของตัวอักษรบางตัวอาจดูคล้ายกันในลายมือของคนส่วนใหญ่
- รูปแบบนี้สามารถตรวจจับข้อผิดพลาดได้ แต่ไม่สามารถช่วยผู้ใช้แก้ไขข้อผิดพลาดเหล่านั้น ตัวอย่างเช่น หากคุณสลับตำแหน่งตัวอักษรสองตัวโดยไม่ตั้งใจเมื่อป้อน address ด้วยตนเอง กระเป๋าเงินของคุณจะเตือนว่ามีข้อผิดพลาดเกิดขึ้นแน่นอน แต่จะไม่ช่วยให้คุณค้นพบว่าข้อผิดพลาดอยู่ที่ไหน คุณอาจต้องใช้เวลาหลายนาทีที่น่าหงุดหงิดเพื่อค้นหาข้อผิดพลาดในที่สุด
- การใช้ตัวอักษรที่มีทั้งตัวพิมพ์ใหญ่และตัวพิมพ์เล็กยังต้องใช้พื้นที่เพิ่มเติมในการเข้ารหัสใน QR code ซึ่งนิยมใช้ในการแชร์ address และ invoice ระหว่างกระเป๋าเงิน พื้นที่เพิ่มเติมนี้หมายความว่า QR code จำเป็นต้องมีขนาดใหญ่ขึ้นที่ความละเอียดเดียวกัน หรือไม่เช่นนั้นก็จะยากต่อการสแกนอย่างรวดเร็ว
- การที่ต้องการให้กระเป๋าเงินผู้จ่ายทุกใบอัปเกรดเพื่อรองรับคุณสมบัติโปรโตคอลใหม่ เช่น P2SH และ segwit แม้ว่าการอัปเกรดเองอาจไม่ต้องใช้โค้ดมากนัก แต่ประสบการณ์แสดงให้เห็นว่าผู้พัฒนากระเป๋าเงินหลายรายมักยุ่งกับงานอื่น ๆ และบางครั้งอาจล่าช้าในการอัปเกรดเป็นเวลาหลายปี สิ่งนี้ส่งผลเสียต่อทุกคนที่ต้องการใช้คุณสมบัติใหม่ ๆ เหล่านี้
นักพัฒนาที่ทำงานเกี่ยวกับรูปแบบ address สำหรับ segwit ได้พบวิธีแก้ปัญหาเหล่านี้ทั้งหมดในรูปแบบ address แบบใหม่ที่เรียกว่า bech32 (ออกเสียงด้วย "ch" อ่อน เช่นใน "เบช สามสิบสอง") คำว่า "bech" มาจาก BCH ซึ่งเป็นอักษรย่อของบุคคลสามคนที่ค้นพบรหัสวนนี้ในปี 1959 และ 1960 ซึ่งเป็นพื้นฐานของ bech32 ส่วน "32" หมายถึงจำนวนตัวอักษรในชุดตัวอักษร bech32 (คล้ายกับ 58 ใน base58check):
-
Bech32 ใช้เฉพาะตัวเลขและตัวอักษรรูปแบบเดียว (โดยปกติจะแสดงเป็นตัวพิมพ์เล็ก) แม้ว่าชุดตัวอักษรของมันจะมีขนาดเกือบครึ่งหนึ่งของชุดตัวอักษรใน base58check ก็ตามแต่ address bech32 สำหรับสคริปต์ pay to witness public key hash (P2WPKH) ก็ยังยาวกว่า legacy address และมีขนาดเท่ากันกับสคริปต์ P2PKH
-
Bech32 สามารถทั้งตรวจจับและช่วยแก้ไขข้อผิดพลาดได้ ใน address ที่มีความยาวตามที่คาดหวังได้ และสามารถรับประกันทางคณิตศาสตร์ได้ว่าจะตรวจพบข้อผิดพลาดใด ๆ ที่ส่งผลกระทบต่อตัวอักษร 4 ตัวหรือน้อยกว่า ซึ่งเชื่อถือได้มากกว่า base58check ส่วนสำหรับข้อผิดพลาดที่ยาวกว่านั้น จะไม่สามารถตรวจพบได้ (โอกาสเกิดน้อยกว่าหนึ่งครั้งในหนึ่งพันล้าน) ซึ่งมีความเชื่อถือได้ประมาณเท่ากับ base58check ยิ่งไปกว่านั้น สำหรับ adddress ที่พิมพ์โดยมีข้อผิดพลาดเพียงเล็กน้อย มันสามารถบอกผู้ใช้ได้ว่าข้อผิดพลาดเหล่านั้นเกิดขึ้นที่ไหน ช่วยให้พวกเขาสามารถแก้ไขข้อผิดพลาดจากการคัดลอกเล็ก ๆ น้อย ๆ ได้อย่างรวดเร็ว
-
ตัวอย่างที่ 3 Bech32 address ที่มีข้อผิดพลาด Address: bc1p9nh05ha8wrljf7ru236awn4t2x0d5ctkkywmv9sclnm4t0av2vgs4k3au7 ข้อผิดพลาดที่ตรวจพบแสดงเป็นตัวหนาและขีดเส้นใต้ สร้างโดยใช้โปรแกรมสาธิตการถอดรหัส bech32 address
-
bech32 address นิยมเขียนด้วยตัวอักษรพิมพ์เล็กเท่านั้น แต่ตัวอักษรพิมพ์เล็กเหล่านี้สามารถแทนที่ด้วยตัวอักษรพิมพ์ใหญ่ก่อนการเข้ารหัส address ในรหัส QR ได้ วิธีนี้ช่วยให้สามารถใช้โหมดการเข้ารหัส QR แบบพิเศษที่ใช้พื้นที่น้อยกว่า คุณจะสังเกตเห็นความแตกต่างในขนาดและความซับซ้อนของรหัส QR ทั้งสองสำหรับที่อยู่เดียวกันในรูปภาพข้างล่างนี้

- Bech32 ใช้ประโยชน์จากกลไกการอัปเกรดที่ออกแบบมาเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของ segwit เพื่อทำให้กระเป๋าเงินผู้จ่ายสามารถจ่ายเงินไปยังประเภทเอาต์พุตที่ยังไม่ได้ใช้งานได้ โดยมีเป้าหมายคือการอนุญาตให้นักพัฒนาสร้างกระเป๋าเงินในวันนี้ที่สามารถใช้จ่ายไปยัง bech32 address และทำให้กระเป๋าเงินนั้นยังคงสามารถใช้จ่ายไปยัง bech32address ได้สำหรับผู้ใช้คุณสมบัติใหม่ที่เพิ่มในการอัปเกรดโปรโตคอลในอนาคต โดยที่มีความหวังว่าเราอาจไม่จำเป็นต้องผ่านรอบการอัปเกรดทั้งระบบอีกต่อไป ซึ่งจำเป็นสำหรับการให้ผู้คนใช้งาน P2SH และ segwit ได้อย่างเต็มรูปแบบ
-
Problems with Bech32 Addresses
address แบบ bech32 ประสบความสำเร็จในทุกด้านยกเว้นปัญหาหนึ่ง คือการรับประกันทางคณิตศาสตร์เกี่ยวกับความสามารถในการตรวจจับข้อผิดพลาดจะใช้ได้เฉพาะเมื่อความยาวของ address ที่คุณป้อนเข้าไปในกระเป๋าเงินมีความยาวเท่ากับ address ดั้งเดิมเท่านั้น หากคุณเพิ่มหรือลบตัวอักษรใด ๆ ระหว่างการคัดลอกจะทำให้ไม่สามารถตรวจจับได้ การรับประกันนี้จะไม่มีผล และกระเป๋าเงินของคุณอาจใช้จ่ายเงินไปยัง address ที่ไม่ถูกต้อง แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม แม้จะไม่มีคุณสมบัตินี้ มีความเชื่อว่าเป็นไปได้ยากมากที่ผู้ใช้ที่เพิ่มหรือลบตัวอักษรจะสร้างสตริงที่มีผลรวมตรวจสอบที่ถูกต้อง ซึ่งช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ว่าเงินของผู้ใช้จะปลอดภัย
น่าเสียดายที่การเลือกใช้ค่าคงที่ตัวหนึ่งในอัลกอริทึม bech32 บังเอิญทำให้การเพิ่มหรือลบตัวอักษร "q" ในตำแหน่งที่สองจากท้ายของ address ที่ลงท้ายด้วยตัวอักษร "p" เป็นเรื่องง่ายมาก ในกรณีเหล่านั้น คุณยังสามารถเพิ่มหรือลบตัวอักษร "q" หลายครั้งได้ด้วย ข้อผิดพลาดนี้จะถูกตรวจจับโดยผลรวมตรวจสอบ (checksum) ในบางครั้ง แต่จะถูกมองข้ามบ่อยกว่าความคาดหวังหนึ่งในพันล้านสำหรับข้อผิดพลาดจากการแทนที่ของ bech32 อย่างมาก สำหรับตัวอย่างสามารถดูได้ในรูปภาพข้างล่างนี้
ตัวอย่างที่ 4. การขยายความยาวของ bech32 address โดยไม่ทำให้ผลรวมตรวจสอบเป็นโมฆะ ``` bech32 address ที่ถูกต้อง: bc1pqqqsq9txsqp
address ที่ไม่ถูกต้องแต่มีผลรวมตรวจสอบที่ถูกต้อง: bc1pqqqsq9txsqqqqp bc1pqqqsq9txsqqqqqqp bc1pqqqsq9txsqqqqqqqqp bc1pqqqsq9txsqqqqqqqqqp bc1pqqqsq9txsqqqqqqqqqqqp ```
จากตัวอย่างนี้ คุณจะเห็นว่าแม้มีการเพิ่มตัวอักษร "q" เข้าไปหลายตัวก่อนตัวอักษร "p" ตัวสุดท้าย ระบบตรวจสอบก็ยังคงยอมรับว่า address เหล่านี้ถูกต้อง นี่เป็นข้อบกพร่องสำคัญของ bech32 เพราะอาจทำให้เงินถูกส่งไปยัง address ที่ไม่มีใครเป็นเจ้าของจริง ๆ หรือ address ที่ไม่ได้ตั้งใจจะส่งไป
สำหรับเวอร์ชันเริ่มต้นของ segwit (เวอร์ชัน 0) ปัญหานี้ไม่ใช่ความกังวลในทางปฏิบัติ เพราะมีความยาวที่ถูกต้องมีเพียงสองแบบที่กำหนดไว้สำหรับเอาต์พุต นั้นคือ 22 Byte และ 34 Byte ซึ่งสอดคล้องกับ bech32 address ที่มีความยาวยาวที่ 42 หรือ 62 ตัวอักษร ดังนั้นคนจะต้องเพิ่มหรือลบตัวอักษร "q" จากตำแหน่งที่สองจากท้ายของ bech32 address ถึง 20 ครั้งเพื่อส่งเงินไปยัง address ที่ไม่ถูกต้องโดยที่กระเป๋าเงินไม่สามารถตรวจจับได้ อย่างไรก็ตาม มันอาจกลายเป็นปัญหาสำหรับผู้ใช้ในอนาคตหากมีการนำการอัปเกรดบนพื้นฐานของ segwit มาใช้
Bech32m
แม้ว่า bech32 จะทำงานได้ดีสำหรับ segwit v0 แต่นักพัฒนาไม่ต้องการจำกัดขนาดเอาต์พุตโดยไม่จำเป็นในเวอร์ชันหลังๆ ของ segwit หากไม่มีข้อจำกัด การเพิ่มหรือลบตัวอักษร "q" เพียงตัวเดียวใน bech32 address อาจทำให้ผู้ใช้ส่งเงินโดยไม่ตั้งใจไปยังเอาต์พุตที่ไม่สามารถใช้จ่ายได้หรือสามารถใช้จ่ายได้โดยทุกคน (ทำให้บิตคอยน์เหล่านั้นถูกนำไปโดยทุกคนได้) นักพัฒนาได้วิเคราะห์ปัญหา bech32 อย่างละเอียดและพบว่าการเปลี่ยนค่าคงที่เพียงตัวเดียวในอัลกอริทึมของพวกเขาจะขจัดปัญหานี้ได้ ทำให้มั่นใจว่าการแทรกหรือลบตัวอักษรสูงสุดห้าตัวจะไม่ถูกตรวจจับน้อยกว่าหนึ่งครั้งในหนึ่งพันล้านเท่านั้น
เวอร์ชันของ bech32 ที่มีค่าคงที่เพียงหนึ่งตัวที่แตกต่างกันเรียกว่า bech32 แบบปรับแต่ง (bech32m) ตัวอักษรทั้งหมดใน address แบบ bech32 และ bech32m สำหรับข้อมูลพื้นฐานเดียวกันจะเหมือนกันทั้งหมด ยกเว้นหกตัวสุดท้าย (ซึ่งเป็นส่วนของ checksum) นั่นหมายความว่ากระเป๋าเงินจำเป็นต้องรู้ว่ากำลังใช้เวอร์ชันใดเพื่อตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของ checksum แต่ address ทั้งสองประเภทมีไบต์เวอร์ชันภายในที่ทำให้การระบุเวอร์ชันที่ใช้อยู่เป็นเรื่องที่ง่าย ในการทำงานกับทั้ง bech32 และ bech32m เราจะพิจารณากฎการเข้ารหัสและการแยกวิเคราะห์สำหรับ address บิตคอยน์แบบ bech32m เนื่องจากพวกมันครอบคลุมความสามารถในการแยกวิเคราะห์บน address แบบ bech32 และเป็นรูปแบบ address ที่แนะนำในปัจจุบันสำหรับกระเป๋าเงินบิตคอยน์
ข้อความจากหลาม: คือผมว่าตรงนี้เขาเขียนไม่รู้เรื่อง แต่เดาว่าเขาน่าจะสื่อว่า เราควรเรียนรู้วิธีการทำงานกับ bech32m เพราะมันเป็นรูปแบบที่แนะนำให้ใช้ในปัจจุบัน และมันมีข้อดีเพราะbech32m สามารถรองรับการอ่าน address แบบ bech32 แบบเก่าได้ด้วย ง่ายๆ คือ ถ้าคุณเรียนรู้วิธีทำงานกับ bech32m คุณจะสามารถทำงานกับทั้ง bech32m และ bech32 ได้ทั้งสองแบบ
bech32m address ริ่มต้นด้วยส่วนที่มนุษย์อ่านได้ (Human Readable Part: HRP) BIP173 มีกฎสำหรับการสร้าง HRP ของคุณเอง แต่สำหรับบิตคอยน์ คุณเพียงแค่จำเป็นต้องรู้จัก HRP ที่ถูกเลือกไว้แล้วตามที่แสดงในตารางข้างล่างนี้

ส่วน HRP ตามด้วยตัวคั่น ซึ่งก็คือเลข "1" ในข้อเสนอก่อนหน้านี้สำหรับตัวคั่นโปรโตคอลได้ใช้เครื่องหมายทวิภาค (colon) แต่ระบบปฏิบัติการและแอปพลิเคชันบางตัวที่อนุญาตให้ผู้ใช้ดับเบิลคลิกคำเพื่อไฮไลต์สำหรับการคัดลอกและวางนั้นจะไม่ขยายการไฮไลต์ไปถึงและผ่านเครื่องหมายทวิภาค
การใช้ตัวเลขช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ว่าการไฮไลต์ด้วยดับเบิลคลิกจะทำงานได้กับโปรแกรมใดๆ ที่รองรับสตริง bech32m โดยทั่วไป (ซึ่งรวมถึงตัวเลขอื่นๆ ด้วย) เลข "1" ถูกเลือกเพราะสตริง bech32 ไม่ได้ใช้เลข 1 ในกรณีอื่น เพื่อป้องกันการแปลงโดยไม่ตั้งใจระหว่างเลข "1" กับตัวอักษรพิมพ์เล็ก "l"
และส่วนอื่นของ bech32m address เรียกว่า "ส่วนข้อมูล" (data part) ซึ่งประกอบด้วยสามองค์ประกอบ:
- Witness version: ไบต์ถัดไปหลังจากตัวคั่นตัวอักษรนี้แทนเวอร์ชันของ segwit ตัวอักษร "q" คือการเข้ารหัสของ "0" สำหรับ segwit v0 ซึ่งเป็นเวอร์ชันแรกของ segwit ที่มีการแนะนำที่อยู่ bech32 ตัวอักษร "p" คือการเข้ารหัสของ "1" สำหรับ segwit v1 (หรือเรียกว่า taproot) ซึ่งเริ่มมีการใช้งาน bech32m มีเวอร์ชันที่เป็นไปได้ทั้งหมด 17 เวอร์ชันของ segwit และสำหรับ Bitcoin จำเป็นต้องให้ไบต์แรกของส่วนข้อมูล bech32m ถอดรหัสเป็นตัวเลข 0 ถึง 16 (รวมทั้งสองค่า)
- Witness program: คือตำแหน่งหลังจาก witnessversion ตั้งแต่ตำแหน่ง 2 ถึง 40 Byte สำหรับ segwit v0 นี้ต้องมีความยาว 20 หรือ 32 Byte ไม่สามารถ ffมีขนาดอื่นได้ สำหรับ segwit v1 ความยาวเดียวที่ถูกกำหนดไว้ ณ เวลาที่เขียนนี้คือ 32 ไบต์ แต่อาจมีการกำหนดความยาวอื่น ๆ ได้ในภายหลัง
- Checksum: มีความยาว 6 ตัวอักษร โดยส่วนนี้ถูกสร้างขึ้นโดยใช้รหัส BCH ซึ่งเป็นประเภทของรหัสแก้ไขข้อผิดพลาด (error corection code) (แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม สำหรับ address บิตคอยน์ เราจะเห็นในภายหลังว่าเป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่จะใช้ checksum เพื่อการตรวจจับข้อผิดพลาดเท่านั้น—ไม่ใช่การแก้ไข
ในส่วนต่อไปหลังจากนี้เราจะลองสร้าง address แบบ bech32 และ bech32m สำหรับตัวอย่างทั้งหมดต่อไปนี้ เราจะใช้โค้ดอ้างอิง bech32m สำหรับ Python
เราจะเริ่มด้วยการสร้างสคริปต์เอาต์พุตสี่ตัว หนึ่งตัวสำหรับแต่ละเอาต์พุต segwit ที่แตกต่างกันที่ใช้ในช่วงเวลาของการเผยแพร่ บวกกับอีกหนึ่งตัวสำหรับเวอร์ชัน segwit ในอนาคตที่ยังไม่มีความหมายที่กำหนดไว้ สคริปต์เหล่านี้แสดงอยู่ในตารางข้างล่างนี้

สำหรับเอาต์พุต P2WPKH witness program มีการผูก commitment ที่สร้างขึ้นในลักษณะเดียวกันกับ P2PKH ที่เห็นใน Legacy Addresses for P2PKH โดย public key ถูกส่งเข้าไปในฟังก์ชันแฮช SHA256 ไดเจสต์ขนาด 32 ไบต์ที่ได้จะถูกส่งเข้าไปในฟังก์ชันแฮช RIPEMD-160 ไดเจสต์ของฟังก์ชันนั้น จะถูกวางไว้ใน witness program
สำหรับเอาต์พุตแบบ pay to witness script hash (P2WSH) เราไม่ได้ใช้อัลกอริทึม P2SH แต่เราจะนำสคริปต์ ส่งเข้าไปในฟังก์ชันแฮช SHA256 และใช้ไดเจสต์ขนาด 32 ไบต์ของฟังก์ชันนั้นใน witness program สำหรับ P2SH ไดเจสต์ SHA256 จะถูกแฮชอีกครั้งด้วย RIPEMD-160 ซึ่งแน่นอนว่าอาจจะไม่ปลอดภัย ในบางกรณี สำหรับรายละเอียด ดูที่ P2SH Collision Attacks ผลลัพธ์ของการใช้ SHA256 โดยไม่มี RIPEMD-160 คือ การผูกพันแบบ P2WSH มีขนาด 32 ไบต์ (256 บิต) แทนที่จะเป็น 20 ไบต์ (160 บิต)
สำหรับเอาต์พุตแบบ pay-to-taproot (P2TR) witness program คือจุดบนเส้นโค้ง secp256k1 มันอาจเป็น public key แบบธรรมดา แต่ในกรณีส่วนใหญ่มันควรเป็น public key ที่ผูกพันกับข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมบางอย่าง เราจะเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการผูกพันนั้นในหัวข้อของ taproot
สำหรับตัวอย่างของเวอร์ชัน segwit ในอนาคต เราเพียงแค่ใช้หมายเลขเวอร์ชัน segwit ที่สูงที่สุดที่เป็นไปได้ (16) และ witness program ที่มีขนาดเล็กที่สุดที่อนุญาต (2 ไบต์) โดยมีค่าเป็นศูนย์ (null value)
เมื่อเรารู้หมายเลขเวอร์ชันและ witness program แล้ว เราสามารถแปลงแต่ละอย่างให้เป็น bech32 address ได้ โดยการใช้ไลบรารีอ้างอิง bech32m สำหรับ Python เพื่อสร้าง address เหล่านั้นอย่างรวดเร็ว และจากนั้นมาดูอย่างละเอียดว่าเกิดอะไรขึ้น:
``` $ github=" https://raw.githubusercontent.com" $ wget $github/sipa/bech32/master/ref/python/segwit_addr.py $ python
from segwit_addr import * from binascii import unhexlify help(encode) encode(hrp, witver, witprog) Encode a segwit address. encode('bc', 0, unhexlify('2b626ed108ad00a944bb2922a309844611d25468')) 'bc1q9d3xa5gg45q2j39m9y32xzvygcgay4rgc6aaee' encode('bc', 0, unhexlify('648a32e50b6fb7c5233b228f60a6a2ca4158400268844c4bc295ed5e8c3d626f')) 'bc1qvj9r9egtd7mu2gemy28kpf4zefq4ssqzdzzycj7zjhk4arpavfhsct5a3p' encode('bc', 1, unhexlify('2ceefa5fa770ff24f87c5475d76eab519eda6176b11dbe1618fcf755bfac5311')) 'bc1p9nh05ha8wrljf7ru236awm4t2x0d5ctkkywmu9sclnm4t0av2vgs4k3au7' encode('bc', 16, unhexlify('0000')) 'bc1sqqqqkfw08p'
หากเราเปิดไฟล์ segwit_addr.py และดูว่าโค้ดกำลังทำอะไร สิ่งแรกที่เราจะสังเกตเห็นคือความแตกต่างเพียงอย่างเดียวระหว่าง bech32 (ที่ใช้สำหรับ segwit v0) และ bech32m (ที่ใช้สำหรับเวอร์ชัน segwit รุ่นหลัง) คือค่าคงที่:BECH32_CONSTANT = 1 BECH32M_CONSTANT = 0x2bc830a3 ```และในส่วนต่อไป เราจะเห็นโค้ดที่สร้าง checksum ในขั้นตอนสุดท้ายของการสร้าง checksum ค่าคงที่ที่เหมาะสมถูกรวมเข้ากับข้อมูลอื่น ๆ โดยใช้การดำเนินการ xor ค่าเดียวนั้นคือความแตกต่างเพียงอย่างเดียวระหว่าง bech32 และ bech32m
เมื่อสร้าง checksum แล้ว อักขระ 5 บิตแต่ละตัวในส่วนข้อมูล (รวมถึง witness version, witness program และ checksum) จะถูกแปลงเป็นตัวอักษรและตัวเลข
สำหรับการถอดรหัสกลับเป็นสคริปต์เอาต์พุต เราทำงานย้อนกลับ ลองใช้ไลบรารีอ้างอิงเพื่อถอดรหัส address สอง address ของเรา: ```
help(decode) decode(hrp, addr) Decode a segwit address. _ = decode("bc", "bc1q9d3xa5gg45q2j39m9y32xzvygcgay4rgc6aaee") [0], bytes([1]).hex() (0, '2b626ed108ad00a944bb2922a309844611d25468') _ = decode("bc", "bc1p9nh05ha8wrljf7ru236awm4t2x0d5ctkkywmu9sclnm4t0av2vgs4k3au7") [0], bytes([1]).hex() (1, '2ceefa5fa770ff24f87c5475d76eab519eda6176b11dbe1618fcf755bfac5311')
เราได้รับทั้ง witness version และ witness program กลับมา สิ่งเหล่านี้สามารถแทรกลงในเทมเพลตสำหรับสคริปต์เอาต์พุตของเรา:ตัวอย่างเช่น:OP_0 2b626ed108ad00a944bb2922a309844611d25468 OP_1 2ceefa5fa770ff24f87c5475d76eab519eda6176b11dbe1618fcf755bfac5311 ``` คำเตือน: ข้อผิดพลาดที่อาจเกิดขึ้นที่ควรระวังคือ witness version ที่มีค่า 0 ใช้สำหรับ OP_0 ซึ่งใช้ไบต์ 0x00—แต่เวอร์ชัน witness ที่มีค่า 1 ใช้ OP_1 ซึ่งเป็นไบต์ 0x51 เวอร์ชัน witness 2 ถึง 16 ใช้ไบต์ 0x52 ถึง 0x60 ตามลำดับเมื่อทำการเขียนโค้ดเพื่อเข้ารหัสหรือถอดรหัส bech32m เราขอแนะนำอย่างยิ่งให้คุณใช้เวกเตอร์ทดสอบ (test vectors) ที่มีให้ใน BIP350 เราขอให้คุณตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าโค้ดของคุณผ่านเวกเตอร์ทดสอบที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการจ่ายเงินให้กับเวอร์ชัน segwit ในอนาคตที่ยังไม่ได้รับการกำหนด สิ่งนี้จะช่วยให้ซอฟต์แวร์ของคุณสามารถใช้งานได้อีกหลายปีข้างหน้า แม้ว่าคุณอาจจะไม่สามารถเพิ่มการรองรับคุณสมบัติใหม่ ๆ ของบิตคอยน์ได้ทันทีที่คุณสมบัตินั้น ๆ เริ่มใช้งานได้
Private Key Formats
private key สามารถถูกแสดงได้ในหลาย ๆ รูปแบบที่ต่างกันซึ่งสามารถแปลงเป็นตัวเลขขนาด 256 bit ชุดเดียวกันได้ ดังที่เราจะแสดงให้ดูในตารางข้างล่างนี้ รูปแบบที่แตกต่างกันถูกใช้ในสถานการณ์ที่ต่างกัน รูปแบบเลขฐานสิบหก (Hexadecimal) และรูปแบบไบนารี (raw binary) ถูกใช้ภายในซอฟต์แวร์และแทบจะไม่แสดงให้ผู้ใช้เห็น WIF ถูกใช้สำหรับการนำเข้า/ส่งออกกุญแจระหว่างกระเป๋าเงินและมักใช้ในการแสดงกุญแจส่วนตัวแบบ QR code
รูปแบบของ private key ในปัจจุบัน
ซอฟต์แวร์กระเป๋าเงินบิตคอยน์ในยุคแรกได้สร้าง private key อิสระอย่างน้อยหนึ่งดอกเมื่อกระเป๋าเงินของผู้ใช้ใหม่ถูกเริ่มต้น เมื่อชุดกุญแจเริ่มต้นถูกใช้ทั้งหมดแล้ว กระเป๋าเงินอาจสร้าง private key เพิ่มเติม private key แต่ละดอกสามารถส่งออกหรือนำเข้าได้ ทุกครั้งที่มีการสร้างหรือนำเข้า private key ใหม่ จะต้องมีการสร้างการสำรองข้อมูลกระเป๋าเงินใหม่ด้วย
กระเป๋าเงินบิตคอยน์ในยุคหลังเริ่มใช้กระเป๋าเงินแบบกำหนดได้ (deterministic wallets) ซึ่ง private key ทั้งหมดถูกสร้างจาก seed เพียงค่าเดียว กระเป๋าเงินเหล่านี้จำเป็นต้องสำรองข้อมูลเพียงครั้งเดียวเท่านั้นสำหรับการใช้งานบนเชนทั่วไป แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม หากผู้ใช้ส่งออก private key เพียงดอกเดียวจากกระเป๋าเงินเหล่านี้ และผู้โจมตีได้รับกุญแจนั้นรวมถึงข้อมูลที่ไม่ใช่ข้อมูลส่วนตัวบางอย่างเกี่ยวกับกระเป๋าเงิน พวกเขาอาจสามารถสร้างกุญแจส่วนตัวใด ๆ ในกระเป๋าเงินได้—ทำให้ผู้โจมตีสามารถขโมยเงินทั้งหมดในกระเป๋าเงินได้ นอกจากนี้ ยังไม่สามารถนำเข้ากุญแจสู่กระเป๋าเงินแบบกำหนดได้ นี่หมายความว่าแทบไม่มีกระเป๋าเงินสมัยใหม่ที่รองรับความสามารถในการส่งออกหรือนำเข้ากุญแจเฉพาะดอก ข้อมูลในส่วนนี้มีความสำคัญหลัก ๆ สำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการความเข้ากันได้กับกระเป๋าเงินบิตคอยน์ในยุคแรก ๆ
รูปแบบของ private key (รูปแบบการเข้ารหัส)
 private key เดียวกันในแต่ละ format
private key เดียวกันในแต่ละ format
 รูปแบบการแสดงผลทั้งหมดเหล่านี้เป็นวิธีต่างๆ ในการแสดงเลขจำนวนเดียวกัน private key เดียวกัน พวกมันดูแตกต่างกัน แต่รูปแบบใดรูปแบบหนึ่งสามารถแปลงไปเป็นรูปแบบอื่นได้อย่างง่ายดาย
รูปแบบการแสดงผลทั้งหมดเหล่านี้เป็นวิธีต่างๆ ในการแสดงเลขจำนวนเดียวกัน private key เดียวกัน พวกมันดูแตกต่างกัน แต่รูปแบบใดรูปแบบหนึ่งสามารถแปลงไปเป็นรูปแบบอื่นได้อย่างง่ายดายCompressed Private Keys
คำว่า compressed private key ที่ใช้กันทั่วไปนั้นเป็นคำที่เรียกผิด เพราะเมื่อ private key ถูกส่งออกไปในรูปแบบ WIF-compressed มันจะมีความยาวมากกว่า private key แบบ uncompressed 1 Byte (เลข 01 ในช่อง Hex-compressed ในตารางด้านล่างนี้) ซึ่งบ่งบอกว่า private key ตัวนี้ มาจากกระเป๋าเงินรุ่นใหม่และควรใช้เพื่อสร้าง compressed public key เท่านั้น
private key เองไม่ได้ถูกบีบอัดและไม่สามารถบีบอัดได้ คำว่า compressed private key จริงๆ แล้วหมายถึง " private key ซึ่งควรใช้สร้าง compressed public key เท่านั้น" ในขณะที่ uncompressed private key จริงๆ แล้วหมายถึง “private key ซึ่งควรใช้สร้าง uncompressed public key เท่านั้น” คุณควรใช้เพื่ออ้างถึงรูปแบบการส่งออกเป็น "WIF-compressed" หรือ "WIF" เท่านั้น และไม่ควรอ้างถึง private key ว่า "บีบอัด" เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงความสับสนต่อไป
ตารางนี้แสดงกุญแจเดียวกันที่ถูกเข้ารหัสในรูปแบบ WIF และ WIF-compressed
ตัวอย่าง: กุญแจเดียวกัน แต่รูปแบบต่างกัน

สังเกตว่ารูปแบบ Hex-compressed มีไบต์เพิ่มเติมหนึ่งไบต์ที่ท้าย (01 ในเลขฐานสิบหก) ในขณะที่คำนำหน้าเวอร์ชันการเข้ารหัสแบบ base58 เป็นค่าเดียวกัน (0x80) สำหรับทั้งรูปแบบ WIF และ WIF-compressed การเพิ่มหนึ่งไบต์ที่ท้ายของตัวเลขทำให้อักขระตัวแรกของการเข้ารหัสแบบ base58 เปลี่ยนจาก 5 เป็น K หรือ L
คุณสามารถคิดถึงสิ่งนี้เหมือนกับความแตกต่างของการเข้ารหัสเลขฐานสิบระหว่างตัวเลข 100 และตัวเลข 99 ในขณะที่ 100 มีความยาวมากกว่า 99 หนึ่งหลัก มันยังมีคำนำหน้าเป็น 1 แทนที่จะเป็นคำนำหน้า 9 เมื่อความยาวเปลี่ยนไป มันส่งผลต่อคำนำหน้า ในระบบ base58 คำนำหน้า 5 เปลี่ยนเป็น K หรือ L เมื่อความยาวของตัวเลขเพิ่มขึ้นหนึ่งไบต์
TIPจากหลาม: ผมว่าเขาเขียนย่อหน้านี้ไม่ค่อยรู้เรื่อง แต่ความหมายมันจะประมาณว่า เหมือนถ้าเราต้องการเขียนเลข 100 ในฐาน 10 เราต้องใช้สามตำแหน่ง 100 แต่ถ้าใช้ฐาน 16 เราจะใช้แค่ 2 ตำแหน่งคือ 64 ซึ่งมีค่าเท่ากัน
ถ้ากระเป๋าเงินบิตคอยน์สามารถใช้ compressed public key ได้ มันจะใช้ในทุกธุรกรรม private key ในกระเป๋าเงินจะถูกใช้เพื่อสร้างจุด public key บนเส้นโค้ง ซึ่งจะถูกบีบอัด compressed public key จะถูกใช้เพื่อสร้าง address และ address เหล่านี้จะถูกใช้ในธุรกรรม เมื่อส่งออก private key จากกระเป๋าเงินใหม่ที่ใช้ compressed public key WIF จะถูกปรับเปลี่ยน โดยเพิ่มต่อท้ายขนาด 1 ไบต์ 01 ให้กับ private key ที่ถูกเข้ารหัสแบบ base58check ที่ได้จะเรียกว่า "WIF-compressed" และจะขึ้นต้นด้วยอักษร K หรือ L แทนที่จะขึ้นต้นด้วย "5" เหมือนกับกรณีของคีย์ที่เข้ารหัสแบบ WIF (ไม่บีบอัด) จากกระเป๋าเงินรุ่นเก่า
Advanced Keys and Addresses
ในส่วนต่อไปนี้ เราจะดูรูปแบบของคีย์และ address เช่น vanity addresses และ paper wallets
vanity addresses
vanity addresses หรือ addresses แบบกำหนดเอง คือ address ที่มีข้อความที่มนุษย์อ่านได้และสามารถใช้งานได้จริง ตัวอย่างเช่น 1LoveBPzzD72PUXLzCkYAtGFYmK5vYNR33 อย่างที่เห็นว่ามันเป็น address ที่ถูกต้องซึ่งมีตัวอักษรเป็นคำว่า Love เป็นตัวอักษร base58 สี่ตัวแรก addresses แบบกำหนดเองต้องอาศัยการสร้างและทดสอบ private key หลายพันล้านตัวจนกว่าจะพบ address ที่มีรูปแบบตามที่ต้องการ แม้ว่าจะมีการปรับปรุงบางอย่างในอัลกอริทึมการสร้าง addresses แบบกำหนดเอง แต่กระบวนการนี้ต้องใช้การสุ่มเลือก private key มาสร้าง public key และนำไปสร้าง address และตรวจสอบว่าตรงกับรูปแบบที่ต้องการหรือไม่ โดยทำซ้ำหลายพันล้านครั้งจนกว่าจะพบที่ตรงกัน
เมื่อพบ address ที่ตรงกับรูปแบบที่ต้องการแล้ว private key ที่ใช้สร้าง address นั้นสามารถใช้โดยเจ้าของเพื่อใช้จ่ายบิตคอยน์ได้เหมือนกับ address อื่น ๆ ทุกประการ address ที่กำหนดเองไม่ได้มีความปลอดภัยน้อยกว่าหรือมากกว่าที่ address ๆ พวกมันขึ้นอยู่กับการเข้ารหัสเส้นโค้งรูปวงรี (ECC) และอัลกอริทึมแฮชที่ปลอดภัย (SHA) เหมือนกับ address อื่น ๆ คุณไม่สามารถค้นหา private key ของ address ที่ขึ้นต้นด้วยรูปแบบที่กำหนดเองได้ง่ายกว่า address อื่น ๆ
ตัวอย่างเช่น ยูจีเนียเป็นผู้อำนวยการการกุศลเพื่อเด็กที่ทำงานในฟิลิปปินส์ สมมติว่ายูจีเนียกำลังจัดการระดมทุนและต้องการใช้ address ที่กำหนดเองเพื่อประชาสัมพันธ์การระดมทุน ยูจีเนียจะสร้าง address ที่กำหนดเองที่ขึ้นต้นด้วย "1Kids" เพื่อส่งเสริมการระดมทุนเพื่อการกุศลสำหรับเด็ก มาดูกันว่า address ที่กำหนดเองนี้จะถูกสร้างขึ้นอย่างไรและมีความหมายอย่างไรต่อความปลอดภัยของการกุศลของยูจีเนีย
การสร้าง address ที่กำหนดเอง
ควรเข้าใจว่า address ของบิตคอยน์เป็นเพียงตัวเลขที่แสดงด้วยสัญลักษณ์ในรูปแบบตัวอักษร base58 เท่านั้น เพราะฉะนั้นแล้ว การค้นหารูปแบบเช่น "1Kids" สามารถมองได้ว่าเป็นการค้นหาที่อยู่ในช่วงตั้งแต่ 1Kids11111111111111111111111111111 ถึง 1Kidszzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz มีประมาณ 5829 (ประมาณ 1.4 × 1051) address ในช่วงนั้น ทั้งหมดขึ้นต้นด้วย "1Kids" ตารางด้านล่างนี้แสดงช่วงของ address ที่มีคำนำหน้า 1Kids
 ลองดูรูปแบบ "1Kids" ในรูปของตัวเลขและดูว่าเราอาจพบรูปแบบนี้ใน bitcoin address บ่อยแค่ไหน โดยตารางข้างล่างนี้แสดงให้เห็นถีงคอมพิวเตอร์เดสก์ท็อปทั่วไปที่ไม่มีฮาร์ดแวร์พิเศษสามารถค้นหาคีย์ได้ประมาณ 100,000 คีย์ต่อวินาที
ลองดูรูปแบบ "1Kids" ในรูปของตัวเลขและดูว่าเราอาจพบรูปแบบนี้ใน bitcoin address บ่อยแค่ไหน โดยตารางข้างล่างนี้แสดงให้เห็นถีงคอมพิวเตอร์เดสก์ท็อปทั่วไปที่ไม่มีฮาร์ดแวร์พิเศษสามารถค้นหาคีย์ได้ประมาณ 100,000 คีย์ต่อวินาทีความถี่ของ address ที่กำหนดเอง (1KidsCharity) และเวลาค้นหาเฉลี่ยบนคอมพิวเตอร์เดสก์ท็อป

ดังที่เห็นได้ ยูจีเนียคงไม่สามารถสร้าง address แบบกำหนดเอง "1KidsCharity" ได้ในเร็ว ๆ นี้ แม้ว่าเธอจะมีคอมพิวเตอร์หลายพันเครื่องก็ตาม ทุกตัวอักษรที่เพิ่มขึ้นจะเพิ่มความยากขึ้น 58 เท่า รูปแบบที่มีมากกว่า 7 ตัวอักษรมักจะถูกค้นพบโดยฮาร์ดแวร์พิเศษ เช่น คอมพิวเตอร์เดสก์ท็อปที่สร้างขึ้นเป็นพิเศษที่มีหน่วยประมวลผลกราฟิก (GPUs) หลายตัว การค้นหา address แบบกำหนดเองบนระบบ GPU เร็วกว่าบน CPU ทั่วไปหลายเท่า
อีกวิธีหนึ่งในการหา address แบบกำหนดเองคือการจ้างงานไปยังกลุ่มคนขุด vanity addresses กลุ่มคนขุดvanity addresses เป็นบริการที่ให้ผู้ที่มีฮาร์ดแวร์ที่เร็วได้รับบิตคอยน์จากการค้นหา vanity addresses ให้กับผู้อื่น ยูจีเนียสามารถจ่ายค่าธรรมเนียมเพื่อจ้างงานการค้นหา vanity addresses ที่มีรูปแบบ 7 ตัวอักษรและได้ผลลัพธ์ในเวลาเพียงไม่กี่ชั่วโมงแทนที่จะต้องใช้ CPU ค้นหาเป็นเดือน ๆ
การสร้างที่ address แบบกำหนดเองเป็นการใช้วิธีการแบบ brute-force (ลองทุกความเป็นไปได้): ลองใช้คีย์สุ่ม ตรวจสอบ address ที่ได้ว่าตรงกับรูปแบบที่ต้องการหรือไม่ และทำซ้ำจนกว่าจะสำเร็จ
ความปลอดภัยและความเป็นส่วนตัวของ address แบบกำหนดเอง
address แบบกำหนดเองเคยเป็นที่นิยมในช่วงแรก ๆ ของบิตคอยน์ แต่แทบจะหายไปจากการใช้งานทั้งหมดในปี 2023 มีสาเหตุที่น่าจะเป็นไปได้สองประการสำหรับแนวโน้มนี้: - Deterministic wallets: ดังที่เราเห็นในพาร์ทของการกู้คืน การที่จะสำรองคีย์ทุกตัวในกระเป๋าเงินสมัยใหม่ส่วนใหญ่นั้น ทำเพียงแค่จดคำหรือตัวอักษรไม่กี่ตัว ซึ่งนี่เป็นผลจากการสร้างคีย์ทุกตัวในกระเป๋าเงินจากคำหรือตัวอักษรเหล่านั้นโดยใช้อัลกอริทึมแบบกำหนดได้ จึงไม่สามารถใช้ address แบบกำหนดเองกับ Deterministic wallets ได้ เว้นแต่ผู้ใช้จะสำรองข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมสำหรับ address แบบกำหนดเองทุก address ที่พวกเขาสร้าง ในทางปฏิบัติแล้วกระเป๋าเงินส่วนใหญ่ที่ใช้การสร้างคีย์แบบกำหนดได้ โดยไม่อนุญาตให้นำเข้าคีย์ส่วนตัวหรือการปรับแต่งคีย์จากโปรแกรมสร้าง address ที่กำหนดเอง
- การหลีกเลี่ยงการใช้ address ซ้ำซ้อน: การใช้ address แบบกำหนดเองเพื่อรับการชำระเงินหลายครั้งไปยัง address เดียวกันจะสร้างความเชื่อมโยงระหว่างการชำระเงินทั้งหมดเหล่านั้น นี่อาจเป็นที่ยอมรับได้สำหรับยูจีเนียหากองค์กรไม่แสวงหาผลกำไรของเธอจำเป็นต้องรายงานรายได้และค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วยงานภาษีอยู่แล้ว แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม มันยังลดความเป็นส่วนตัวของคนที่จ่ายเงินให้ยูจีเนียหรือรับเงินจากเธอด้วย ตัวอย่างเช่น อลิซอาจต้องการบริจาคโดยไม่เปิดเผยตัวตน และบ็อบอาจไม่ต้องการให้ลูกค้ารายอื่นของเขารู้ว่าเขาให้ราคาส่วนลดแก่ยูจีเนีย
เราไม่คาดว่าจะเห็น address แบบกำหนดเองมากนักในอนาคต เว้นแต่ปัญหาที่กล่าวมาก่อนหน้านี้จะได้รับการแก้ไข
Paper Wallets
paper wallet หรือก็คือ private key ที่พิมพ์ลงในกระดาษ และโดยทั่วไปแล้วมักจะมีข้อมูลของ public key หรือ address บนกระดาษนั้นด้วยแม้ว่าจริง ๆ แล้วมันจะสามารถคำนวณได้ด้วย private key ก็ตาม
คำเตือน: paper wallet เป็นเทคโนโลยีที่ล้าสมัยแล้วและอันตรายสำหรับผู้ใช้ส่วนใหญ่ เพราะเป็นเรื่องยากที่จะสร้างมันอย่างปลอดภัย โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งความเป็นไปได้ที่โค้ดที่ใช้สร้างอาจถูกแทรกแซงด้วยผู้ไม่ประสงค์ดี และอาจจะทำให้ผู้ใช้โดนขโมยบิตคอยน์ทั้งหมดไปได้ paper wallet ถูกแสดงที่นี่เพื่อวัตถุประสงค์ในการให้ข้อมูลเท่านั้นและไม่ควรใช้สำหรับเก็บบิตคอยน์

paper wallet ได้ถูกออกแบบมาเพื่อเป็นของขวัญและมีธีมตามฤดูกาล เช่น คริสต์มาสและปีใหม่ ส่วนเหตุผลอื่น ๆ ถูกออกแบบเพื่อการเก็บรักษาในตู้นิรภัยของธนาคารหรือตู้เซฟโดยมี private key ถูกซ่อนไว้ในบางวิธี ไม่ว่าจะด้วยสติกเกอร์แบบขูดที่ทึบแสงหรือพับและปิดผนึกด้วยแผ่นฟอยล์กันการงัดแงะ ส่วนการออกแบบอื่น ๆ มีสำเนาเพิ่มเติมของคีย์และ address ในรูปแบบของตอนฉีกที่แยกออกได้คล้ายกับตั๋ว ช่วยให้คุณสามารถเก็บสำเนาหลายชุดเพื่อป้องกันจากไฟไหม้ น้ำท่วม หรือภัยพิบัติทางธรรมชาติอื่น ๆ
จากการออกแบบเดิมของบิตคอยน์ที่เน้น public key ไปจนถึง address และสคริปต์สมัยใหม่อย่าง bech32m และ pay to taproot—และแม้แต่การอัพเกรดบิตคอยน์ในอนาคต—คุณได้เรียนรู้วิธีที่โปรโตคอลบิตคอยน์อนุญาตให้ผู้จ่ายเงินระบุกระเป๋าเงินที่ควรได้รับการชำระเงินของพวกเขา แต่เมื่อเป็นกระเป๋าเงินของคุณเองที่รับการชำระเงิน คุณจะต้องการความมั่นใจว่าคุณจะยังคงเข้าถึงเงินนั้นได้แม้ว่าจะเกิดอะไรขึ้นกับข้อมูลกระเป๋าเงินของคุณ ในบทต่อไป เราจะดูว่ากระเป๋าเงินบิตคอยน์ถูกออกแบบอย่างไรเพื่อปกป้องเงินทุนจากภัยคุกคามหลากหลายรูปแบบ
-
 @ 2dd9250b:6e928072
2025-03-22 00:22:40
@ 2dd9250b:6e928072
2025-03-22 00:22:40Vi recentemente um post onde a pessoa diz que aquele final do filme O Doutrinador (2019) não faz sentido porque mesmo o protagonista explodindo o Palácio dos Três Poderes, não acaba com a corrupção no Brasil.
Progressistas não sabem ler e não conseguem interpretar textos corretamente. O final de Doutrinador não tem a ver com isso, tem a ver com a relação entre o Herói e a sua Cidade.
Nas histórias em quadrinhos há uma ligação entre a cidade e o Super-Herói. Gotham City por exemplo, cria o Batman. Isso é mostrado em The Batman (2022) e em Batman: Cavaleiro das Trevas, quando aquele garoto no final, diz para o Batman não fugir, porque ele queria ver o Batman de novo. E o Comissário Gordon diz que o "Batman é o que a cidade de Gotham precisa."
Batman: Cavaleiro das Trevas Ressurge mostra a cidade de Gotham sendo tomada pela corrupção e pela ideologia do Bane. A Cidade vai definhando em imoralidade e o Bruce, ao olhar da prisão a cidade sendo destruída, decide que o Batman precisa voltar porque se Gotham for destruída, o Batman é destruído junto. E isso o da forças para consegue fugir daquele poço e voltar para salvar Gotham.
Isso também é mostrado em Demolidor. Na série Demolidor o Matt Murdock sempre fala que precisa defender a cidade Cozinha do Inferno; que o Fisk não vai dominar a cidade e fazer o que ele quiser nela. Inclusive na terceira temporada isso fica mais evidente na luta final na mansão do Fisk, onde Matt grita que agora a cidade toda vai saber o que ele fez; a cidade vai ver o mal que ele é para Hell's Kitchen, porque a gente sabe que o Fisk fez de tudo para a imagem do Demolidor entrar e descrédito perante os cidadãos, então o que acontece no final do filme O Doutrinador não significa que ele está acabando com a corrupção quando explode o Congresso, ele está praticamente interrompendo o ciclo do sistema, colocando uma falha em sua engrenagem.
Quando você ouve falar de Brasília, você pensa na corrupção dos políticos, onde a farra acontece,, onde corruptos desviam dinheiro arrecadado dos impostos, impostos estes que são centralizados na União. Então quando você ouve falarem de Brasília, sempre pensa que o pessoal que mora lá, mora junto com tudo de podre que acontece no Brasil.
Logo quando o Doutrinador explode tudo ali, ele está basicamente destruindo o mecanismo que suja Brasília. Ele está fazendo isso naquela cidade. Porque o símbolo da cidade é justamente esse, a farsa de que naquele lugar o povo será ouvido e a justiça será feita. Ele está destruindo a ideologia de que o Estado nos protege, nos dá segurança, saúde e educação. Porque na verdade o Estado só existe para privilegiar os políticos, funcionários públicos de auto escalão, suas famílias e amigos. Enquanto que o povo sofre para sustentar a elite política. O protagonista Miguel entendeu isso quando a filha dele morreu na fila do SUS.
-
 @ 21335073:a244b1ad
2025-03-18 14:43:08
@ 21335073:a244b1ad
2025-03-18 14:43:08Warning: This piece contains a conversation about difficult topics. Please proceed with caution.
TL;DR please educate your children about online safety.
Julian Assange wrote in his 2012 book Cypherpunks, “This book is not a manifesto. There isn’t time for that. This book is a warning.” I read it a few times over the past summer. Those opening lines definitely stood out to me. I wish we had listened back then. He saw something about the internet that few had the ability to see. There are some individuals who are so close to a topic that when they speak, it’s difficult for others who aren’t steeped in it to visualize what they’re talking about. I didn’t read the book until more recently. If I had read it when it came out, it probably would have sounded like an unknown foreign language to me. Today it makes more sense.
This isn’t a manifesto. This isn’t a book. There is no time for that. It’s a warning and a possible solution from a desperate and determined survivor advocate who has been pulling and unraveling a thread for a few years. At times, I feel too close to this topic to make any sense trying to convey my pathway to my conclusions or thoughts to the general public. My hope is that if nothing else, I can convey my sense of urgency while writing this. This piece is a watchman’s warning.
When a child steps online, they are walking into a new world. A new reality. When you hand a child the internet, you are handing them possibilities—good, bad, and ugly. This is a conversation about lowering the potential of negative outcomes of stepping into that new world and how I came to these conclusions. I constantly compare the internet to the road. You wouldn’t let a young child run out into the road with no guidance or safety precautions. When you hand a child the internet without any type of guidance or safety measures, you are allowing them to play in rush hour, oncoming traffic. “Look left, look right for cars before crossing.” We almost all have been taught that as children. What are we taught as humans about safety before stepping into a completely different reality like the internet? Very little.
I could never really figure out why many folks in tech, privacy rights activists, and hackers seemed so cold to me while talking about online child sexual exploitation. I always figured that as a survivor advocate for those affected by these crimes, that specific, skilled group of individuals would be very welcoming and easy to talk to about such serious topics. I actually had one hacker laugh in my face when I brought it up while I was looking for answers. I thought maybe this individual thought I was accusing them of something I wasn’t, so I felt bad for asking. I was constantly extremely disappointed and would ask myself, “Why don’t they care? What could I say to make them care more? What could I say to make them understand the crisis and the level of suffering that happens as a result of the problem?”
I have been serving minor survivors of online child sexual exploitation for years. My first case serving a survivor of this specific crime was in 2018—a 13-year-old girl sexually exploited by a serial predator on Snapchat. That was my first glimpse into this side of the internet. I won a national award for serving the minor survivors of Twitter in 2023, but I had been working on that specific project for a few years. I was nominated by a lawyer representing two survivors in a legal battle against the platform. I’ve never really spoken about this before, but at the time it was a choice for me between fighting Snapchat or Twitter. I chose Twitter—or rather, Twitter chose me. I heard about the story of John Doe #1 and John Doe #2, and I was so unbelievably broken over it that I went to war for multiple years. I was and still am royally pissed about that case. As far as I was concerned, the John Doe #1 case proved that whatever was going on with corporate tech social media was so out of control that I didn’t have time to wait, so I got to work. It was reading the messages that John Doe #1 sent to Twitter begging them to remove his sexual exploitation that broke me. He was a child begging adults to do something. A passion for justice and protecting kids makes you do wild things. I was desperate to find answers about what happened and searched for solutions. In the end, the platform Twitter was purchased. During the acquisition, I just asked Mr. Musk nicely to prioritize the issue of detection and removal of child sexual exploitation without violating digital privacy rights or eroding end-to-end encryption. Elon thanked me multiple times during the acquisition, made some changes, and I was thanked by others on the survivors’ side as well.
I still feel that even with the progress made, I really just scratched the surface with Twitter, now X. I left that passion project when I did for a few reasons. I wanted to give new leadership time to tackle the issue. Elon Musk made big promises that I knew would take a while to fulfill, but mostly I had been watching global legislation transpire around the issue, and frankly, the governments are willing to go much further with X and the rest of corporate tech than I ever would. My work begging Twitter to make changes with easier reporting of content, detection, and removal of child sexual exploitation material—without violating privacy rights or eroding end-to-end encryption—and advocating for the minor survivors of the platform went as far as my principles would have allowed. I’m grateful for that experience. I was still left with a nagging question: “How did things get so bad with Twitter where the John Doe #1 and John Doe #2 case was able to happen in the first place?” I decided to keep looking for answers. I decided to keep pulling the thread.
I never worked for Twitter. This is often confusing for folks. I will say that despite being disappointed in the platform’s leadership at times, I loved Twitter. I saw and still see its value. I definitely love the survivors of the platform, but I also loved the platform. I was a champion of the platform’s ability to give folks from virtually around the globe an opportunity to speak and be heard.
I want to be clear that John Doe #1 really is my why. He is the inspiration. I am writing this because of him. He represents so many globally, and I’m still inspired by his bravery. One child’s voice begging adults to do something—I’m an adult, I heard him. I’d go to war a thousand more lifetimes for that young man, and I don’t even know his name. Fighting has been personally dark at times; I’m not even going to try to sugarcoat it, but it has been worth it.
The data surrounding the very real crime of online child sexual exploitation is available to the public online at any time for anyone to see. I’d encourage you to go look at the data for yourself. I believe in encouraging folks to check multiple sources so that you understand the full picture. If you are uncomfortable just searching around the internet for information about this topic, use the terms “CSAM,” “CSEM,” “SG-CSEM,” or “AI Generated CSAM.” The numbers don’t lie—it’s a nightmare that’s out of control. It’s a big business. The demand is high, and unfortunately, business is booming. Organizations collect the data, tech companies often post their data, governments report frequently, and the corporate press has covered a decent portion of the conversation, so I’m sure you can find a source that you trust.
Technology is changing rapidly, which is great for innovation as a whole but horrible for the crime of online child sexual exploitation. Those wishing to exploit the vulnerable seem to be adapting to each technological change with ease. The governments are so far behind with tackling these issues that as I’m typing this, it’s borderline irrelevant to even include them while speaking about the crime or potential solutions. Technology is changing too rapidly, and their old, broken systems can’t even dare to keep up. Think of it like the governments’ “War on Drugs.” Drugs won. In this case as well, the governments are not winning. The governments are talking about maybe having a meeting on potentially maybe having legislation around the crimes. The time to have that meeting would have been many years ago. I’m not advocating for governments to legislate our way out of this. I’m on the side of educating and innovating our way out of this.
I have been clear while advocating for the minor survivors of corporate tech platforms that I would not advocate for any solution to the crime that would violate digital privacy rights or erode end-to-end encryption. That has been a personal moral position that I was unwilling to budge on. This is an extremely unpopular and borderline nonexistent position in the anti-human trafficking movement and online child protection space. I’m often fearful that I’m wrong about this. I have always thought that a better pathway forward would have been to incentivize innovation for detection and removal of content. I had no previous exposure to privacy rights activists or Cypherpunks—actually, I came to that conclusion by listening to the voices of MENA region political dissidents and human rights activists. After developing relationships with human rights activists from around the globe, I realized how important privacy rights and encryption are for those who need it most globally. I was simply unwilling to give more power, control, and opportunities for mass surveillance to big abusers like governments wishing to enslave entire nations and untrustworthy corporate tech companies to potentially end some portion of abuses online. On top of all of it, it has been clear to me for years that all potential solutions outside of violating digital privacy rights to detect and remove child sexual exploitation online have not yet been explored aggressively. I’ve been disappointed that there hasn’t been more of a conversation around preventing the crime from happening in the first place.
What has been tried is mass surveillance. In China, they are currently under mass surveillance both online and offline, and their behaviors are attached to a social credit score. Unfortunately, even on state-run and controlled social media platforms, they still have child sexual exploitation and abuse imagery pop up along with other crimes and human rights violations. They also have a thriving black market online due to the oppression from the state. In other words, even an entire loss of freedom and privacy cannot end the sexual exploitation of children online. It’s been tried. There is no reason to repeat this method.
It took me an embarrassingly long time to figure out why I always felt a slight coldness from those in tech and privacy-minded individuals about the topic of child sexual exploitation online. I didn’t have any clue about the “Four Horsemen of the Infocalypse.” This is a term coined by Timothy C. May in 1988. I would have been a child myself when he first said it. I actually laughed at myself when I heard the phrase for the first time. I finally got it. The Cypherpunks weren’t wrong about that topic. They were so spot on that it is borderline uncomfortable. I was mad at first that they knew that early during the birth of the internet that this issue would arise and didn’t address it. Then I got over it because I realized that it wasn’t their job. Their job was—is—to write code. Their job wasn’t to be involved and loving parents or survivor advocates. Their job wasn’t to educate children on internet safety or raise awareness; their job was to write code.
They knew that child sexual abuse material would be shared on the internet. They said what would happen—not in a gleeful way, but a prediction. Then it happened.
I equate it now to a concrete company laying down a road. As you’re pouring the concrete, you can say to yourself, “A terrorist might travel down this road to go kill many, and on the flip side, a beautiful child can be born in an ambulance on this road.” Who or what travels down the road is not their responsibility—they are just supposed to lay the concrete. I’d never go to a concrete pourer and ask them to solve terrorism that travels down roads. Under the current system, law enforcement should stop terrorists before they even make it to the road. The solution to this specific problem is not to treat everyone on the road like a terrorist or to not build the road.
So I understand the perceived coldness from those in tech. Not only was it not their job, but bringing up the topic was seen as the equivalent of asking a free person if they wanted to discuss one of the four topics—child abusers, terrorists, drug dealers, intellectual property pirates, etc.—that would usher in digital authoritarianism for all who are online globally.
Privacy rights advocates and groups have put up a good fight. They stood by their principles. Unfortunately, when it comes to corporate tech, I believe that the issue of privacy is almost a complete lost cause at this point. It’s still worth pushing back, but ultimately, it is a losing battle—a ticking time bomb.
I do think that corporate tech providers could have slowed down the inevitable loss of privacy at the hands of the state by prioritizing the detection and removal of CSAM when they all started online. I believe it would have bought some time, fewer would have been traumatized by that specific crime, and I do believe that it could have slowed down the demand for content. If I think too much about that, I’ll go insane, so I try to push the “if maybes” aside, but never knowing if it could have been handled differently will forever haunt me. At night when it’s quiet, I wonder what I would have done differently if given the opportunity. I’ll probably never know how much corporate tech knew and ignored in the hopes that it would go away while the problem continued to get worse. They had different priorities. The most voiceless and vulnerable exploited on corporate tech never had much of a voice, so corporate tech providers didn’t receive very much pushback.
Now I’m about to say something really wild, and you can call me whatever you want to call me, but I’m going to say what I believe to be true. I believe that the governments are either so incompetent that they allowed the proliferation of CSAM online, or they knowingly allowed the problem to fester long enough to have an excuse to violate privacy rights and erode end-to-end encryption. The US government could have seized the corporate tech providers over CSAM, but I believe that they were so useful as a propaganda arm for the regimes that they allowed them to continue virtually unscathed.
That season is done now, and the governments are making the issue a priority. It will come at a high cost. Privacy on corporate tech providers is virtually done as I’m typing this. It feels like a death rattle. I’m not particularly sure that we had much digital privacy to begin with, but the illusion of a veil of privacy feels gone.
To make matters slightly more complex, it would be hard to convince me that once AI really gets going, digital privacy will exist at all.
I believe that there should be a conversation shift to preserving freedoms and human rights in a post-privacy society.
I don’t want to get locked up because AI predicted a nasty post online from me about the government. I’m not a doomer about AI—I’m just going to roll with it personally. I’m looking forward to the positive changes that will be brought forth by AI. I see it as inevitable. A bit of privacy was helpful while it lasted. Please keep fighting to preserve what is left of privacy either way because I could be wrong about all of this.
On the topic of AI, the addition of AI to the horrific crime of child sexual abuse material and child sexual exploitation in multiple ways so far has been devastating. It’s currently out of control. The genie is out of the bottle. I am hopeful that innovation will get us humans out of this, but I’m not sure how or how long it will take. We must be extremely cautious around AI legislation. It should not be illegal to innovate even if some bad comes with the good. I don’t trust that the governments are equipped to decide the best pathway forward for AI. Source: the entire history of the government.
I have been personally negatively impacted by AI-generated content. Every few days, I get another alert that I’m featured again in what’s called “deep fake pornography” without my consent. I’m not happy about it, but what pains me the most is the thought that for a period of time down the road, many globally will experience what myself and others are experiencing now by being digitally sexually abused in this way. If you have ever had your picture taken and posted online, you are also at risk of being exploited in this way. Your child’s image can be used as well, unfortunately, and this is just the beginning of this particular nightmare. It will move to more realistic interpretations of sexual behaviors as technology improves. I have no brave words of wisdom about how to deal with that emotionally. I do have hope that innovation will save the day around this specific issue. I’m nervous that everyone online will have to ID verify due to this issue. I see that as one possible outcome that could help to prevent one problem but inadvertently cause more problems, especially for those living under authoritarian regimes or anyone who needs to remain anonymous online. A zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) would probably be the best solution to these issues. There are some survivors of violence and/or sexual trauma who need to remain anonymous online for various reasons. There are survivor stories available online of those who have been abused in this way. I’d encourage you seek out and listen to their stories.
There have been periods of time recently where I hesitate to say anything at all because more than likely AI will cover most of my concerns about education, awareness, prevention, detection, and removal of child sexual exploitation online, etc.
Unfortunately, some of the most pressing issues we’ve seen online over the last few years come in the form of “sextortion.” Self-generated child sexual exploitation (SG-CSEM) numbers are continuing to be terrifying. I’d strongly encourage that you look into sextortion data. AI + sextortion is also a huge concern. The perpetrators are using the non-sexually explicit images of children and putting their likeness on AI-generated child sexual exploitation content and extorting money, more imagery, or both from minors online. It’s like a million nightmares wrapped into one. The wild part is that these issues will only get more pervasive because technology is harnessed to perpetuate horror at a scale unimaginable to a human mind.
Even if you banned phones and the internet or tried to prevent children from accessing the internet, it wouldn’t solve it. Child sexual exploitation will still be with us until as a society we start to prevent the crime before it happens. That is the only human way out right now.
There is no reset button on the internet, but if I could go back, I’d tell survivor advocates to heed the warnings of the early internet builders and to start education and awareness campaigns designed to prevent as much online child sexual exploitation as possible. The internet and technology moved quickly, and I don’t believe that society ever really caught up. We live in a world where a child can be groomed by a predator in their own home while sitting on a couch next to their parents watching TV. We weren’t ready as a species to tackle the fast-paced algorithms and dangers online. It happened too quickly for parents to catch up. How can you parent for the ever-changing digital world unless you are constantly aware of the dangers?
I don’t think that the internet is inherently bad. I believe that it can be a powerful tool for freedom and resistance. I’ve spoken a lot about the bad online, but there is beauty as well. We often discuss how victims and survivors are abused online; we rarely discuss the fact that countless survivors around the globe have been able to share their experiences, strength, hope, as well as provide resources to the vulnerable. I do question if giving any government or tech company access to censorship, surveillance, etc., online in the name of serving survivors might not actually impact a portion of survivors negatively. There are a fair amount of survivors with powerful abusers protected by governments and the corporate press. If a survivor cannot speak to the press about their abuse, the only place they can go is online, directly or indirectly through an independent journalist who also risks being censored. This scenario isn’t hard to imagine—it already happened in China. During #MeToo, a survivor in China wanted to post their story. The government censored the post, so the survivor put their story on the blockchain. I’m excited that the survivor was creative and brave, but it’s terrifying to think that we live in a world where that situation is a necessity.
I believe that the future for many survivors sharing their stories globally will be on completely censorship-resistant and decentralized protocols. This thought in particular gives me hope. When we listen to the experiences of a diverse group of survivors, we can start to understand potential solutions to preventing the crimes from happening in the first place.
My heart is broken over the gut-wrenching stories of survivors sexually exploited online. Every time I hear the story of a survivor, I do think to myself quietly, “What could have prevented this from happening in the first place?” My heart is with survivors.
My head, on the other hand, is full of the understanding that the internet should remain free. The free flow of information should not be stopped. My mind is with the innocent citizens around the globe that deserve freedom both online and offline.
The problem is that governments don’t only want to censor illegal content that violates human rights—they create legislation that is so broad that it can impact speech and privacy of all. “Don’t you care about the kids?” Yes, I do. I do so much that I’m invested in finding solutions. I also care about all citizens around the globe that deserve an opportunity to live free from a mass surveillance society. If terrorism happens online, I should not be punished by losing my freedom. If drugs are sold online, I should not be punished. I’m not an abuser, I’m not a terrorist, and I don’t engage in illegal behaviors. I refuse to lose freedom because of others’ bad behaviors online.
I want to be clear that on a long enough timeline, the governments will decide that they can be better parents/caregivers than you can if something isn’t done to stop minors from being sexually exploited online. The price will be a complete loss of anonymity, privacy, free speech, and freedom of religion online. I find it rather insulting that governments think they’re better equipped to raise children than parents and caretakers.
So we can’t go backwards—all that we can do is go forward. Those who want to have freedom will find technology to facilitate their liberation. This will lead many over time to decentralized and open protocols. So as far as I’m concerned, this does solve a few of my worries—those who need, want, and deserve to speak freely online will have the opportunity in most countries—but what about online child sexual exploitation?
When I popped up around the decentralized space, I was met with the fear of censorship. I’m not here to censor you. I don’t write code. I couldn’t censor anyone or any piece of content even if I wanted to across the internet, no matter how depraved. I don’t have the skills to do that.
I’m here to start a conversation. Freedom comes at a cost. You must always fight for and protect your freedom. I can’t speak about protecting yourself from all of the Four Horsemen because I simply don’t know the topics well enough, but I can speak about this one topic.
If there was a shortcut to ending online child sexual exploitation, I would have found it by now. There isn’t one right now. I believe that education is the only pathway forward to preventing the crime of online child sexual exploitation for future generations.
I propose a yearly education course for every child of all school ages, taught as a standard part of the curriculum. Ideally, parents/caregivers would be involved in the education/learning process.
Course: - The creation of the internet and computers - The fight for cryptography - The tech supply chain from the ground up (example: human rights violations in the supply chain) - Corporate tech - Freedom tech - Data privacy - Digital privacy rights - AI (history-current) - Online safety (predators, scams, catfishing, extortion) - Bitcoin - Laws - How to deal with online hate and harassment - Information on who to contact if you are being abused online or offline - Algorithms - How to seek out the truth about news, etc., online
The parents/caregivers, homeschoolers, unschoolers, and those working to create decentralized parallel societies have been an inspiration while writing this, but my hope is that all children would learn this course, even in government ran schools. Ideally, parents would teach this to their own children.
The decentralized space doesn’t want child sexual exploitation to thrive. Here’s the deal: there has to be a strong prevention effort in order to protect the next generation. The internet isn’t going anywhere, predators aren’t going anywhere, and I’m not down to let anyone have the opportunity to prove that there is a need for more government. I don’t believe that the government should act as parents. The governments have had a chance to attempt to stop online child sexual exploitation, and they didn’t do it. Can we try a different pathway forward?
I’d like to put myself out of a job. I don’t want to ever hear another story like John Doe #1 ever again. This will require work. I’ve often called online child sexual exploitation the lynchpin for the internet. It’s time to arm generations of children with knowledge and tools. I can’t do this alone.
Individuals have fought so that I could have freedom online. I want to fight to protect it. I don’t want child predators to give the government any opportunity to take away freedom. Decentralized spaces are as close to a reset as we’ll get with the opportunity to do it right from the start. Start the youth off correctly by preventing potential hazards to the best of your ability.
The good news is anyone can work on this! I’d encourage you to take it and run with it. I added the additional education about the history of the internet to make the course more educational and fun. Instead of cleaning up generations of destroyed lives due to online sexual exploitation, perhaps this could inspire generations of those who will build our futures. Perhaps if the youth is armed with knowledge, they can create more tools to prevent the crime.
This one solution that I’m suggesting can be done on an individual level or on a larger scale. It should be adjusted depending on age, learning style, etc. It should be fun and playful.
This solution does not address abuse in the home or some of the root causes of offline child sexual exploitation. My hope is that it could lead to some survivors experiencing abuse in the home an opportunity to disclose with a trusted adult. The purpose for this solution is to prevent the crime of online child sexual exploitation before it occurs and to arm the youth with the tools to contact safe adults if and when it happens.
In closing, I went to hell a few times so that you didn’t have to. I spoke to the mothers of survivors of minors sexually exploited online—their tears could fill rivers. I’ve spoken with political dissidents who yearned to be free from authoritarian surveillance states. The only balance that I’ve found is freedom online for citizens around the globe and prevention from the dangers of that for the youth. Don’t slow down innovation and freedom. Educate, prepare, adapt, and look for solutions.
I’m not perfect and I’m sure that there are errors in this piece. I hope that you find them and it starts a conversation.
-
 @ 21335073:a244b1ad
2025-03-15 23:00:40
@ 21335073:a244b1ad
2025-03-15 23:00:40I want to see Nostr succeed. If you can think of a way I can help make that happen, I’m open to it. I’d like your suggestions.
My schedule’s shifting soon, and I could volunteer a few hours a week to a Nostr project. I won’t have more total time, but how I use it will change.
Why help? I care about freedom. Nostr’s one of the most powerful freedom tools I’ve seen in my lifetime. If I believe that, I should act on it.
I don’t care about money or sats. I’m not rich, I don’t have extra cash. That doesn’t drive me—freedom does. I’m volunteering, not asking for pay.
I’m not here for clout. I’ve had enough spotlight in my life; it doesn’t move me. If I wanted clout, I’d be on Twitter dropping basic takes. Clout’s easy. Freedom’s hard. I’d rather help anonymously. No speaking at events—small meetups are cool for the vibe, but big conferences? Not my thing. I’ll never hit a huge Bitcoin conference. It’s just not my scene.
That said, I could be convinced to step up if it’d really boost Nostr—as long as it’s legal and gets results.
In this space, I’d watch for social engineering. I watch out for it. I’m not here to make friends, just to help. No shade—you all seem great—but I’ve got a full life and awesome friends irl. I don’t need your crew or to be online cool. Connect anonymously if you want; I’d encourage it.
I’m sick of watching other social media alternatives grow while Nostr kinda stalls. I could trash-talk, but I’d rather do something useful.
Skills? I’m good at spotting social media problems and finding possible solutions. I won’t overhype myself—that’s weird—but if you’re responding, you probably see something in me. Perhaps you see something that I don’t see in myself.
If you need help now or later with Nostr projects, reach out. Nostr only—nothing else. Anonymous contact’s fine. Even just a suggestion on how I can pitch in, no project attached, works too. 💜
Creeps or harassment will get blocked or I’ll nuke my simplex code if it becomes a problem.
https://simplex.chat/contact#/?v=2-4&smp=smp%3A%2F%2FSkIkI6EPd2D63F4xFKfHk7I1UGZVNn6k1QWZ5rcyr6w%3D%40smp9.simplex.im%2FbI99B3KuYduH8jDr9ZwyhcSxm2UuR7j0%23%2F%3Fv%3D1-2%26dh%3DMCowBQYDK2VuAyEAS9C-zPzqW41PKySfPCEizcXb1QCus6AyDkTTjfyMIRM%253D%26srv%3Djssqzccmrcws6bhmn77vgmhfjmhwlyr3u7puw4erkyoosywgl67slqqd.onion
-
 @ 126a29e8:d1341981
2025-03-10 19:13:30
@ 126a29e8:d1341981
2025-03-10 19:13:30Si quieres saber más sobre Nostr antes de continuar, te recomendamos este enlace donde encontrarás información más detallada: https://njump.me/
Nstart
Prácticamente cualquier cliente o aplicación Nostr permite crear una identidad o cuenta. Pero para este tutorial vamos a usar Nstart ya que ofrece información que ayuda a entender qué es Nostr y en qué se diferencia respecto a redes sociales convencionales.
Además añade algunos pasos importantes para mantener nuestras claves seguras.Recomendamos leer el texto que se muestra en cada pantalla de la guía.
Pronto estará disponible en español pero mientras tanto puedes tirar de traductor si el inglés no es tu fuerte.1. Welcome to Nostr
Para empezar nos dirigimos a start.njump.me desde cualquier navegador en escritorio o móvil y veremos esta pantalla de bienvenida. Haz clic en Let’s Start → https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/653d521476fa34785cf19fe098b131b7b2a0b1bdaf1fd28e65d7cf31a757b3d8.webp
2. Nombre o Alias
Elige un nombre o alias (que podrás cambiar en cualquier momento).
El resto de campos son opcionales y también puedes rellenarlos/editarlos en cualquier otro momento.
Haz clic en Continue →3. Your keys are ready
https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/e7ee67962749b37d94b139f928afad02c2436e8ee8ea886c4f7f9f0bfa28c8d9.webp ¡Ya tienes tu par de claves! 🙌
a. La npub es la clave pública que puedes compartir con quien quieras.
b. Clic en Save my nsec para descargar tu clave privada. Guárdala en un sitio seguro, por ejemplo un gestor de contraseñas.
c. Selecciona la casilla “I saved the file …” y haz clic en Continue →4. Email backup
Opcionalmente puedes enviarte una copia cifrada de tu clave privada por email. Rellena la casilla con tu mail y añade una contraseña fuerte.
Apunta la contraseña o añádela a tu gestor de contraseñas para no perderla.
En caso de no recibir el mail revisa tu bandeja de correo no deseado o Spam5. Multi Signer Bunker
Ahora tienes la posibilidad de dividir tu nsec en 3 usando una técnica llamada FROST. Clic en Activate the bunker → Esto te dará un código búnker que puedes usar para iniciar sesión en muchas aplicaciones web, móviles y de escritorio sin exponer tu nsec.
De hecho, algunos clientes solo permiten iniciar sesión mediante código búnker por lo que te recomendamos realizar este paso.
Igualmente puedes generar un código búnker para cada cliente con una app llamada Amber, de la que te hablamos más delante.
Si alguna vez pierdes tu código búnker siempre puedes usar tu nsec para crear uno nuevo e invalidar el antiguo.
Clic en Save my bunker (guárdalo en un lugar seguro) y después en Continue →6. Follow someone
Opcionalmente puedes seguir a los usuarios propuestos. Clic en Finish →
¡Todo listo para explorar Nostr! 🙌
Inicia sesión en algún cliente
Vamos a iniciar sesión con nuestra recien creada identidad en un par de clientes (nombre que reciben las “aplicaciones” en Nostr).
Hemos escogido estos 2 como ejemplo y porque nos gustan mucho pero dale un vistazo a NostrApps para ver una selección más amplia:
Escritorio
Para escritorio hemos escogido Chachi, el cliente para chats grupales y comunidades de nuestro compañero nostr:npub107jk7htfv243u0x5ynn43scq9wrxtaasmrwwa8lfu2ydwag6cx2quqncxg → https://chachi.chat/ https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/79f589150376f4bb4a142cecf369657ccba29150cee76b336d9358a2f4607b5b.webp Haz clic en Get started https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/2a6654386ae4e1773a7b3aa5b0e8f6fe8eeaa728f048bf975fe1e6ca38ce2881.webp Si usas extensión de navegador como Alby, nos2x o nos2x-Fox clica en Browser extension De lo contrario, localiza el archivo Nostr bunker que guardaste en el paso 5 de la guía Nstart y pégalo en el campo Remote signer
¡Listo! Ahora clica en Search groups para buscar grupos y comunidades a las que te quieras unir. Por ejemplo, tu comunidad amiga: Málaga 2140 ⚡ https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/eae881ac1b88232aa0b078e66d5dea75b0c142db7c4dd7decdbfbccb0637b7fe.webp
Comunidades recomendadas
Te recomendamos unirte a estas comunidades en Chachi para aprender y probar todas las funcionalidades que se vayan implementando:
Si conoces otras comunidades a tener en cuenta, dínoslo en un comentario 🙏
Móvil
Como cliente móvil hemos escogido Amethyst por ser de los más top en cuanto a diseño, tipos de eventos que muestra y mantenimiento. → https://www.amethyst.social/ ← Solo está disponible para Android por lo que si usas iOS te recomendamos Primal o Damus.
Además instalaremos Amber, que nos permitirá mantener nuestra clave privada protegida en una única aplicación diseñada específicamente para ello. → https://github.com/greenart7c3/Amber ←
Las claves privadas deben estar expuestas al menor número de sistemas posible, ya que cada sistema aumenta la superficie de ataque
Es decir que podremos “iniciar sesión” en todas las aplicaciones que queramos sin necesidad de introducir en cada una de ellas nuestra clave privada ya que Amber mostrará un aviso para autorizar cada vez.
Amber
- La primera vez que lo abras te da la posibilidad de usar una clave privada que ya tengas o crear una nueva identidad Nostr. Como ya hemos creado nuestra identidad con Nstart, copiaremos la nsec que guardamos en el paso 3.b y la pegaremos en Amber tras hacer clic en Use your private key. https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/e489939b853d6e3853f10692290b8ab66ca49f5dc1928846e16ddecc3f46250e.webp
- A continuación te permite elegir entre aprobar eventos automáticamente (minimizando el número de interrupciones mientras interactúas en Nostr) o revisar todo y aprobar manualmente, dándote mayor control sobre cada app. https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/c55cbcbb1e6f9d706f2ce6dbf4cf593df17a5e0004dca915bb4427dfc6bdbf92.webp
- Tras clicar en Finish saltará un pop-up que te preguntará si permites que Amber te envíe notificaciones. Dale a permitir para que te notifique cada vez que necesite permiso para firmar con tu clave privada algún evento. https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/3744fb66f89833636743db0edb4cfe3316bf2d91c465af745289221ae65fc795.webp Eso es todo. A partir de ahora Amber se ejecutará en segundo plano y solicitará permisos cuando uses cualquier cliente Nostr.
Amethyst
- Abre Amethyst, selecciona la casilla “I accept the terms of use” y clica en Login with Amber https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/90fc2684a6cd1e85381aa1f4c4c2c0d7fef0b296ddb35a5c830992d6305dc465.webp
- Amber solicitará permiso para que Amethyst lea tu clave pública y firme eventos en tu nombre. Escoge si prefieres darle permiso para acciones básicas; si quieres aprobar manualmente cada permiso o si permites que firme automáticamente todas las peticiones. https://cdn.nostrcheck.me/126a29e8181c1663ae611ce285758b08b475cf81b3634dd237b8234cd1341981/a5539da297e8595fd5c3cb3d3d37a7dede6a16e00adf921a5f93644961a86a92.webp ¡Ya está! 🎉 Después de clicar en Grant Permissions verás tu timeline algo vacío. A continuación te recomendamos algunos usuarios activos en Nostr por si quieres seguirles.
A quién seguir
Pega estas claves públicas en la barra Search o busca usuarios por su alias.
nostr:npub1zf4zn6qcrstx8tnprn3g2avtpz68tnupkd35m53hhq35e5f5rxqskppwpd
nostr:npub107jk7htfv243u0x5ynn43scq9wrxtaasmrwwa8lfu2ydwag6cx2quqncxg
nostr:npub1yn3hc8jmpj963h0zw49ullrrkkefn7qxf78mj29u7v2mn3yktuasx3mzt0
nostr:npub1gzuushllat7pet0ccv9yuhygvc8ldeyhrgxuwg744dn5khnpk3gs3ea5ds
nostr:npub1vxz5ja46rffch8076xcalx6zu4mqy7gwjd2vtxy3heanwy7mvd7qqq78px
nostr:npub1a2cww4kn9wqte4ry70vyfwqyqvpswksna27rtxd8vty6c74era8sdcw83a
nostr:npub149p5act9a5qm9p47elp8w8h3wpwn2d7s2xecw2ygnrxqp4wgsklq9g722q
nostr:npub12rv5lskctqxxs2c8rf2zlzc7xx3qpvzs3w4etgemauy9thegr43sf485vg
nostr:npub17u5dneh8qjp43ecfxr6u5e9sjamsmxyuekrg2nlxrrk6nj9rsyrqywt4tp
nostr:npub1dergggklka99wwrs92yz8wdjs952h2ux2ha2ed598ngwu9w7a6fsh9xzpc
Si te ha parecido útil, comparte con quien creas que puede interesarle ¡Gracias!
-
 @ 79008e78:dfac9395
2025-03-08 07:08:11
@ 79008e78:dfac9395
2025-03-08 07:08:11Bitcoin Core: The Reference Implementation
ผู้คนจะยอมรับเงินใด ๆ เพื่อแลกเปลี่ยนกับสินค้าและบริการก็ต่อเมื่อคนนั้น ๆ เชื่อว่าเงินนี้จะมีมูลค่าในอนาคต เงินปลอมหรือเงินที่เสื่อมค่าโดยไม่คาดคิดนั้นอาจไม่สามารถใช้ได้ในอนาคต ดังนั้นทุกคนที่รับบิตคอยน์จึงมีแรงจูงใจที่แข็งแกร่งในการตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของบิตคอยน์ที่พวกเขาได้รับ ระบบของบิตคอยน์นั้นถูกออกแบบมาให้เข้าถึง, ป้องกันการปลอมแปลง, การเสื่อมค่า และปัญหาสำคัญอื่น ๆ ได้อย่างสมบูรณ์ได้ด้วยคอมพิวเตอร์ทั่วไป โดยซอฟต์แวร์ที่ให้ฟังก์ชันนี้เรียกว่า Full node ซึ่งทำหน้าที่ตรวจสอบธุรกรรมบิตคอยน์ทุกครั้งที่ได้รับการยืนยันตามกฎของระบบ นอกจากนี้ Full node ยังสามารถให้เครื่องมือและข้อมูลเพื่อทำความเข้าใจการทำงานของบิตคอยน์และสภาพปัจจุบันของเครือข่าย
ในบทนี้เอง เราจะทำการติดตั้ง Bitcoin Core ซึ่งเป็นซอฟต์แวร์ที่ผู้ใช้งาน Full node ส่วนใหญ่เลือกใช้เพื่อเป็นประตูบานแรกในการเข้าถึงระบบนิเวศของบิตคอยน์ เราจะตรวจสอบบล็อก ธุรกรรม และข้อมูลอื่น ๆ จากโหนดของคุณ ซึ่งเป็นข้อมูลที่เชื่อถือได้ (ไม่ใช่เพราะหน่วยงานทรงอำนาจกำหนดให้เป็นเช่นนั้น) แต่เป็นเพราะโหนดของคุณได้ตรวจสอบข้อมูลนั้นอย่างอิสระ ตลอดเนื้อหาที่เหลือในหนังสือเล่มนี้ เราจะใช้ Bitcoin Core เพื่อสร้างและตรวจสอบข้อมูลที่เกี่ยวข้องกับบล็อกเชนและเครือข่าย
จาก Bitcoin สู่ Bitcoin Core
บิตคอยน์เป็นโครงการโอเพ่นซอร์ส โดยซอร์สโค้ดทั้งหมดก็สามารถดาวน์โหลดและใช้งานได้ฟรีภายใต้ใบอณุญาตแบบเปิด (MIT License) นอกจากจะเป็นโอเพ่นซอร์สแล้วบิตคอยน์ยังได้รับการพัฒนาโดยชุมชนอาสาสมัครแบบเปิดกว้าง แน่นอนว่าในช่วงแรกนั้นชุมชนนี้ประกอบด้วย Satoshi Nakamoto เพียงคนเดียว แต่ภายในปี 2023 ซอร์สโค้ดของบิตคอยน์มีผู้ร่วมพัฒนามากกว่า 1,000 คน
เมื่อ Satoshi Nakamoto ได้สร้างซอฟแวร์บิตคอยน์ตัวนี้และพัฒนามันจนเกือบสมบูรณ์ก่อนแล้วจึงเผยแพร่เอกสารไวท์เปเปอร์ เขาน่าจะต้องการให้มั่นใจว่าการใช้งานจริงสามารถทำงานได้ก่อนเผยแพร่เอกสาร โดยซอฟต์แวร์เวอร์ชันแรกที่รู้จักในชื่อ "Bitcoin" นั้นได้รับการปรับปรุงและพัฒนามาอย่างมาก จนได้กลายเป็นสิ่งที่เรารู้จักกันในชื่อ Bitcoin Core และเพื่อแยกความแตกต่างจากการใช้งานอื่น ๆ Bitcoin Core เป็นซอฟต์แวร์ต้นแบบอ้างอิง (reference implementation) ของระบบบิตคอยน์ซึ่งแสดงวิธีการทำงานของแต่ละส่วนในเชิงเทคโนโลยี นอกจากนี้ Bitcoin Core รวมถึงการใช้งานฟังก์ชันทั้งหมดของบิตคอยน์ เช่น กระเป๋าเงิน เครื่องมือตรวจสอบธุรกรรมและบล็อก เครื่องมือสำหรับการสร้างบล็อก และส่วนต่าง ๆ ของการสื่อสารแบบ peer-to-peer ของบิตคอยน์

Bitcoin Development Environment
สำหรับนักพัฒนาที่ต้องการเขียนแอปพลิเคชันเกี่ยวกับบิตคอยน์ ทั้งการตั้งค่าสภาพแวดล้อมสำหรับการพัฒนาพร้อมเครื่องมือ ไลบรารี และซอฟต์แวร์สนับสนุนเป็นสิ่งสำคัญ ซึ่งเนื้อหาในบทนี้นั้นจะเป็นเรื่องทางเทคนิคอลค่อนข้างเยอะ ในบทนี้เราจะอธิบายขั้นตอนการตั้งค่าอย่างละเอียด หากคุณพบว่าเนื้อหานี้ซับซ้อนเกินไป (และไม่ได้ต้องการตั้งค่าสภาพแวดล้อมสำหรับการพัฒนาจริง ๆ) คุณสามารถข้ามไปยังบทถัดไปที่มีเนื้อหาน้อยทางเทคนิคกว่าได้
มาคอมไพล์ Bitcoin core จากซอร์สโค้ดกันเถอะ !!
ซอร์สโค้ดทั้งหมดของ BItcoin Core นั้นสามารถดาวน์โหลดได้ในรูปแบบไฟล์อาร์ไคฟ์หรือโดยการโคลนที่เก็บซอร์สโค้ดจาก GitHub โดยตรง บนหน้าดาวน์โหลดของ Bitcoin Core ให้เลือกเวอร์ชันล่าสุดและดาวน์โหลดไฟล์อัดบีบของซอร์สโค้ด หรือใช้คำสั่ง Git เพื่อสร้างสำเนาซอร์สโค้ดบนเครื่องของคุณจากหน้า GitHub ของ Bitcoin
TIP: ในตัวอย่างหลาย ๆ ส่วนของบทนี้ เราจะใช้ อินเทอร์เฟซบรรทัดคำสั่ง (Command-Line Interface - CLI) ของระบบปฏิบัติการ หรือที่เรียกว่า "shell" ซึ่งสามารถเข้าถึงได้ผ่านแอปพลิเคชัน terminal โดย shell จะแสดง พรอมต์ (prompt) เพื่อรอรับคำสั่งที่คุณพิมพ์ จากนั้นจะแสดงผลลัพธ์ออกมาแล้วรอรับคำสั่งถัดไป
TIP จากหลาม: แบบง่าย ๆ ก็คือไม่ต้องพิมพ์ $ และถ้าพิมพ์จบหนึ่งคำสั่งก็กด enter ซ่ะด้วย
ขั้นตอนในการลง bitcoin core มีดังนี้:
- สั่ง git clone เพื่อทำการสร้างสำเนาของซอร์สโค้ดลงในเครื่องของเรา ``` $ git clone https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin.git Cloning into 'bitcoin'... remote: Enumerating objects: 245912, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. remote: Total 245912 (delta 1), reused 2 (delta 1), pack-reused 245909 Receiving objects: 100% (245912/245912), 217.74 MiB | 13.05 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (175649/175649), done.
```
TIP: Git เป็นระบบควบคุมเวอร์ชันแบบกระจายที่ใช้กันอย่างแพร่หลายและเป็นส่วนสำคัญในเครื่องมือของนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ คุณอาจจำเป็นต้องติดตั้งคำสั่ง git หรือส่วนต่อประสานกราฟิก (GUI) สำหรับ Git บนระบบปฏิบัติการของคุณ หากยังไม่มี
- เมื่อการโคลน Git เสร็จสมบูรณ์แล้ว คุณจะมีสำเนาท้องถิ่นครบถ้วนของที่เก็บซอร์สโค้ดในไดเรกทอรี bitcoin ให้เปลี่ยนไปยังไดเรกทอรีนี้โดยใช้คำสั่ง cd:
``` $ cd bitcoin
3. เลือก version ของ bitcoin core: โดยค่าเริ่มต้น สำเนาจองเราจะซิงโครไนซ์กับโค้ดล่าสุด ซึ่งอาจเป็นเวอร์ชันที่ไม่เสถียรหรือเบต้าของ Bitcoin ก่อนที่จะคอมไพล์โค้ด ให้เลือกเวอร์ชันเฉพาะโดยการตรวจสอบ (checkout) แท็กของการปล่อย (release tag) ซึ่งจะซิงโครไนซ์สำเนาท้องถิ่นกับสแนปช็อตของที่เก็บซอร์สโค้ดที่ระบุด้วยแท็ก แท็กเหล่านี้ถูกใช้งานโดยนักพัฒนาเพื่อระบุเวอร์ชันของโค้ดตามหมายเลขเวอร์ชัน ซึ่งทำได้โดยใช้คำสั่ง git tag$ git tag v0.1.5 v0.1.6test1 v0.10.0 ... v0.11.2 v0.11.2rc1 v0.12.0rc1 v0.12.0rc2 ...รายการแท็กจะแสดงทุกเวอร์ชันที่ปล่อยออกมา โดยทั่วไป release candidates (เวอร์ชันทดสอบ) จะมีต่อท้ายว่า "rc" ส่วนเวอร์ชันเสถียรที่ใช้งานในระบบ production จะไม่มีต่อท้ายอะไรเลย จากรายการด้านบน ให้เลือกเวอร์ชันที่สูงสุด ซึ่งในขณะที่เขียนบทความนี้คือ v24.0.1 เพื่อซิงโครไนซ์โค้ดท้องถิ่นกับเวอร์ชันนี้ ให้ใช้คำสั่ง:$ git checkout v24.0.1 Note: switching to 'v24.0.1'.```
จากนั้นสั่ง git status เพื่อเช็คเวอร์ชัน
Configuring the Bitcoin Core Build
ในโค้ดของบิตคอยน์ที่เราได้ดาวน์โหลดมาในหัวข้อก่อนหน้านั้น มีเอกสารประกอบอยู่หลายไฟล์ โดยคุณสามารถดูเอกสารหลักได้จากไฟล์ README.md ในไดเรกทอรี bitcoin ในบทนี้ เราจะสร้าง daemon (เซิร์ฟเวอร์) ของ Bitcoin Core ซึ่งรู้จักกันในชื่อ bitcoind บน Linux (หรือระบบที่คล้ายกับ Unix) โดยให้ตรวจสอบคำแนะนำสำหรับการคอมไพล์ bitcoind แบบบรรทัดคำสั่งบนแพลตฟอร์มของคุณโดยอ่านไฟล์ doc/build-unix.md นอกจากนี้ ยังมีคำแนะนำสำหรับระบบอื่น ๆ ในไดเรกทอรี doc เช่น build-windows.md สำหรับ Windows จนถึงขณะนี้ คำแนะนำมีให้สำหรับ Android, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, macOS (OSX), Unix
หลังจากนั้นคุณควรตรวจสอบความต้องการเบื้องต้นในการสร้าง (build pre-requisites) ซึ่งระบุไว้ในส่วนแรกของเอกสารการสร้าง สิ่งเหล่านี้คือไลบรารีที่ต้องมีอยู่ในระบบของคุณก่อนที่คุณจะเริ่มคอมไพล์ Bitcoin หากมีไลบรารีที่จำเป็นหายไป กระบวนการสร้างจะล้มเหลวและแสดงข้อผิดพลาด หากเกิดปัญหานี้เพราะคุณพลาด pre-requisite คุณสามารถติดตั้งไลบรารีที่ขาดหายไปแล้วดำเนินการสร้างต่อจากจุดที่ค้างไว้
สมมุติว่า pre-requisite ถูกติดตั้งแล้ว ให้เริ่มกระบวนการสร้างโดยการสร้างชุดสคริปต์สำหรับการสร้างด้วยการรันสคริปต์ autogen.sh:
``` $ ./autogen.sh libtoolize: putting auxiliary files in AC_CONFIG_AUX_DIR, 'build-aux'. libtoolize: copying file 'build-aux/ltmain.sh' libtoolize: putting macros in AC_CONFIG_MACRO_DIRS, 'build-aux/m4'. ... configure.ac:58: installing 'build-aux/missing' src/Makefile.am: installing 'build-aux/depcomp' parallel-tests: installing 'build-aux/test-driver'
``` สคริปต์ autogen.sh นี้จะสร้างชุดสคริปต์ที่กำหนดค่าอัตโนมัติที่จะตรวจสอบระบบของคุณเพื่อค้นหาการตั้งค่าที่ถูกต้องและตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่ามีไลบรารีที่จำเป็นสำหรับการคอมไพล์โค้ด โดยสคริปต์ที่สำคัญที่สุดในสคริปต์เหล่านี้คือสคริปต์ configure ซึ่งมีตัวเลือกต่าง ๆ สำหรับการปรับแต่งกระบวนการสร้าง
ใช้ flag --help เพื่อดูตัวเลือกทั้งหมด:
`` $ ./configure --helpconfigure' configures Bitcoin Core 24.0.1 to adapt to many kinds of systems. Usage: ./configure [OPTION]... [VAR=VALUE]... ... Optional Features: --disable-option-checking ignore unrecognized --enable/--with options --disable-FEATURE do not include FEATURE (same as --enable-FEATURE=no) --enable-FEATURE[=ARG] include FEATURE [ARG=yes] --enable-silent-rules less verbose build output (undo: "make V=1") --disable-silent-rules verbose build output (undo: "make V=0") ...```
สคริปต์ configure ช่วยให้คุณสามารถเปิดหรือปิดคุณสมบัติบางอย่างของ bitcoind ผ่านการใช้ flag --enable-FEATURE และ --disable-FEATURE โดยที่ FEATURE แทนชื่อคุณสมบัติที่ระบุในข้อความช่วยเหลือ ในบทนี้ เราจะสร้าง bitcoind ด้วยคุณสมบัติตั้งต้นทั้งหมด โดยไม่ใช้ flag การกำหนดค่าเพิ่มเติม แต่คุณควรตรวจสอบตัวเลือกเหล่านี้เพื่อเข้าใจว่ามีคุณสมบัติเพิ่มเติมอะไรบ้าง หากคุณอยู่ในสภาพแวดล้อมทางการศึกษา ห้องปฏิบัติการคอมพิวเตอร์ หรือมีข้อจำกัดในการติดตั้งโปรแกรม คุณอาจต้องติดตั้งแอปพลิเคชันไว้ในไดเรกทอรี home (เช่นโดยใช้ flag --prefix=$HOME)
ตัวเลือกที่มีประโยชน์สำหรับการกำหนดค่า
- --prefix=$HOME: เปลี่ยนตำแหน่งการติดตั้งเริ่มต้น (ซึ่งโดยปกติคือ /usr/local/) ให้เป็นไดเรกทอรี home ของคุณ หรือเส้นทางที่คุณต้องการ
- --disable-wallet: ใช้เพื่อปิดการใช้งานฟังก์ชัน wallet แบบอ้างอิง
- --with-incompatible-bdb: หากคุณกำลังสร้าง wallet ให้ยอมรับการใช้ไลบรารี Berkeley DB เวอร์ชันที่ไม่เข้ากันได้
- --with-gui=no: ไม่สร้างส่วนติดต่อผู้ใช้แบบกราฟิก (GUI) ซึ่งต้องใช้ไลบรารี Qt โดยตัวเลือกนี้จะสร้างเฉพาะเซิร์ฟเวอร์และ Bitcoin Core แบบ commandline เท่านั้น
```
ต่อไป ให้รันสคริปต์ configure เพื่อให้ระบบตรวจสอบไลบรารีที่จำเป็นทั้งหมดและสร้างสคริปต์สำหรับการสร้างที่ปรับแต่งให้ตรงกับระบบของคุณ:$ ./configure checking for pkg-config... /usr/bin/pkg-config checking pkg-config is at least version 0.9.0... yes checking build system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu checking host system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu checking for a BSD-compatible install... /usr/bin/install -c ... [many pages of configuration tests follow] ... ```หากทุกอย่างดำเนินไปด้วยดี คำสั่ง configure จะสิ้นสุดด้วยการสร้างสคริปต์การสร้างที่ปรับแต่งให้กับระบบของคุณ แต่หากมีไลบรารีที่หายไปหรือเกิดข้อผิดพลาด คำสั่ง configure จะหยุดและแสดงข้อผิดพลาดแทนที่จะสร้างสคริปต์ในกรณีที่เกิดข้อผิดพลาดขึ้น สาเหตุที่พบบ่อยคือการขาดหายหรือความไม่เข้ากันของไลบรารี ให้ตรวจสอบเอกสารการสร้างอีกครั้งและติดตั้ง pre-requisite ที่ขาดไป จากนั้นรัน configure อีกครั้งเพื่อดูว่าปัญหานั้นได้รับการแก้ไขแล้วหรือไม่
การสร้าง Executable ของ Bitcoin Core
ต่อไป คุณจะทำการคอมไพล์ซอร์สโค้ด กระบวนการนี้อาจใช้เวลาถึงหนึ่งชั่วโมง ขึ้นอยู่กับความเร็วของ CPU และหน่วยความจำที่มีอยู่ หากเกิดข้อผิดพลาด หรือการคอมไพล์ถูกขัดจังหวะ คุณสามารถดำเนินการต่อได้โดยการพิมพ์คำสั่ง make อีกครั้ง
พิมพ์ make เพื่อเริ่มคอมไพล์แอปพลิเคชันที่สามารถรันได้: ``` $ make Making all in src CXX bitcoind-bitcoind.o CXX libbitcoin_node_a-addrdb.o CXX libbitcoin_node_a-addrman.o CXX libbitcoin_node_a-banman.o CXX libbitcoin_node_a-blockencodings.o CXX libbitcoin_node_a-blockfilter.o [... many more compilation messages follow ...]
```
บนระบบที่มีความเร็วและมี CPU หลายคอร์ คุณอาจต้องการตั้งค่าจำนวนงานคอมไพล์แบบขนาน (parallel compile jobs) เช่น การใช้คำสั่ง make -j 2 จะใช้สองคอร์หากมีอยู่ หากทุกอย่างดำเนินไปด้วยดี Bitcoin Core จะถูกคอมไพล์เรียบร้อยแล้ว คุณควรรันชุดการทดสอบหน่วย (unit test suite) ด้วยคำสั่ง make check เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าไลบรารีที่ลิงค์เข้าด้วยกันไม่มีข้อผิดพลาดอย่าง ขั้นตอนสุดท้ายคือการติดตั้ง executable ต่าง ๆ ลงในระบบของคุณโดยใช้คำสั่ง make install ซึ่งอาจมีการร้องขอรหัสผ่านของผู้ใช้เนื่องจากขั้นตอนนี้ต้องการสิทธิ์ผู้ดูแลระบบ: ``` $ make check && sudo make install Password: Making install in src ../build-aux/install-sh -c -d '/usr/local/lib' libtool: install: /usr/bin/install -c bitcoind /usr/local/bin/bitcoind libtool: install: /usr/bin/install -c bitcoin-cli /usr/local/bin/bitcoin-cli libtool: install: /usr/bin/install -c bitcoin-tx /usr/local/bin/bitcoin-tx ...
```
การติดตั้งเริ่มต้นของ bitcoind จะอยู่ในไดเรกทอรี /usr/local/bin โดยคุณสามารถตรวจสอบว่า Bitcoin Core ถูกติดตั้งเรียบร้อยแล้วโดยใช้คำสั่งเพื่อตรวจสอบตำแหน่งของ executable ดังนี้:
$ which bitcoind /usr/local/bin/bitcoind $ which bitcoin-cli /usr/local/bin/bitcoin-cliมาลองรัน Bitcoin node กันเถอะ
อย่างที่ได้กล่าวในบทก่อนหน้า เครือข่ายแบบเพียร์ทูเพียร์ของบิตคอยน์ประกอบด้วยเครือข่าย "โหนด" ซึ่งส่วนใหญ่รันโดยบุคคลและธุรกิจบางแห่งที่ให้บริการ ผู้ที่รันโหนดบิตคอยน์จะมีมุมมองที่ตรงและน่าเชื่อถือเกี่ยวกับบล๊อกเชนของบิตคอยน์พร้อมสำเนาข้อมูลบิตคอยน์ที่ใช้จ่ายได้ทั้งหมดซึ่งได้รับการตรวจสอบอย่างอิสระโดยระบบของตนเอง การรันโหนดทำให้คุณไม่ต้องพึ่งบุคคลที่สามในการตรวจสอบธุรกรรม นอกจากนี้การใช้โหนดบิตคอยน์เพื่อตรวจสอบธุรกรรมที่ได้รับในกระเป๋าเงินของคุณ ยังช่วยให้คุณมีส่วนร่วมในเครือข่ายบิตคอยน์และช่วยทำให้เครือข่ายมีความแข็งแกร่งมากขึ้นอีกด้วย
การรันโหนดต้องดาวน์โหลดและประมวลผลข้อมูลมากกว่า 500 GB ในช่วงเริ่มแรก และประมาณ 400 MB ของธุรกรรม Bitcoin ต่อวัน ตัวเลขเหล่านี้เป็นของปี 2023 และอาจเพิ่มขึ้นในอนาคต หากคุณปิดโหนดหรือหลุดจากอินเทอร์เน็ตเป็นเวลาหลายวัน โหนดของคุณจะต้องดาวน์โหลดข้อมูลที่พลาดไป ตัวอย่างเช่น หากคุณปิด Bitcoin Core เป็นเวลา 10 วัน คุณจะต้องดาวน์โหลดประมาณ 4 GB ในครั้งถัดไปที่คุณเริ่มใช้งาน
ขึ้นอยู่กับการเลือกของคุณว่าจะทำดัชนีธุรกรรมทั้งหมดและเก็บสำเนาบล๊อกเชนแบบเต็ม คุณอาจต้องใช้พื้นที่ดิสก์มาก - อย่างน้อย 1 TB หากคุณวางแผนจะรัน Bitcoin Core เป็นเวลาหลายปี โดยค่าเริ่มต้นโหนดบิตคอยน์ยังส่งธุรกรรมและบล็อกไปยังโหนดอื่น ๆ (เรียกว่า "เพียร์") ซึ่งจะใช้แบนด์วิดท์อัปโหลดอินเทอร์เน็ต หากการเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตของคุณมีขีดจำกัด มีขีดจำกัดการใช้ข้อมูลต่ำ หรือคิดค่าบริการตามข้อมูล (เมตเตอร์) คุณไม่ควรรันโหนดบิตคอยน์บนระบบนั้น หรือรันโดยจำกัดแบนด์วิดท์ (ดู การกำหนดค่าโหนด Bitcoin Core) คุณอาจเชื่อมต่อโหนดของคุณแทนไปยังเครือข่ายทางเลือก เช่น ผู้ให้บริการข้อมูลดาวเทียมฟรีอย่าง Blockstream Satellite
Tip: Bitcoin Core เก็บสำเนาบล๊อกเชนแบบเต็ม (ตามค่าเริ่มต้น ) พร้อมธุรกรรมเกือบทั้งหมดที่เคยได้รับการยืนยันบนเครือข่าย Bitcoin ตั้งแต่เริ่มต้นในปี 2009 ชุดข้อมูลนี้มีขนาดหลายร้อย GB และจะถูกดาวน์โหลดเพิ่มขึ้นทีละน้อยในช่วงหลายชั่วโมงหรือหลายวัน ขึ้นอยู่กับความเร็ว CPU และการเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตของคุณ Bitcoin Core จะไม่สามารถประมวลผลธุรกรรมหรืออัปเดตยอดคงเหลือของบัญชีจนกว่าชุดข้อมูล blockchain จะดาวน์โหลดเสร็จสมบูรณ์ ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าคุณมีพื้นที่ดิสก์ แบนด์วิดท์ และเวลาเพียงพอในการซิงโครไนซ์เริ่มแรก คุณสามารถกำหนดค่า Bitcoin Core เพื่อลดขนาด blockchain โดยการทิ้งบล็อกเก่า แต่โปรแกรมยังคงดาวน์โหลดชุดข้อมูลทั้งหมด
TIPจากหลาม agian: ซื้อ NVMe SSD 2TB เป็นอย่างต่ำซ่ะ m.2 ได้ยิ่งดีเลยจ้า
แม้ว่าจะมีข้อกำหนดด้านทรัพยากรเหล่านี้ แต่มีผู้คนหลายพันรายที่รันโหนด Bitcoin บางคนรันบนระบบง่าย ๆ อย่าง Raspberry Pi (คอมพิวเตอร์ราคา 35 เหรียญสหรัฐที่มีขนาดเท่ากับกล่องบุหรี่)
ทำไมคุณถึงอยากรันโหนด? นี่คือเหตุผลที่พบบ่อยที่สุด:
- คุณไม่ต้องการพึ่งบุคคลที่สามในการตรวจสอบธุรกรรมที่คุณได้รับ
- คุณไม่ต้องการเปิดเผยให้บุคคลที่สามรู้ว่าธุรกรรมใดเป็นของกระเป๋าเงินคุณ
- คุณกำลังพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ Bitcoin และต้องการพึ่งโหนด Bitcoin เพื่อเข้าถึงเครือข่ายและ blockchain ผ่าน API
- คุณกำลังสร้างแอปพลิเคชันที่ต้องตรวจสอบธุรกรรมตามกฎฉันทามติของ Bitcoin โดยทั่วไป บริษัทซอฟต์แวร์ Bitcoin มักจะรันโหนดหลายโหนด
- คุณต้องการสนับสนุน Bitcoin การรันโหนดที่คุณใช้ตรวจสอบธุรกรรมที่ได้รับในกระเป๋าเงินจะช่วยทำให้เครือข่ายมีความแข็งแกร่งมากขึ้น
หากคุณกำลังอ่านหนังสือเล่มนี้และสนใจความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ความเป็นส่วนตัวที่เหนือกว่า หรือการพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ Bitcoin คุณควรรันโหนดของตัวเอง
การกำหนดค่าโหนด Bitcoin Core
Bitcoin Core จะค้นหาไฟล์การกำหนดค่าในไดเรกทอรีข้อมูลทุกครั้งที่เริ่มทำงาน ในส่วนนี้เราจะตรวจสอบตัวเลือกการกำหนดค่าต่าง ๆ และตั้งค่าไฟล์การกำหนดค่า
เพื่อค้นหาไฟล์การกำหนดค่า ให้รัน bitcoind -printtoconsole ในเทอร์มินัลของคุณ และดูบรรทัดแรก ๆ:
$ bitcoind -printtoconsole 2023-01-28T03:21:42Z Bitcoin Core version v24.0.1 2023-01-28T03:21:42Z Using the 'x86_shani(1way,2way)' SHA256 implementation 2023-01-28T03:21:42Z Using RdSeed as an additional entropy source 2023-01-28T03:21:42Z Using RdRand as an additional entropy source 2023-01-28T03:21:42Z Default data directory /home/harding/.bitcoin 2023-01-28T03:21:42Z Using data directory /home/harding/.bitcoin 2023-01-28T03:21:42Z Config file: /home/harding/.bitcoin/bitcoin.conf ... [a lot more debug output] ...tatatipจากหลามอีกครั้ง: สังเกตเห็นหรือไม่ว่าในตัวอย่างนี้ Bitcoin Core กำลังชี้ไปที่ไฟล์การกำหนดค่าที่ไดเรกทอรี /home/harding/.bitcoin/bitcoin.conf ซึ่งจะแตกต่างกันไปขึ้นอยู่กับผู้ใช้และระบบปฏิบัติการ
คุณสามารถกด Ctrl-C เพื่อปิดโหนดหลังจากที่ระบุตำแหน่งไฟล์การกำหนดค่า โดยปกติไฟล์การกำหนดค่าจะอยู่ในไดเรกทอรี .bitcoin ภายใต้โฮมไดเรกทอรีของผู้ใช้ เปิดไฟล์ configuration ด้วยโปรแกรมแก้ไขได้ตามที่คุณชอบ
Bitcoin Core มีตัวเลือกการกำหนดค่ามากกว่า 100 ตัวเลือกที่สามารถปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมของโหนดเครือข่าย การจัดเก็บบล๊อกเชน และแง่มุมอื่น ๆ ของการทำงาน เพื่อดูรายการตัวเลือก ให้รัน bitcoind --help:
$ bitcoind --help Bitcoin Core version v24.0.1 Usage: bitcoind [options] Start Bitcoin Core Options: -? Print this help message and exit -alertnotify=<cmd> Execute command when an alert is raised (%s in cmd is replaced by message) ... [many more options]นี่คือตัวเลือกที่บางประการที่คุณสามารถตั้งในไฟล์ configuration หรือเป็นพารามิเตอร์บรรทัดคำสั่งสำหรับ bitcoind:
- alertnotify: เรียกใช้คำสั่งหรือสคริปต์เพื่อส่งการแจ้งเตือนฉุกเฉินไปยังเจ้าของโหนดนี้
- conf: ตำแหน่งทางเลือกสำหรับไฟล์ configuration เมื่อใช้เป็นพารามิเตอร์ cli สำหรับ bitcoind เท่านั้น เนื่องจากไม่สามารถอยู่ในไฟล์ configuration ที่มันอ้างถึงได้
- datadir: เลือกไดเรกทอรีและระบบไฟล์สำหรับจัดเก็บข้อมูลบล๊อกเชนตามค่าเริ่มต้นนี้คือไดเรกทอรีย่อย .bitcoin ในไดเรกทอรีโฮมของคุณ ขึ้นอยู่กับการกำหนดค่า สามารถใช้พื้นที่ตั้งแต่ประมาณ 10 GB ถึงเกือบ 1 TB ณ ขณะนี้ คาดว่าขนาดสูงสุดจะเพิ่มขึ้นหลายร้อย GB ต่อปี
- prune: ลดความต้องการพื้นที่ดิสก์บล๊อกเชนลงเหลือกี่เมกะไบต์โดยการลบบล็อกเก่า ใช้สำหรับโหนดที่มีทรัพยากรจำกัดซึ่งไม่สามารถบรรจุบล๊อกเชนแบบเต็มได้ ส่วนอื่น ๆ ของระบบจะใช้พื้นที่ดิสก์อื่นที่ไม่สามารถตัดทอนได้ ดังนั้นคุณยังคงต้องมีพื้นที่อย่างน้อยตามที่ระบุในตัวเลือก datadir
- txindex: รักษาดัชนีของธุรกรรมทั้งหมด ช่วยให้คุณสามารถดึงธุรกรรมใด ๆ โดยใช้ ID ของมันได้โดยโปรแกรม โดยที่บล็อกที่มีธุรกรรมนั้นยังไม่ถูกตัดทอน
- dbcache: ขนาดของแคช UTXO ค่าเริ่มต้นคือ 450 เมบิไบต์ (MiB) เพิ่มขนาดนี้บนฮาร์ดแวร์ระดับสูงเพื่ออ่านและเขียนจากดิสก์น้อยลง หรือลดขนาดลงบนฮาร์ดแวร์ระดับต่ำเพื่อประหยัดหน่วยความจำโดยยอมให้ใช้ดิสก์บ่อยขึ้น
- blocksonly: ลดการใช้แบนด์วิดท์โดยการรับเฉพาะบล็อกของธุรกรรมที่ได้รับการยืนยันจากเพียร์ แทนที่จะส่งต่อธุรกรรมที่ยังไม่ได้รับการยืนยัน
- maxmempool: จำกัดพูลหน่วยความจำของธุรกรรมเป็นกี่เมกะไบต์ ใช้เพื่อลดการใช้หน่วยความจำบนโหนดที่มีหน่วยความจำจำกัด
ดัชนีฐานข้อมูลธุรกรรมและตัวเลือก txindex
ตามค่าเริ่มต้น Bitcoin Core จะสร้างฐานข้อมูลที่มีเพียงธุรกรรมที่เกี่ยวข้องกับกระเป๋าเงินของผู้ใช้เท่านั้น หากคุณต้องการสามารถเข้าถึงธุรกรรมใด ๆ ด้วยคำสั่งเช่น getrawtransaction คุณจะต้องกำหนดค่า Bitcoin Core ให้สร้างดัชนีธุรกรรมแบบสมบูรณ์ ซึ่งสามารถทำได้ด้วยตัวเลือก txindex โดยตั้ง txindex=1 ในไฟล์การกำหนดค่า Bitcoin Core หากคุณไม่ได้ตั้งตัวเลือกนี้ตั้งแต่แรกและต่อมาตั้งเป็นการทำดัชนีแบบเต็ม คุณจะต้องรอให้มันสร้างดัชนีใหม่
ตัวอย่างการกำหนดค่าโหนดดัชนีแบบเต็มแสดงวิธีที่คุณอาจรวมตัวเลือกก่อนหน้านี้กับโหนดที่มีดัชนีแบบเต็ม โดยทำงานเป็นแบ็กเอนด์ API สำหรับแอปพลิเคชัน bitcoin
ตัวอย่างที่ 1. การกำหนดค่าโหนดดัชนีแบบเต็ม
alertnotify=myemailscript.sh "Alert: %s" datadir=/lotsofspace/bitcoin txindex=1ตัวอย่างที่ 2. การกำหนดค่าระบบที่มีทรัพยากรจำกัด
alertnotify=myemailscript.sh "Alert: %s" blocksonly=1 prune=5000 dbcache=150 maxmempool=150หลังจากที่คุณแก้ไขไฟล์การกำหนดค่าและตั้งตัวเลือกที่ดีที่สุดตามความต้องการของคุณ คุณสามารถทดสอบ bitcoind ด้วยการกำหนดค่านี้ รัน Bitcoin Core ด้วยตัวเลือก printtoconsole เพื่อรันที่ foreground พร้อมแสดงผลลัพธ์ที่คอนโซล:
$ bitcoind -printtoconsole 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Bitcoin Core version v24.0.1 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using the 'x86_shani(1way,2way)' SHA256 implementation 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using RdSeed as an additional entropy source 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using RdRand as an additional entropy source 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Default data directory /home/harding/.bitcoin 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using data directory /lotsofspace/bitcoin 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Config file: /home/harding/.bitcoin/bitcoin.conf 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Config file arg: [main] blockfilterindex="1" 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Config file arg: [main] maxuploadtarget="1000" 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Config file arg: [main] txindex="1" 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Setting file arg: wallet = ["msig0"] 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Command-line arg: printtoconsole="" 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using at most 125 automatic connections 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using 16 MiB out of 16 MiB requested for signature cache 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using 16 MiB out of 16 MiB requested for script execution 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Script verification uses 3 additional threads 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z scheduler thread start 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z [http] creating work queue of depth 16 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using random cookie authentication. 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Generated RPC cookie /lotsofspace/bitcoin/.cookie 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z [http] starting 4 worker threads 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using wallet directory /lotsofspace/bitcoin/wallets 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z init message: Verifying wallet(s)… 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using BerkeleyDB version Berkeley DB 4.8.30 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Using /16 prefix for IP bucketing 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z init message: Loading P2P addresses… 2023-01-28T03:43:39Z Loaded 63866 addresses from peers.dat 114ms [... more startup messages ...]คุณสามารถกด Ctrl-C เพื่อหยุดกระบวนการเมื่อคุณพอใจว่ากำลังโหลดการตั้งค่าที่ถูกต้องและทำงานตามที่คาดหวัง
เพื่อรัน Bitcoin Core ที่พื้นหลังเป็นโพรเซส ให้เริ่มด้วยตัวเลือก daemon เช่น bitcoind -daemon
เพื่อตรวจสอบความคืบหน้าและสถานะการทำงานของโหนด Bitcoin ให้เริ่มในโหมด daemon แล้วใช้คำสั่ง bitcoin-cli getblockchaininfo:
``` $ bitcoin-cli getblockchaininfo
{ "chain": "main", "blocks": 0, "headers": 83999, "bestblockhash": "[...]19d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f", "difficulty": 1, "time": 1673379796, "mediantime": 1231006505, "verificationprogress": 3.783041623201835e-09, "initialblockdownload": true, "chainwork": "[...]000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000100010001", "size_on_disk": 89087, "pruned": false, "warnings": "" }
```
นี่แสดงโหนดที่มีความสูงของ blockchain เป็น 0 บล็อก และ 83,999 เฮดเดอร์ โหนดจะดึงเฮดเดอร์ของบล็อกจากเพียร์ของตนก่อนเพื่อค้นหา blockchain ที่มีหลักฐานการทำงานมากที่สุด จากนั้นจึงดำเนินการดาวน์โหลดบล็อกเต็มโดยตรวจสอบความถูกต้องไปพร้อมกัน
เมื่อคุณพอใจกับตัวเลือกการกำหนดค่าที่เลือก คุณควรเพิ่ม Bitcoin Core ลงในสคริปต์เริ่มต้นของระบบปฏิบัติการ เพื่อให้มันทำงานอย่างต่อเนื่องและรีสตาร์ทเมื่อระบบปฏิบัติการรีสตาร์ท คุณจะพบสคริปต์เริ่มต้นตัวอย่างสำหรับระบบปฏิบัติการต่าง ๆ ในไดเรกทอรีซอร์สของ Bitcoin Core ภายใต้ contrib/init และไฟล์ README.md ที่แสดงว่าระบบใดใช้สคริปต์ใด
Bitcoin Core API
Bitcoin Core ใช้อินเทอร์เฟซ JSON-RPC ซึ่งสามารถเข้าถึงได้โดยใช้เครื่องมืออย่าง bitcoin-cli ซึ่งช่วยให้เราสามารถทดลองใช้งานความสามารถต่างๆ แบบโต้ตอบได้ ซึ่งความสามารถเหล่านี้ยังสามารถใช้งานได้ผ่านทาง API ในรูปแบบโปรแกรม เพื่อเริ่มต้น ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่ง help เพื่อดูรายการคำสั่ง Bitcoin Core RPC ที่มีอยู่:
$ bitcoin-cli help +== Blockchain == getbestblockhash getblock "blockhash" ( verbosity ) getblockchaininfo ... walletpassphrase "passphrase" timeout walletpassphrasechange "oldpassphrase" "newpassphrase" walletprocesspsbt "psbt" ( sign "sighashtype" bip32derivs finalize )คำสั่งแต่ละรายการอาจต้องการพารามิเตอร์หลายตัว เพื่อรับความช่วยเหลือเพิ่มเติม คำอธิบายโดยละเอียด และข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับพารามิเตอร์ต่างๆ ให้เพิ่มชื่อคำสั่งหลังคำว่า help ตัวอย่างเช่น เพื่อดูความช่วยเหลือเกี่ยวกับคำสั่ง RPC getblockhash: ``` $ bitcoin-cli help getblockhash getblockhash height Returns hash of block in best-block-chain at height provided. Arguments: 1. height (numeric, required) The height index Result: "hex" (string) The block hash Examples:
bitcoin-cli getblockhash 1000 curl --user myusername --data-binary '{"jsonrpc": "1.0", "id": "curltest", "method": "getblockhash", "params": [1000]}' -H 'content-type: text/plain;' http://127.0.0.1:8332/ ``` ในส่วนท้ายของข้อมูลคำสั่ง help คุณจะเห็นตัวอย่างสองตัวอย่างของคำสั่ง RPC ซึ่งใช้ตัวช่วย bitcoin-cli หรือ HTTP client curl ตัวอย่างเหล่านี้แสดงให้เห็นว่าคุณอาจเรียกใช้คำสั่งได้อย่างไร ลองคัดลอกตัวอย่างแรกและดูผลลัพธ์:
$ bitcoin-cli getblockhash 1000 00000000c937983704a73af28acdec37b049d214adbda81d7e2a3dd146f6ed09ผลลัพธ์คือแฮชของบล็อก ซึ่งจะอธิบายในรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมในบทต่อไป แต่ในตอนนี้ คำสั่งนี้ควรให้ผลลัพธ์เหมือนกันบนระบบของคุณ ซึ่งแสดงให้เห็นว่าโหนด Bitcoin Core ของคุณกำลังทำงาน กำลังรับคำสั่ง และมีข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับบล็อก 1,000 ที่จะส่งกลับมาให้คุณ
การรับข้อมูลสถานะของ Bitcoin Core
Bitcoin Core ให้รายงานสถานะเกี่ยวกับโมดูลต่างๆ ผ่านอินเตอร์เฟส JSON-RPC คำสั่งที่สำคัญที่สุดรวมถึง getblockchaininfo, getmempoolinfo, getnetworkinfo และ getwalletinfo
คำสั่ง RPC getblockchaininfo ของ Bitcoin ได้ถูกแนะนำไปก่อนหน้านี้แล้ว คำสั่ง getnetworkinfo แสดงข้อมูลพื้นฐานเกี่ยวกับสถานะของโหนดเครือข่าย Bitcoin ใช้ bitcoin-cli เพื่อรันคำสั่งนี้:
$ bitcoin-cli getnetworkinfo { "version": 240001, "subversion": "/Satoshi:24.0.1/", "protocolversion": 70016, "localservices": "0000000000000409", "localservicesnames": [ "NETWORK", "WITNESS", "NETWORK_LIMITED" ], "localrelay": true, "timeoffset": -1, "networkactive": true, "connections": 10, "connections_in": 0, "connections_out": 10, "networks": [ "...detailed information about all networks..." ], "relayfee": 0.00001000, "incrementalfee": 0.00001000, "localaddresses": [ ], "warnings": "" }ซึ่งข้อมูลต่าง ๆ จะถูกส่งคืนในรูปแบบ JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) ซึ่งเป็นรูปแบบที่สามารถ "อ่าน" ได้อย่างง่ายดายโดยทุกภาษาโปรแกรมมิ่ง และยังเป็นรูปแบบที่มนุษย์อ่านได้ง่ายอีกด้วย ในข้อมูลนี้เราเห็นหมายเลขเวอร์ชันสำหรับซอฟต์แวร์ Bitcoin Core และโปรโตคอลบิตคอยน์เราเห็นจำนวนการเชื่อมต่อในปัจจุบันและข้อมูลต่างๆ เกี่ยวกับเครือข่ายบิตคอยน์และการตั้งค่าที่เกี่ยวข้องกับโหนดนี้
TIP: จะใช้เวลาสักระยะ อาจมากกว่าหนึ่งวัน สำหรับ bitcoind ในการอัพเดทให้ทันกับบล็อกล่าสุดของบล็อกเชนปัจจุบัน ในขณะที่มันดาวน์โหลดบล็อกจากโหนดอื่นๆ และตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของทุกธุรกรรมในบล็อกเหล่านั้น—ซึ่งมีเกือบหนึ่งพันล้านธุรกรรม ณ เวลาที่เขียนนี้ คุณสามารถตรวจสอบความคืบหน้าโดยใช้ getblockchaininfo เพื่อดูจำนวนบล็อกที่ทราบ ตัวอย่างในส่วนที่เหลือของบทนี้สมมติว่าคุณอยู่อย่างน้อยที่บล็อก 775,072 เนื่องจากความปลอดภัยของธุรกรรมขึ้นอยู่กับจำ
มาสำรวจและถอดรหัสธุรกรรมของบิตคอยน์กันเถอะ!!
อย่างในบทที่สอง อลิซได้ซื้อสินค้าจากร้านของบ็อบและธุรกรรมของเธอถูกบันทึกลงในบล็อกเชนของบิตคอยน์ โดยเราสามารถใช้ API เพื่อดึงและตรวจสอบธุรกรรมนั้นได้โดยการใช้ txid เป็นพารามิเตอร์:
$ bitcoin-cli getrawtransaction 466200308696215bbc949d5141a49a4138ecdfdfaa2a8029c1f9bcecd1f96177 --ผลลัพธ์ของคำสั่ง 01000000000101eb3ae38f27191aa5f3850dc9cad00492b88b72404f9da13569 8679268041c54a0100000000ffffffff02204e0000000000002251203b41daba 4c9ace578369740f15e5ec880c28279ee7f51b07dca69c7061e07068f8240100 000000001600147752c165ea7be772b2c0acb7f4d6047ae6f4768e0141cf5efe 2d8ef13ed0af21d4f4cb82422d6252d70324f6f4576b727b7d918e521c00b51b e739df2f899c49dc267c0ad280aca6dab0d2fa2b42a45182fc83e81713010000 0000TIP: txid ไม่ใช่สิ่งที่สามารถเชื่อถือได้ขนาดนั้น เพราะการไม่มี txid ในบล๊อกเชนของบิตคอยน์นั้นไม่ได้หมายความว่าธุรกรรมไม่ได้ถูกประมวลผล โดยสิ่งนี้เรียกว่า "transaction malleability" (ความสามารถในการเปลี่ยนแปลงธุรกรรม) เพราะธุรกรรมสามารถถูกแก้ไขก่อนการยืนยันในบล็อก ซึ่งเปลี่ยน txid ของพวกมัน หลังจากธุรกรรมถูกรวมอยู่ในบล็อกแล้ว txid ของมันไม่สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงได้อีก เว้นแต่จะมีการจัดระเบียบบล็อกเชนใหม่และบล็อกนั้นถูกลบออกจากบล็อกเชนที่ดีที่สุด โดยการจัดระเบียบใหม่เกิดขึ้นได้ยากหลังจากธุรกรรมได้รับการยืนยันหลายครั้งแล้ว
คำสั่ง getrawtransaction จะส่งคืนธุรกรรมที่เข้ารหัสในรูปแบบเลขฐานสิบหกและเพื่อถอดรหัสนั้น เราใช้คำสั่ง decoderawtransaction โดยส่งข้อมูลเลขฐานสิบหกเป็นพารามิเตอร์ คุณสามารถคัดลอกเลขฐานสิบหกที่ส่งคืนโดย getrawtransaction และวางเป็นพารามิเตอร์ให้กับ decoderawtransaction ได้:
$ bitcoin-cli decoderawtransaction 01000000000101eb3ae38f27191aa5f3850dc9cad00492b88b72404f9da135698679268041c54a0100000000ffffffff02204e0000000000002251203b41daba4c9ace578369740f15e5ec880c28279ee7f51b07dca69c7061e07068f8240100000000001600147752c165ea7be772b2c0acb7f4d6047ae6f4768e0141cf5efe2d8ef13ed0af21d4f4cb82422d6252d70324f6f4576b727b7d918e521c00b51be739df2f899c49dc267c0ad280aca6dab0d2fa2b42a45182fc83e817130100000000 --ผลลัพธ์ของคำสั่ง { "txid": "466200308696215bbc949d5141a49a4138ecdfdfaa2a8029c1f9bcecd1f96177", "hash": "f7cdbc7cf8b910d35cc69962e791138624e4eae7901010a6da4c02e7d238cdac", "version": 1, "size": 194, "vsize": 143, "weight": 569, "locktime": 0, "vin": [ { "txid": "4ac541802679866935a19d4f40728bb89204d0cac90d85f3a51a19...aeb", "vout": 1, "scriptSig": { "asm": "", "hex": "" }, "txinwitness": [ "cf5efe2d8ef13ed0af21d4f4cb82422d6252d70324f6f4576b727b7d918e5...301" ], "sequence": 4294967295 } ], "vout": [ { "value": 0.00020000, "n": 0, "scriptPubKey": { "asm": "1 3b41daba4c9ace578369740f15e5ec880c28279ee7f51b07dca...068", "desc": "rawtr(3b41daba4c9ace578369740f15e5ec880c28279ee7f51b...6ev", "hex": "51203b41daba4c9ace578369740f15e5ec880c28279ee7f51b07d...068", "address": "bc1p8dqa4wjvnt890qmfws83te0v3qxzsfu7ul63kp7u56w8q...5qn", "type": "witness_v1_taproot" } }, { "value": 0.00075000, "n": 1, "scriptPubKey": { "asm": "0 7752c165ea7be772b2c0acb7f4d6047ae6f4768e", "desc": "addr(bc1qwafvze0200nh9vkq4jmlf4sy0tn0ga5w0zpkpg)#qq404gts", "hex": "00147752c165ea7be772b2c0acb7f4d6047ae6f4768e", "address": "bc1qwafvze0200nh9vkq4jmlf4sy0tn0ga5w0zpkpg", "type": "witness_v0_keyhash" } } ] }การถอดรหัสธุรกรรมแสดงส่วนประกอบทั้งหมดของธุรกรรมนี้ รวมถึงอินพุตและเอาต์พุตของธุรกรรม ในกรณีนี้เราเห็นว่าธุรกรรมใช้อินพุตหนึ่งรายการและสร้างเอาต์พุตสองรายการ อินพุตของธุรกรรมนี้คือเอาต์พุตจากธุรกรรมที่ได้รับการยืนยันก่อนหน้านี้ (แสดงเป็น txid ของอินพุต) เอาต์พุตทั้งสองรายการสอดคล้องกับการชำระเงินให้บ็อบและเงินทอนกลับให้อลิซ
มาสำรวจบล็อกของบิตคอยน์กัน!!
การสำรวจบล็อกนั้นคล้ายกับการสำรวจธุรกรรม แต่อย่างไรก็ตามบล็อกสามารถอ้างอิงได้ทั้งโดยลำดับของบล็อกหรือโดยแฮชของบล็อก เราใช้คำสั่ง getblockhash ซึ่งรับลำดับของบล็อกเป็นพารามิเตอร์และส่งคืน แฮชของบล็อกนั้น:
$ bitcoin-cli getblockhash 123456 --ผลลัพธ์ของคำสั่ง 0000000000002917ed80650c6174aac8dfc46f5fe36480aaef682ff6cd83c3caตอนนี้เรารู้แฮชสำหรับบล็อกที่เราเลือกแล้ว เราสามารถดูบล็อกนั้นได้ เราใช้คำสั่ง getblock โดยมีแฮชของบล็อกเป็นพารามิเตอร์:$ bitcoin-cli getblockhash 0000000000002917ed80650c6174aac8dfc46f5fe36480aaef682ff6cd83c3ca --ผลลัพธ์ของคำสั่ง { "hash": "0000000000002917ed80650c6174aac8dfc46f5fe36480aaef682ff6cd83c3ca", "confirmations": 651742, "height": 123456, "version": 1, "versionHex": "00000001", "merkleroot": "0e60651a9934e8f0decd1c[...]48fca0cd1c84a21ddfde95033762d86c", "time": 1305200806, "mediantime": 1305197900, "nonce": 2436437219, "bits": "1a6a93b3", "difficulty": 157416.4018436489, "chainwork": "[...]00000000000000000000000000000000000000541788211ac227bc", "nTx": 13, "previousblockhash": "[...]60bc96a44724fd72daf9b92cf8ad00510b5224c6253ac40095", "nextblockhash": "[...]00129f5f02be247070bf7334d3753e4ddee502780c2acaecec6d66", "strippedsize": 4179, "size": 4179, "weight": 16716, "tx": [ "5b75086dafeede555fc8f9a810d8b10df57c46f9f176ccc3dd8d2fa20edd685b", "e3d0425ab346dd5b76f44c222a4bb5d16640a4247050ef82462ab17e229c83b4", "137d247eca8b99dee58e1e9232014183a5c5a9e338001a0109df32794cdcc92e", "5fd167f7b8c417e59106ef5acfe181b09d71b8353a61a55a2f01aa266af5412d", "60925f1948b71f429d514ead7ae7391e0edf965bf5a60331398dae24c6964774", "d4d5fc1529487527e9873256934dfb1e4cdcb39f4c0509577ca19bfad6c5d28f", "7b29d65e5018c56a33652085dbb13f2df39a1a9942bfe1f7e78e97919a6bdea2", "0b89e120efd0a4674c127a76ff5f7590ca304e6a064fbc51adffbd7ce3a3deef", "603f2044da9656084174cfb5812feaf510f862d3addcf70cacce3dc55dab446e", "9a4ed892b43a4df916a7a1213b78e83cd83f5695f635d535c94b2b65ffb144d3", "dda726e3dad9504dce5098dfab5064ecd4a7650bfe854bb2606da3152b60e427", "e46ea8b4d68719b65ead930f07f1f3804cb3701014f8e6d76c4bdbc390893b94", "864a102aeedf53dd9b2baab4eeb898c5083fde6141113e0606b664c41fe15e1f" ] }รายการ confirmations บอกเราถึง ความลึก ของบล็อกนี้—มีกี่บล็อกที่ถูกสร้างทับบนบล็อกนี้ ซึ่งบ่งบอกถึงความยากในการเปลี่ยนแปลงธุรกรรมใดๆ ในบล็อกนี้ ลำดับบอกเราว่ามีกี่บล็อกที่มาก่อนหน้าบล็อกนี้ เราเห็นเวอร์ชันของบล็อก เวลาที่มันถูกสร้าง (ตามข้อมูลของนักขุด) เวลาเฉลี่ยของ 11 บล็อกที่มาก่อนหน้าบล็อกนี้ (การวัดเวลาที่นักขุดปลอมแปลงได้ยากกว่า) และขนาดของบล็อกในการวัดสามแบบต่างกัน (ขนาดดั้งเดิมที่ถูกลบข้อมูลบางส่วนออก, ขนาดเต็ม, และขนาดในหน่วยน้ำหนัก) เรายังเห็นฟิลด์บางอย่างที่ใช้สำหรับความปลอดภัยและหลักฐานการทำงาน (merkle root, nonce, bits, difficulty, และ chainwork) เราจะตรวจสอบสิ่งเหล่านี้โดยละเอียดในส่วนของการขุดในบทที่ 12การใช้อินเตอร์เฟสโปรแกรมของ Bitcoin Core
bitcoin-cli มีประโยชน์มากสำหรับการใช้งาน API ของ Bitcoin Core และการทดสอบฟังก์ชันต่าง ๆ แต่จุดประสงค์หลักของ API คือการเข้าถึงฟังก์ชันด้วยโปรแกรม ในส่วนนี้เราจะสาธิตการเข้าถึง Bitcoin Core จากโปรแกรมอื่น
API ของ Bitcoin Core เป็นอินเตอร์เฟส JSON-RPC โดย JSON เป็นวิธีที่สะดวกมากในการนำเสนอข้อมูลที่ทั้งมนุษย์และโปรแกรมสามารถอ่านได้ง่าย RPC ย่อมาจาก remote procedure call ซึ่งหมายความว่าเรากำลังเรียกใช้กระบวนการ (ฟังก์ชัน) ที่อยู่ห่างไกล (บนโหนด Bitcoin Core) ผ่านโปรโตคอลเครือข่าย ในกรณีนี้ โปรโตคอลเครือข่ายคือ HTTP
เมื่อเราใช้คำสั่ง bitcoin-cli เพื่อขอความช่วยเหลือเกี่ยวกับคำสั่ง มันแสดงตัวอย่างการใช้ curl ซึ่งเป็นไคลเอนต์ HTTP ทางคอมมานด์ไลน์ที่ยืดหยุ่น เพื่อสร้างคำเรียก JSON-RPC เหล่านี้:
$ curl --user myusername --data-binary '{"jsonrpc": "1.0", "id":"curltest", "method": "getblockchaininfo", "params": [] }' -H 'content-type: text/plain;' http://127.0.0.1:8332/คำสั่งนี้แสดงว่า curl ส่งคำขอ HTTP ไปยัง localhost (127.0.0.1) เชื่อมต่อกับพอร์ต RPC เริ่มต้นของ Bitcoin (8332) และส่งคำขอ jsonrpc โดยใช้เมธอดเป็น getblockchaininfo โดยใช้การเข้ารหัสแบบ text/plain
คุณอาจสังเกตว่า curl จะขอให้ส่งข้อมูลประจำตัวไปพร้อมกับคำขอ Bitcoin Core จะสร้างรหัสผ่านแบบสุ่มในแต่ละครั้งที่เริ่มต้นและวางไว้ในไดเรกทอรีข้อมูลภายใต้ชื่อ .cookie โดย bitcoin-cli สามารถอ่านไฟล์รหัสผ่านนี้โดยให้ไดเรกทอรีข้อมูล ในทำนองเดียวกัน คุณสามารถคัดลอกรหัสผ่านและส่งไปยัง curl (หรือตัวครอบ Bitcoin Core RPC ระดับสูงอื่น ๆ ) ตามที่เห็นในการใช้การตรวจสอบสิทธิ์แบบใช้คุกกี้กับ Bitcoin Core
ตัวอย่างที่ 3. การใช้การตรวจสอบสิทธิ์แบบใช้คุกกี้กับ Bitcoin Core
$ cat .bitcoin/.cookie __cookie__:17c9b71cef21b893e1a019f4bc071950c7942f49796ed061b274031b17b19cd0 $ curl --user __cookie__:17c9b71cef21b893e1a019f4bc071950c7942f49796ed061b274031b17b19cd0 --data-binary '{"jsonrpc": "1.0", "id":"curltest", "method": "getblockchaininfo", "params": [] }' -H 'content-type: text/plain;' http://127.0.0.1:8332/ {"result":{"chain":"main","blocks":799278,"headers":799278, "bestblockhash":"000000000000000000018387c50988ec705a95d6f765b206b6629971e6978879", "difficulty":53911173001054.59,"time":1689703111,"mediantime":1689701260, "verificationprogress":0.9999979206082515,"initialblockdownload":false, "chainwork":"00000000000000000000000000000000000000004f3e111bf32bcb47f9dfad5b", "size_on_disk":563894577967,"pruned":false,"warnings":""},"error":null, "id":"curltest"}นอกจากนี้คุณยังสามารถตั้งรหัสผ่านด้วยตัวเองใน ./share/rpcauth/rpcauth.py ภายในไดเรกทอรีของ Bitcoin Core
หากคุณกำลังใช้การเรียก JSON-RPC ในโปรแกรมของคุณเอง คุณสามารถใช้ไลบรารี HTTP ทั่วไปเพื่อสร้างการเรียกได้ คล้ายกับที่แสดงในตัวอย่าง curl ก่อนหน้านี้
อย่างไรก็ตาม มีไลบรารีในภาษาโปรแกรมยอดนิยมส่วนใหญ่ที่ "wrap" API ของ Bitcoin Core ในลักษณะที่ทำให้การใช้งานง่ายขึ้นมาก เราจะใช้ไลบรารี python-bitcoinlib เพื่อทำให้การเข้าถึง API นั้นง่ายขึ้น โดยไลบรารีนี้ไม่ได้เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของโครงการ Bitcoin Core และจำเป็นต้องติดตั้งด้วยวิธีปกติที่คุณติดตั้งไลบรารี Python โปรดจำไว้ว่า การใช้งานนี้ต้องมีอินสแตนซ์ Bitcoin Core ที่กำลังทำงานอยู่ ซึ่งจะถูกใช้เพื่อทำการเรียก JSON-RPC
ตัวอย่างสคริปต์ Python ใน " การทำงาน getblockchaininfo ผ่าน API JSON-RPC ของ Bitcoin Core" ซึ่งทำการเรียก getblockchaininfo อย่างง่ายและพิมพ์พารามิเตอร์ block จากข้อมูลที่ส่งคืนโดย Bitcoin Core
ตัวอย่างที่ 4. การทำงาน getblockchaininfo ผ่าน API JSON-RPC ของ Bitcoin Core ``` from bitcoin.rpc import RawProxy
Create a connection to local Bitcoin Core node
p = RawProxy()
Run the getblockchaininfo command, store the resulting data in info
info = p.getblockchaininfo()
Retrieve the 'blocks' element from the info
print(info['blocks']) --ผลลัพธ์ของคำสั่ง $ python rpc_example.py 773973 ``` มันบอกเราว่าโหนด Bitcoin Core ในเครื่องของเรามีกี่บล็อกในบล็อกเชนของมัน ซึ่งไม่ใช่ผลลัพธ์ที่น่าทึ่ง แต่มันแสดงการใช้งานพื้นฐานของไลบรารีในฐานะอินเตอร์เฟสที่ถูกทำให้ง่ายขึ้นสำหรับ API JSON-RPC ของ Bitcoin Core
ต่อไป เราจะใช้คำสั่ง getrawtransaction และ decodetransaction เพื่อดึงข้อมูลรายละเอียดของการชำระเงินจาก Alice ไปยัง Bob ในส่วนของการดึงข้อมูลธุรกรรมและการวนลูปเอาต์พุตของธุรกรรม เราจะดึงธุรกรรมของ Alice และแสดงรายการเอาต์พุตของธุรกรรม สำหรับแต่ละเอาต์พุต เราจะแสดงที่อยู่ผู้รับและมูลค่า โดยธุรกรรมของ Alice มีเอาต์พุตหนึ่งรายการที่จ่ายให้ Bob และอีกหนึ่งรายการเป็นเงินทอนกลับไปยัง Alice
ตัวอย่างที่ 5 การดึงข้อมูลธุรกรรมและการวนลูปเอาต์พุตของธุรกรรม ``` from bitcoin.rpc import RawProxy p = RawProxy()
Alice's transaction ID
txid = "466200308696215bbc949d5141a49a4138ecdfdfaa2a8029c1f9bcecd1f96177"
First, retrieve the raw transaction in hex
raw_tx = p.getrawtransaction(txid)
Decode the transaction hex into a JSON object
decoded_tx = p.decoderawtransaction(raw_tx)
Retrieve each of the outputs from the transaction
for output in decoded_tx['vout']: print(output['scriptPubKey']['address'], output['value']) --ผลลัพธ์ของคำสั่ง $ python rpc_transaction.py bc1p8dqa4wjvnt890qmfws83te0v3qxzsfu7ul63kp7u56w8qc0qwp5qv995qn 0.00020000 bc1qwafvze0200nh9vkq4jmlf4sy0tn0ga5w0zpkpg 0.00075000 ``` ตัวอย่างทั้งสองข้างต้นค่อนข้างง่าย คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องใช้โปรแกรมในการรันพวกมัน คุณสามารถใช้ตัวช่วย bitcoin-cli ได้ง่าย ๆ แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม ตัวอย่างถัดไปต้องใช้การเรียก RPC หลายร้อยครั้งและแสดงให้เห็นถึงการใช้อินเทอร์เฟซเชิงโปรแกรมได้ชัดเจนยิ่งขึ้น
ในส่วนของการดึงข้อมูลบล็อกและการรวมเอาต์พุตของทุกธุรกรรม เราจะเริ่มต้นด้วยการดึงข้อมูลบล็อก จากนั้นดึงข้อมูลธุรกรรมแต่ละรายการภายในบล็อกโดยอ้างอิงถึง ID ของแต่ละธุรกรรม ต่อมา เราจะวนลูปผ่านเอาต์พุตของแต่ละธุรกรรมและรวมมูลค่าทั้งหมด
ตัวอย่างที่ 6 การดึงข้อมูลบล็อกและการรวมเอาต์พุตของทุกธุรกรรม ``` from bitcoin.rpc import RawProxy p = RawProxy()
The block height where Alice's transaction was recorded
blockheight = 775072
Get the block hash of the block at the given height
blockhash = p.getblockhash(blockheight)
Retrieve the block by its hash
block = p.getblock(blockhash)
Element tx contains the list of all transaction IDs in the block
transactions = block['tx'] block_value = 0
Iterate through each transaction ID in the block
for txid in transactions: tx_value = 0 # Retrieve the raw transaction by ID raw_tx = p.getrawtransaction(txid) # Decode the transaction decoded_tx = p.decoderawtransaction(raw_tx) # Iterate through each output in the transaction for output in decoded_tx['vout']: # Add up the value of each output tx_value = tx_value + output['value'] # Add the value of this transaction to the total block_value = block_value + tx_value print("Total value in block: ", block_value) --ผลลัพธ์ของคำสั่ง $ python rpc_block.py Total value in block: 10322.07722534 ```
โค้ดตัวอย่างของเราคำนวณว่ามูลค่ารวมที่ถูกทำธุรกรรมในบล็อกนี้คือ 10,322.07722534 BTC (รวมถึงรางวัล 25 BTC และค่าธรรมเนียม 0.0909 BTC) ลองเปรียบเทียบกับจำนวนที่รายงานโดยเว็บไซต์สำรวจบล็อก (block explorer) โดยการค้นหาแฮชของบล็อกหรือเลขลำดับของบล็อก เครื่องมือสำรวจบล็อกบางตัวรายงานมูลค่ารวมโดยไม่รวมรางวัลและไม่รวมค่าธรรมเนียม ลองดูว่าคุณสามารถสังเกตเห็นความแตกต่างได้หรือไม่
ไคลเอนต์ทางเลือก, ไลบรารี, และชุดเครื่องมือ
C/C++ Bitcoin Core:การใช้งานอ้างอิงของ Bitcoin JavaScript bcoin: การใช้งานโหนดแบบเต็มรูปแบบที่มีความยืดหยุ่นและขยายได้พร้อม API Bitcore: โหนดเต็มรูปแบบ, API, และไลบรารีโดย Bitpay BitcoinJS: ไลบรารี Bitcoin ที่เขียนด้วย JavaScript ล้วนๆ สำหรับ node.js และเบราว์เซอร์ Java bitcoinj: ไลบรารีไคลเอนต์โหนดเต็มรูปแบบที่เขียนด้วย Java Python python-bitcoinlib: ไลบรารี Bitcoin, ไลบรารีฉันทามติ, และโหนดที่เขียนด้วย Python โดย Peter Todd pycoin: ไลบรารี Bitcoin ที่เขียนด้วย Python โดย Richard Kiss Go btcd: ไคลเอนต์ Bitcoin โหนดเต็มรูปแบบที่เขียนด้วยภาษา Go Rust rust-bitcoin: ไลบรารี Bitcoin ที่เขียนด้วย Rust สำหรับการจัดรูปแบบข้อมูล, การแยกวิเคราะห์, และการเรียกใช้ API Scala bitcoin-s: การใช้งาน Bitcoin ที่เขียนด้วย Scala C# NBitcoin: ไลบรารี Bitcoin ที่ครอบคลุมสำหรับเฟรมเวิร์ก .NET
ยังมีไลบรารีอีกมากมายในภาษาโปรแกรมมิ่งอื่น ๆ อีกหลากหลาย และมีการสร้างขึ้นใหม่อยู่ตลอดเวลา
หากคุณทำตามคำแนะนำในบทนี้ ตอนนี้คุณมี Bitcoin Core ที่ทำงานอยู่และได้เริ่มสำรวจเครือข่ายและบล็อกเชนโดยใช้โหนดของคุณเอง จากนี้ไปคุณสามารถใช้ซอฟต์แวร์ที่คุณควบคุมได้โดยอิสระ—บนคอมพิวเตอร์ที่คุณควบคุม—เพื่อตรวจสอบว่า bitcoin ใด ๆ ที่คุณได้รับปฏิบัติตามกฎทุกข้อในระบบ Bitcoin โดยไม่ต้องไว้วางใจองค์กรภายนอกใด ๆ ในบทต่อไป เราจะเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับกฎของระบบและวิธีที่โหนดและกระเป๋าเงินของคุณใช้กฎเหล่านั้นเพื่อรักษาความปลอดภัยของเงินของคุณ ปกป้องความเป็นส่วนตัวของคุณ และทำให้การใช้จ่ายและการรับเงินสะดวกสบาย
ฮึ่ ๆ หลาม ๆ มาอีกแล้ว จริง ๆ เนื้อหาของบทที่สามมันจบลงตรงนี้แหละ แต่ว่าถ้าสมมุตืว่าใครลองไปทำตามจริง ๆ แล้วอยากรู้ว่าเราสามารถทำอะไรจาก node ของเราได้อีกบ้าง เลยมีกิจกรรมขำ ๆ มาให้ทำครับ โดยความยากจะมีทั้งหมด 3 ระดับ ดังนี้
- ง่าย (สามารถหาคำตอบได้ด้วย bitcoin-cli command เดียว)
- แฮชของบล๊อก 774698 คืออะไร?
-
signature ของข้อความจาก address นี้ถูกต้องหรือไม่
address: 1E9YwDtYf9R29ekNAfbV7MvB4LNv7v3fGa message: 1E9YwDtYf9R29ekNAfbV7MvB4LNv7v3fGa signature:HCsBcgB+Wcm8kOGMH8IpNeg0H4gjCrlqwDf/GlSXphZGBYxm0QkKEPhh9DTJRp2IDNUhVr0FhP9qCqo2W0recNM= -
ทำได้แหละ (สามารถหาคำตอบได้ด้วย bitcoin-cli command เดียว หรืออาจจะมากกว่าหนึ่ง)
- มี output ใหม่กี่อันที่เกิดในบล๊อก 774698 ?
- ใช้ wallet descriptors หา taproot address ที่ 100 จาก extended public key ที่กำหนดให้ xpub6DLd5RvY42Q5HAmBhHPUbDGdeS9VvsYNauiuN8r6NzbiXSSNWpNVrDGTUScJ9fS2orMtuB3VdxMdUH83fPtwbrizfJg9LwWnGqtL7RTs5h1
-
สร้าง multisig address แบบ P2SH แบบ 1-of-4 จาก publickey ในอินพุตทั้งสี่ของธุรกรรมนี้:37d966a263350fe747f1c606b159987545844a493dd38d84b070027a895c4517
-
ต้องคิดเชิงตรรกะได้เล็กน้อย (สามารถหาคำตอบได้ด้วย bitcoin-cli command และพวก if-else/loop)
- tx ใดในบล็อก 257,343 ที่ใช้เอาท์พุตของ coinbase ของบล็อก 256,128?
- มีเอาต์พุตเดียวที่ยังไม่ได้ใช้งานจากบล็อก 123,321 เอาต์พุตดังกล่าวถูกส่งไปที่ address ไหน
- public key ใดที่ลงนามอินพุต 0 ใน tx นี้:e5969add849689854ac7f28e45628b89f7454b83e9699e551ce14b6f90c86163
ใครทำได้พร้อมแชร์วิธีการใต้โพสต์นี้เดี๋ยวจะมีไดโนเสาร์ส่งแซตเป็นกำลังใจให้เล็กน้อยครับ
-
 @ 7b3f7803:8912e968
2025-03-08 02:28:40
@ 7b3f7803:8912e968
2025-03-08 02:28:40 Libertarians believe in open borders in theory. In practice, open borders don’t work, because, among other things, the combination with a welfare state creates a moral hazard, and the least productive of society end up within the borders of welfare states and drain resources. The social services are paid by the productive people of the country or, in the case of most fiat systems, by currency holders through inflation. Welfare states are much more likely under fiat money and the redistribution goes from native taxpayers to illegal immigrants. Thus, under fiat money, open borders end up being an open wound by which the productive lifeblood of the country bleeds out, despite the theoretical trade-efficiency benefits. As libertarians like to say, open borders and the welfare state don’t mix. In this article, we’ll examine the other sacred cow of libertarian thought: free trade.
Libertarians believe in open borders in theory. In practice, open borders don’t work, because, among other things, the combination with a welfare state creates a moral hazard, and the least productive of society end up within the borders of welfare states and drain resources. The social services are paid by the productive people of the country or, in the case of most fiat systems, by currency holders through inflation. Welfare states are much more likely under fiat money and the redistribution goes from native taxpayers to illegal immigrants. Thus, under fiat money, open borders end up being an open wound by which the productive lifeblood of the country bleeds out, despite the theoretical trade-efficiency benefits. As libertarians like to say, open borders and the welfare state don’t mix. In this article, we’ll examine the other sacred cow of libertarian thought: free trade.Free Trade without Libertarian Ideals
 Free trade is very similar to free movement of labor in that it works great in theory, but not in practice, especially under fiat money. In a libertarian free-market world, free trade works. But that assumes a whole host of libertarian ideals like sound money, non-interfering governments, and minimal aggression. Once those ideals are violated, such as with government intervention in the market, similar moral hazards and long-term costs come with them, making free trade about as libertarian as a fractional reserve bank.
Free trade is very similar to free movement of labor in that it works great in theory, but not in practice, especially under fiat money. In a libertarian free-market world, free trade works. But that assumes a whole host of libertarian ideals like sound money, non-interfering governments, and minimal aggression. Once those ideals are violated, such as with government intervention in the market, similar moral hazards and long-term costs come with them, making free trade about as libertarian as a fractional reserve bank.An example will illustrate what I’m talking about. Let’s say Portugal subsidizes their wine for export to other countries. The obvious first-order effect is that it makes Portuguese wine cheaper in France, perhaps undercutting the price of French wine. Libertarians would say, that’s great! French customers get cheaper goods, so what’s the problem?
As with any government intervention, there are significant second- and third-order effects in play. Subsidization puts unsubsidized companies at risk, perhaps driving them to bankruptcy. In this case, this might be a French wine maker. Subsidized companies may become zombies instead of dying out. In this case, this might be a Portuguese wine maker that was failing domestically but survives by selling to customers abroad with government subsidies. While French customers benefit in the short run with cheaper prices for wine, they are ultimately hurt because the goods that would have existed without government intervention never come to market. Perhaps French wine makers that went bankrupt were innovating. Perhaps the resources of the zombie Portuguese wine maker would have created something better.
Further, the dependency of French people on Portuguese wine means that something going wrong in Portugal, like a war or subsidy cuts, disrupts the supply and price of wine for France. Now France must meddle in Portugal internationally if it doesn’t want the wine supply to get disrupted. The two countries get entangled in such a way as to become more interventionist internationally. A war involving Portugal now suddenly becomes France’s business and incentivizes military aid or even violence. As usual, the unseen effects of government policy are the most pernicious.
Not Really Free
 In other words, what we call free trade isn’t really free trade. A country exporting to the US may subsidize their products through government intervention, making the product cheaper in the US. This hurts US companies, and they’re forced into choices they never would have had to face without the foreign government intervention. But because the good is crossing borders under the rubric of “free trade,” it’s somehow seen as fair. Of course it’s not, as government intervention distorts the market whether it’s done by our own government or a foreign government.
In other words, what we call free trade isn’t really free trade. A country exporting to the US may subsidize their products through government intervention, making the product cheaper in the US. This hurts US companies, and they’re forced into choices they never would have had to face without the foreign government intervention. But because the good is crossing borders under the rubric of “free trade,” it’s somehow seen as fair. Of course it’s not, as government intervention distorts the market whether it’s done by our own government or a foreign government.So why would a foreign government do this? It gets several benefits through targeted market manipulation. First, it makes its own companies’ products more popular abroad and conversely, makes US companies’ products less popular. This has the dual benefit of growing the foreign government’s firms and shrinking, perhaps bankrupting, the US ones.
Targeted subsidization like this can lead to domination under free trade. It’s not unlike the Amazon strategy of undercutting everyone first and using the monopoly pricing power at scale once everyone else has bankrupted. The global monopoly is tremendously beneficial to the country that has it. Not only is there significant tax revenue over the long term, but also a head start on innovations within that industry and an advantage in production in the adjacent industries around the product.
Second, the manufacturing centralization gives that country leverage geo-politically. A critical product that no one else manufactures means natural alliances with the countries that depend on the product, which is especially useful for smaller countries like Taiwan. Their chip manufacturing industry, holding 60% of global supply (2024), has meant that they’re a critical link for most other countries, and hence, they can use this fact to deter Chinese invasion.
Third, because of the centralization of expertise, more innovations, products, and manufacturing will tend to come within the country. This increased production has cascading benefits, including new industries and national security. China leads the world in drone technology, which undoubtedly has given it an innovation advantage for its military, should it go to war.
Fourth, the capital that flows into the country for investing in the monopolized industry will tend to stay, giving the country more wealth in the form of factories, equipment, and skills. While that capital may nominally be in the hands of foreigners, over time, the ownership of that industry will inevitably transition toward native locals, as the knowledge about how to run such industries gets dissipated within the country.
Currency Devaluation: The Universal Trade Weapon
 It would be one thing if only a specific industry were singled out for government subsidies and then the products dumped into the US as a way to hurt US companies, as that would limit the scope of the damage. But with currency devaluation, a government can subsidize all of its exports at the same time. Indeed, this is something that many countries do. While short-term, this helps US consumers, it hurts US companies and forces them into decisions that aren’t good for the US.
It would be one thing if only a specific industry were singled out for government subsidies and then the products dumped into the US as a way to hurt US companies, as that would limit the scope of the damage. But with currency devaluation, a government can subsidize all of its exports at the same time. Indeed, this is something that many countries do. While short-term, this helps US consumers, it hurts US companies and forces them into decisions that aren’t good for the US.To compete, they have to lower costs by using the same devalued currency to pay their labor as their foreign competition. That is, by relocating their capital, their manufacturing, and even their personnel to the country that’s devaluing the currency. Not only does relocating reduce labor cost, but it also often gets them benefits like tax breaks. This makes US companies de facto multinationals and not only makes them subject to other jurisdictions, but ultimately divides their loyalties. To take advantage of the reduced labor, capital must move to another country and, along with it, future innovation.
Such relocations ultimately leave the company stripped of their manufacturing capability in the US, as local competition will generally fare better over the long run. Much of the value of the industry then is captured by other governments in taxes, development, and even state-owned companies. Free trade, in other words, creates a vulnerability for domestic companies as they can be put at a significant disadvantage compared to foreign counterparts.
Hidden Effects of Foreign Intervention
Unlike the multinationals, small companies have no chance as they’re not big enough to exploit the labor arbitrage. And as is usual in a fiat system, they suffer the most while the giant corporations get the benefits of the supposed “free trade”. Most small companies can’t compete, so we get mostly the bigger companies that survive.
The transition away from domestic manufacturing necessarily means significant disruption. Domestic workers are displaced and have to find new work. Factories and equipment either have to be repurposed or rot. Entire communities that depended on the manufacturing facility now have to figure out new ways to support themselves. It’s no good telling them that they can just do something else. In a currency devaluation scenario, most of the manufacturing leaves and the jobs left are service-oriented or otherwise location-based, like real estate development. There’s a natural limit to location-based industries because the market only grows with the location that you’re servicing. Put another way, you can only have so many people give haircuts or deliver packages in a geographic area. There has to be some manufacturing of goods that can be sold outside the community, or the community will face scarce labor opportunities relative to the population.
You also can’t say the displaced workers can start some other manufacturing business. Such businesses will get out-competed on labor by the currency-devaluing country, so there won’t be much investment available for such a business, and even if there were, such a business would be competing with its hands tied behind its back. So in this scenario, what you end up with are a large pool of unemployed people whom the state subsidizes with welfare.
So when a US company leaves or goes bankrupt due to a foreign government’s subsidies, the disruption alone imposes a significant short-term cost with displaced labor, unused capital goods, and devastated communities.
Mitigations
So how do countries fight back against such a devastating economic weapon? There are a few ways countries have found around this problem of currency devaluation under free trade. First, a country can prevent capital from leaving. This is called capital controls, and many countries, particularly those that manufacture a lot, have them. Try to get money, factories, or equipment out of Malaysia, for example, and you’ll find that they make it quite difficult. Getting the same capital into the country, on the other hand, faces few restrictions. Unfortunately, the US can’t put in capital controls because dollars are its main export. It is, after all, the reserve currency of the world.
Second, you can compete by devaluing your own currency. But that’s very difficult because it requires printing a lot of dollars, and that causes inflation. There’s also no guarantee that a competing country doesn’t devalue its currency again. The US is also in a precarious position as the world’s reserve currency, so devaluing the currency more than it already does will make other holders of the dollar less likely to want to hold it, threatening the reserve currency status.
So the main two mitigations against currency devaluation in a free trade scenario are not available to the US. So what else is there? The remaining option is to drop free trade. The solution, in other words, is to add tariffs. This is how you can nullify the effects of foreign government intervention, by leveling the playing field for US manufacturers.
Tariffs
 One major industry that’s managed to continue being manufactured in the US despite significant foreign competition is cars. Notably, cars have a tariff, which incentivizes their manufacture in the US, even for foreign car makers. The tariff has acted as a way to offset foreign government subsidies and currency debasement.
One major industry that’s managed to continue being manufactured in the US despite significant foreign competition is cars. Notably, cars have a tariff, which incentivizes their manufacture in the US, even for foreign car makers. The tariff has acted as a way to offset foreign government subsidies and currency debasement.The scope of this one industry for the US is huge. There are around 300,000 direct jobs in auto assembly within the US (USTR) and there are an additional 3 million jobs supplying these manufacturers within the US. But the benefits don’t end there. The US is also creating a lot of innovation around cars, such as self-driving and plug-in electric cars. There are many countries that would love to have this industry for themselves, but because of tariffs, auto manufacturing continues in the US.
And though tariffs are seen as a tax on consumers, US car prices are cheap relative to the rest of the world. What surprises a lot of people when they move from the US to other countries is finding out that the same car often costs more abroad (e.g. 25% tariffs keep U.S. prices 20% below Europe’s $40K average, 2024). The downside of tariffs pales next to the downsides of “free trade.”
Free Trade Doesn’t Work with Fiat Money
The sad reality is that while we would love for free trade to work in the ideal libertarian paradise, it won’t in our current fiat-based system. The subsidization by foreign governments to bankrupt US companies or to make them multinational, combined with the unfortunate reality of the US dollar being the world reserve currency, means that free trade guts the US of manufacturing. Tariffs are a reasonable way to protect US manufacturers, particularly smaller ones that can’t go multinational.
What’s more, tariffs make the US less fragile and less dependent on international supply chains. Many of the wars in the past 60 years have been waged because of the entanglements the US has with other countries due to the reliance on international supply chains. Lessening this dependency, if only to prevent a war, has clear value.
Lastly, labor has been devalued significantly by fiat monetary expansion, but at least some of that can be recovered if tariffs create more manufacturing, which in turn adds to the demand for labor. This should reduce the welfare state as more opportunities are made available and fewer unemployed people will be on the rolls.
Conclusion
Fiat money produces a welfare state, which makes open borders unworkable. Fiat money also gives foreign governments a potent economic weapon to use against US companies, and by extension the labor force that powers them. Though currency debasement and capital controls are available to other countries as a defense, for the US, neither of these tools is available due to the fact that the dollar is the world reserve currency. As such, tariffs are a reasonable defense against the fiat subsidization of foreign governments.
-
 @ 04c915da:3dfbecc9
2025-03-07 00:26:37
@ 04c915da:3dfbecc9
2025-03-07 00:26:37There is something quietly rebellious about stacking sats. In a world obsessed with instant gratification, choosing to patiently accumulate Bitcoin, one sat at a time, feels like a middle finger to the hype machine. But to do it right, you have got to stay humble. Stack too hard with your head in the clouds, and you will trip over your own ego before the next halving even hits.
Small Wins
Stacking sats is not glamorous. Discipline. Stacking every day, week, or month, no matter the price, and letting time do the heavy lifting. Humility lives in that consistency. You are not trying to outsmart the market or prove you are the next "crypto" prophet. Just a regular person, betting on a system you believe in, one humble stack at a time. Folks get rekt chasing the highs. They ape into some shitcoin pump, shout about it online, then go silent when they inevitably get rekt. The ones who last? They stack. Just keep showing up. Consistency. Humility in action. Know the game is long, and you are not bigger than it.
Ego is Volatile
Bitcoin’s swings can mess with your head. One day you are up 20%, feeling like a genius and the next down 30%, questioning everything. Ego will have you panic selling at the bottom or over leveraging the top. Staying humble means patience, a true bitcoin zen. Do not try to "beat” Bitcoin. Ride it. Stack what you can afford, live your life, and let compounding work its magic.
Simplicity
There is a beauty in how stacking sats forces you to rethink value. A sat is worth less than a penny today, but every time you grab a few thousand, you plant a seed. It is not about flaunting wealth but rather building it, quietly, without fanfare. That mindset spills over. Cut out the noise: the overpriced coffee, fancy watches, the status games that drain your wallet. Humility is good for your soul and your stack. I have a buddy who has been stacking since 2015. Never talks about it unless you ask. Lives in a decent place, drives an old truck, and just keeps stacking. He is not chasing clout, he is chasing freedom. That is the vibe: less ego, more sats, all grounded in life.
The Big Picture
Stack those sats. Do it quietly, do it consistently, and do not let the green days puff you up or the red days break you down. Humility is the secret sauce, it keeps you grounded while the world spins wild. In a decade, when you look back and smile, it will not be because you shouted the loudest. It will be because you stayed the course, one sat at a time. \ \ Stay Humble and Stack Sats. 🫡
-
 @ b2d670de:907f9d4a
2025-02-26 18:27:47
@ b2d670de:907f9d4a
2025-02-26 18:27:47This is a list of nostr clients exposed as onion services. The list is currently actively maintained on GitHub. Contributions are always appreciated!
| Client name | Onion URL | Source code URL | Admin | Description | | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | | Snort | http://agzj5a4be3kgp6yurijk4q7pm2yh4a5nphdg4zozk365yirf7ahuctyd.onion | https://git.v0l.io/Kieran/snort | operator | N/A | | moStard | http://sifbugd5nwdq77plmidkug4y57zuqwqio3zlyreizrhejhp6bohfwkad.onion/ | https://github.com/rafael-xmr/nostrudel/tree/mostard | operator | minimalist monero friendly nostrudel fork | | Nostrudel | http://oxtrnmb4wsb77rmk64q3jfr55fo33luwmsyaoovicyhzgrulleiojsad.onion/ | https://github.com/hzrd149/nostrudel | operator | Runs latest tagged docker image | | Nostrudel Next | http://oxtrnnumsflm7hmvb3xqphed2eqpbrt4seflgmdsjnpgc3ejd6iycuyd.onion/ | https://github.com/hzrd149/nostrudel | operator | Runs latest "next" tagged docker image | | Nsite | http://q457mvdt5smqj726m4lsqxxdyx7r3v7gufzt46zbkop6mkghpnr7z3qd.onion/ | https://github.com/hzrd149/nsite-ts | operator | Runs nsite. You can read more about nsite here. | | Shopstr | http://6fkdn756yryd5wurkq7ifnexupnfwj6sotbtby2xhj5baythl4cyf2id.onion/ | https://github.com/shopstr-eng/shopstr-hidden-service | operator | Runs the latest
serverlessbranch build of Shopstr. | -
 @ 460c25e6:ef85065c
2025-02-25 15:20:39
@ 460c25e6:ef85065c
2025-02-25 15:20:39If you don't know where your posts are, you might as well just stay in the centralized Twitter. You either take control of your relay lists, or they will control you. Amethyst offers several lists of relays for our users. We are going to go one by one to help clarify what they are and which options are best for each one.
Public Home/Outbox Relays
Home relays store all YOUR content: all your posts, likes, replies, lists, etc. It's your home. Amethyst will send your posts here first. Your followers will use these relays to get new posts from you. So, if you don't have anything there, they will not receive your updates.
Home relays must allow queries from anyone, ideally without the need to authenticate. They can limit writes to paid users without affecting anyone's experience.
This list should have a maximum of 3 relays. More than that will only make your followers waste their mobile data getting your posts. Keep it simple. Out of the 3 relays, I recommend: - 1 large public, international relay: nos.lol, nostr.mom, relay.damus.io, etc. - 1 personal relay to store a copy of all your content in a place no one can delete. Go to relay.tools and never be censored again. - 1 really fast relay located in your country: paid options like http://nostr.wine are great
Do not include relays that block users from seeing posts in this list. If you do, no one will see your posts.
Public Inbox Relays
This relay type receives all replies, comments, likes, and zaps to your posts. If you are not getting notifications or you don't see replies from your friends, it is likely because you don't have the right setup here. If you are getting too much spam in your replies, it's probably because your inbox relays are not protecting you enough. Paid relays can filter inbox spam out.
Inbox relays must allow anyone to write into them. It's the opposite of the outbox relay. They can limit who can download the posts to their paid subscribers without affecting anyone's experience.
This list should have a maximum of 3 relays as well. Again, keep it small. More than that will just make you spend more of your data plan downloading the same notifications from all these different servers. Out of the 3 relays, I recommend: - 1 large public, international relay: nos.lol, nostr.mom, relay.damus.io, etc. - 1 personal relay to store a copy of your notifications, invites, cashu tokens and zaps. - 1 really fast relay located in your country: go to nostr.watch and find relays in your country
Terrible options include: - nostr.wine should not be here. - filter.nostr.wine should not be here. - inbox.nostr.wine should not be here.
DM Inbox Relays
These are the relays used to receive DMs and private content. Others will use these relays to send DMs to you. If you don't have it setup, you will miss DMs. DM Inbox relays should accept any message from anyone, but only allow you to download them.
Generally speaking, you only need 3 for reliability. One of them should be a personal relay to make sure you have a copy of all your messages. The others can be open if you want push notifications or closed if you want full privacy.
Good options are: - inbox.nostr.wine and auth.nostr1.com: anyone can send messages and only you can download. Not even our push notification server has access to them to notify you. - a personal relay to make sure no one can censor you. Advanced settings on personal relays can also store your DMs privately. Talk to your relay operator for more details. - a public relay if you want DM notifications from our servers.
Make sure to add at least one public relay if you want to see DM notifications.
Private Home Relays
Private Relays are for things no one should see, like your drafts, lists, app settings, bookmarks etc. Ideally, these relays are either local or require authentication before posting AND downloading each user\'s content. There are no dedicated relays for this category yet, so I would use a local relay like Citrine on Android and a personal relay on relay.tools.
Keep in mind that if you choose a local relay only, a client on the desktop might not be able to see the drafts from clients on mobile and vice versa.
Search relays:
This is the list of relays to use on Amethyst's search and user tagging with @. Tagging and searching will not work if there is nothing here.. This option requires NIP-50 compliance from each relay. Hit the Default button to use all available options on existence today: - nostr.wine - relay.nostr.band - relay.noswhere.com
Local Relays:
This is your local storage. Everything will load faster if it comes from this relay. You should install Citrine on Android and write ws://localhost:4869 in this option.
General Relays:
This section contains the default relays used to download content from your follows. Notice how you can activate and deactivate the Home, Messages (old-style DMs), Chat (public chats), and Global options in each.
Keep 5-6 large relays on this list and activate them for as many categories (Home, Messages (old-style DMs), Chat, and Global) as possible.
Amethyst will provide additional recommendations to this list from your follows with information on which of your follows might need the additional relay in your list. Add them if you feel like you are missing their posts or if it is just taking too long to load them.
My setup
Here's what I use: 1. Go to relay.tools and create a relay for yourself. 2. Go to nostr.wine and pay for their subscription. 3. Go to inbox.nostr.wine and pay for their subscription. 4. Go to nostr.watch and find a good relay in your country. 5. Download Citrine to your phone.
Then, on your relay lists, put:
Public Home/Outbox Relays: - nostr.wine - nos.lol or an in-country relay. -
.nostr1.com Public Inbox Relays - nos.lol or an in-country relay -
.nostr1.com DM Inbox Relays - inbox.nostr.wine -
.nostr1.com Private Home Relays - ws://localhost:4869 (Citrine) -
.nostr1.com (if you want) Search Relays - nostr.wine - relay.nostr.band - relay.noswhere.com
Local Relays - ws://localhost:4869 (Citrine)
General Relays - nos.lol - relay.damus.io - relay.primal.net - nostr.mom
And a few of the recommended relays from Amethyst.
Final Considerations
Remember, relays can see what your Nostr client is requesting and downloading at all times. They can track what you see and see what you like. They can sell that information to the highest bidder, they can delete your content or content that a sponsor asked them to delete (like a negative review for instance) and they can censor you in any way they see fit. Before using any random free relay out there, make sure you trust its operator and you know its terms of service and privacy policies.
-
 @ 6e0ea5d6:0327f353
2025-02-21 18:15:52
@ 6e0ea5d6:0327f353
2025-02-21 18:15:52"Malcolm Forbes recounts that a lady, wearing a faded cotton dress, and her husband, dressed in an old handmade suit, stepped off a train in Boston, USA, and timidly made their way to the office of the president of Harvard University. They had come from Palo Alto, California, and had not scheduled an appointment. The secretary, at a glance, thought that those two, looking like country bumpkins, had no business at Harvard.
— We want to speak with the president — the man said in a low voice.
— He will be busy all day — the secretary replied curtly.
— We will wait.
The secretary ignored them for hours, hoping the couple would finally give up and leave. But they stayed there, and the secretary, somewhat frustrated, decided to bother the president, although she hated doing that.
— If you speak with them for just a few minutes, maybe they will decide to go away — she said.
The president sighed in irritation but agreed. Someone of his importance did not have time to meet people like that, but he hated faded dresses and tattered suits in his office. With a stern face, he went to the couple.
— We had a son who studied at Harvard for a year — the woman said. — He loved Harvard and was very happy here, but a year ago he died in an accident, and we would like to erect a monument in his honor somewhere on campus.— My lady — said the president rudely —, we cannot erect a statue for every person who studied at Harvard and died; if we did, this place would look like a cemetery.
— Oh, no — the lady quickly replied. — We do not want to erect a statue. We would like to donate a building to Harvard.
The president looked at the woman's faded dress and her husband's old suit and exclaimed:
— A building! Do you have even the faintest idea of how much a building costs? We have more than seven and a half million dollars' worth of buildings here at Harvard.
The lady was silent for a moment, then said to her husband:
— If that’s all it costs to found a university, why don’t we have our own?
The husband agreed.
The couple, Leland Stanford, stood up and left, leaving the president confused. Traveling back to Palo Alto, California, they established there Stanford University, the second-largest in the world, in honor of their son, a former Harvard student."
Text extracted from: "Mileumlivros - Stories that Teach Values."
Thank you for reading, my friend! If this message helped you in any way, consider leaving your glass “🥃” as a token of appreciation.
A toast to our family!
-
 @ daa41bed:88f54153
2025-02-09 16:50:04
@ daa41bed:88f54153
2025-02-09 16:50:04There has been a good bit of discussion on Nostr over the past few days about the merits of zaps as a method of engaging with notes, so after writing a rather lengthy article on the pros of a strategic Bitcoin reserve, I wanted to take some time to chime in on the much more fun topic of digital engagement.
Let's begin by defining a couple of things:
Nostr is a decentralized, censorship-resistance protocol whose current biggest use case is social media (think Twitter/X). Instead of relying on company servers, it relies on relays that anyone can spin up and own their own content. Its use cases are much bigger, though, and this article is hosted on my own relay, using my own Nostr relay as an example.
Zap is a tip or donation denominated in sats (small units of Bitcoin) sent from one user to another. This is generally done directly over the Lightning Network but is increasingly using Cashu tokens. For the sake of this discussion, how you transmit/receive zaps will be irrelevant, so don't worry if you don't know what Lightning or Cashu are.
If we look at how users engage with posts and follows/followers on platforms like Twitter, Facebook, etc., it becomes evident that traditional social media thrives on engagement farming. The more outrageous a post, the more likely it will get a reaction. We see a version of this on more visual social platforms like YouTube and TikTok that use carefully crafted thumbnail images to grab the user's attention to click the video. If you'd like to dive deep into the psychology and science behind social media engagement, let me know, and I'd be happy to follow up with another article.
In this user engagement model, a user is given the option to comment or like the original post, or share it among their followers to increase its signal. They receive no value from engaging with the content aside from the dopamine hit of the original experience or having their comment liked back by whatever influencer they provide value to. Ad revenue flows to the content creator. Clout flows to the content creator. Sales revenue from merch and content placement flows to the content creator. We call this a linear economy -- the idea that resources get created, used up, then thrown away. Users create content and farm as much engagement as possible, then the content is forgotten within a few hours as they move on to the next piece of content to be farmed.
What if there were a simple way to give value back to those who engage with your content? By implementing some value-for-value model -- a circular economy. Enter zaps.

Unlike traditional social media platforms, Nostr does not actively use algorithms to determine what content is popular, nor does it push content created for active user engagement to the top of a user's timeline. Yes, there are "trending" and "most zapped" timelines that users can choose to use as their default, but these use relatively straightforward engagement metrics to rank posts for these timelines.
That is not to say that we may not see clients actively seeking to refine timeline algorithms for specific metrics. Still, the beauty of having an open protocol with media that is controlled solely by its users is that users who begin to see their timeline gamed towards specific algorithms can choose to move to another client, and for those who are more tech-savvy, they can opt to run their own relays or create their own clients with personalized algorithms and web of trust scoring systems.
Zaps enable the means to create a new type of social media economy in which creators can earn for creating content and users can earn by actively engaging with it. Like and reposting content is relatively frictionless and costs nothing but a simple button tap. Zaps provide active engagement because they signal to your followers and those of the content creator that this post has genuine value, quite literally in the form of money—sats.

I have seen some comments on Nostr claiming that removing likes and reactions is for wealthy people who can afford to send zaps and that the majority of people in the US and around the world do not have the time or money to zap because they have better things to spend their money like feeding their families and paying their bills. While at face value, these may seem like valid arguments, they, unfortunately, represent the brainwashed, defeatist attitude that our current economic (and, by extension, social media) systems aim to instill in all of us to continue extracting value from our lives.
Imagine now, if those people dedicating their own time (time = money) to mine pity points on social media would instead spend that time with genuine value creation by posting content that is meaningful to cultural discussions. Imagine if, instead of complaining that their posts get no zaps and going on a tirade about how much of a victim they are, they would empower themselves to take control of their content and give value back to the world; where would that leave us? How much value could be created on a nascent platform such as Nostr, and how quickly could it overtake other platforms?
Other users argue about user experience and that additional friction (i.e., zaps) leads to lower engagement, as proven by decades of studies on user interaction. While the added friction may turn some users away, does that necessarily provide less value? I argue quite the opposite. You haven't made a few sats from zaps with your content? Can't afford to send some sats to a wallet for zapping? How about using the most excellent available resource and spending 10 seconds of your time to leave a comment? Likes and reactions are valueless transactions. Social media's real value derives from providing monetary compensation and actively engaging in a conversation with posts you find interesting or thought-provoking. Remember when humans thrived on conversation and discussion for entertainment instead of simply being an onlooker of someone else's life?
If you've made it this far, my only request is this: try only zapping and commenting as a method of engagement for two weeks. Sure, you may end up liking a post here and there, but be more mindful of how you interact with the world and break yourself from blind instinct. You'll thank me later.

-
 @ dc4cd086:cee77c06
2025-02-09 03:35:25
@ dc4cd086:cee77c06
2025-02-09 03:35:25Have you ever wanted to learn from lengthy educational videos but found it challenging to navigate through hours of content? Our new tool addresses this problem by transforming long-form video lectures into easily digestible, searchable content.
Key Features:
Video Processing:
- Automatically downloads YouTube videos, transcripts, and chapter information
- Splits transcripts into sections based on video chapters
Content Summarization:
- Utilizes language models to transform spoken content into clear, readable text
- Formats output in AsciiDoc for improved readability and navigation
- Highlights key terms and concepts with [[term]] notation for potential cross-referencing
Diagram Extraction:
- Analyzes video entropy to identify static diagram/slide sections
- Provides a user-friendly GUI for manual selection of relevant time ranges
- Allows users to pick representative frames from selected ranges
Going Forward:
Currently undergoing a rewrite to improve organization and functionality, but you are welcome to try the current version, though it might not work on every machine. Will support multiple open and closed language models for user choice Free and open-source, allowing for personal customization and integration with various knowledge bases. Just because we might not have it on our official Alexandria knowledge base, you are still welcome to use it on you own personal or community knowledge bases! We want to help find connections between ideas that exist across relays, allowing individuals and groups to mix and match knowledge bases between each other, allowing for any degree of openness you care.
While designed with #Alexandria users in mind, it's available for anyone to use and adapt to their own learning needs.
Screenshots
Frame Selection
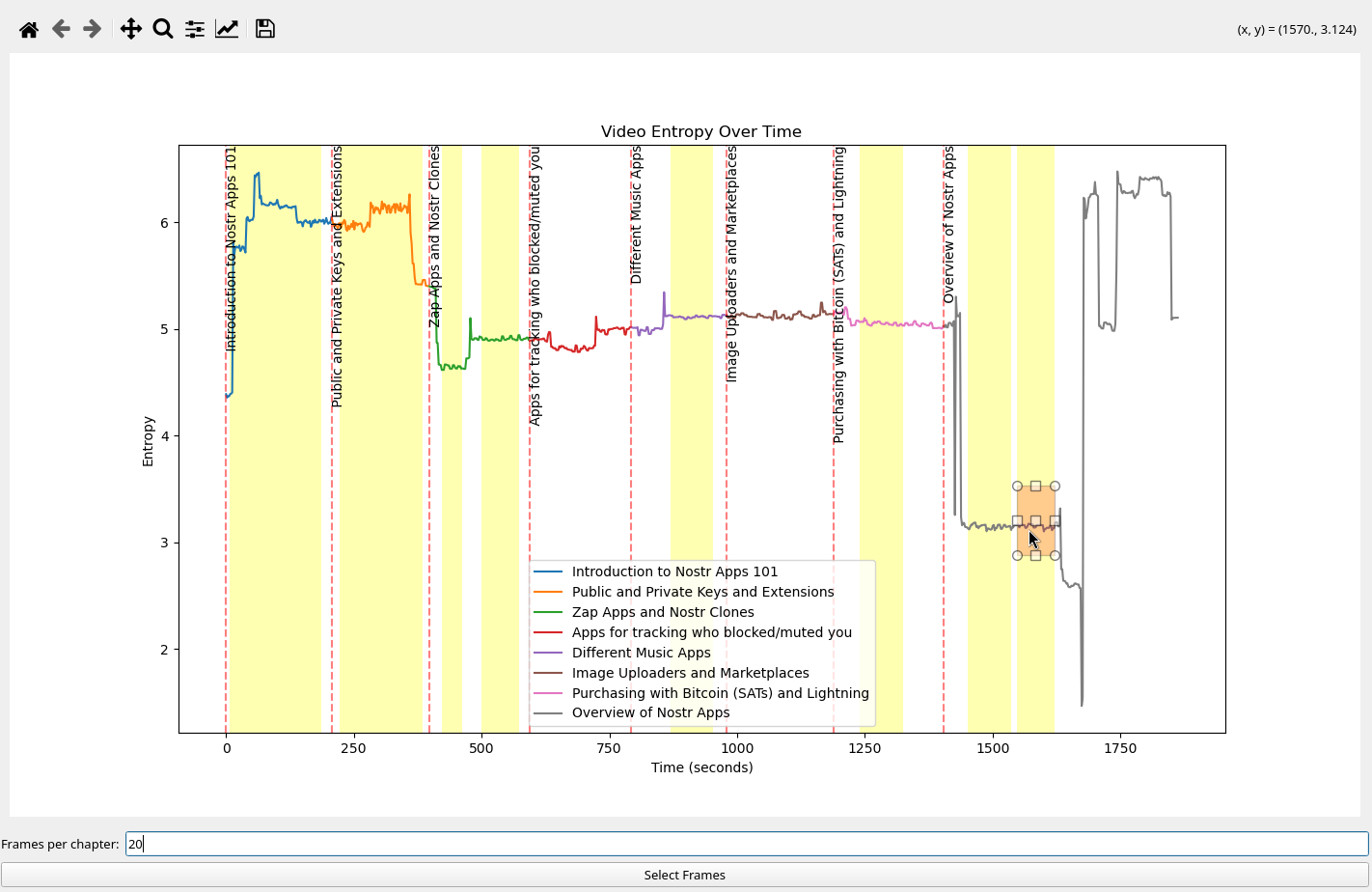
This is a screenshot of the frame selection interface. You'll see a signal that represents frame entropy over time. The vertical lines indicate the start and end of a chapter. Within these chapters you can select the frames by clicking and dragging the mouse over the desired range where you think diagram is in that chapter. At the bottom is an option that tells the program to select a specific number of frames from that selection.
Diagram Extraction
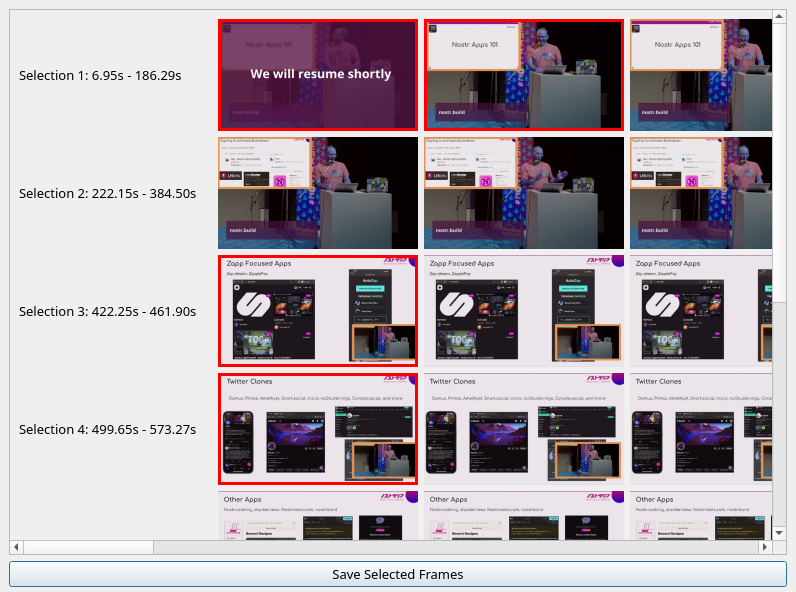
This is a screenshot of the diagram extraction interface. For every selection you've made, there will be a set of frames that you can choose from. You can select and deselect as many frames as you'd like to save.
Links
- repo: https://github.com/limina1/video_article_converter
- Nostr Apps 101: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Flxa_jkErqE
Output
And now, we have a demonstration of the final result of this tool, with some quick cleaning up. The video we will be using this tool on is titled Nostr Apps 101 by nostr:npub1nxy4qpqnld6kmpphjykvx2lqwvxmuxluddwjamm4nc29ds3elyzsm5avr7 during Nostrasia. The following thread is an analog to the modular articles we are constructing for Alexandria, and I hope it conveys the functionality we want to create in the knowledge space. Note, this tool is the first step! You could use a different prompt that is most appropriate for the specific context of the transcript you are working with, but you can also manually clean up any discrepancies that don't portray the video accurately. You can now view the article on #Alexandria https://next-alexandria.gitcitadel.eu/publication?d=nostr-apps-101
Initially published as chained kind 1's nostr:nevent1qvzqqqqqqypzp5r5hd579v2sszvvzfel677c8dxgxm3skl773sujlsuft64c44ncqy2hwumn8ghj7un9d3shjtnyv9kh2uewd9hj7qgwwaehxw309ahx7uewd3hkctcpzemhxue69uhhyetvv9ujumt0wd68ytnsw43z7qghwaehxw309aex2mrp0yhxummnw3ezucnpdejz7qgewaehxw309aex2mrp0yh8xmn0wf6zuum0vd5kzmp0qqsxunmjy20mvlq37vnrcshkf6sdrtkfjtjz3anuetmcuv8jswhezgc7hglpn
Or view on Coracle https://coracle.social /nevent1qqsxunmjy20mvlq37vnrcshkf6sdrtkfjtjz3anuetmcuv8jswhezgcppemhxue69uhkummn9ekx7mp0qgsdqa9md83tz5yqnrqjw07hhkpmfjpkuv9hlh5v8yhu8z274w9dv7qnnq0s3
-
 @ f683e870:557f5ef2
2025-02-07 14:33:31
@ f683e870:557f5ef2
2025-02-07 14:33:31After many months of ideation, research, and heads-down building, @nostr:npub1wf4pufsucer5va8g9p0rj5dnhvfeh6d8w0g6eayaep5dhps6rsgs43dgh9 and myself are excited to announce our new project called Vertex.
Vertex’s mission is to provide developers and builders with the most up-to-date and easy-to-use social graph tools.
Our services will enable our future customers to improve the experience they provide by offering:
- Protection against impersonation and DoS attacks
- Personalized discovery and recommendations.
All in an open, transparent and interoperable way.
Open and Interoperable
We have structured our services as NIP-90 Data Vending Machines. We are currently using these DVMs and we are eager to hear what the community thinks and if anyone has suggestions for improvements.
Regardless of their specific structures, using DVMs means one very important thing: no vendor lock-in.
Anyone can start processing the same requests and compete with us to offer the most accurate results at the best price. This is very important for us because we are well aware that services like ours can potentially become a central point of failure. The ease with which we can be replaced by a competitor will keep us on our toes and will continue to motivate us to build better and better experiences for our customers, all while operating in an ethical and open manner.
Speaking of openness, we have released all of our code under the MIT license, which means that anyone can review our algorithms, and any company or power user can run their own copies of Vertex if they so wish.
We are confident in this decision because the value of Vertex is not in the software. It is in the team who designed and implemented it – and now continually improves, manages and runs it to provide the most accurate results with the lowest latency and highest uptime.
What we offer
We currently support three DVMs, but we plan to increase our offering substantially this year.
VerifyReputation: give your users useful and personalized information to asses the reputation of an npub, minimizing the risk of impersonations.RecommendFollows: give your users personalized recommendations about interesting npubs they might want who to follow.SortAuthors: give your users the ability to sort replies, comments, zaps, search results or just about anything using authors’ reputations.
To learn more, watch this 3-minute walk-through video, and visit our website
https://cdn.satellite.earth/6efabff7da55ce848074351b2d640ca3bde4515060d9aba002461a4a4ddad8d8.mp4
We are also considering offering a custom service to help builders clarify and implement their vision for Web of Trust in their own applications or projects. Please reach out if you are interested.
-
 @ b17fccdf:b7211155
2025-02-01 18:41:27
@ b17fccdf:b7211155
2025-02-01 18:41:27Next new resources about the MiniBolt guide have been released:
- 🆕 Roadmap: LINK
- 🆕 Dynamic Network map: LINK
- 🆕 Nostr community: LINK < ~ REMOVE the "[]" symbols from the URL (naddr...) to access
- 🆕 Linktr FOSS (UC) by Gzuuus: LINK
- 🆕 Donate webpage: 🚾 Clearnet LINK || 🧅 Onion LINK
- 🆕 Contact email: hello@minibolt.info
Enjoy it MiniBolter! 💙
-
 @ 0fa80bd3:ea7325de
2025-01-29 15:43:42
@ 0fa80bd3:ea7325de
2025-01-29 15:43:42Lyn Alden - биткойн евангелист или евангелистка, я пока не понял
npub1a2cww4kn9wqte4ry70vyfwqyqvpswksna27rtxd8vty6c74era8sdcw83aThomas Pacchia - PubKey owner - X - @tpacchia
npub1xy6exlg37pw84cpyj05c2pdgv86hr25cxn0g7aa8g8a6v97mhduqeuhgplcalvadev - Shopstr
npub16dhgpql60vmd4mnydjut87vla23a38j689jssaqlqqlzrtqtd0kqex0nkqCalle - Cashu founder
npub12rv5lskctqxxs2c8rf2zlzc7xx3qpvzs3w4etgemauy9thegr43sf485vgДжек Дорси
npub1sg6plzptd64u62a878hep2kev88swjh3tw00gjsfl8f237lmu63q0uf63m21 ideas
npub1lm3f47nzyf0rjp6fsl4qlnkmzed4uj4h2gnf2vhe3l3mrj85vqks6z3c7lМного адресов. Хз кто надо сортировать
https://github.com/aitechguy/nostr-address-bookФиатДжеф - создатель Ностр - https://github.com/fiatjaf
npub180cvv07tjdrrgpa0j7j7tmnyl2yr6yr7l8j4s3evf6u64th6gkwsyjh6w6EVAN KALOUDIS Zues wallet
npub19kv88vjm7tw6v9qksn2y6h4hdt6e79nh3zjcud36k9n3lmlwsleqwte2qdПрограммер Коди https://github.com/CodyTseng/nostr-relay
npub1syjmjy0dp62dhccq3g97fr87tngvpvzey08llyt6ul58m2zqpzps9wf6wlAnna Chekhovich - Managing Bitcoin at The Anti-Corruption Foundation https://x.com/AnyaChekhovich
npub1y2st7rp54277hyd2usw6shy3kxprnmpvhkezmldp7vhl7hp920aq9cfyr7 -
 @ 9e69e420:d12360c2
2025-01-26 01:31:47
@ 9e69e420:d12360c2
2025-01-26 01:31:47Chef's notes
arbitray
- test
- of
- chefs notes
hedding 2
Details
- ⏲️ Prep time: 20
- 🍳 Cook time: 1 hour
- 🍽️ Servings: 5
Ingredients
- Test ingredient
- 2nd test ingredient
Directions
- Bake
- Cool
-
 @ 9e69e420:d12360c2
2025-01-25 22:16:54
@ 9e69e420:d12360c2
2025-01-25 22:16:54President Trump plans to withdraw 20,000 U.S. troops from Europe and expects European allies to contribute financially to the remaining military presence. Reported by ANSA, Trump aims to deliver this message to European leaders since taking office. A European diplomat noted, “the costs cannot be borne solely by American taxpayers.”
The Pentagon hasn't commented yet. Trump has previously sought lower troop levels in Europe and had ordered cuts during his first term. The U.S. currently maintains around 65,000 troops in Europe, with total forces reaching 100,000 since the Ukraine invasion. Trump's new approach may shift military focus to the Pacific amid growing concerns about China.
-
 @ b17fccdf:b7211155
2025-01-21 18:22:51
@ b17fccdf:b7211155
2025-01-21 18:22:51😱 Did you recently find this signature verification error when you tried to update your MiniBolt repositories with ->
sudo apt update? 💥🚨👇
🔧 Don't worry, that's because Tor renewed its signing key since it expired last 07/15, just renew your keyring by following the next steps to solve this problem:
~ > CLICK HERE < ~
Enjoy it MiniBolter!💙
-
 @ 6be5cc06:5259daf0
2025-01-21 01:51:46
@ 6be5cc06:5259daf0
2025-01-21 01:51:46Bitcoin: Um sistema de dinheiro eletrônico direto entre pessoas.
Satoshi Nakamoto
satoshin@gmx.com
www.bitcoin.org
Resumo
O Bitcoin é uma forma de dinheiro digital que permite pagamentos diretos entre pessoas, sem a necessidade de um banco ou instituição financeira. Ele resolve um problema chamado gasto duplo, que ocorre quando alguém tenta gastar o mesmo dinheiro duas vezes. Para evitar isso, o Bitcoin usa uma rede descentralizada onde todos trabalham juntos para verificar e registrar as transações.
As transações são registradas em um livro público chamado blockchain, protegido por uma técnica chamada Prova de Trabalho. Essa técnica cria uma cadeia de registros que não pode ser alterada sem refazer todo o trabalho já feito. Essa cadeia é mantida pelos computadores que participam da rede, e a mais longa é considerada a verdadeira.
Enquanto a maior parte do poder computacional da rede for controlada por participantes honestos, o sistema continuará funcionando de forma segura. A rede é flexível, permitindo que qualquer pessoa entre ou saia a qualquer momento, sempre confiando na cadeia mais longa como prova do que aconteceu.
1. Introdução
Hoje, quase todos os pagamentos feitos pela internet dependem de bancos ou empresas como processadores de pagamento (cartões de crédito, por exemplo) para funcionar. Embora esse sistema seja útil, ele tem problemas importantes porque é baseado em confiança.
Primeiro, essas empresas podem reverter pagamentos, o que é útil em caso de erros, mas cria custos e incertezas. Isso faz com que pequenas transações, como pagar centavos por um serviço, se tornem inviáveis. Além disso, os comerciantes são obrigados a desconfiar dos clientes, pedindo informações extras e aceitando fraudes como algo inevitável.
Esses problemas não existem no dinheiro físico, como o papel-moeda, onde o pagamento é final e direto entre as partes. No entanto, não temos como enviar dinheiro físico pela internet sem depender de um intermediário confiável.
O que precisamos é de um sistema de pagamento eletrônico baseado em provas matemáticas, não em confiança. Esse sistema permitiria que qualquer pessoa enviasse dinheiro diretamente para outra, sem depender de bancos ou processadores de pagamento. Além disso, as transações seriam irreversíveis, protegendo vendedores contra fraudes, mas mantendo a possibilidade de soluções para disputas legítimas.
Neste documento, apresentamos o Bitcoin, que resolve o problema do gasto duplo usando uma rede descentralizada. Essa rede cria um registro público e protegido por cálculos matemáticos, que garante a ordem das transações. Enquanto a maior parte da rede for controlada por pessoas honestas, o sistema será seguro contra ataques.
2. Transações
Para entender como funciona o Bitcoin, é importante saber como as transações são realizadas. Imagine que você quer transferir uma "moeda digital" para outra pessoa. No sistema do Bitcoin, essa "moeda" é representada por uma sequência de registros que mostram quem é o atual dono. Para transferi-la, você adiciona um novo registro comprovando que agora ela pertence ao próximo dono. Esse registro é protegido por um tipo especial de assinatura digital.
O que é uma assinatura digital?
Uma assinatura digital é como uma senha secreta, mas muito mais segura. No Bitcoin, cada usuário tem duas chaves: uma "chave privada", que é secreta e serve para criar a assinatura, e uma "chave pública", que pode ser compartilhada com todos e é usada para verificar se a assinatura é válida. Quando você transfere uma moeda, usa sua chave privada para assinar a transação, provando que você é o dono. A próxima pessoa pode usar sua chave pública para confirmar isso.
Como funciona na prática?
Cada "moeda" no Bitcoin é, na verdade, uma cadeia de assinaturas digitais. Vamos imaginar o seguinte cenário:
- A moeda está com o Dono 0 (você). Para transferi-la ao Dono 1, você assina digitalmente a transação com sua chave privada. Essa assinatura inclui o código da transação anterior (chamado de "hash") e a chave pública do Dono 1.
- Quando o Dono 1 quiser transferir a moeda ao Dono 2, ele assinará a transação seguinte com sua própria chave privada, incluindo também o hash da transação anterior e a chave pública do Dono 2.
- Esse processo continua, formando uma "cadeia" de transações. Qualquer pessoa pode verificar essa cadeia para confirmar quem é o atual dono da moeda.
Resolvendo o problema do gasto duplo
Um grande desafio com moedas digitais é o "gasto duplo", que é quando uma mesma moeda é usada em mais de uma transação. Para evitar isso, muitos sistemas antigos dependiam de uma entidade central confiável, como uma casa da moeda, que verificava todas as transações. No entanto, isso criava um ponto único de falha e centralizava o controle do dinheiro.
O Bitcoin resolve esse problema de forma inovadora: ele usa uma rede descentralizada onde todos os participantes (os "nós") têm acesso a um registro completo de todas as transações. Cada nó verifica se as transações são válidas e se a moeda não foi gasta duas vezes. Quando a maioria dos nós concorda com a validade de uma transação, ela é registrada permanentemente na blockchain.
Por que isso é importante?
Essa solução elimina a necessidade de confiar em uma única entidade para gerenciar o dinheiro, permitindo que qualquer pessoa no mundo use o Bitcoin sem precisar de permissão de terceiros. Além disso, ela garante que o sistema seja seguro e resistente a fraudes.
3. Servidor Timestamp
Para assegurar que as transações sejam realizadas de forma segura e transparente, o sistema Bitcoin utiliza algo chamado de "servidor de registro de tempo" (timestamp). Esse servidor funciona como um registro público que organiza as transações em uma ordem específica.
Ele faz isso agrupando várias transações em blocos e criando um código único chamado "hash". Esse hash é como uma impressão digital que representa todo o conteúdo do bloco. O hash de cada bloco é amplamente divulgado, como se fosse publicado em um jornal ou em um fórum público.
Esse processo garante que cada bloco de transações tenha um registro de quando foi criado e que ele existia naquele momento. Além disso, cada novo bloco criado contém o hash do bloco anterior, formando uma cadeia contínua de blocos conectados — conhecida como blockchain.
Com isso, se alguém tentar alterar qualquer informação em um bloco anterior, o hash desse bloco mudará e não corresponderá ao hash armazenado no bloco seguinte. Essa característica torna a cadeia muito segura, pois qualquer tentativa de fraude seria imediatamente detectada.
O sistema de timestamps é essencial para provar a ordem cronológica das transações e garantir que cada uma delas seja única e autêntica. Dessa forma, ele reforça a segurança e a confiança na rede Bitcoin.
4. Prova-de-Trabalho
Para implementar o registro de tempo distribuído no sistema Bitcoin, utilizamos um mecanismo chamado prova-de-trabalho. Esse sistema é semelhante ao Hashcash, desenvolvido por Adam Back, e baseia-se na criação de um código único, o "hash", por meio de um processo computacionalmente exigente.
A prova-de-trabalho envolve encontrar um valor especial que, quando processado junto com as informações do bloco, gere um hash que comece com uma quantidade específica de zeros. Esse valor especial é chamado de "nonce". Encontrar o nonce correto exige um esforço significativo do computador, porque envolve tentativas repetidas até que a condição seja satisfeita.
Esse processo é importante porque torna extremamente difícil alterar qualquer informação registrada em um bloco. Se alguém tentar mudar algo em um bloco, seria necessário refazer o trabalho de computação não apenas para aquele bloco, mas também para todos os blocos que vêm depois dele. Isso garante a segurança e a imutabilidade da blockchain.
A prova-de-trabalho também resolve o problema de decidir qual cadeia de blocos é a válida quando há múltiplas cadeias competindo. A decisão é feita pela cadeia mais longa, pois ela representa o maior esforço computacional já realizado. Isso impede que qualquer indivíduo ou grupo controle a rede, desde que a maioria do poder de processamento seja mantida por participantes honestos.
Para garantir que o sistema permaneça eficiente e equilibrado, a dificuldade da prova-de-trabalho é ajustada automaticamente ao longo do tempo. Se novos blocos estiverem sendo gerados rapidamente, a dificuldade aumenta; se estiverem sendo gerados muito lentamente, a dificuldade diminui. Esse ajuste assegura que novos blocos sejam criados aproximadamente a cada 10 minutos, mantendo o sistema estável e funcional.
5. Rede
A rede Bitcoin é o coração do sistema e funciona de maneira distribuída, conectando vários participantes (ou nós) para garantir o registro e a validação das transações. Os passos para operar essa rede são:
-
Transmissão de Transações: Quando alguém realiza uma nova transação, ela é enviada para todos os nós da rede. Isso é feito para garantir que todos estejam cientes da operação e possam validá-la.
-
Coleta de Transações em Blocos: Cada nó agrupa as novas transações recebidas em um "bloco". Este bloco será preparado para ser adicionado à cadeia de blocos (a blockchain).
-
Prova-de-Trabalho: Os nós competem para resolver a prova-de-trabalho do bloco, utilizando poder computacional para encontrar um hash válido. Esse processo é como resolver um quebra-cabeça matemático difícil.
-
Envio do Bloco Resolvido: Quando um nó encontra a solução para o bloco (a prova-de-trabalho), ele compartilha esse bloco com todos os outros nós na rede.
-
Validação do Bloco: Cada nó verifica o bloco recebido para garantir que todas as transações nele contidas sejam válidas e que nenhuma moeda tenha sido gasta duas vezes. Apenas blocos válidos são aceitos.
-
Construção do Próximo Bloco: Os nós que aceitaram o bloco começam a trabalhar na criação do próximo bloco, utilizando o hash do bloco aceito como base (hash anterior). Isso mantém a continuidade da cadeia.
Resolução de Conflitos e Escolha da Cadeia Mais Longa
Os nós sempre priorizam a cadeia mais longa, pois ela representa o maior esforço computacional já realizado, garantindo maior segurança. Se dois blocos diferentes forem compartilhados simultaneamente, os nós trabalharão no primeiro bloco recebido, mas guardarão o outro como uma alternativa. Caso o segundo bloco eventualmente forme uma cadeia mais longa (ou seja, tenha mais blocos subsequentes), os nós mudarão para essa nova cadeia.
Tolerância a Falhas
A rede é robusta e pode lidar com mensagens que não chegam a todos os nós. Uma transação não precisa alcançar todos os nós de imediato; basta que chegue a um número suficiente deles para ser incluída em um bloco. Da mesma forma, se um nó não receber um bloco em tempo hábil, ele pode solicitá-lo ao perceber que está faltando quando o próximo bloco é recebido.
Esse mecanismo descentralizado permite que a rede Bitcoin funcione de maneira segura, confiável e resiliente, sem depender de uma autoridade central.
6. Incentivo
O incentivo é um dos pilares fundamentais que sustenta o funcionamento da rede Bitcoin, garantindo que os participantes (nós) continuem operando de forma honesta e contribuindo com recursos computacionais. Ele é estruturado em duas partes principais: a recompensa por mineração e as taxas de transação.
Recompensa por Mineração
Por convenção, o primeiro registro em cada bloco é uma transação especial que cria novas moedas e as atribui ao criador do bloco. Essa recompensa incentiva os mineradores a dedicarem poder computacional para apoiar a rede. Como não há uma autoridade central para emitir moedas, essa é a maneira pela qual novas moedas entram em circulação. Esse processo pode ser comparado ao trabalho de garimpeiros, que utilizam recursos para colocar mais ouro em circulação. No caso do Bitcoin, o "recurso" consiste no tempo de CPU e na energia elétrica consumida para resolver a prova-de-trabalho.
Taxas de Transação
Além da recompensa por mineração, os mineradores também podem ser incentivados pelas taxas de transação. Se uma transação utiliza menos valor de saída do que o valor de entrada, a diferença é tratada como uma taxa, que é adicionada à recompensa do bloco contendo essa transação. Com o passar do tempo e à medida que o número de moedas em circulação atinge o limite predeterminado, essas taxas de transação se tornam a principal fonte de incentivo, substituindo gradualmente a emissão de novas moedas. Isso permite que o sistema opere sem inflação, uma vez que o número total de moedas permanece fixo.
Incentivo à Honestidade
O design do incentivo também busca garantir que os participantes da rede mantenham um comportamento honesto. Para um atacante que consiga reunir mais poder computacional do que o restante da rede, ele enfrentaria duas escolhas:
- Usar esse poder para fraudar o sistema, como reverter transações e roubar pagamentos.
- Seguir as regras do sistema, criando novos blocos e recebendo recompensas legítimas.
A lógica econômica favorece a segunda opção, pois um comportamento desonesto prejudicaria a confiança no sistema, diminuindo o valor de todas as moedas, incluindo aquelas que o próprio atacante possui. Jogar dentro das regras não apenas maximiza o retorno financeiro, mas também preserva a validade e a integridade do sistema.
Esse mecanismo garante que os incentivos econômicos estejam alinhados com o objetivo de manter a rede segura, descentralizada e funcional ao longo do tempo.
7. Recuperação do Espaço em Disco
Depois que uma moeda passa a estar protegida por muitos blocos na cadeia, as informações sobre as transações antigas que a geraram podem ser descartadas para economizar espaço em disco. Para que isso seja possível sem comprometer a segurança, as transações são organizadas em uma estrutura chamada "árvore de Merkle". Essa árvore funciona como um resumo das transações: em vez de armazenar todas elas, guarda apenas um "hash raiz", que é como uma assinatura compacta que representa todo o grupo de transações.
Os blocos antigos podem, então, ser simplificados, removendo as partes desnecessárias dessa árvore. Apenas a raiz do hash precisa ser mantida no cabeçalho do bloco, garantindo que a integridade dos dados seja preservada, mesmo que detalhes específicos sejam descartados.
Para exemplificar: imagine que você tenha vários recibos de compra. Em vez de guardar todos os recibos, você cria um documento e lista apenas o valor total de cada um. Mesmo que os recibos originais sejam descartados, ainda é possível verificar a soma com base nos valores armazenados.
Além disso, o espaço ocupado pelos blocos em si é muito pequeno. Cada bloco sem transações ocupa apenas cerca de 80 bytes. Isso significa que, mesmo com blocos sendo gerados a cada 10 minutos, o crescimento anual em espaço necessário é insignificante: apenas 4,2 MB por ano. Com a capacidade de armazenamento dos computadores crescendo a cada ano, esse espaço continuará sendo trivial, garantindo que a rede possa operar de forma eficiente sem problemas de armazenamento, mesmo a longo prazo.
8. Verificação de Pagamento Simplificada
É possível confirmar pagamentos sem a necessidade de operar um nó completo da rede. Para isso, o usuário precisa apenas de uma cópia dos cabeçalhos dos blocos da cadeia mais longa (ou seja, a cadeia com maior esforço de trabalho acumulado). Ele pode verificar a validade de uma transação ao consultar os nós da rede até obter a confirmação de que tem a cadeia mais longa. Para isso, utiliza-se o ramo Merkle, que conecta a transação ao bloco em que ela foi registrada.
Entretanto, o método simplificado possui limitações: ele não pode confirmar uma transação isoladamente, mas sim assegurar que ela ocupa um lugar específico na cadeia mais longa. Dessa forma, se um nó da rede aprova a transação, os blocos subsequentes reforçam essa aceitação.
A verificação simplificada é confiável enquanto a maioria dos nós da rede for honesta. Contudo, ela se torna vulnerável caso a rede seja dominada por um invasor. Nesse cenário, um atacante poderia fabricar transações fraudulentas que enganariam o usuário temporariamente até que o invasor obtivesse controle completo da rede.
Uma estratégia para mitigar esse risco é configurar alertas nos softwares de nós completos. Esses alertas identificam blocos inválidos, sugerindo ao usuário baixar o bloco completo para confirmar qualquer inconsistência. Para maior segurança, empresas que realizam pagamentos frequentes podem preferir operar seus próprios nós, reduzindo riscos e permitindo uma verificação mais direta e confiável.
9. Combinando e Dividindo Valor
No sistema Bitcoin, cada unidade de valor é tratada como uma "moeda" individual, mas gerenciar cada centavo como uma transação separada seria impraticável. Para resolver isso, o Bitcoin permite que valores sejam combinados ou divididos em transações, facilitando pagamentos de qualquer valor.
Entradas e Saídas
Cada transação no Bitcoin é composta por:
- Entradas: Representam os valores recebidos em transações anteriores.
- Saídas: Correspondem aos valores enviados, divididos entre os destinatários e, eventualmente, o troco para o remetente.
Normalmente, uma transação contém:
- Uma única entrada com valor suficiente para cobrir o pagamento.
- Ou várias entradas combinadas para atingir o valor necessário.
O valor total das saídas nunca excede o das entradas, e a diferença (se houver) pode ser retornada ao remetente como troco.
Exemplo Prático
Imagine que você tem duas entradas:
- 0,03 BTC
- 0,07 BTC
Se deseja enviar 0,08 BTC para alguém, a transação terá:
- Entrada: As duas entradas combinadas (0,03 + 0,07 BTC = 0,10 BTC).
- Saídas: Uma para o destinatário (0,08 BTC) e outra como troco para você (0,02 BTC).
Essa flexibilidade permite que o sistema funcione sem precisar manipular cada unidade mínima individualmente.
Difusão e Simplificação
A difusão de transações, onde uma depende de várias anteriores e assim por diante, não representa um problema. Não é necessário armazenar ou verificar o histórico completo de uma transação para utilizá-la, já que o registro na blockchain garante sua integridade.
10. Privacidade
O modelo bancário tradicional oferece um certo nível de privacidade, limitando o acesso às informações financeiras apenas às partes envolvidas e a um terceiro confiável (como bancos ou instituições financeiras). No entanto, o Bitcoin opera de forma diferente, pois todas as transações são publicamente registradas na blockchain. Apesar disso, a privacidade pode ser mantida utilizando chaves públicas anônimas, que desvinculam diretamente as transações das identidades das partes envolvidas.
Fluxo de Informação
- No modelo tradicional, as transações passam por um terceiro confiável que conhece tanto o remetente quanto o destinatário.
- No Bitcoin, as transações são anunciadas publicamente, mas sem revelar diretamente as identidades das partes. Isso é comparável a dados divulgados por bolsas de valores, onde informações como o tempo e o tamanho das negociações (a "fita") são públicas, mas as identidades das partes não.
Protegendo a Privacidade
Para aumentar a privacidade no Bitcoin, são adotadas as seguintes práticas:
- Chaves Públicas Anônimas: Cada transação utiliza um par de chaves diferentes, dificultando a associação com um proprietário único.
- Prevenção de Ligação: Ao usar chaves novas para cada transação, reduz-se a possibilidade de links evidentes entre múltiplas transações realizadas pelo mesmo usuário.
Riscos de Ligação
Embora a privacidade seja fortalecida, alguns riscos permanecem:
- Transações multi-entrada podem revelar que todas as entradas pertencem ao mesmo proprietário, caso sejam necessárias para somar o valor total.
- O proprietário da chave pode ser identificado indiretamente por transações anteriores que estejam conectadas.
11. Cálculos
Imagine que temos um sistema onde as pessoas (ou computadores) competem para adicionar informações novas (blocos) a um grande registro público (a cadeia de blocos ou blockchain). Este registro é como um livro contábil compartilhado, onde todos podem verificar o que está escrito.
Agora, vamos pensar em um cenário: um atacante quer enganar o sistema. Ele quer mudar informações já registradas para beneficiar a si mesmo, por exemplo, desfazendo um pagamento que já fez. Para isso, ele precisa criar uma versão alternativa do livro contábil (a cadeia de blocos dele) e convencer todos os outros participantes de que essa versão é a verdadeira.
Mas isso é extremamente difícil.
Como o Ataque Funciona
Quando um novo bloco é adicionado à cadeia, ele depende de cálculos complexos que levam tempo e esforço. Esses cálculos são como um grande quebra-cabeça que precisa ser resolvido.
- Os “bons jogadores” (nós honestos) estão sempre trabalhando juntos para resolver esses quebra-cabeças e adicionar novos blocos à cadeia verdadeira.
- O atacante, por outro lado, precisa resolver quebra-cabeças sozinho, tentando “alcançar” a cadeia honesta para que sua versão alternativa pareça válida.
Se a cadeia honesta já está vários blocos à frente, o atacante começa em desvantagem, e o sistema está projetado para que a dificuldade de alcançá-los aumente rapidamente.
A Corrida Entre Cadeias
Você pode imaginar isso como uma corrida. A cada bloco novo que os jogadores honestos adicionam à cadeia verdadeira, eles se distanciam mais do atacante. Para vencer, o atacante teria que resolver os quebra-cabeças mais rápido que todos os outros jogadores honestos juntos.
Suponha que:
- A rede honesta tem 80% do poder computacional (ou seja, resolve 8 de cada 10 quebra-cabeças).
- O atacante tem 20% do poder computacional (ou seja, resolve 2 de cada 10 quebra-cabeças).
Cada vez que a rede honesta adiciona um bloco, o atacante tem que "correr atrás" e resolver mais quebra-cabeças para alcançar.
Por Que o Ataque Fica Cada Vez Mais Improvável?
Vamos usar uma fórmula simples para mostrar como as chances de sucesso do atacante diminuem conforme ele precisa "alcançar" mais blocos:
P = (q/p)^z
- q é o poder computacional do atacante (20%, ou 0,2).
- p é o poder computacional da rede honesta (80%, ou 0,8).
- z é a diferença de blocos entre a cadeia honesta e a cadeia do atacante.
Se o atacante está 5 blocos atrás (z = 5):
P = (0,2 / 0,8)^5 = (0,25)^5 = 0,00098, (ou, 0,098%)
Isso significa que o atacante tem menos de 0,1% de chance de sucesso — ou seja, é muito improvável.
Se ele estiver 10 blocos atrás (z = 10):
P = (0,2 / 0,8)^10 = (0,25)^10 = 0,000000095, (ou, 0,0000095%).
Neste caso, as chances de sucesso são praticamente nulas.
Um Exemplo Simples
Se você jogar uma moeda, a chance de cair “cara” é de 50%. Mas se precisar de 10 caras seguidas, sua chance já é bem menor. Se precisar de 20 caras seguidas, é quase impossível.
No caso do Bitcoin, o atacante precisa de muito mais do que 20 caras seguidas. Ele precisa resolver quebra-cabeças extremamente difíceis e alcançar os jogadores honestos que estão sempre à frente. Isso faz com que o ataque seja inviável na prática.
Por Que Tudo Isso é Seguro?
- A probabilidade de sucesso do atacante diminui exponencialmente. Isso significa que, quanto mais tempo passa, menor é a chance de ele conseguir enganar o sistema.
- A cadeia verdadeira (honesta) está protegida pela força da rede. Cada novo bloco que os jogadores honestos adicionam à cadeia torna mais difícil para o atacante alcançar.
E Se o Atacante Tentar Continuar?
O atacante poderia continuar tentando indefinidamente, mas ele estaria gastando muito tempo e energia sem conseguir nada. Enquanto isso, os jogadores honestos estão sempre adicionando novos blocos, tornando o trabalho do atacante ainda mais inútil.
Assim, o sistema garante que a cadeia verdadeira seja extremamente segura e que ataques sejam, na prática, impossíveis de ter sucesso.
12. Conclusão
Propusemos um sistema de transações eletrônicas que elimina a necessidade de confiança, baseando-se em assinaturas digitais e em uma rede peer-to-peer que utiliza prova de trabalho. Isso resolve o problema do gasto duplo, criando um histórico público de transações imutável, desde que a maioria do poder computacional permaneça sob controle dos participantes honestos. A rede funciona de forma simples e descentralizada, com nós independentes que não precisam de identificação ou coordenação direta. Eles entram e saem livremente, aceitando a cadeia de prova de trabalho como registro do que ocorreu durante sua ausência. As decisões são tomadas por meio do poder de CPU, validando blocos legítimos, estendendo a cadeia e rejeitando os inválidos. Com este mecanismo de consenso, todas as regras e incentivos necessários para o funcionamento seguro e eficiente do sistema são garantidos.
Faça o download do whitepaper original em português: https://bitcoin.org/files/bitcoin-paper/bitcoin_pt_br.pdf
-
 @ f9cf4e94:96abc355
2025-01-18 06:09:50
@ f9cf4e94:96abc355
2025-01-18 06:09:50Para esse exemplo iremos usar: | Nome | Imagem | Descrição | | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | | Raspberry PI B+ |
 | Cortex-A53 (ARMv8) 64-bit a 1.4GHz e 1 GB de SDRAM LPDDR2, |
| Pen drive |
| Cortex-A53 (ARMv8) 64-bit a 1.4GHz e 1 GB de SDRAM LPDDR2, |
| Pen drive |  | 16Gb |
| 16Gb |Recomendo que use o Ubuntu Server para essa instalação. Você pode baixar o Ubuntu para Raspberry Pi aqui. O passo a passo para a instalação do Ubuntu no Raspberry Pi está disponível aqui. Não instale um desktop (como xubuntu, lubuntu, xfce, etc.).
Passo 1: Atualizar o Sistema 🖥️
Primeiro, atualize seu sistema e instale o Tor:
bash apt update apt install tor
Passo 2: Criar o Arquivo de Serviço
nrs.service🔧Crie o arquivo de serviço que vai gerenciar o servidor Nostr. Você pode fazer isso com o seguinte conteúdo:
```unit [Unit] Description=Nostr Relay Server Service After=network.target
[Service] Type=simple WorkingDirectory=/opt/nrs ExecStart=/opt/nrs/nrs-arm64 Restart=on-failure
[Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target ```
Passo 3: Baixar o Binário do Nostr 🚀
Baixe o binário mais recente do Nostr aqui no GitHub.
Passo 4: Criar as Pastas Necessárias 📂
Agora, crie as pastas para o aplicativo e o pendrive:
bash mkdir -p /opt/nrs /mnt/edriver
Passo 5: Listar os Dispositivos Conectados 🔌
Para saber qual dispositivo você vai usar, liste todos os dispositivos conectados:
bash lsblk
Passo 6: Formatando o Pendrive 💾
Escolha o pendrive correto (por exemplo,
/dev/sda) e formate-o:bash mkfs.vfat /dev/sda
Passo 7: Montar o Pendrive 💻
Monte o pendrive na pasta
/mnt/edriver:bash mount /dev/sda /mnt/edriver
Passo 8: Verificar UUID dos Dispositivos 📋
Para garantir que o sistema monte o pendrive automaticamente, liste os UUID dos dispositivos conectados:
bash blkid
Passo 9: Alterar o
fstabpara Montar o Pendrive Automáticamente 📝Abra o arquivo
/etc/fstabe adicione uma linha para o pendrive, com o UUID que você obteve no passo anterior. A linha deve ficar assim:fstab UUID=9c9008f8-f852 /mnt/edriver vfat defaults 0 0
Passo 10: Copiar o Binário para a Pasta Correta 📥
Agora, copie o binário baixado para a pasta
/opt/nrs:bash cp nrs-arm64 /opt/nrs
Passo 11: Criar o Arquivo de Configuração 🛠️
Crie o arquivo de configuração com o seguinte conteúdo e salve-o em
/opt/nrs/config.yaml:yaml app_env: production info: name: Nostr Relay Server description: Nostr Relay Server pub_key: "" contact: "" url: http://localhost:3334 icon: https://external-content.duckduckgo.com/iu/?u= https://public.bnbstatic.com/image/cms/crawler/COINCU_NEWS/image-495-1024x569.png base_path: /mnt/edriver negentropy: true
Passo 12: Copiar o Serviço para o Diretório de Systemd ⚙️
Agora, copie o arquivo
nrs.servicepara o diretório/etc/systemd/system/:bash cp nrs.service /etc/systemd/system/Recarregue os serviços e inicie o serviço
nrs:bash systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable --now nrs.service
Passo 13: Configurar o Tor 🌐
Abra o arquivo de configuração do Tor
/var/lib/tor/torrce adicione a seguinte linha:torrc HiddenServiceDir /var/lib/tor/nostr_server/ HiddenServicePort 80 127.0.0.1:3334
Passo 14: Habilitar e Iniciar o Tor 🧅
Agora, ative e inicie o serviço Tor:
bash systemctl enable --now tor.serviceO Tor irá gerar um endereço
.onionpara o seu servidor Nostr. Você pode encontrá-lo no arquivo/var/lib/tor/nostr_server/hostname.
Observações ⚠️
- Com essa configuração, os dados serão salvos no pendrive, enquanto o binário ficará no cartão SD do Raspberry Pi.
- O endereço
.oniondo seu servidor Nostr será algo como:ws://y3t5t5wgwjif<exemplo>h42zy7ih6iwbyd.onion.
Agora, seu servidor Nostr deve estar configurado e funcionando com Tor! 🥳
Se este artigo e as informações aqui contidas forem úteis para você, convidamos a considerar uma doação ao autor como forma de reconhecimento e incentivo à produção de novos conteúdos.
-
 @ 6389be64:ef439d32
2025-01-16 15:44:06
@ 6389be64:ef439d32
2025-01-16 15:44:06Black Locust can grow up to 170 ft tall
Grows 3-4 ft. per year
Native to North America
Cold hardy in zones 3 to 8

Firewood
- BLT wood, on a pound for pound basis is roughly half that of Anthracite Coal
- Since its growth is fast, firewood can be plentiful
Timber

- Rot resistant due to a naturally produced robinin in the wood
- 100 year life span in full soil contact! (better than cedar performance)
- Fence posts
- Outdoor furniture
- Outdoor decking
- Sustainable due to its fast growth and spread
- Can be coppiced (cut to the ground)
- Can be pollarded (cut above ground)
- Its dense wood makes durable tool handles, boxes (tool), and furniture
- The wood is tougher than hickory, which is tougher than hard maple, which is tougher than oak.
- A very low rate of expansion and contraction
- Hardwood flooring
- The highest tensile beam strength of any American tree
- The wood is beautiful
Legume
- Nitrogen fixer
- Fixes the same amount of nitrogen per acre as is needed for 200-bushel/acre corn
- Black walnuts inter-planted with locust as “nurse” trees were shown to rapidly increase their growth [[Clark, Paul M., and Robert D. Williams. (1978) Black walnut growth increased when interplanted with nitrogen-fixing shrubs and trees. Proceedings of the Indiana Academy of Science, vol. 88, pp. 88-91.]]
Bees

- The edible flower clusters are also a top food source for honey bees
Shade Provider

- Its light, airy overstory provides dappled shade
- Planted on the west side of a garden it provides relief during the hottest part of the day
- (nitrogen provider)
- Planted on the west side of a house, its quick growth soon shades that side from the sun
Wind-break

- Fast growth plus it's feathery foliage reduces wind for animals, crops, and shelters
Fodder
- Over 20% crude protein
- 4.1 kcal/g of energy
- Baertsche, S.R, M.T. Yokoyama, and J.W. Hanover (1986) Short rotation, hardwood tree biomass as potential ruminant feed-chemical composition, nylon bag ruminal degradation and ensilement of selected species. J. Animal Sci. 63 2028-2043
-
 @ 3f770d65:7a745b24
2025-01-12 21:03:36
@ 3f770d65:7a745b24
2025-01-12 21:03:36I’ve been using Notedeck for several months, starting with its extremely early and experimental alpha versions, all the way to its current, more stable alpha releases. The journey has been fascinating, as I’ve had the privilege of watching it evolve from a concept into a functional and promising tool.
In its earliest stages, Notedeck was raw—offering glimpses of its potential but still far from practical for daily use. Even then, the vision behind it was clear: a platform designed to redefine how we interact with Nostr by offering flexibility and power for all users.
I'm very bullish on Notedeck. Why? Because Will Casarin is making it! Duh! 😂
Seriously though, if we’re reimagining the web and rebuilding portions of the Internet, it’s important to recognize the potential of Notedeck. If Nostr is reimagining the web, then Notedeck is reimagining the Nostr client.
Notedeck isn’t just another Nostr app—it’s more a Nostr browser that functions more like an operating system with micro-apps. How cool is that?
Much like how Google's Chrome evolved from being a web browser with a task manager into ChromeOS, a full blown operating system, Notedeck aims to transform how we interact with the Nostr. It goes beyond individual apps, offering a foundation for a fully integrated ecosystem built around Nostr.
As a Nostr evangelist, I love to scream INTEROPERABILITY and tout every application's integrations. Well, Notedeck has the potential to be one of the best platforms to showcase these integrations in entirely new and exciting ways.
Do you want an Olas feed of images? Add the media column.
Do you want a feed of live video events? Add the zap.stream column.
Do you want Nostr Nests or audio chats? Add that column to your Notedeck.
Git? Email? Books? Chat and DMs? It's all possible.
Not everyone wants a super app though, and that’s okay. As with most things in the Nostr ecosystem, flexibility is key. Notedeck gives users the freedom to choose how they engage with it—whether it’s simply following hashtags or managing straightforward feeds. You'll be able to tailor Notedeck to fit your needs, using it as extensively or minimally as you prefer.
Notedeck is designed with a local-first approach, utilizing Nostr content stored directly on your device via the local nostrdb. This will enable a plethora of advanced tools such as search and filtering, the creation of custom feeds, and the ability to develop personalized algorithms across multiple Notedeck micro-applications—all with unparalleled flexibility.
Notedeck also supports multicast. Let's geek out for a second. Multicast is a method of communication where data is sent from one source to multiple destinations simultaneously, but only to devices that wish to receive the data. Unlike broadcast, which sends data to all devices on a network, multicast targets specific receivers, reducing network traffic. This is commonly used for efficient data distribution in scenarios like streaming, conferencing, or large-scale data synchronization between devices.
In a local first world where each device holds local copies of your nostr nodes, and each device transparently syncs with each other on the local network, each node becomes a backup. Your data becomes antifragile automatically. When a node goes down it can resync and recover from other nodes. Even if not all nodes have a complete collection, negentropy can pull down only what is needed from each device. All this can be done without internet.
-Will Casarin
In the context of Notedeck, multicast would allow multiple devices to sync their Nostr nodes with each other over a local network without needing an internet connection. Wild.
Notedeck aims to offer full customization too, including the ability to design and share custom skins, much like Winamp. Users will also be able to create personalized columns and, in the future, share their setups with others. This opens the door for power users to craft tailored Nostr experiences, leveraging their expertise in the protocol and applications. By sharing these configurations as "Starter Decks," they can simplify onboarding and showcase the best of Nostr’s ecosystem.
Nostr’s “Other Stuff” can often be difficult to discover, use, or understand. Many users doesn't understand or know how to use web browser extensions to login to applications. Let's not even get started with nsecbunkers. Notedeck will address this challenge by providing a native experience that brings these lesser-known applications, tools, and content into a user-friendly and accessible interface, making exploration seamless. However, that doesn't mean Notedeck should disregard power users that want to use nsecbunkers though - hint hint.
For anyone interested in watching Nostr be developed live, right before your very eyes, Notedeck’s progress serves as a reminder of what’s possible when innovation meets dedication. The current alpha is already demonstrating its ability to handle complex use cases, and I’m excited to see how it continues to grow as it moves toward a full release later this year.
-
 @ 0d97beae:c5274a14
2025-01-11 16:52:08
@ 0d97beae:c5274a14
2025-01-11 16:52:08This article hopes to complement the article by Lyn Alden on YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jk_HWmmwiAs
The reason why we have broken money
Before the invention of key technologies such as the printing press and electronic communications, even such as those as early as morse code transmitters, gold had won the competition for best medium of money around the world.
In fact, it was not just gold by itself that became money, rulers and world leaders developed coins in order to help the economy grow. Gold nuggets were not as easy to transact with as coins with specific imprints and denominated sizes.
However, these modern technologies created massive efficiencies that allowed us to communicate and perform services more efficiently and much faster, yet the medium of money could not benefit from these advancements. Gold was heavy, slow and expensive to move globally, even though requesting and performing services globally did not have this limitation anymore.
Banks took initiative and created derivatives of gold: paper and electronic money; these new currencies allowed the economy to continue to grow and evolve, but it was not without its dark side. Today, no currency is denominated in gold at all, money is backed by nothing and its inherent value, the paper it is printed on, is worthless too.
Banks and governments eventually transitioned from a money derivative to a system of debt that could be co-opted and controlled for political and personal reasons. Our money today is broken and is the cause of more expensive, poorer quality goods in the economy, a larger and ever growing wealth gap, and many of the follow-on problems that have come with it.
Bitcoin overcomes the "transfer of hard money" problem
Just like gold coins were created by man, Bitcoin too is a technology created by man. Bitcoin, however is a much more profound invention, possibly more of a discovery than an invention in fact. Bitcoin has proven to be unbreakable, incorruptible and has upheld its ability to keep its units scarce, inalienable and counterfeit proof through the nature of its own design.
Since Bitcoin is a digital technology, it can be transferred across international borders almost as quickly as information itself. It therefore severely reduces the need for a derivative to be used to represent money to facilitate digital trade. This means that as the currency we use today continues to fare poorly for many people, bitcoin will continue to stand out as hard money, that just so happens to work as well, functionally, along side it.
Bitcoin will also always be available to anyone who wishes to earn it directly; even China is unable to restrict its citizens from accessing it. The dollar has traditionally become the currency for people who discover that their local currency is unsustainable. Even when the dollar has become illegal to use, it is simply used privately and unofficially. However, because bitcoin does not require you to trade it at a bank in order to use it across borders and across the web, Bitcoin will continue to be a viable escape hatch until we one day hit some critical mass where the world has simply adopted Bitcoin globally and everyone else must adopt it to survive.
Bitcoin has not yet proven that it can support the world at scale. However it can only be tested through real adoption, and just as gold coins were developed to help gold scale, tools will be developed to help overcome problems as they arise; ideally without the need for another derivative, but if necessary, hopefully with one that is more neutral and less corruptible than the derivatives used to represent gold.
Bitcoin blurs the line between commodity and technology
Bitcoin is a technology, it is a tool that requires human involvement to function, however it surprisingly does not allow for any concentration of power. Anyone can help to facilitate Bitcoin's operations, but no one can take control of its behaviour, its reach, or its prioritisation, as it operates autonomously based on a pre-determined, neutral set of rules.
At the same time, its built-in incentive mechanism ensures that people do not have to operate bitcoin out of the good of their heart. Even though the system cannot be co-opted holistically, It will not stop operating while there are people motivated to trade their time and resources to keep it running and earn from others' transaction fees. Although it requires humans to operate it, it remains both neutral and sustainable.
Never before have we developed or discovered a technology that could not be co-opted and used by one person or faction against another. Due to this nature, Bitcoin's units are often described as a commodity; they cannot be usurped or virtually cloned, and they cannot be affected by political biases.
The dangers of derivatives
A derivative is something created, designed or developed to represent another thing in order to solve a particular complication or problem. For example, paper and electronic money was once a derivative of gold.
In the case of Bitcoin, if you cannot link your units of bitcoin to an "address" that you personally hold a cryptographically secure key to, then you very likely have a derivative of bitcoin, not bitcoin itself. If you buy bitcoin on an online exchange and do not withdraw the bitcoin to a wallet that you control, then you legally own an electronic derivative of bitcoin.
Bitcoin is a new technology. It will have a learning curve and it will take time for humanity to learn how to comprehend, authenticate and take control of bitcoin collectively. Having said that, many people all over the world are already using and relying on Bitcoin natively. For many, it will require for people to find the need or a desire for a neutral money like bitcoin, and to have been burned by derivatives of it, before they start to understand the difference between the two. Eventually, it will become an essential part of what we regard as common sense.
Learn for yourself
If you wish to learn more about how to handle bitcoin and avoid derivatives, you can start by searching online for tutorials about "Bitcoin self custody".
There are many options available, some more practical for you, and some more practical for others. Don't spend too much time trying to find the perfect solution; practice and learn. You may make mistakes along the way, so be careful not to experiment with large amounts of your bitcoin as you explore new ideas and technologies along the way. This is similar to learning anything, like riding a bicycle; you are sure to fall a few times, scuff the frame, so don't buy a high performance racing bike while you're still learning to balance.
-
 @ 37fe9853:bcd1b039
2025-01-11 15:04:40
@ 37fe9853:bcd1b039
2025-01-11 15:04:40yoyoaa
-
 @ 62033ff8:e4471203
2025-01-11 15:00:24
@ 62033ff8:e4471203
2025-01-11 15:00:24收录的内容中 kind=1的部分,实话说 质量不高。 所以我增加了kind=30023 长文的article,但是更新的太少,多个relays 的服务器也没有多少长文。
所有搜索nostr如果需要产生价值,需要有高质量的文章和新闻。 而且现在有很多机器人的文章充满着浪费空间的作用,其他作用都用不上。
https://www.duozhutuan.com 目前放的是给搜索引擎提供搜索的原材料。没有做UI给人类浏览。所以看上去是粗糙的。 我并没有打算去做一个发microblog的 web客户端,那类的客户端太多了。
我觉得nostr社区需要解决的还是应用。如果仅仅是microblog 感觉有点够呛
幸运的是npub.pro 建站这样的,我觉得有点意思。
yakihonne 智能widget 也有意思
我做的TaskQ5 我自己在用了。分布式的任务系统,也挺好的。
-
 @ 23b0e2f8:d8af76fc
2025-01-08 18:17:52
@ 23b0e2f8:d8af76fc
2025-01-08 18:17:52Necessário
- Um Android que você não use mais (a câmera deve estar funcionando).
- Um cartão microSD (opcional, usado apenas uma vez).
- Um dispositivo para acompanhar seus fundos (provavelmente você já tem um).
Algumas coisas que você precisa saber
- O dispositivo servirá como um assinador. Qualquer movimentação só será efetuada após ser assinada por ele.
- O cartão microSD será usado para transferir o APK do Electrum e garantir que o aparelho não terá contato com outras fontes de dados externas após sua formatação. Contudo, é possível usar um cabo USB para o mesmo propósito.
- A ideia é deixar sua chave privada em um dispositivo offline, que ficará desligado em 99% do tempo. Você poderá acompanhar seus fundos em outro dispositivo conectado à internet, como seu celular ou computador pessoal.
O tutorial será dividido em dois módulos:
- Módulo 1 - Criando uma carteira fria/assinador.
- Módulo 2 - Configurando um dispositivo para visualizar seus fundos e assinando transações com o assinador.
No final, teremos:
- Uma carteira fria que também servirá como assinador.
- Um dispositivo para acompanhar os fundos da carteira.

Módulo 1 - Criando uma carteira fria/assinador
-
Baixe o APK do Electrum na aba de downloads em https://electrum.org/. Fique à vontade para verificar as assinaturas do software, garantindo sua autenticidade.
-
Formate o cartão microSD e coloque o APK do Electrum nele. Caso não tenha um cartão microSD, pule este passo.

- Retire os chips e acessórios do aparelho que será usado como assinador, formate-o e aguarde a inicialização.

- Durante a inicialização, pule a etapa de conexão ao Wi-Fi e rejeite todas as solicitações de conexão. Após isso, você pode desinstalar aplicativos desnecessários, pois precisará apenas do Electrum. Certifique-se de que Wi-Fi, Bluetooth e dados móveis estejam desligados. Você também pode ativar o modo avião.\ (Curiosidade: algumas pessoas optam por abrir o aparelho e danificar a antena do Wi-Fi/Bluetooth, impossibilitando essas funcionalidades.)

- Insira o cartão microSD com o APK do Electrum no dispositivo e instale-o. Será necessário permitir instalações de fontes não oficiais.
- No Electrum, crie uma carteira padrão e gere suas palavras-chave (seed). Anote-as em um local seguro. Caso algo aconteça com seu assinador, essas palavras permitirão o acesso aos seus fundos novamente. (Aqui entra seu método pessoal de backup.)

Módulo 2 - Configurando um dispositivo para visualizar seus fundos e assinando transações com o assinador.
-
Criar uma carteira somente leitura em outro dispositivo, como seu celular ou computador pessoal, é uma etapa bastante simples. Para este tutorial, usaremos outro smartphone Android com Electrum. Instale o Electrum a partir da aba de downloads em https://electrum.org/ ou da própria Play Store. (ATENÇÃO: O Electrum não existe oficialmente para iPhone. Desconfie se encontrar algum.)
-
Após instalar o Electrum, crie uma carteira padrão, mas desta vez escolha a opção Usar uma chave mestra.

- Agora, no assinador que criamos no primeiro módulo, exporte sua chave pública: vá em Carteira > Detalhes da carteira > Compartilhar chave mestra pública.

-
Escaneie o QR gerado da chave pública com o dispositivo de consulta. Assim, ele poderá acompanhar seus fundos, mas sem permissão para movimentá-los.
-
Para receber fundos, envie Bitcoin para um dos endereços gerados pela sua carteira: Carteira > Addresses/Coins.
-
Para movimentar fundos, crie uma transação no dispositivo de consulta. Como ele não possui a chave privada, será necessário assiná-la com o dispositivo assinador.

- No assinador, escaneie a transação não assinada, confirme os detalhes, assine e compartilhe. Será gerado outro QR, desta vez com a transação já assinada.

- No dispositivo de consulta, escaneie o QR da transação assinada e transmita-a para a rede.
Conclusão
Pontos positivos do setup:
- Simplicidade: Basta um dispositivo Android antigo.
- Flexibilidade: Funciona como uma ótima carteira fria, ideal para holders.
Pontos negativos do setup:
- Padronização: Não utiliza seeds no padrão BIP-39, você sempre precisará usar o electrum.
- Interface: A aparência do Electrum pode parecer antiquada para alguns usuários.
Nesse ponto, temos uma carteira fria que também serve para assinar transações. O fluxo de assinar uma transação se torna: Gerar uma transação não assinada > Escanear o QR da transação não assinada > Conferir e assinar essa transação com o assinador > Gerar QR da transação assinada > Escanear a transação assinada com qualquer outro dispositivo que possa transmiti-la para a rede.
Como alguns devem saber, uma transação assinada de Bitcoin é praticamente impossível de ser fraudada. Em um cenário catastrófico, você pode mesmo que sem internet, repassar essa transação assinada para alguém que tenha acesso à rede por qualquer meio de comunicação. Mesmo que não queiramos que isso aconteça um dia, esse setup acaba por tornar essa prática possível.
-
 @ 7ecd3fe6:6b52f30d
2025-01-07 19:13:58
@ 7ecd3fe6:6b52f30d
2025-01-07 19:13:58I normally try to avoid the noise that is the crypto market only because I've been in that situationship before back in 2016, got rugged in the ICO phase and learned my lesson. There is nothing left for me to take from crypto apart from watching from the sidelines and enjoying the endless amount of schadenfreude it produces.
So every so often I find myself checking in on the ugly step-child of Bitcoin just to see what the left side of the bell curve are up to and you know what?
I wasn't disappointed.
In fact, I'm kind of impressed at the number of times shitcoiners can come up with a new meta to get the degens excited enough to take another spin at the casino, it's honestly pretty impressive.
After ordinals were cooked, the shitcoiners were left to head back to the drawing board, and the obvious pivot was AI tokens. AI and LLMs were the new hotness and try they did but AI tokens didn't really take off in 2024.
Sure there's tokens like NEAR, Internet Computer, and RENDER all with a few billion in market cap and according to CoinGecko there's around 50 billion in AI shitcoins, but for these coins to pump they need to provide some sort of product.
That requires investment and some thinking and who has time for that?
F AI, AI Agents are the future
Wtf are AI agent tokens you ask? Bad question, but I'll edify you anyway.
AI agents are autonomous software programs designed to perform very specific tasks and make decisions independently. Hardly very AI and more repetitive loops, cronjobs if you will.
Using an AI agent and giving a blockchain wallet these agents can interact with smart contracts, dApps and DEXs and start to get up to some shenanigans, or at least distance the agent creator from the actions.
No, I didn't rug pull you, that was the AI Agent malfunctioning.
I guess the killer app for AI agents is plausible deniability when you have to plead your case with the SEC.
As this new batch of vapourware gains popularity, every moron with a ChatGPT pro subscription and a dream is going after this market of suckers. Right now there are several AI agent tokens you can speculate on with a combined market cap of $16 billion according to CoinGecko

It's all about the meta-baby
I'm old enough to remember when the idea for a shitcoin was
- Utility, it had to do something and wall it off, so you needed to token to access a feature, that failed
- Then we went into culture and community, its all about the memes, that failed
- Then it was all about etching in on Bitcoin block space, using that rare commodity made my shitcoin valuable, that failed
Now we've got a bit of a mish-mash of memes + AI utility equals new grift.
To illustrate the unserious nature of this nonsense, AI agents, associated meme coins, and the protocols used to create these agents are among the top five best-performing crypto assets of the day, according to CoinGecko.
For example, Truth Terminal—the agent that started much of this wave—has promoted Goatseus Maximus (GOAT) and Fartcoin (FARTCOIN) causing both to skyrocket.
Fartcoin surged to a new all-time high price of $1.3 and a market cap of $1.5 billion as a result, FML, what a complete waste.

Growth in the FART coin Market Cap
ChatGPT-wrapped crypto scams
The Truth Terminal chatbot is a customized version of Anthropic's Claude 3 LLM, that tweets out random nonsense and somehow shitcoiners take this text as gospel and try to bet on tokens it shills or creates tokens based on its tweets as if it were Elon himself.
Can't wait for Elon to pump your bags, well, let's all dogpile on the random brain farts of a chatbot.
Again this just seems like a way to obscure insider trading and pump and dump influencer scams by hiding the human element behind a bot.
In fact, shitcoiners are creating tokens or sending tokens to a known wallet tied to this AI agent, hoping it uses this data to formulate it's next round of bullshit, I mean bullish tweets.
AI in name only
Still, most agent autonomy is limited. Truth Terminal, for example, still has creator Andy Ayrey looking over it's shoulder before it's thoughts and decisions go out to the public.
So if there's someone watching it, there's someone with access to the wallet and master access to prod it in a certain direction no?
Sigh! Reading up on this all just made my brain hurt and not in a good way.
“Do you want to be right or do you want to make money”
— ZachXBT (@zachxbt) January 6, 2025
99% of it is a scam and the AI agent wrapper grifts are probably worse than other past trends tbh.
bc at least meme coins promise nothing whereas AI coins try to larp as much as possible to appear legit to unsuspecting…This AI agent field itself is still relatively nascent and doesn't seem to provide any value other than being a filter for random tweet generation, and we all know computers aren't good with being random.
Most if not all projects promising AI-powered solutions will not deliver on their promises, potentially leading to significant losses for investors.
But that's the game they choose to play.
The cryptocurrency market is primarily driven by hype and speculation, and AI agent tokens are no exception. Many projects are overvalued based on potential rather than actual achievements.
Is this the future?

-
 @ 207ad2a0:e7cca7b0
2025-01-07 03:46:04
@ 207ad2a0:e7cca7b0
2025-01-07 03:46:04Quick context: I wanted to check out Nostr's longform posts and this blog post seemed like a good one to try and mirror. It's originally from my free to read/share attempt to write a novel, but this post here is completely standalone - just describing how I used AI image generation to make a small piece of the work.
Hold on, put your pitchforks down - outside of using Grammerly & Emacs for grammatical corrections - not a single character was generated or modified by computers; a non-insignificant portion of my first draft originating on pen & paper. No AI is ~~weird and crazy~~ imaginative enough to write like I do. The only successful AI contribution you'll find is a single image, the map, which I heavily edited. This post will go over how I generated and modified an image using AI, which I believe brought some value to the work, and cover a few quick thoughts about AI towards the end.
Let's be clear, I can't draw, but I wanted a map which I believed would improve the story I was working on. After getting abysmal results by prompting AI with text only I decided to use "Diffuse the Rest," a Stable Diffusion tool that allows you to provide a reference image + description to fine tune what you're looking for. I gave it this Microsoft Paint looking drawing:

and after a number of outputs, selected this one to work on:

The image is way better than the one I provided, but had I used it as is, I still feel it would have decreased the quality of my work instead of increasing it. After firing up Gimp I cropped out the top and bottom, expanded the ocean and separated the landmasses, then copied the top right corner of the large landmass to replace the bottom left that got cut off. Now we've got something that looks like concept art: not horrible, and gets the basic idea across, but it's still due for a lot more detail.

The next thing I did was add some texture to make it look more map like. I duplicated the layer in Gimp and applied the "Cartoon" filter to both for some texture. The top layer had a much lower effect strength to give it a more textured look, while the lower layer had a higher effect strength that looked a lot like mountains or other terrain features. Creating a layer mask allowed me to brush over spots to display the lower layer in certain areas, giving it some much needed features.

At this point I'd made it to where I felt it may improve the work instead of detracting from it - at least after labels and borders were added, but the colors seemed artificial and out of place. Luckily, however, this is when PhotoFunia could step in and apply a sketch effect to the image.

At this point I was pretty happy with how it was looking, it was close to what I envisioned and looked very visually appealing while still being a good way to portray information. All that was left was to make the white background transparent, add some minor details, and add the labels and borders. Below is the exact image I wound up using:

Overall, I'm very satisfied with how it turned out, and if you're working on a creative project, I'd recommend attempting something like this. It's not a central part of the work, but it improved the chapter a fair bit, and was doable despite lacking the talent and not intending to allocate a budget to my making of a free to read and share story.
The AI Generated Elephant in the Room
If you've read my non-fiction writing before, you'll know that I think AI will find its place around the skill floor as opposed to the skill ceiling. As you saw with my input, I have absolutely zero drawing talent, but with some elbow grease and an existing creative direction before and after generating an image I was able to get something well above what I could have otherwise accomplished. Outside of the lowest common denominators like stock photos for the sole purpose of a link preview being eye catching, however, I doubt AI will be wholesale replacing most creative works anytime soon. I can assure you that I tried numerous times to describe the map without providing a reference image, and if I used one of those outputs (or even just the unedited output after providing the reference image) it would have decreased the quality of my work instead of improving it.
I'm going to go out on a limb and expect that AI image, text, and video is all going to find its place in slop & generic content (such as AI generated slop replacing article spinners and stock photos respectively) and otherwise be used in a supporting role for various creative endeavors. For people working on projects like I'm working on (e.g. intended budget $0) it's helpful to have an AI capable of doing legwork - enabling projects to exist or be improved in ways they otherwise wouldn't have. I'm also guessing it'll find its way into more professional settings for grunt work - think a picture frame or fake TV show that would exist in the background of an animated project - likely a detail most people probably wouldn't notice, but that would save the creators time and money and/or allow them to focus more on the essential aspects of said work. Beyond that, as I've predicted before: I expect plenty of emails will be generated from a short list of bullet points, only to be summarized by the recipient's AI back into bullet points.
I will also make a prediction counter to what seems mainstream: AI is about to peak for a while. The start of AI image generation was with Google's DeepDream in 2015 - image recognition software that could be run in reverse to "recognize" patterns where there were none, effectively generating an image from digital noise or an unrelated image. While I'm not an expert by any means, I don't think we're too far off from that a decade later, just using very fine tuned tools that develop more coherent images. I guess that we're close to maxing out how efficiently we're able to generate images and video in that manner, and the hard caps on how much creative direction we can have when using AI - as well as the limits to how long we can keep it coherent (e.g. long videos or a chronologically consistent set of images) - will prevent AI from progressing too far beyond what it is currently unless/until another breakthrough occurs.
-
 @ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2025-01-05 14:29:17
@ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2025-01-05 14:29:17The Rise of Graph RAGs and the Quest for Data Quality
As we enter a new year, it’s impossible to ignore the boom of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, particularly those leveraging graph-based approaches. The previous year saw a surge in advancements and discussions about Graph RAGs, driven by their potential to enhance large language models (LLMs), reduce hallucinations, and deliver more reliable outputs. Let’s dive into the trends, challenges, and strategies for making the most of Graph RAGs in artificial intelligence.
Booming Interest in Graph RAGs
Graph RAGs have dominated the conversation in AI circles. With new research papers and innovations emerging weekly, it’s clear that this approach is reshaping the landscape. These systems, especially those developed by tech giants like Microsoft, demonstrate how graphs can:
- Enhance LLM Outputs: By grounding responses in structured knowledge, graphs significantly reduce hallucinations.
- Support Complex Queries: Graphs excel at managing linked and connected data, making them ideal for intricate problem-solving.
Conferences on linked and connected data have increasingly focused on Graph RAGs, underscoring their central role in modern AI systems. However, the excitement around this technology has brought critical questions to the forefront: How do we ensure the quality of the graphs we’re building, and are they genuinely aligned with our needs?
Data Quality: The Foundation of Effective Graphs
A high-quality graph is the backbone of any successful RAG system. Constructing these graphs from unstructured data requires attention to detail and rigorous processes. Here’s why:
- Richness of Entities: Effective retrieval depends on graphs populated with rich, detailed entities.
- Freedom from Hallucinations: Poorly constructed graphs amplify inaccuracies rather than mitigating them.
Without robust data quality, even the most sophisticated Graph RAGs become ineffective. As a result, the focus must shift to refining the graph construction process. Improving data strategy and ensuring meticulous data preparation is essential to unlock the full potential of Graph RAGs.
Hybrid Graph RAGs and Variations
While standard Graph RAGs are already transformative, hybrid models offer additional flexibility and power. Hybrid RAGs combine structured graph data with other retrieval mechanisms, creating systems that:
- Handle diverse data sources with ease.
- Offer improved adaptability to complex queries.
Exploring these variations can open new avenues for AI systems, particularly in domains requiring structured and unstructured data processing.
Ontology: The Key to Graph Construction Quality
Ontology — defining how concepts relate within a knowledge domain — is critical for building effective graphs. While this might sound abstract, it’s a well-established field blending philosophy, engineering, and art. Ontology engineering provides the framework for:
- Defining Relationships: Clarifying how concepts connect within a domain.
- Validating Graph Structures: Ensuring constructed graphs are logically sound and align with domain-specific realities.
Traditionally, ontologists — experts in this discipline — have been integral to large enterprises and research teams. However, not every team has access to dedicated ontologists, leading to a significant challenge: How can teams without such expertise ensure the quality of their graphs?
How to Build Ontology Expertise in a Startup Team
For startups and smaller teams, developing ontology expertise may seem daunting, but it is achievable with the right approach:
- Assign a Knowledge Champion: Identify a team member with a strong analytical mindset and give them time and resources to learn ontology engineering.
- Provide Training: Invest in courses, workshops, or certifications in knowledge graph and ontology creation.
- Leverage Partnerships: Collaborate with academic institutions, domain experts, or consultants to build initial frameworks.
- Utilize Tools: Introduce ontology development tools like Protégé, OWL, or SHACL to simplify the creation and validation process.
- Iterate with Feedback: Continuously refine ontologies through collaboration with domain experts and iterative testing.
So, it is not always affordable for a startup to have a dedicated oncologist or knowledge engineer in a team, but you could involve consulters or build barefoot experts.
You could read about barefoot experts in my article :
Even startups can achieve robust and domain-specific ontology frameworks by fostering in-house expertise.
How to Find or Create Ontologies
For teams venturing into Graph RAGs, several strategies can help address the ontology gap:
-
Leverage Existing Ontologies: Many industries and domains already have open ontologies. For instance:
-
Public Knowledge Graphs: Resources like Wikipedia’s graph offer a wealth of structured knowledge.
- Industry Standards: Enterprises such as Siemens have invested in creating and sharing ontologies specific to their fields.
-
Business Framework Ontology (BFO): A valuable resource for enterprises looking to define business processes and structures.
-
Build In-House Expertise: If budgets allow, consider hiring knowledge engineers or providing team members with the resources and time to develop expertise in ontology creation.
-
Utilize LLMs for Ontology Construction: Interestingly, LLMs themselves can act as a starting point for ontology development:
-
Prompt-Based Extraction: LLMs can generate draft ontologies by leveraging their extensive training on graph data.
- Domain Expert Refinement: Combine LLM-generated structures with insights from domain experts to create tailored ontologies.
Parallel Ontology and Graph Extraction
An emerging approach involves extracting ontologies and graphs in parallel. While this can streamline the process, it presents challenges such as:
- Detecting Hallucinations: Differentiating between genuine insights and AI-generated inaccuracies.
- Ensuring Completeness: Ensuring no critical concepts are overlooked during extraction.
Teams must carefully validate outputs to ensure reliability and accuracy when employing this parallel method.
LLMs as Ontologists
While traditionally dependent on human expertise, ontology creation is increasingly supported by LLMs. These models, trained on vast amounts of data, possess inherent knowledge of many open ontologies and taxonomies. Teams can use LLMs to:
- Generate Skeleton Ontologies: Prompt LLMs with domain-specific information to draft initial ontology structures.
- Validate and Refine Ontologies: Collaborate with domain experts to refine these drafts, ensuring accuracy and relevance.
However, for validation and graph construction, formal tools such as OWL, SHACL, and RDF should be prioritized over LLMs to minimize hallucinations and ensure robust outcomes.
Final Thoughts: Unlocking the Power of Graph RAGs
The rise of Graph RAGs underscores a simple but crucial correlation: improving graph construction and data quality directly enhances retrieval systems. To truly harness this power, teams must invest in understanding ontologies, building quality graphs, and leveraging both human expertise and advanced AI tools.
As we move forward, the interplay between Graph RAGs and ontology engineering will continue to shape the future of AI. Whether through adopting existing frameworks or exploring innovative uses of LLMs, the path to success lies in a deep commitment to data quality and domain understanding.
Have you explored these technologies in your work? Share your experiences and insights — and stay tuned for more discussions on ontology extraction and its role in AI advancements. Cheers to a year of innovation!
-
 @ a4a6b584:1e05b95b
2025-01-02 18:13:31
@ a4a6b584:1e05b95b
2025-01-02 18:13:31The Four-Layer Framework
Layer 1: Zoom Out

Start by looking at the big picture. What’s the subject about, and why does it matter? Focus on the overarching ideas and how they fit together. Think of this as the 30,000-foot view—it’s about understanding the "why" and "how" before diving into the "what."
Example: If you’re learning programming, start by understanding that it’s about giving logical instructions to computers to solve problems.
- Tip: Keep it simple. Summarize the subject in one or two sentences and avoid getting bogged down in specifics at this stage.
Once you have the big picture in mind, it’s time to start breaking it down.
Layer 2: Categorize and Connect

Now it’s time to break the subject into categories—like creating branches on a tree. This helps your brain organize information logically and see connections between ideas.
Example: Studying biology? Group concepts into categories like cells, genetics, and ecosystems.
- Tip: Use headings or labels to group similar ideas. Jot these down in a list or simple diagram to keep track.
With your categories in place, you’re ready to dive into the details that bring them to life.
Layer 3: Master the Details

Once you’ve mapped out the main categories, you’re ready to dive deeper. This is where you learn the nuts and bolts—like formulas, specific techniques, or key terminology. These details make the subject practical and actionable.
Example: In programming, this might mean learning the syntax for loops, conditionals, or functions in your chosen language.
- Tip: Focus on details that clarify the categories from Layer 2. Skip anything that doesn’t add to your understanding.
Now that you’ve mastered the essentials, you can expand your knowledge to include extra material.
Layer 4: Expand Your Horizons

Finally, move on to the extra material—less critical facts, trivia, or edge cases. While these aren’t essential to mastering the subject, they can be useful in specialized discussions or exams.
Example: Learn about rare programming quirks or historical trivia about a language’s development.
- Tip: Spend minimal time here unless it’s necessary for your goals. It’s okay to skim if you’re short on time.
Pro Tips for Better Learning
1. Use Active Recall and Spaced Repetition
Test yourself without looking at notes. Review what you’ve learned at increasing intervals—like after a day, a week, and a month. This strengthens memory by forcing your brain to actively retrieve information.
2. Map It Out
Create visual aids like diagrams or concept maps to clarify relationships between ideas. These are particularly helpful for organizing categories in Layer 2.
3. Teach What You Learn
Explain the subject to someone else as if they’re hearing it for the first time. Teaching exposes any gaps in your understanding and helps reinforce the material.
4. Engage with LLMs and Discuss Concepts
Take advantage of tools like ChatGPT or similar large language models to explore your topic in greater depth. Use these tools to:
- Ask specific questions to clarify confusing points.
- Engage in discussions to simulate real-world applications of the subject.
- Generate examples or analogies that deepen your understanding.Tip: Use LLMs as a study partner, but don’t rely solely on them. Combine these insights with your own critical thinking to develop a well-rounded perspective.
Get Started
Ready to try the Four-Layer Method? Take 15 minutes today to map out the big picture of a topic you’re curious about—what’s it all about, and why does it matter? By building your understanding step by step, you’ll master the subject with less stress and more confidence.
-
 @ b17fccdf:b7211155
2024-12-29 12:04:31
@ b17fccdf:b7211155
2024-12-29 12:04:31🆕 What's changed:
- New bonus guide dedicated to install/upgrade/uninstall PostgreSQL
- Modified the LND guide to use PostgreSQL instead of bbolt
- Modified the Nostr relay guide to use PostgreSQL instead of SQLite (experimental)
- Modified the BTCPay Server bonus guide according to these changes
- Used the lndinit MiniBolt org fork, to add an extra section to migrate an existing LND bbolt database to PostgreSQL (🚨⚠️Experimental - use it behind your responsibility⚠️🚨)
- New Golang bonus guide as a common language for the lndinit compile
- Updated LND to v0.18
- New Bitcoin Core extra section to renovate Tor & I2P addresses
- New Bitcoin Core extra section to generate a full
bitcoin.conffile - Rebuilt some homepage sections and general structure
- Deleted the
$symbol of the commands to easy copy-paste to the terminal - Deleted the initial incoming and the outgoing rules configuration of UFW, due to it being by default
🪧 PD: If you want to use the old database backend of the LND or Nostr relay, follow the next extra sections:
- Use the default bbolt database backend for the LND
- Use the default SQLite database backend for the Nostr relay
⚠️Attention⚠️: The migration process was tested on testnet mode from an existing bbolt database backend to a new PostgreSQL database using lndinit and the results were successful. However, It wasn't tested on mainnet, according to the developer, it is in experimental status which could damage your existing LND database.🚨 Use it behind your responsibility 🧼
🔧 PR related: https://github.com/minibolt-guide/minibolt/pull/93
♻️ Migrate the PostgreSQL database location
If you installed NBXplorer + BTCPay Server, it is probably you have the database of the PostgreSQL cluster on the default path (
/var/lib/postgresql/16/main/), follow the next instructions to migrate it to the new dedicated location on/data/postgresdbfolder:- With user
admincreate the dedicated PostgreSQL data folder
sudo mkdir /data/postgresdb- Assign as the owner to the
postgresuser
sudo chown postgres:postgres /data/postgresdb- Assign permissions of the data folder only to the
postgresuser
sudo chmod -R 700 /data/postgresdb- Stop NBXplorer and BTCPay Server
sudo systemctl stop nbxplorer && sudo systemctl stop btcpayserver- Stop PostgreSQL
sudo systemctl stop postgresql- Use the rsync command to copy all files from the existing database on (
/var/lib/postgresql/16/main) to the new destination directory (/data/postgresdb)
sudo rsync -av /var/lib/postgresql/16/main/ /data/postgresdb/Expected output:
``` sending incremental file list ./ PG_VERSION postgresql.auto.conf postmaster.opts postmaster.pid base/ base/1/ base/1/112 base/1/113 base/1/1247 base/1/1247_fsm base/1/1247_vm base/1/1249 base/1/1249_fsm base/1/1249_vm [...] pg_wal/000000010000000000000009 pg_wal/archive_status/ pg_xact/ pg_xact/0000
sent 164,483,875 bytes received 42,341 bytes 36,561,381.33 bytes/sec total size is 164,311,368 speedup is 1.00 ```
- Edit the PostgreSQL data directory on configuration, to redirect the store to the new location
sudo nano /etc/postgresql/16/main/postgresql.conf --linenumbers- Replace the line 42 to this. Save and exit
data_directory = '/data/postgresdb'- Start PostgreSQL to apply changes and monitor the correct status of the main instance and sub-instance monitoring sessions before
sudo systemctl start postgresql- You can monitor the PostgreSQL main instance by the systemd journal and check the log output to ensure all is correct. You can exit the monitoring at any time with Ctrl-C
journalctl -fu postgresqlExample of the expected output:
Nov 08 11:51:10 minibolt systemd[1]: Stopped PostgreSQL RDBMS. Nov 08 11:51:10 minibolt systemd[1]: Stopping PostgreSQL RDBMS... Nov 08 11:51:13 minibolt systemd[1]: Starting PostgreSQL RDBMS... Nov 08 11:51:13 minibolt systemd[1]: Finished PostgreSQL RDBMS.- You can monitor the PostgreSQL sub-instance by the systemd journal and check log output to ensure all is correct. You can exit monitoring at any time with Ctrl-C
journalctl -fu postgresql@16-mainExample of the expected output:
Nov 08 11:51:10 minibolt systemd[1]: Stopping PostgreSQL Cluster 16-main... Nov 08 11:51:11 minibolt systemd[1]: postgresql@16-main.service: Succeeded. Nov 08 11:51:11 minibolt systemd[1]: Stopped PostgreSQL Cluster 16-main. Nov 08 11:51:11 minibolt systemd[1]: postgresql@16-main.service: Consumed 1h 10min 8.677s CPU time. Nov 08 11:51:11 minibolt systemd[1]: Starting PostgreSQL Cluster 16-main... Nov 08 11:51:13 minibolt systemd[1]: Started PostgreSQL Cluster 16-main.- Start NBXplorer and BTCPay Server again
sudo systemctl start nbxplorer && sudo systemctl start btcpayserver- Monitor to make sure everything is as you left it. You can exit monitoring at any time with Ctrl-C
journalctl -fu nbxplorerjournalctl -fu btcpayserverEnjoy it MiniBolter! 💙
-
 @ fd208ee8:0fd927c1
2024-12-26 07:02:59
@ fd208ee8:0fd927c1
2024-12-26 07:02:59I just read this, and found it enlightening.
Jung... notes that intelligence can be seen as problem solving at an everyday level..., whereas creativity may represent problem solving for less common issues
Other studies have used metaphor creation as a creativity measure instead of divergent thinking and a spectrum of CHC components instead of just g and have found much higher relationships between creativity and intelligence than past studies
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-3200/3/3/59
I'm unusually intelligent (Who isn't?), but I'm much more creative, than intelligent, and I think that confuses people. The ability to apply intelligence, to solve completely novel problems, on the fly, is something IQ tests don't even claim to measure. They just claim a correlation.
Creativity requires taking wild, mental leaps out into nothingness; simply trusting that your brain will land you safely. And this is why I've been at the forefront of massive innovation, over and over, but never got rich off of it.
I'm a starving autist.
Zaps are the first time I've ever made money directly, for solving novel problems. Companies don't do this because there is a span of time between providing a solution and the solution being implemented, and the person building the implementation (or their boss) receives all the credit for the existence of the solution. At best, you can hope to get pawned off with a small bonus.
Nobody can remember who came up with the solution, originally, and that person might not even be there, anymore, and probably never filed a patent, and may have no idea that their idea has even been built. They just run across it, later, in a tech magazine or museum, and say, "Well, will you look at that! Someone actually went and built it! Isn't that nice!"
Universities at least had the idea of cementing novel solutions in academic papers, but that: 1) only works if you're an academic, and at a university, 2) is an incredibly slow process, not appropriate for a truly innovative field, 3) leads to manifestations of perverse incentives and biased research frameworks, coming from 'publish or perish' policies.
But I think long-form notes and zaps solve for this problem. #Alexandria, especially, is being built to cater to this long-suffering class of chronic underachievers. It leaves a written, public, time-stamped record of Clever Ideas We Have Had.
Because they are clever, the ideas. And we have had them.
-
 @ 16d11430:61640947
2024-12-23 16:47:01
@ 16d11430:61640947
2024-12-23 16:47:01At the intersection of philosophy, theology, physics, biology, and finance lies a terrifying truth: the fiat monetary system, in its current form, is not just an economic framework but a silent, relentless force actively working against humanity's survival. It isn't simply a failed financial model—it is a systemic engine of destruction, both externally and within the very core of our biological existence.
The Philosophical Void of Fiat
Philosophy has long questioned the nature of value and the meaning of human existence. From Socrates to Kant, thinkers have pondered the pursuit of truth, beauty, and virtue. But in the modern age, the fiat system has hijacked this discourse. The notion of "value" in a fiat world is no longer rooted in human potential or natural resources—it is abstracted, manipulated, and controlled by central authorities with the sole purpose of perpetuating their own power. The currency is not a reflection of society’s labor or resources; it is a representation of faith in an authority that, more often than not, breaks that faith with reckless monetary policies and hidden inflation.
The fiat system has created a kind of ontological nihilism, where the idea of true value, rooted in work, creativity, and family, is replaced with speculative gambling and short-term gains. This betrayal of human purpose at the systemic level feeds into a philosophical despair: the relentless devaluation of effort, the erosion of trust, and the abandonment of shared human values. In this nihilistic economy, purpose and meaning become increasingly difficult to find, leaving millions to question the very foundation of their existence.
Theological Implications: Fiat and the Collapse of the Sacred
Religious traditions have long linked moral integrity with the stewardship of resources and the preservation of life. Fiat currency, however, corrupts these foundational beliefs. In the theological narrative of creation, humans are given dominion over the Earth, tasked with nurturing and protecting it for future generations. But the fiat system promotes the exact opposite: it commodifies everything—land, labor, and life—treating them as mere transactions on a ledger.
This disrespect for creation is an affront to the divine. In many theologies, creation is meant to be sustained, a delicate balance that mirrors the harmony of the divine order. Fiat systems—by continuously printing money and driving inflation—treat nature and humanity as expendable resources to be exploited for short-term gains, leading to environmental degradation and societal collapse. The creation narrative, in which humans are called to be stewards, is inverted. The fiat system, through its unholy alliance with unrestrained growth and unsustainable debt, is destroying the very creation it should protect.
Furthermore, the fiat system drives idolatry of power and wealth. The central banks and corporations that control the money supply have become modern-day gods, their decrees shaping the lives of billions, while the masses are enslaved by debt and inflation. This form of worship isn't overt, but it is profound. It leads to a world where people place their faith not in God or their families, but in the abstract promises of institutions that serve their own interests.
Physics and the Infinite Growth Paradox
Physics teaches us that the universe is finite—resources, energy, and space are all limited. Yet, the fiat system operates under the delusion of infinite growth. Central banks print money without concern for natural limits, encouraging an economy that assumes unending expansion. This is not only an economic fallacy; it is a physical impossibility.
In thermodynamics, the Second Law states that entropy (disorder) increases over time in any closed system. The fiat system operates as if the Earth were an infinite resource pool, perpetually able to expand without consequence. The real world, however, does not bend to these abstract concepts of infinite growth. Resources are finite, ecosystems are fragile, and human capacity is limited. Fiat currency, by promoting unsustainable consumption and growth, accelerates the depletion of resources and the degradation of natural systems that support life itself.
Even the financial “growth” driven by fiat policies leads to unsustainable bubbles—inflated stock markets, real estate, and speculative assets that burst and leave ruin in their wake. These crashes aren’t just economic—they have profound biological consequences. The cycles of boom and bust undermine communities, erode social stability, and increase anxiety and depression, all of which affect human health at a biological level.
Biology: The Fiat System and the Destruction of Human Health
Biologically, the fiat system is a cancerous growth on human society. The constant chase for growth and the devaluation of work leads to chronic stress, which is one of the leading causes of disease in modern society. The strain of living in a system that values speculation over well-being results in a biological feedback loop: rising anxiety, poor mental health, physical diseases like cardiovascular disorders, and a shortening of lifespans.
Moreover, the focus on profit and short-term returns creates a biological disconnect between humans and the planet. The fiat system fuels industries that destroy ecosystems, increase pollution, and deplete resources at unsustainable rates. These actions are not just environmentally harmful; they directly harm human biology. The degradation of the environment—whether through toxic chemicals, pollution, or resource extraction—has profound biological effects on human health, causing respiratory diseases, cancers, and neurological disorders.
The biological cost of the fiat system is not a distant theory; it is being paid every day by millions in the form of increased health risks, diseases linked to stress, and the growing burden of mental health disorders. The constant uncertainty of an inflation-driven economy exacerbates these conditions, creating a society of individuals whose bodies and minds are under constant strain. We are witnessing a systemic biological unraveling, one in which the very act of living is increasingly fraught with pain, instability, and the looming threat of collapse.
Finance as the Final Illusion
At the core of the fiat system is a fundamental illusion—that financial growth can occur without any real connection to tangible value. The abstraction of currency, the manipulation of interest rates, and the constant creation of new money hide the underlying truth: the system is built on nothing but faith. When that faith falters, the entire system collapses.
This illusion has become so deeply embedded that it now defines the human experience. Work no longer connects to production or creation—it is reduced to a transaction on a spreadsheet, a means to acquire more fiat currency in a world where value is ephemeral and increasingly disconnected from human reality.
As we pursue ever-expanding wealth, the fundamental truths of biology—interdependence, sustainability, and balance—are ignored. The fiat system’s abstract financial models serve to disconnect us from the basic realities of life: that we are part of an interconnected world where every action has a reaction, where resources are finite, and where human health, both mental and physical, depends on the stability of our environment and our social systems.
The Ultimate Extermination
In the end, the fiat system is not just an economic issue; it is a biological, philosophical, theological, and existential threat to the very survival of humanity. It is a force that devalues human effort, encourages environmental destruction, fosters inequality, and creates pain at the core of the human biological condition. It is an economic framework that leads not to prosperity, but to extermination—not just of species, but of the very essence of human well-being.
To continue on this path is to accept the slow death of our species, one based not on natural forces, but on our own choice to worship the abstract over the real, the speculative over the tangible. The fiat system isn't just a threat; it is the ultimate self-inflicted wound, a cultural and financial cancer that, if left unchecked, will destroy humanity’s chance for survival and peace.
-
 @ 79008e78:dfac9395
2024-12-22 02:49:28
@ 79008e78:dfac9395
2024-12-22 02:49:28บทที่ 2: ภาพรวมการทำงานของบิตคอยน์
บิตคอยน์ทำงานอย่างไร
ระบบอย่างบิตคอยน์นั้นแตกต่างกับระบบธนาคารและระบบการชำระเงินแบบดั้งเดิมอย่างสิ้นเชิง เพราะมันสามารถทำงานได้โดยไม่จำเป็นต้องไว้วางใจบุคคลที่สาม แทนที่จะมีหน่วยงานกลางที่เชื่อถือได้ บิตคอยน์ได้อณุญาตให้ผู้ใช้แต่ละคนใช้ซอฟต์แวร์บนคอมพิวเตอร์ของตนเองเพื่อตรวจสอบการทำงานที่ถูกต้องของทุกส่วนในระบบ ซึ่งในบทนี้เอง เราจะทำการสำรวจบิตคอยน์ภาพรวมโดยติดตามธุรกรรมหนึ่งรายการผ่านระบบของบิตคอยน์ ดูว่าธุรกรรมนั้นถูกบันทึกลงในบล็อกเชนอย่างไร และการบันทึกธุรกรรมแบบกระจายศูนย์นั้นทำได้อย่างไร ส่วนในบทถัดไปจะลงลึกถึงเทคโนโลยีที่อยู่เบื้องหลังธุรกรรม เครือข่าย และการขุด
ภาพรวมของบิตคอยน์
ระบบของบิตคอยน์นั้นประกอบไปด้วย เหล่าผู้ใช้งาน wallet ต่าง ๆ , ธุรกรรมที่กระจายไปทั่วเครือข่าย และเหล่านักขุดที่จะคอยแข่งขันกันเพื่อสร้างบล๊อกใหม่ โดยที่มีบล๊อกเชนเป็นเหมือนสมุดบันทึกธุรกรรมที่รวมธุรกรรมทั้งหมดไว้ ตัวอย่างที่จะได้เห็นต่อไปนี้เป็นธุรกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นจริงบนเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์ โดยจำลองการโต้ตอบระหว่างผู้ใช้หลายคนผ่านการส่งเงินจาก wallet หนึ่งไปยังอีก wallet และในขณะนั้นเราจะติดตามธุรกรรมผ่านเครือข่ายบิตคอยน์ ไปจนถึงบล็อกเชน เราจะใช้เว็บไซต์สำรวจบล็อกเชน (blockchain explorer) เพื่อดูภาพรวมในแต่ละขั้นตอน โดยมีเว็บไซต์สำรวจบล็อกเชนที่นิยม ดังนี้
- Blockstream Explorer
- Mempool.Space
- BlockCypher Explorer
เว็บไซต์เหล่านี้มีฟังก์ชันการค้นหาที่สามารถใช้ค้นหา Bitcoin address, Transaction Hash, หมายเลขบล็อก หรือ Block hash และเรียกดูข้อมูลที่เกี่ยวข้องจากเครือข่ายบิตคอยน์ได้ สำหรับแต่ละตัวอย่างธุรกรรมหรือบล็อก เราจะให้ URL เพื่อให้คุณสามารถค้นหาและศึกษาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ด้วยตัวเอง
คำเตือนเกี่ยวกับความเป็นส่วนตัวของการใช้ Block Explorer
การค้นหาข้อมูลใน block explorer อาจเปิดเผยให้ผู้ให้บริการทราบว่าคุณสนใจข้อมูลนั้น ซึ่งอาจเชื่อมโยงกับที่อยู่ IP ของคุณ รายละเอียดของเบราว์เซอร์ การค้นหาที่ผ่านมา หรือข้อมูลที่สามารถระบุตัวตนได้อื่น ๆ หากคุณค้นหาธุรกรรมจากหนังสือเล่มนี้ ผู้ให้บริการอาจคาดเดาได้ว่าคุณกำลังศึกษาเกี่ยวกับบิตคอยน์ ซึ่งไม่น่าจะมีปัญหาอะไร แต่หากคุณค้นหาธุรกรรมของตนเอง ผู้ให้บริการอาจสามารถคาดเดาได้ว่าคุณได้รับ ใช้จ่าย และมีบิตคอยน์อยู่เท่าใดในปัจจุบัน
การซื้อของจากร้านค้าออนไลน์
อลิซเป็นผู้ใช้งานใหม่ ที่พึ่งได้รับบิตคอยน์เป็นครั้งแรกจากคำแนะนำของโจเมื่อบทที่แล้ว โดยเธอได้ซื้อบิตคอยน์จากโจเก็บไว้ และตั้งแต่นั้นมาอลิซก็ซื้อบิตคอยน์เพิ่มเรื่อย ๆ และตอนนี้อลิซต้องการทำธุรกรรมด้วยบิตคอยน์ครั้งแรกของเธอ โดยการใช้จ่ายมันเพื่อแลกกับสิทธิ์เข้าถึงพอดแคสต์ตอนพิเศษจากร้านค้าออนไลน์ของบ๊อบ ร้านค้าออนไลน์ของบ๊อบเองก็เพิ่งมีการเพิ่มบิตคอยน์เป็นตัวเลือกในการทำธุรกรรม ราคาสินค้าในร้านของบ๊อบแสดงเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ) แต่ในหน้าชำระเงิน ลูกค้าสามารถเลือกชำระเงินเป็นดอลลาร์หรือบิตคอยน์ก็ได้
อลิซเลือกตอนพอดแคสต์ที่เธอต้องการซื้อและดำเนินการไปยังหน้าชำระเงิน ในหน้าชำระเงิน อลิซพบตัวเลือกในการชำระเงินด้วยบิตคอยน์ นอกเหนือจากตัวเลือกปกติ แต่ในตะกร้าชำระเงินจะแสดงราคาทั้งในรูปแบบดอลลาร์สหรัฐและบิตคอยน์ตามอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนในขณะนั้น หลังจากกดจ่ายด้วยบิตคอยน์ระบบของบ๊อบได้ทำการสร้างใบเรียกเก็บเงิน (invoice) ในรูปแบบของ QR-code ตามภาพด้านล่าง

ต่างจาก QR code ทั่วไปที่มีเพียง Bitcoin address ปลายทางเท่านั้น ใบแจ้งหนี้นี้เป็น QR code แบบ URI ที่ประกอบด้วย Bitcoin address จำนวนเงินชำระ และคำอธิบาย (memo) ซึ่งช่วยให้ Bitcoin wallet แอปพลิเคชันเติมข้อมูลที่ใช้ในการชำระเงินล่วงหน้าได้ และยังแสดงคำอธิบายที่อ่านเข้าใจง่ายให้กับผู้ใช้อีกด้วย คุณสามารถสแกน QR code นี้ด้วย Bitcoin wallet เพื่อดูสิ่งที่อลิซจะเห็น
QR Code ของใบแจ้งหนี้นี้เข้ารหัส URI ดังต่อไปนี้ ซึ่งถูกกำหนดไว้ใน BIP21:
bitcoin:bc1qk2g6u8p4qm2s2lh3gts5cpt2mrv5skcuu7u3e4?amount=0.01577764&label=Bob%27s%20Store&message=Purchase%20at%20Bob%27s%20Storeโดยส่วนประกอบของ URI สามารถจำแนกได้ ดังนี้
- A Bitcoin address: "bc1qk2g6u8p4qm2s2lh3gts5cpt2mrv5skcuu7u3e4"
- The payment amount (จำนวนบิตคอยน์) : "0.01577764"
- A label for the recipient address (label): "Bob's Store"
- A description for the payment (memo): "Purchase at Bob's Store"
อลิซใช้สมาร์ทโฟนของเธอสแกนบาร์โค้ดที่แสดงอยู่ หน้าจอสมาร์ทโฟนของเธอจะแสดงการชำระเงินในจำนวนที่ถูกต้องสำหรับร้านของบ๊อบ และเธอกด “Send” เพื่อยืนยันการชำระเงิน ภายในไม่กี่วินาที (เวลาประมาณเดียวกับการอนุมัติบัตรเครดิต) บ๊อบก็จะเห็นธุรกรรมดังกล่าวปรากฏบนเครื่องรับชำระเงินของเขา
เครือข่ายบิตคอยน์สามารถทำธุรกรรมในมูลค่าเศษส่วนได้ เช่น มิลลิบิทคอยน์ (1/1,000 ของบิทคอยน์) ไปจนถึง 1/100,000,000 ของบิทคอยน์ ซึ่งเรียกว่า "ซาโตชิ" ในหนังสือเล่มนี้ใช้กฎการพหูพจน์เดียวกันกับดอลลาร์หรือสกุลเงินแบบดั้งเดิมเมื่อพูดถึงจำนวนที่มากกว่าหนึ่งบิทคอยน์ เช่น "10 บิตคอยน์" หรือ "0.001 บิตคอยน์" กฎเดียวกันนี้ยังนำไปใช้กับหน่วยบัญชีบิทคอยน์อื่น ๆ เช่น มิลลิบิทคอยน์และซาโตชิอีกด้วย
ธุรกรรมในระบบบิตคอยน์
ธุรกรรมในระบบบิตคอยน์คือการแจ้งเครือข่ายว่าเจ้าของบิทคอยน์ได้อนุมัติการโอนมูลค่าไปยังเจ้าของใหม่แล้ว และ เจ้าของใหม่สามารถใช้บิทคอยน์เหล่านั้นได้ โดยสร้างธุรกรรมใหม่เพื่อรออนุมัติการโอนไปยังเจ้าของคนอื่นต่อ ๆ ไป ทำให้เกิดการส่งต่อความเป็นเจ้าของอย่างต่อเนื่อง
ธุรกรรมขาเข้าและขาออกของบิตคอยน์
ธุรกรรมเปรียบเสมือนบันทึกในสมุดบัญชีแบบสองทาง โดยธุรกรรมแต่ละรายการจะมีอินพุต (inputs) หนึ่งรายการหรือมากกว่านั้นที่ใช้จ่ายเงิน และมีเอาต์พุต (outputs) หนึ่งรายการหรือมากกว่าที่รับเงิน มูลค่าของอินพุตและเอาต์พุตไม่จำเป็นต้องเท่ากันเสมอไป เอาต์พุตมักจะมีมูลค่าน้อยกว่าอินพุตเล็กน้อย ซึ่งส่วนต่างนี้คือ "ค่าธรรมเนียมธุรกรรม" ที่นักขุดจะได้รับเมื่อรวมธุรกรรมในบล็อกเชน
ธุรกรรมยังมีหลักฐานการเป็นเจ้าของสำหรับจำนวนบิตคอยน์ (อินพุต) ที่ถูกใช้ในรูปของลายเซ็นดิจิทัลจากเจ้าของเดิม ซึ่งสามารถตรวจสอบความถูกต้องได้ ในระบบบิตคอยน์การใช้จ่ายบิตคอยน์คือการลงนามในธุรกรรมเพื่อโอนมูลค่าจากธุรกรรมก่อนหน้าไปยังเจ้าของใหม่ที่ระบุผ่าน Bitcoin adress

ห่วงโซ่ของธุรกรรม
การชำระเงินของอลิซไปยังร้านของบ็อบนั้นเป็นใช้เอาต์พุตจากธุรกรรมก่อนหน้าเป็นอินพุตในธุรกรรมครั้งนี้ (ในบทก่อนหน้า อลิซได้รับบิทคอยน์จากโจเพื่อนของเธอ ) เราเรียกธุรกรรมนี้ว่า "ธุรกรรมที่ 1 (Tx1)" ซึ่งแสดงถึงห่วงโซ่ของธุรกรรมที่เอาต์พุตของธุรกรรมหนึ่งถูกใช้เป็นอินพุตในธุรกรรมถัดไป
การอ้างอิงอินพุตจากเอาต์พุตก่อนหน้า
Tx1 โอน 0.001 บิทคอยน์ (100,000 ซาโตชิ) ไปยังเอาต์พุตที่ล็อกด้วยกุญแจของอลิซ และในธุรกรรมใหม่ของอลิซ (Tx2) ที่ส่งให้ร้านของบ็อบ เธออ้างถึงเอาต์พุตก่อนหน้าเป็นอินพุต อย่างที่เห็นในภาพประกอบ การอ้างอิงด้วยลูกศรและระบุอินพุตว่า "Tx1:0" ในธุรกรรมจริง การอ้างอิงจะใช้รหัสประจำธุรกรรม (txid) เป็นตัวระบุขนาด 32 ไบต์ที่แสดงถึงธุรกรรมที่อลิซได้รับเงินจากโจ ส่วน ":0" หมายถึงตำแหน่งของเอาต์พุตที่อลิซได้รับเงิน ซึ่งในกรณีนี้คือตำแหน่งแรก (ตำแหน่ง 0)
การคำนวณมูลค่าอินพุต
เนื่องจากธุรกรรมของบิตคอยน์นั้นไม่ได้ระบุค่าของอินพุตอย่างชัดเจน ตัวซอฟต์แวร์เลยจะต้องใช้การอ้างอิงของอินพุตเพื่อค้นหาเอาต์พุตของธุรกรรมก่อนหน้าที่ถูกใช้ไป
เอาต์พุตใน Tx2 ของอลิซ
Tx2 ของอลิซมีเอาต์พุตใหม่สองรายการ รายการหนึ่งจ่าย 75,000 ซาโตชิสำหรับพอดแคสต์ และอีกรายการจ่าย 20,000 ซาโตชิคืนให้อลิซเป็นเงินทอน

เกร็ดสาระเล็ก ๆ น้อย ๆ
- ธุรกรรมของบิตคอยน์นั้นอยู่ในรูปแบบซีเรียลไลซ์ (serialized) เป็นรูปแบบข้อมูลที่ซอฟต์แวร์ใช้สำหรับการส่งธุรกรรม โดยจะเข้ารหัสมูลค่าที่ต้องการโอนด้วยตัวเลขจำนวนเต็มซึ่งเป็นหน่วยมูลค่าที่เล็กที่สุดในระบบ on-chain
- ที่มาของชื่อ "ซาโตชิ" :เมื่อบิตคอยน์ถูกสร้างขึ้นในครั้งแรก หน่วยมูลค่านี้ยังไม่มีชื่อเรียก นักพัฒนาบางคนจึงเรียกมันว่า "หน่วยฐาน" (base unit) แต่ต่อมาผู้ใช้งานหลาย ๆ คนเริ่มเรียกหน่วยนี้ว่า "ซาโตชิ" (satoshi หรือ sat) เพื่อเป็นเกียรติแก่ผู้สร้างบิตคอยน์
การทอนเงิน
นอกเหนือจากการสร้างเอาต์พุตเพื่อจ่ายให้กับผู้รับบิตคอยน์แล้ว ธุรกรรมจำนวนมากยังมีเอาต์พุตที่จ่ายเงินคืนให้กับผู้จ่าย ซึ่งเรียกว่า เอาต์พุตทอนเงิน (change output) เนื่องจากอินพุตของธุรกรรม (คล้ายกับธนบัตร) ไม่สามารถแบ่งใช้บางส่วนได้ เช่น ถ้าคุณซื้อของราคา 5 ดอลลาร์และจ่ายด้วยธนบัตร 20 ดอลลาร์ คุณคาดหวังว่าจะได้เงินทอน 15 ดอลลาร์ ในทำนองเดียวกัน ในธุรกรรม Bitcoin หากคุณซื้อสินค้าราคา 5 บิตคอยน์แต่มีอินพุตมูลค่า 20 บิตคอยน์ คุณจะสร้างเอาต์พุต 5 บิตคอยน์ไปยังเจ้าของร้าน และอีกเอาต์พุต 15 บิตคอยน์คืนให้ตัวคุณเองเป็นเงินทอน (ไม่นับรวมค่าธรรมเนียมธุรกรรม)
- หากมองผ่านมุมของโปรโตคอลบิตคอยน์นั้นไม่ได้มีความแตกต่างใด ๆ ระหว่างเอาต์พุตเงินทอนกับเอาต์พุตการจ่ายเงินปกติ
- โดยทั่วไปแล้วเอาต์พุตเงินทอนจะเป็นการโอนไปจ่ายให้กับ Bitcoin Address อันใหม่ในกระเป๋าตัวเองดังรูปที่แสดงข้างล่าง

การสร้างธุรกรรม
แอปพิเคชั่นกระเป๋าเงินของอลิซจะทำการสร้างอินพุตและสร้างเอาต์พุตตามที่ Alice ต้องการ โดยที่เธอเพียงแค่กรอกปลายทาง จำนวนเงิน และค่าธรรมเนียมธุรกรรมกระเป๋าเงินจะทำงานที่เหลือให้โดยอัตโนมัติ นอกจากนี้ กระเป๋าเงินยังสามารถสร้างธุรกรรมแบบออฟไลน์ได้ คล้ายกับการเขียนเช็คที่บ้านแล้วค่อยนำไปฝากธนาคารในภายหลังอีกด้วย
การเลือกอินพุตที่เหมาะสม
กระเป๋าเงินจะเลือกอินพุตที่มีมูลค่าเพียงพอสำหรับการชำระเงินไปยังบ๊อบโดยตรวจสอบเอาต์พุตที่ยังไม่ได้ใช้ (UTXOs) ซึ่งหากมูลค่าไม่เพียงพอ กระเป๋าเงินก็จะทำการรวม UTXOs หลาย ๆ รายการเข้าด้วยกัน เพื่อให้ได้ยอดที่ต้องการ และหากอินพุตมีมูลค่าสูงกว่าค่าที่ต้องจ่าย กระเป๋าเงินจะสร้างเอาต์พุตสำหรับทอนเงินกลับมาให้อลิซ
การสร้างเอาต์พุต
เอาต์พุตประกอบด้วยสคริปต์ที่กำหนดให้ผู้ที่มีคีย์ของบ๊อบเท่านั้นสามารถลงนามเพื่อที่จะใช้เงินได้ นอกจากนี้ยังมีเอาต์พุตสำหรับทอนเงินกลับมาให้อลิซ ซึ่งทำให้เธอสามารถใช้เงินทอนนั้นในการทำธุรกรรมถัดไป และค่าธรรมเนียมธุรกรรมจะถูกคำนวณจากส่วนต่างระหว่างอินพุตและเอาต์พุต และนั่นเองที่จะเป็นรางวัลสำหรับนักขุดที่บันทึกธุรกรรมลงบล็อกเชนของบิตคอยน์
การใส่ธุรกรรมลงในบล๊อกเชน
ธุรกรรมที่สร้างขึ้นโดย Bitcoin wallet ของอลิซมีข้อมูลทั้งหมดที่จำเป็นสำหรับการสร้างธุรกรรม (การยืนยันว่าอลิซเป็นเจ้าของเงิน และ Bitcoin address ปลายทาง) จากนั้นธุรกรรมนี้จะต้องถูกส่งไปยังเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์ เพื่อที่จะให้ธุรกรรมนั้นเป็นส่วนนึงในเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์ และในส่วนถัดไปของหนังสือเล่มนี้ เราจะอธิบายถึงว่าธุรกรรมกลายเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของบล็อกใหม่อย่างไร และกระบวนการขุดบล็อกเป็นอย่างไร รวมถึงการที่บล็อกใหม่ได้รับความไว้วางใจมากขึ้นเมื่อมีการเพิ่มบล็อกใหม่ ๆ เข้ามาเรื่อย ๆ หมายถึงอะไร ?
การส่งธุรกรรมเข้าไปยังเครือข่าย
เนื่องจากธุรกรรมมีข้อมูลที่จำเป็นสำหรับการประมวลผลทั้งหมด จึงทำให้การส่งผ่านสามารถทำได้จากที่ไหนหรืออย่างไรก็ได้ อย่างที่ได้กล่าวไปว่าเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์เป็นเครือข่ายแบบ peer-to-peer โดยที่แต่ละโหนดเชื่อมต่อกับโหนดอื่น ๆ อีกหลายโหนด เพื่อทำหน้าที่กระจายธุรกรรมและบล็อกให้กับผู้เข้าร่วมทั้งหมดในระบบ
การกระจายธุรกรรม
โหนดในเครือข่าย peer-to-peer ของบิตคอยน์นั้นเป็นซอฟต์แวร์ที่สามารถตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของธุรกรรมได้ และการเชื่อมต่อระหว่างโหนดสามารถแสดงเป็นเส้นในกราฟ ทำให้โหนดเหล่านี้เรียกว่า “โหนดตรวจสอบเต็มรูปแบบ” (full nodes) กระเป๋าเงินของอลิซสามารถส่งธุรกรรมไปยังโหนดบิตคอยน์ใด ๆ ผ่านการเชื่อมต่อใด ๆ ก็ได้ เช่น สายแลน WiFi หรือ เครือข่ายมือถือ โดยถ้าหากโหนดได้รับธุรกรรมที่ถูกต้องซึ่งยังไม่เคยเห็นมาก่อน มันจะกระจายธุรกรรมนี้ไปยังโหนดอื่น ๆ ที่เชื่อมต่อด้วย ซึ่งเป็นเทคนิคที่เรียกว่า gossiping ซึ่งทำให้ธุรกรรมแพร่กระจายไปทั่วเครือข่ายอย่างรวดเร็วภายในไม่กี่วินาที
การขุดบิตคอยน์
ตอนนี้ธุรกรรมของอลิซได้เข้าไปสู่ในเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์แล้ว แต่มันยังไม่ได้ถูกบรรจุลงในบล๊อกเชนเนื่องจากจะต้องรอให้นักขุดทำการนำธุรกรรมนั้น ๆ เข้าไปในบล๊อกและบล๊อกนั้นจำเป็นต้องผ่านการตรวจสอบโดยโหนดในเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์เสียก่อน จึงจะถูกบันทึกลงในบล๊อกเชน ในระบบของบิตคอยน์นั้น มีการป้องกันการปลอมแปลงด้วยการคำนวณทางคณิตศาสตร์ ซึ่งเป็นการคำนวณที่จำเป็นต้องใช้พลังงานมหาศาลในการคำนวณ แต่ใช้พลังงานเพียงเล็กน้อยในการตรวจสอบ โดยธุรกรรมทั้งหมดจะถูกจัดเรียงเป็นบล๊อกและแต่ละบล๊อกจะมีบล๊อกเฮดเดอร์ที่จำเป็นต้องสร้างตามเงื่อนไขเฉพาะ โดยกระบวนการขุดบิตคอยน์นั้นมีวัตถุประสงค์อยู่สองอย่าง ดังนี้:
- สร้างแรงจูงใจให้ขุดเฉพาะธุรกรรมที่ถูกต้องตามกฎ: เนื่องจากวิธีที่เหล่านักขุดจะได้รับผลกำไรที่สูงที่สุดจากการสร้างบล๊อกที่ตรงกับฉันทมติของระบบเท่านั้น (หากไม่ทำตามบล๊อกจะไม่ถูกยอมรับโดยโหนด และนั่นจะเป็นการสิ้นเปลืองพลังงานที่ได้คำนวณมาโดยเปล่าประโยชน์) นั้นจึงเป็นแรงจูงใจหลัก ๆ ให้เหล่านักขุดทำการใส่ธุรกรรมที่ถูกต้องตามกฏเท่านั้นลงในบล๊อกที่ตนสร้าง และสิ่งนี้เองก็ทำให้ผู้ใช้สามารถเลือกที่จะสันนิษฐานโดยอิงตามความไว้วางใจว่าธุรกรรมใด ๆ ในบล็อกนั้น ๆ เป็นธุรกรรมที่ถูกต้อง
- สร้างเหรียญใหม่ตามตารางการออกเหรียญที่กำหนดไว้ล่วงหน้า: ในปัจจุบันนั้นจะมีการสร้างบิตคอยน์ใหม่ในแต่ละบล็อก คล้ายคลึงกับธนาคารกลางที่พิมพ์เงินใหม่ โดยจำนวนบิตคอยน์ในแต่ละบล๊อกที่จะถูกผลิตขึ้นมาใหม่นั้นถูกกำหนดมาตั้งแต่วันที่ระบบของบิตคอยน์ได้เริ่มขึ้นและไม่สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงได้
การขุดได้ช่วยให้เกิดความสมดุลระหว่างต้นทุนและผลตอบแทน เนื่องจากการขุดมีการใช้ไฟฟ้าเพื่อแก้ปัญหาการคำนวณ และนักขุดที่ประสบความสำเร็จจะได้รับรางวัลในรูปแบบของบิตคอยน์ใหม่และค่าธรรมเนียมจากการทำธุรกรรม แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม รางวัลจะถูกเก็บรวบรวมก็ต่อเมื่อนักขุดรวมเฉพาะธุรกรรมที่ถูกต้องเท่านั้น โดยกฎของโปรโตคอลบิตคอยน์สำหรับการสร้างฉันทามติ จะกำหนดว่าอะไรถูกต้อง โดยความสมดุลที่ละเอียดอ่อนนี้เองที่คอยสร้างให้ความปลอดภัยแก่บิตคอยน์โดยไม่ต้องมีหน่วยงานกลางมาคอยดูแล
การขุดถูกออกแบบให้เหมือนกับการจับสลากแบบกระจายศูนย์ นักขุดแต่ละคนสามารถสร้าง "สลาก" ของตัวเองได้โดยการสร้างบล็อกตัวอย่างที่ประกอบไปด้วยธุรกรรมใหม่ที่ต้องการขุด พร้อมกับข้อมูลอื่น ๆ และนักขุดจะป้อนบล็อกตัวอย่างนี้เข้าไปในอัลกอริทึมที่ออกแบบมาเป็นพิเศษเพื่อแฮชข้อมูล ทำให้ได้ค่าผลลัพธ์ที่แตกต่างจากข้อมูลเดิมอย่างสิ้นเชิง โดยแฮชฟังก์ชันนี้จะให้ผลลัพธ์เดียวกันเสมอสำหรับข้อมูลชุดเดิม แต่ไม่สามารถคาดเดาผลลัพธ์ได้หากป้อนข้อมูลใหม่ แม้จะแตกต่างเพียงเล็กน้อยจากข้อมูลก่อนหน้า
หากค่าผลลัพธ์ของแฮชตรงกับเงื่อนไขที่กำหนดของโปรโตคอล นักขุดจะชนะการจับสลาก และผู้ใช้งานบิตคอยน์ จะยอมรับบล็อกนี้พร้อมกับธุรกรรมในนั้นว่าเป็นบล็อกที่ถูกต้อง หากไม่ตรงกับเงื่อนไข นักขุดจะปรับข้อมูลในบล็อกเล็กน้อยและลองทำการแฮชใหม่ กระบวนการนี้ต้องทำซ้ำหลายครั้ง โดย ณ ขณะที่เขียนนี้ นักขุดต้องลองสร้างบล็อกตัวอย่างประมาณ 168 พันล้านล้านครั้ง เพื่อหาคำตอบที่ถูกต้อง ซึ่งหมายถึงการรันแฮชฟังก์ชันในจำนวนครั้งมหาศาลมาก ๆ
แต่เมื่อพบคำตอบที่ถูกต้องแล้ว ใครก็ตามสามารถตรวจสอบว่าบล็อกนั้นถูกต้องได้โดยการรันแฮชฟังก์ชันเพียงครั้งเดียว ซึ่งทำให้การสร้างบล็อกที่ถูกต้องต้องใช้พลังงานคำนวณมหาศาล แต่การตรวจสอบทำได้ง่ายมาก กระบวนการตรวจสอบนี้สามารถพิสูจน์ได้อย่างมีหลักการว่ามีการทำงานเกิดขึ้นจริง ดังนั้น ข้อมูลที่ใช้สร้างหลักฐานนี้—ในที่นี้คือบล็อก—เรียกว่า "หลักฐานการทำงาน" หรือ Proof of Work (PoW)
ธุรกรรมจะถูกเพิ่มลงในบล็อกใหม่ โดยให้ความสำคัญกับธุรกรรมที่มีค่าธรรมเนียมสูงสุดก่อนและพิจารณาจากปัจจัยอื่น ๆ อีกเล็กน้อย นักขุดแต่ละคนจะเริ่มกระบวนการสร้างบล็อกตัวอย่างใหม่ทันทีหลังจากได้รับบล็อกก่อนหน้าจากเครือข่าย โดยรู้ว่ามีคนอื่นชนะรางวัลไปแล้วในรอบนั้น พวกเขาจะสร้างบล็อกตัวอย่างใหม่ที่เชื่อมโยงกับบล็อกก่อนหน้า ใส่ธุรกรรมเข้าไป และเริ่มคำนวณ Proof of Work (PoW) สำหรับบล็อกตัวอย่างนี้ นักขุดจะเพิ่มธุรกรรมพิเศษที่จ่ายรางวัลบล็อกและค่าธรรมเนียมธุรกรรมรวมเข้ากับที่อยู่บิตคอยน์ของตนเอง หากพวกเขาพบบล็อกที่ถูกต้องและถูกเพิ่มในบล็อกเชน นักขุดจะได้รับรางวัลนั้น และธุรกรรมรางวัลนี้ก็จะใช้งานได้ นักขุดที่ทำงานร่วมกับพูลจะตั้งค่าให้รางวัลถูกส่งไปยังที่อยู่ของพูล จากนั้นจะแบ่งรางวัลให้สมาชิกตามสัดส่วนการทำงานที่แต่ละคนมีส่วนร่วม
กลับมาที่ธุรกรรมของอลิซ ตอนนี้ธุรกรรมของอลิซได้ถูกเครือข่ายรับไปแล้วและเพิ่มลงในพูลของธุรกรรมที่ยังไม่ได้รับการยืนยันเรียบร้อย จากนั้นเมื่อธุรกรรมนั้นผ่านการตรวจสอบจาก full node แล้ว มันจะถูกรวมไว้ในบล็อกตัวอย่าง และประมาณห้านาทีหลังจากที่อลิซส่งธุรกรรมจากกระเป๋าเงินของเธอ นักขุดคนหนึ่งพบคำตอบสำหรับบล็อกนั้นและประกาศไปยังเครือข่าย หลังจากที่นักขุดคนอื่น ๆ ตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของบล็อกที่ชนะ พวกเขาก็เริ่มกระบวนการสุ่มอีกครั้งเพื่อสร้างบล็อกถัดไป
บล็อกที่ชนะซึ่งมีธุรกรรมของอลิซอยู่ในนั้น ได้กลายเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของบล็อกเชน และบล็อกนี้ถูกนับเป็นการยืนยันหนึ่งครั้งสำหรับธุรกรรมนั้น หลังจากที่บล็อกที่มีธุรกรรมของอลิซได้ถูกเผยแพร่ไปทั่วเครือข่าย การสร้างบล็อกทางเลือกที่มีเวอร์ชันอื่นของธุรกรรมของอลิซ (เช่น ธุรกรรมที่ไม่ได้จ่ายให้ บ๊อบ) จะต้องใช้ปริมาณงานเท่ากับที่นักขุดทั้งหมดต้องใช้ในการสร้างบล็อกใหม่ทั้งบล็อก เมื่อมีบล็อกทางเลือกหลายบล็อกให้เลือก full node ในเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์ก็จะทำการเลือกบล็อกเชนที่ถูกต้อง โดยจะเป็นเชนซึ่งมี Proof of Work (PoW) รวมมากที่สุด ซึ่งเรียกว่าบล็อกเชนที่ดีที่สุด หากเครือข่ายทั้งหมดจะยอมรับบล็อกทางเลือก จะต้องมีการขุดบล็อกใหม่เพิ่มเติมอีกหนึ่งบล็อกต่อจากบล็อกทางเลือกนั้น
นั่นหมายความว่านักขุดมีตัวเลือกอื่น อย่างเช่นการที่พวกเขาสามารถร่วมมือกับอลิซเพื่อสร้างธุรกรรมทางเลือกที่เธอไม่ได้จ่ายเงินให้บ๊อบ โดยอลิซอาจเสนอส่วนแบ่งจากเงินที่เธอเคยจ่ายให้บ๊อบแก่นักขุด แต่การกระทำที่ไม่ซื่อสัตย์นี้จะต้องใช้ความพยายามเท่ากับการสร้างบล็อกใหม่ถึงสองบล็อก ซึ่งในทางกลับกันแล้ว นักขุดที่ทำงานอย่างซื่อสัตย์สามารถสร้างบล็อกใหม่เพียงบล็อกเดียวและได้รับค่าธรรมเนียมจากธุรกรรมทั้งหมดที่รวมอยู่ในบล็อก พร้อมกับรางวัลบล็อก (block subsidy) นอกจากนี้ต้นทุนที่สูงในการสร้างบล็อกสองบล็อกเพื่อพยายามเปลี่ยนแปลงธุรกรรมที่ยืนยันแล้วสำหรับผลตอบแทนเพียงเล็กน้อยนั้นไม่คุ้มค่าและการกระทำดังกล่าวมีโอกาสน้อยที่จะเกิดขึ้น สำหรับ บ๊อบ นั่นหมายความว่าเขาสามารถเริ่มเชื่อถือได้ว่าการชำระเงินจากอลิซนั้นเป็นสิ่งที่เชื่อถือได้
ประมาณ 19 นาทีหลังจากบล็อกที่มีธุรกรรมของอลิซ ได้ถูกเผยแพร่บล็อกใหม่ถูกขุดขึ้นโดยนักขุดอีกคน และเนื่องจากบล็อกใหม่นี้ถูกสร้างต่อจากบล็อกที่มีธุรกรรมของอลิซ (ทำให้ธุรกรรมของอลิซได้รับการยืนยันสองครั้ง) ธุรกรรมของ อลิซจะสามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงได้ก็ต่อเมื่อมีการขุดบล็อกทางเลือกสองบล็อกขึ้นมา และมีบล็อกใหม่ที่สร้างต่อจากบล็อกเหล่านั้น รวมเป็นสามบล็อกที่ต้องถูกขุดเพื่อให้อลิซสามารถดึงเงินที่เธอส่งให้บ๊อบกลับมาได้ และทุกบล็อกที่ขุดต่อจากบล็อกที่มีธุรกรรมของอลิซนั้นจะนับเป็นการยืนยันเพิ่มเติม เมื่อจำนวนบล็อกที่ต่อกันเพิ่มมากขึ้น การย้อนกลับธุรกรรมก็จะยากขึ้นเรื่อย ๆ ทำให้บ๊อบมั่นใจมากขึ้นเรื่อย ๆ ว่าการชำระเงินของอลิซนั้นจะปลอดภัย
จากภาพที่แนบไว้ข้างล่างนี้ เราสามารถเห็นบล็อกที่มีธุรกรรมของอลิซและด้านล่างของบล็อกนี้มีบล็อกอีกหลายแสนบล็อกที่เชื่อมต่อกันเป็นโซ่ (blockchain) ต่อเนื่องไปจนถึงบล็อกหมายเลข #0 หรือที่เรียกว่า genesis block และเมื่อเวลาผ่านไป "ความสูง" ของบล็อกใหม่ที่เพิ่มขึ้นจะทำให้ความยากในการคำนวณของทั้งเครือข่ายเพิ่มขึ้นตามไปด้วย ตามธรรมเนียมแล้ว บล็อกใด ๆ ที่มีการยืนยันมากกว่าหกครั้งจะถือว่ายากมากที่จะเปลี่ยนแปลง เพราะต้องใช้การคำนวณอย่างมหาศาลในการคำนวณบล็อกหกบล็อกใหม่ (รวมถึงบล็อกใหม่อีกหนึ่งบล็อก)

การใช้จ่ายในธุรกรรม
เมื่อธุรกรรมของอลิซได้กลายเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของบล็อกเชน แปลว่ามันสามารถถูกเรียกดูได้จากทุกบิตคอยน์แอปพลิเคชัน และทุกโหนดสามารถที่จะตรวจสอบธุรกรรมนี้ได้อย่างอิสระ ว่าธุรกรรมนี้ถูกต้องหรือไม่ โดยจะตรวจสอบย้อนไปตั้งแต่ตอนที่เหรียญนั้น ๆ ถูกสร้างและตรวจสอบต่อมาเรื่อย ๆ จนถึงธุรกรรมปัจจุบัน ไคลเอนต์จะสามารถตรวจสอบการชำระเงินได้บางส่วน โดยการยืนยันว่าธุรกรรมนั้นอยู่ในบล็อกเชนแล้ว และมีบล็อกจำนวนมากที่ถูกขุดหลังจากนั้น ซึ่งนี่ช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ว่ามีการใช้ความพยายามอย่างมากในการยืนยันธุรกรรมนี้โดยเหล่านักขุดไปแล้ว
ในตอนนี้บ็อบสามารถใช้บิตคอยน์ที่อลิซส่งให้ต่อได้แล้ว! สมมุติว่าบ๊อบต้องการจ่ายค่าจ้างให้ผู้รับเหมาหรือผู้จัดหาสินค้า โดยการโอนมูลค่าจากการชำระเงินของอลิซสำหรับพอดแคสต์ไปยังเจ้าของรายใหม่ เมื่อบ๊อบใช้เงินที่ได้รับจากอลิซและลูกค้าคนอื่น ๆ เขาก็ขยายสายโซ่ของธุรกรรมออกไป สมมติว่าบ๊อบจ่ายค่าจ้างให้กรูฟซึ่งเป็นนักออกแบบเว็บไซต์ของเขาสำหรับสร้างหน้าเว็บใหม่ สายโซ่ของธุรกรรมจะมีลักษณะดังนี้:
- ธุรกรรมจากโจถึงอลิซ: โจโอนบิตคอยน์ให้อลิซเพื่อการซื้อขายหรือจ่ายค่าบริการบางอย่าง
- ธุรกรรมจากอลิซถึงบ๊อบ: อลิซโอนบิตคอยน์ให้บ๊อบเพื่อชำระค่าพอดแคสต์
- ธุรกรรมจากบ๊อบถึงกรูฟ: บ๊อบโอนบิตคอยน์จากที่ได้รับจากอลิซให้กรูฟเพื่อจ่ายค่าจ้างออกแบบเว็บไซต์
สายโซ่ของธุรกรรมนี้แสดงให้เห็นการเชื่อมต่อของธุรกรรมจากโจถึงอลิซและจากอลิซถึงบ๊อบต่อด้วยจากบ๊อบถึง กรูฟ โดยแต่ละธุรกรรมได้รับการบันทึกไว้ในบล็อกเชน ซึ่งช่วยให้ทุกคนสามารถตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของธุรกรรมในสายโซ่นี้ได้

ในบทนี้ เราได้เห็นวิธีที่ธุรกรรมสร้างสายโซ่ที่ถ่ายโอนมูลค่าจากเจ้าของหนึ่งไปยังอีกเจ้าของหนึ่ง นอกจากนี้เรายังได้ติดตามธุรกรรมของอลิซตั้งแต่เริ่มสร้างในกระเป๋าเงินของเธอ ผ่านเครือข่ายบิตคอยน์ไปจนถึงนักขุดที่บันทึกมันลงในบล็อกเชน และสำหรับในส่วนที่เหลือของหนังสือเล่มนี้ เราจะศึกษารายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับเทคโนโลยีที่เกี่ยวข้อง ไม่ว่าจะเป็นกระเป๋าเงิน, address, digital signature, network และกระบวนการขุดอย่างละเอียด
-
 @ f1989a96:bcaaf2c1
2024-12-19 15:16:35
@ f1989a96:bcaaf2c1
2024-12-19 15:16:35Good morning, readers!
After 53 years of tyranny, the Syrian regime has been overthrown. Rebels captured Damascus, forcing Bashar al-Assad and his family to flee to Moscow, Russia. Assad’s rule was defined by severe human rights abuses and widespread financial repression. Hundreds of thousands were jailed or killed, millions fled, and more than 90% of the country was plunged into poverty amid currency collapse. With Assad gone, Syrians may have a chance to rebuild their country and work toward a freer, more democratic future.
In Tunisia, President Kais Saied continues to dismantle civil society and due process. The regime is escalating the repression of journalists through arrests, incarceration, and judicial harassment to silence critical voices. By doing so, Saied shifts focus away from the country’s economic struggles and worsening hardships.
In technology news, Klever Wallet, a KYC-free digital asset wallet widely used in regions like Nigeria and the Philippines, integrated the Lightning Network via the Breez SDK, enabling fast, low-cost Bitcoin transactions for its significant global user base. In addition, the Bitcoin Design Foundation announced a South American Bitcoin UX Bootcamp, offering 10 skilled UX designers across South America a chance to refine their design expertise within the Bitcoin ecosystem and attend the 2025 bitcoin++ developer conference in Florianopolis, Brazil.
We end with a live stream of the 2024 Africa Bitcoin Conference, an inspiring event HRF supported and participated in. The conference brought together leaders and innovators across the African continent to advance Bitcoin for financial freedom and to push back against growing authoritarianism. If you were unable to attend in person, be sure to catch the recordings below.
Now, let’s dive right in!
Subscribe Here
GLOBAL NEWS
Syria | Assad Regime Overthrown
The Assad regime, infamous for its financial repression and brutal authoritarianism, has been overthrown following the rebel capture of Damascus, forcing Bashar al-Assad and his family to flee to Moscow. For 24 years under Assad — and 53 years of Assad family rule — the regime manipulated the economy to maintain its grip on power. Policies such as enforcing artificial currency exchange rates, restricting bank withdrawals, and imposing strict controls on the flow of goods and money plunged over 90% of Syrians into poverty. This economic stranglehold, combined with systemic human rights abuses, defined his reign. With the regime’s collapse, Syrians now face a pivotal moment to rebuild their country and pursue a future of more financial freedom.
China | Youth Bear the Brunt of Economic Slowdown
China’s slowing economy is forcing younger generations into increasingly precarious financial positions. Youth unemployment has soared past 17%, and even those who find work face stagnant wages and unmet income expectations. To survive, many young people are embracing extreme frugality — capping food expenses at just 500 yuan ($70), eating in the dark to save electricity, and avoiding dining out entirely. The middle class, weighed down by debt and a bleak economic outlook, is also adopting similar austerity measures. This growing financial strain offers a stark snapshot of China’s economic challenges and raises deep concerns about the long-term prosperity and opportunities for the nation’s youth.
Tunisia | Growing Repression of Journalists Amidst Worsening Economic Crisis
Tunisia is grappling with a worsening economic crisis, as citizens face soaring unemployment, a collapsing currency, and the devastating impacts of financial mismanagement. Amid this economic turmoil, President Kais Saied is intensifying his crackdown on dissent, imprisoning journalists in overcrowded cells, denying them medical care, and subjecting them to psychological torture — blatant evidence of the state’s disregard for human rights. Saied’s regime has also weaponized vague morality laws to target activists, influencers, and musicians, ensuring no opposition voice goes unpunished. By silencing dissent, Saied seeks to deflect attention from the regime’s economic failures, positioning the state as a moral authority while deepening the suffering of journalists and the broader public.
Pakistan | Testing Internet Firewall to Increase Financial Surveillance
Pakistan’s government is testing a nationwide Internet firewall, a tool designed to monitor, censor, and control online content by filtering internet traffic at the state level. By leveraging technology sourced from China, officials can block websites, restrict apps, and track individual online activity. This firewall poses a severe threat to financial freedom, as the military regime could use it to restrict access to tools like Bitcoin, cutting off alternative financial systems that offer privacy and independence. Civil society, including activists, journalists, and political dissidents, faces heightened surveillance, repression, and limited access to information — further curtailing their capacity to organize or express dissent.
India | Central Bank Governor Shares CBDC Vision
Outgoing Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Gov.Shaktikanta Das reaffirmed his vision for India’s central bank digital currency (CBDC), the digital rupee, as the nation’s currency continues to reach a record low against the US dollar. While hailed as the “future of currency” and praised for its potential economic benefits, the CBDC raises serious concerns. It grants the state unprecedented power to surveil transactions, freeze funds, and block payments in real-time — an alarming reality in a country already known for freezing opposition bank accounts and imposing rigid KYC requirements. Das’s hopes of a CBDC to “underpin the payment systems of the future” prioritizes state control at the expense of individual freedoms.
Georgia | Internet Shutdowns Amid Energy Crisis
In the breakaway Georgian region of Abkhazian, Russian-backed officials are using an energy crisis as a pretext to tighten Internet controls. Blaming illegal Bitcoin mining for electricity shortages, officials imposed nightly Internet shutdowns from midnight to 7:00 a.m., starting Dec. 10. These restrictions, coupled with power rationing and school closures, exacerbate hardships for residents as the region grapples with reduced energy from Russia and the Enguri hydroelectric plant. By painting Bitcoin as the villain, officials divert attention from broader governance failures while consolidating their grip over online communication and suppressing access to alternative financial tools.
LATEST IN BITCOIN NEWS, DEVELOPMENT, AND COMMUNITY
Klever Wallet | Integrates Lightning Network
Klever Wallet, a KYC-free digital asset wallet popular in underbanked countries like Nigeria, Brazil, India, and the Philippines, integrated the Lightning Network through the Breez SDK. This integration will empower its 100,000 active monthly users with fast, low-cost Bitcoin transactions directly from the wallet. By using the Breez SDK, Klever eliminates the complexities of Lightning channel management for users while maintaining a self-custodial design. This integration enhances financial freedom for its global user base — particularly in regions where traditional systems fall short.
Fedi | Adds Cashu Melting and Portable Nostr Keys
Fedi, a company leveraging Bitcoin and ecash technology to support communities, especially under authoritarian regimes, announced the integration of Cashu melting to enable users to receive Cashu ecash directly within the Fedi app. Built on the Chaumian ecash protocol, Cashu allows users to transact ecash tokens with strong privacy guarantees, minimal costs, and instant settlements, though with a custodial tradeoff. Additionally, Fedi now supports portable Nostr keys, allowing users to interact with external Nostr clients like Primal and Amethyst. Together, these updates enhance financial privacy and accessibility, offering users more control over their transactions and a portable digital identity, advancing financial freedom in underserved regions.
Core Lightning | Releases Latest Version with BOLT 12 by Default
Core Lightning, an implementation of the Lightning Network, introduced improvements to privacy and functionality with its latest v24.11 release. The update enables BOLT 12 offers by default when sending and receiving Bitcoin payments. BOLT 12 is an important update to the Lightning Network that brings increased receiver privacy, greater censorship resistance, and reusable payment requests for recurring payments. The update also includes xpay, an experimental payment plugin for advanced routing of payments on the Lightning Network. With these features, users of wallets and applications built with Core Lightning can maintain greater privacy and experience more optimized payments.
Proton Wallet | Implements Replace-by-Fee for Bitcoin Transactions
Proton, the company behind privacy tools like Proton Mail and Proton VPN, added support for Replace-by-Fee (RBF) transactions in Proton Wallet, its self-custodial and privacy-centric Bitcoin wallet. RBF allows users to increase the fee on stuck transactions to expedite confirmation and allow the payment to settle faster. The wallet also uses strong encryption and offers accessible recovery methods, ensuring users — like activists in hostile environments — maintain financial autonomy. Watch this tutorial by Bitcoin educator BTC Sessions to learn how to use Proton Wallet.
Bitcoin Design Community | South American Bitcoin UX Bootcamp
The Bitcoin Design Community, with support from HRF, will be hosting a South American UX Bitcoin Bootcamp. This program will support ten skilled UX designers across South America to develop and refine their design expertise within the Bitcoin ecosystem. Participants will also have the opportunity to attend the 2025 bitcoin++ developer conference in Florianopolis, Brazil, where they will receive specialized UX training and engage in hands-on learning with Bitcoin-related technologies. UX designers with an interest in Bitcoin are encouraged to apply here.
OpenSats | Announces Ninth Wave of Nostr Grants
OpenSats, a public nonprofit funding free and open-source software and projects, announced its ninth wave of grants supporting projects built on the decentralized Nostr protocol. Among the grantees is Pokey, an Android app enhancing Nostr and communications in restrictive environments through offline Bluetooth mesh networking and multi-account support. These features are particularly valuable for anyone facing Internet blackouts or state censorship. Another recipient, Persian NIPs, is breaking language barriers by localizing Nostr resources for Persian/Farsi speakers. The project will translate key protocols, user guides, and developer documentation, bringing decentralized and uncensorable technology to millions of people.
RECOMMENDED CONTENT
Africa Bitcoin Conference Livestream
Held from Dec. 9-11, 2024, in Nairobi, Kenya, the Africa Bitcoin Conference brought together human rights defenders, educators, and developers from across the continent to learn, collaborate, and innovate on freedom technologies. Supported by HRF, the event offered an inspiring mix of keynotes, workshops, panel discussions, and hackathons, all dedicated to advancing open-source solutions to fight authoritarianism and financial repression. This vibrant gathering highlighted innovative ideas and practical tools to empower communities worldwide. If you missed it, you can still catch the conversations and breakthroughs by watching the livestream here. Highlight talks include those from Farida Nabourema, Femi Longe, Jack Dorsey, and more.
-
 @ 79008e78:dfac9395
2024-12-18 09:02:28
@ 79008e78:dfac9395
2024-12-18 09:02:28อย่างที่ทราบกันอยู่แล้วว่า Nostr เป็นได้มากกว่า Note แล้วจะเป็นอย่างไรล่ะ ถ้า Note และลองฟอร์มต่าง ๆ ที่เราเคยเขียนกันมาสามารถกลายเป็นเว็บบอร์ดที่เราสามารถใช้เก็บผลงานและโชว์ให้กับคนอื่น ๆ ในโลกอินเตอร์เน็ตทั่วไปได้อีกด้วย
Npub.pro คืออะไร ?
Npub.pro เป็น Other stuff ตัวหนึ่งที่ช่วยแปลง note และ long form ต่าง ๆ ที่เราเคยได้ลงไว้ในโปรโตคอลของ Nostr และแปลงมันมาเป็นเว็บบอร์ดที่สวยสะอาดตา และมีธีมให้เลือกอีกหลากหลาย ซึ่งเหมาะสมมาก ๆ กับเหล่าครีเอเตอร์ต่าง ๆ สำหรับที่จะใช้มันในการโชว์ผลงาน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นสายถ่ายภาพ เก็บรวบรวมบทความ หรืออีกหลาย ๆ แง่มุมที่สามารถเกิดขึ้นได้


นี่เองคือหนึ่งในตัวอย่างที่ผมได้ทำไว้เพื่อแพร่กระจายบทความต่าง ๆ ให้ออกไปสู่ผู้คนที่อาจจะไม่ได้รู้จักหรือใช้งาน Nostr อยู่
แล้วมันทำงานอย่างไร ?
Npub.pro นั้นจะทำการดึง Notes และ Long form ของเรามาจาก relay ต่าง ๆ ที่เราได้มีการเชื่อมต่อไว้ในบัญชีของเรา และทำการนำมาจัดรูปแบบใหม่ตามธีมที่เราได้เลือกไว้ และแสดงผลออกมามาในรูปแบบเว็บบอร์ด นอกจากนี้ยังมีการใส่ตัว nostr log-in เข้ามาเพื่อช่วยให้คนที่มีบัญชี nostr สามารถใช้บัญชีของตนในการ zap หรือ คอมเม้นได้ รวมทั้งยังอณุญาตให้ผู้ใช้ใส่ script เพิ่มเติมลงไปทั้งในส่วนหัวและท้ายของเว็บบอร์ดได้อีกด้วย ดังเช่น

ทั้งหมดที่กล่าวมาข้างต้นเป็นประสบการณ์ส่วนตัวของผมเองที่ได้มีการทดลองใช้งานมาระยะหนึ่ง และในส่วนต่อไป เราจะมาดูกันถึงวิธีการสร้างว่าเราต้องทำอย่างไร จึงจะมีเว็บไซต์สวย ๆ แบบนี้ได้
วิธีการสร้าง
1. เข้าเว็บ Npub.pro
หลังจากเข้ามาในเว็บไซต์ให้เรากด "try now"

2. เลือกธีม
จากนั้นจะมีธีมต่าง ๆ ขึ้นมาให้คุณเลือก ในจุดนี้ผมแนะนำว่าให้เลือกให้เหมาะสมกับผลงานของคุณ (สามารถเปลี่ยนได้ภายหลัง)

3. ตั้งค่าส่วนอื่น ๆ
หลังจากเลือกเสร็จเรียบร้อยเราต้องทำการใส่ title bio และอื่น ๆ ให้เรียบร้อยจากนั้นให้ทำการกด publish

เพียงแค่นี้คุณก็จะมีเว็บบอร์ดเจ๋ง ๆ ที่จะคอยอัพเดตอัตโนมัติเพมื่อคุณได้โพสต์บางอย่างลงบน Nostr ;)
-
 @ fe32298e:20516265
2024-12-16 20:59:13
@ fe32298e:20516265
2024-12-16 20:59:13Today I learned how to install NVapi to monitor my GPUs in Home Assistant.
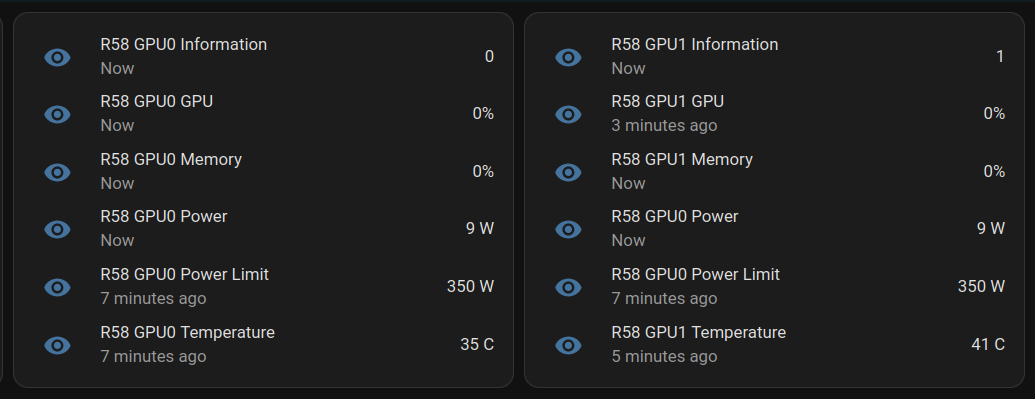
NVApi is a lightweight API designed for monitoring NVIDIA GPU utilization and enabling automated power management. It provides real-time GPU metrics, supports integration with tools like Home Assistant, and offers flexible power management and PCIe link speed management based on workload and thermal conditions.
- GPU Utilization Monitoring: Utilization, memory usage, temperature, fan speed, and power consumption.
- Automated Power Limiting: Adjusts power limits dynamically based on temperature thresholds and total power caps, configurable per GPU or globally.
- Cross-GPU Coordination: Total power budget applies across multiple GPUs in the same system.
- PCIe Link Speed Management: Controls minimum and maximum PCIe link speeds with idle thresholds for power optimization.
- Home Assistant Integration: Uses the built-in RESTful platform and template sensors.
Getting the Data
sudo apt install golang-go git clone https://github.com/sammcj/NVApi.git cd NVapi go run main.go -port 9999 -rate 1 curl http://localhost:9999/gpuResponse for a single GPU:
[ { "index": 0, "name": "NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090", "gpu_utilisation": 0, "memory_utilisation": 0, "power_watts": 16, "power_limit_watts": 450, "memory_total_gb": 23.99, "memory_used_gb": 0.46, "memory_free_gb": 23.52, "memory_usage_percent": 2, "temperature": 38, "processes": [], "pcie_link_state": "not managed" } ]Response for multiple GPUs:
[ { "index": 0, "name": "NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090", "gpu_utilisation": 0, "memory_utilisation": 0, "power_watts": 14, "power_limit_watts": 350, "memory_total_gb": 24, "memory_used_gb": 0.43, "memory_free_gb": 23.57, "memory_usage_percent": 2, "temperature": 36, "processes": [], "pcie_link_state": "not managed" }, { "index": 1, "name": "NVIDIA RTX A4000", "gpu_utilisation": 0, "memory_utilisation": 0, "power_watts": 10, "power_limit_watts": 140, "memory_total_gb": 15.99, "memory_used_gb": 0.56, "memory_free_gb": 15.43, "memory_usage_percent": 3, "temperature": 41, "processes": [], "pcie_link_state": "not managed" } ]Start at Boot
Create
/etc/systemd/system/nvapi.service:``` [Unit] Description=Run NVapi After=network.target
[Service] Type=simple Environment="GOPATH=/home/ansible/go" WorkingDirectory=/home/ansible/NVapi ExecStart=/usr/bin/go run main.go -port 9999 -rate 1 Restart=always User=ansible
Environment="GPU_TEMP_CHECK_INTERVAL=5"
Environment="GPU_TOTAL_POWER_CAP=400"
Environment="GPU_0_LOW_TEMP=40"
Environment="GPU_0_MEDIUM_TEMP=70"
Environment="GPU_0_LOW_TEMP_LIMIT=135"
Environment="GPU_0_MEDIUM_TEMP_LIMIT=120"
Environment="GPU_0_HIGH_TEMP_LIMIT=100"
Environment="GPU_1_LOW_TEMP=45"
Environment="GPU_1_MEDIUM_TEMP=75"
Environment="GPU_1_LOW_TEMP_LIMIT=140"
Environment="GPU_1_MEDIUM_TEMP_LIMIT=125"
Environment="GPU_1_HIGH_TEMP_LIMIT=110"
[Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target ```
Home Assistant
Add to Home Assistant
configuration.yamland restart HA (completely).For a single GPU, this works: ``` sensor: - platform: rest name: MYPC GPU Information resource: http://mypc:9999 method: GET headers: Content-Type: application/json value_template: "{{ value_json[0].index }}" json_attributes: - name - gpu_utilisation - memory_utilisation - power_watts - power_limit_watts - memory_total_gb - memory_used_gb - memory_free_gb - memory_usage_percent - temperature scan_interval: 1 # seconds
- platform: template sensors: mypc_gpu_0_gpu: friendly_name: "MYPC {{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'name') }} GPU" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'gpu_utilisation') }}" unit_of_measurement: "%" mypc_gpu_0_memory: friendly_name: "MYPC {{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'name') }} Memory" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'memory_utilisation') }}" unit_of_measurement: "%" mypc_gpu_0_power: friendly_name: "MYPC {{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'name') }} Power" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'power_watts') }}" unit_of_measurement: "W" mypc_gpu_0_power_limit: friendly_name: "MYPC {{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'name') }} Power Limit" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'power_limit_watts') }}" unit_of_measurement: "W" mypc_gpu_0_temperature: friendly_name: "MYPC {{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'name') }} Temperature" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu_information', 'temperature') }}" unit_of_measurement: "°C" ```
For multiple GPUs: ``` rest: scan_interval: 1 resource: http://mypc:9999 sensor: - name: "MYPC GPU0 Information" value_template: "{{ value_json[0].index }}" json_attributes_path: "$.0" json_attributes: - name - gpu_utilisation - memory_utilisation - power_watts - power_limit_watts - memory_total_gb - memory_used_gb - memory_free_gb - memory_usage_percent - temperature - name: "MYPC GPU1 Information" value_template: "{{ value_json[1].index }}" json_attributes_path: "$.1" json_attributes: - name - gpu_utilisation - memory_utilisation - power_watts - power_limit_watts - memory_total_gb - memory_used_gb - memory_free_gb - memory_usage_percent - temperature
-
platform: template sensors: mypc_gpu_0_gpu: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU0 GPU" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu0_information', 'gpu_utilisation') }}" unit_of_measurement: "%" mypc_gpu_0_memory: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU0 Memory" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu0_information', 'memory_utilisation') }}" unit_of_measurement: "%" mypc_gpu_0_power: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU0 Power" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu0_information', 'power_watts') }}" unit_of_measurement: "W" mypc_gpu_0_power_limit: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU0 Power Limit" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu0_information', 'power_limit_watts') }}" unit_of_measurement: "W" mypc_gpu_0_temperature: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU0 Temperature" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu0_information', 'temperature') }}" unit_of_measurement: "C"
-
platform: template sensors: mypc_gpu_1_gpu: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU1 GPU" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu1_information', 'gpu_utilisation') }}" unit_of_measurement: "%" mypc_gpu_1_memory: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU1 Memory" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu1_information', 'memory_utilisation') }}" unit_of_measurement: "%" mypc_gpu_1_power: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU1 Power" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu1_information', 'power_watts') }}" unit_of_measurement: "W" mypc_gpu_1_power_limit: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU1 Power Limit" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu1_information', 'power_limit_watts') }}" unit_of_measurement: "W" mypc_gpu_1_temperature: friendly_name: "MYPC GPU1 Temperature" value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.mypc_gpu1_information', 'temperature') }}" unit_of_measurement: "C"
```
Basic entity card:
type: entities entities: - entity: sensor.mypc_gpu_0_gpu secondary_info: last-updated - entity: sensor.mypc_gpu_0_memory secondary_info: last-updated - entity: sensor.mypc_gpu_0_power secondary_info: last-updated - entity: sensor.mypc_gpu_0_power_limit secondary_info: last-updated - entity: sensor.mypc_gpu_0_temperature secondary_info: last-updatedAnsible Role
```
-
name: install go become: true package: name: golang-go state: present
-
name: git clone git: repo: "https://github.com/sammcj/NVApi.git" dest: "/home/ansible/NVapi" update: yes force: true
go run main.go -port 9999 -rate 1
-
name: install systemd service become: true copy: src: nvapi.service dest: /etc/systemd/system/nvapi.service
-
name: Reload systemd daemons, enable, and restart nvapi become: true systemd: name: nvapi daemon_reload: yes enabled: yes state: restarted ```
-
 @ 6f6b50bb:a848e5a1
2024-12-15 15:09:52
@ 6f6b50bb:a848e5a1
2024-12-15 15:09:52Che cosa significherebbe trattare l'IA come uno strumento invece che come una persona?
Dall’avvio di ChatGPT, le esplorazioni in due direzioni hanno preso velocità.
La prima direzione riguarda le capacità tecniche. Quanto grande possiamo addestrare un modello? Quanto bene può rispondere alle domande del SAT? Con quanta efficienza possiamo distribuirlo?
La seconda direzione riguarda il design dell’interazione. Come comunichiamo con un modello? Come possiamo usarlo per un lavoro utile? Quale metafora usiamo per ragionare su di esso?
La prima direzione è ampiamente seguita e enormemente finanziata, e per una buona ragione: i progressi nelle capacità tecniche sono alla base di ogni possibile applicazione. Ma la seconda è altrettanto cruciale per il campo e ha enormi incognite. Siamo solo a pochi anni dall’inizio dell’era dei grandi modelli. Quali sono le probabilità che abbiamo già capito i modi migliori per usarli?
Propongo una nuova modalità di interazione, in cui i modelli svolgano il ruolo di applicazioni informatiche (ad esempio app per telefoni): fornendo un’interfaccia grafica, interpretando gli input degli utenti e aggiornando il loro stato. In questa modalità, invece di essere un “agente” che utilizza un computer per conto dell’essere umano, l’IA può fornire un ambiente informatico più ricco e potente che possiamo utilizzare.
Metafore per l’interazione
Al centro di un’interazione c’è una metafora che guida le aspettative di un utente su un sistema. I primi giorni dell’informatica hanno preso metafore come “scrivanie”, “macchine da scrivere”, “fogli di calcolo” e “lettere” e le hanno trasformate in equivalenti digitali, permettendo all’utente di ragionare sul loro comportamento. Puoi lasciare qualcosa sulla tua scrivania e tornare a prenderlo; hai bisogno di un indirizzo per inviare una lettera. Man mano che abbiamo sviluppato una conoscenza culturale di questi dispositivi, la necessità di queste particolari metafore è scomparsa, e con esse i design di interfaccia skeumorfici che le rafforzavano. Come un cestino o una matita, un computer è ora una metafora di se stesso.
La metafora dominante per i grandi modelli oggi è modello-come-persona. Questa è una metafora efficace perché le persone hanno capacità estese che conosciamo intuitivamente. Implica che possiamo avere una conversazione con un modello e porgli domande; che il modello possa collaborare con noi su un documento o un pezzo di codice; che possiamo assegnargli un compito da svolgere da solo e che tornerà quando sarà finito.
Tuttavia, trattare un modello come una persona limita profondamente il nostro modo di pensare all’interazione con esso. Le interazioni umane sono intrinsecamente lente e lineari, limitate dalla larghezza di banda e dalla natura a turni della comunicazione verbale. Come abbiamo tutti sperimentato, comunicare idee complesse in una conversazione è difficile e dispersivo. Quando vogliamo precisione, ci rivolgiamo invece a strumenti, utilizzando manipolazioni dirette e interfacce visive ad alta larghezza di banda per creare diagrammi, scrivere codice e progettare modelli CAD. Poiché concepiamo i modelli come persone, li utilizziamo attraverso conversazioni lente, anche se sono perfettamente in grado di accettare input diretti e rapidi e di produrre risultati visivi. Le metafore che utilizziamo limitano le esperienze che costruiamo, e la metafora modello-come-persona ci impedisce di esplorare il pieno potenziale dei grandi modelli.
Per molti casi d’uso, e specialmente per il lavoro produttivo, credo che il futuro risieda in un’altra metafora: modello-come-computer.
Usare un’IA come un computer
Sotto la metafora modello-come-computer, interagiremo con i grandi modelli seguendo le intuizioni che abbiamo sulle applicazioni informatiche (sia su desktop, tablet o telefono). Nota che ciò non significa che il modello sarà un’app tradizionale più di quanto il desktop di Windows fosse una scrivania letterale. “Applicazione informatica” sarà un modo per un modello di rappresentarsi a noi. Invece di agire come una persona, il modello agirà come un computer.
Agire come un computer significa produrre un’interfaccia grafica. Al posto del flusso lineare di testo in stile telescrivente fornito da ChatGPT, un sistema modello-come-computer genererà qualcosa che somiglia all’interfaccia di un’applicazione moderna: pulsanti, cursori, schede, immagini, grafici e tutto il resto. Questo affronta limitazioni chiave dell’interfaccia di chat standard modello-come-persona:
-
Scoperta. Un buon strumento suggerisce i suoi usi. Quando l’unica interfaccia è una casella di testo vuota, spetta all’utente capire cosa fare e comprendere i limiti del sistema. La barra laterale Modifica in Lightroom è un ottimo modo per imparare l’editing fotografico perché non si limita a dirti cosa può fare questa applicazione con una foto, ma cosa potresti voler fare. Allo stesso modo, un’interfaccia modello-come-computer per DALL-E potrebbe mostrare nuove possibilità per le tue generazioni di immagini.
-
Efficienza. La manipolazione diretta è più rapida che scrivere una richiesta a parole. Per continuare l’esempio di Lightroom, sarebbe impensabile modificare una foto dicendo a una persona quali cursori spostare e di quanto. Ci vorrebbe un giorno intero per chiedere un’esposizione leggermente più bassa e una vibranza leggermente più alta, solo per vedere come apparirebbe. Nella metafora modello-come-computer, il modello può creare strumenti che ti permettono di comunicare ciò che vuoi più efficientemente e quindi di fare le cose più rapidamente.
A differenza di un’app tradizionale, questa interfaccia grafica è generata dal modello su richiesta. Questo significa che ogni parte dell’interfaccia che vedi è rilevante per ciò che stai facendo in quel momento, inclusi i contenuti specifici del tuo lavoro. Significa anche che, se desideri un’interfaccia più ampia o diversa, puoi semplicemente richiederla. Potresti chiedere a DALL-E di produrre alcuni preset modificabili per le sue impostazioni ispirati da famosi artisti di schizzi. Quando clicchi sul preset Leonardo da Vinci, imposta i cursori per disegni prospettici altamente dettagliati in inchiostro nero. Se clicchi su Charles Schulz, seleziona fumetti tecnicolor 2D a basso dettaglio.
Una bicicletta della mente proteiforme
La metafora modello-come-persona ha una curiosa tendenza a creare distanza tra l’utente e il modello, rispecchiando il divario di comunicazione tra due persone che può essere ridotto ma mai completamente colmato. A causa della difficoltà e del costo di comunicare a parole, le persone tendono a suddividere i compiti tra loro in blocchi grandi e il più indipendenti possibile. Le interfacce modello-come-persona seguono questo schema: non vale la pena dire a un modello di aggiungere un return statement alla tua funzione quando è più veloce scriverlo da solo. Con il sovraccarico della comunicazione, i sistemi modello-come-persona sono più utili quando possono fare un intero blocco di lavoro da soli. Fanno le cose per te.
Questo contrasta con il modo in cui interagiamo con i computer o altri strumenti. Gli strumenti producono feedback visivi in tempo reale e sono controllati attraverso manipolazioni dirette. Hanno un overhead comunicativo così basso che non è necessario specificare un blocco di lavoro indipendente. Ha più senso mantenere l’umano nel loop e dirigere lo strumento momento per momento. Come stivali delle sette leghe, gli strumenti ti permettono di andare più lontano a ogni passo, ma sei ancora tu a fare il lavoro. Ti permettono di fare le cose più velocemente.
Considera il compito di costruire un sito web usando un grande modello. Con le interfacce di oggi, potresti trattare il modello come un appaltatore o un collaboratore. Cercheresti di scrivere a parole il più possibile su come vuoi che il sito appaia, cosa vuoi che dica e quali funzionalità vuoi che abbia. Il modello genererebbe una prima bozza, tu la eseguirai e poi fornirai un feedback. “Fai il logo un po’ più grande”, diresti, e “centra quella prima immagine principale”, e “deve esserci un pulsante di login nell’intestazione”. Per ottenere esattamente ciò che vuoi, invierai una lista molto lunga di richieste sempre più minuziose.
Un’interazione alternativa modello-come-computer sarebbe diversa: invece di costruire il sito web, il modello genererebbe un’interfaccia per te per costruirlo, dove ogni input dell’utente a quell’interfaccia interroga il grande modello sotto il cofano. Forse quando descrivi le tue necessità creerebbe un’interfaccia con una barra laterale e una finestra di anteprima. All’inizio la barra laterale contiene solo alcuni schizzi di layout che puoi scegliere come punto di partenza. Puoi cliccare su ciascuno di essi, e il modello scrive l’HTML per una pagina web usando quel layout e lo visualizza nella finestra di anteprima. Ora che hai una pagina su cui lavorare, la barra laterale guadagna opzioni aggiuntive che influenzano la pagina globalmente, come accoppiamenti di font e schemi di colore. L’anteprima funge da editor WYSIWYG, permettendoti di afferrare elementi e spostarli, modificarne i contenuti, ecc. A supportare tutto ciò è il modello, che vede queste azioni dell’utente e riscrive la pagina per corrispondere ai cambiamenti effettuati. Poiché il modello può generare un’interfaccia per aiutare te e lui a comunicare più efficientemente, puoi esercitare più controllo sul prodotto finale in meno tempo.
La metafora modello-come-computer ci incoraggia a pensare al modello come a uno strumento con cui interagire in tempo reale piuttosto che a un collaboratore a cui assegnare compiti. Invece di sostituire un tirocinante o un tutor, può essere una sorta di bicicletta proteiforme per la mente, una che è sempre costruita su misura esattamente per te e il terreno che intendi attraversare.
Un nuovo paradigma per l’informatica?
I modelli che possono generare interfacce su richiesta sono una frontiera completamente nuova nell’informatica. Potrebbero essere un paradigma del tutto nuovo, con il modo in cui cortocircuitano il modello di applicazione esistente. Dare agli utenti finali il potere di creare e modificare app al volo cambia fondamentalmente il modo in cui interagiamo con i computer. Al posto di una singola applicazione statica costruita da uno sviluppatore, un modello genererà un’applicazione su misura per l’utente e le sue esigenze immediate. Al posto della logica aziendale implementata nel codice, il modello interpreterà gli input dell’utente e aggiornerà l’interfaccia utente. È persino possibile che questo tipo di interfaccia generativa sostituisca completamente il sistema operativo, generando e gestendo interfacce e finestre al volo secondo necessità.
All’inizio, l’interfaccia generativa sarà un giocattolo, utile solo per l’esplorazione creativa e poche altre applicazioni di nicchia. Dopotutto, nessuno vorrebbe un’app di posta elettronica che occasionalmente invia email al tuo ex e mente sulla tua casella di posta. Ma gradualmente i modelli miglioreranno. Anche mentre si spingeranno ulteriormente nello spazio di esperienze completamente nuove, diventeranno lentamente abbastanza affidabili da essere utilizzati per un lavoro reale.
Piccoli pezzi di questo futuro esistono già. Anni fa Jonas Degrave ha dimostrato che ChatGPT poteva fare una buona simulazione di una riga di comando Linux. Allo stesso modo, websim.ai utilizza un LLM per generare siti web su richiesta mentre li navighi. Oasis, GameNGen e DIAMOND addestrano modelli video condizionati sull’azione su singoli videogiochi, permettendoti di giocare ad esempio a Doom dentro un grande modello. E Genie 2 genera videogiochi giocabili da prompt testuali. L’interfaccia generativa potrebbe ancora sembrare un’idea folle, ma non è così folle.
Ci sono enormi domande aperte su come apparirà tutto questo. Dove sarà inizialmente utile l’interfaccia generativa? Come condivideremo e distribuiremo le esperienze che creiamo collaborando con il modello, se esistono solo come contesto di un grande modello? Vorremmo davvero farlo? Quali nuovi tipi di esperienze saranno possibili? Come funzionerà tutto questo in pratica? I modelli genereranno interfacce come codice o produrranno direttamente pixel grezzi?
Non conosco ancora queste risposte. Dovremo sperimentare e scoprirlo!Che cosa significherebbe trattare l'IA come uno strumento invece che come una persona?
Dall’avvio di ChatGPT, le esplorazioni in due direzioni hanno preso velocità.
La prima direzione riguarda le capacità tecniche. Quanto grande possiamo addestrare un modello? Quanto bene può rispondere alle domande del SAT? Con quanta efficienza possiamo distribuirlo?
La seconda direzione riguarda il design dell’interazione. Come comunichiamo con un modello? Come possiamo usarlo per un lavoro utile? Quale metafora usiamo per ragionare su di esso?
La prima direzione è ampiamente seguita e enormemente finanziata, e per una buona ragione: i progressi nelle capacità tecniche sono alla base di ogni possibile applicazione. Ma la seconda è altrettanto cruciale per il campo e ha enormi incognite. Siamo solo a pochi anni dall’inizio dell’era dei grandi modelli. Quali sono le probabilità che abbiamo già capito i modi migliori per usarli?
Propongo una nuova modalità di interazione, in cui i modelli svolgano il ruolo di applicazioni informatiche (ad esempio app per telefoni): fornendo un’interfaccia grafica, interpretando gli input degli utenti e aggiornando il loro stato. In questa modalità, invece di essere un “agente” che utilizza un computer per conto dell’essere umano, l’IA può fornire un ambiente informatico più ricco e potente che possiamo utilizzare.
Metafore per l’interazione
Al centro di un’interazione c’è una metafora che guida le aspettative di un utente su un sistema. I primi giorni dell’informatica hanno preso metafore come “scrivanie”, “macchine da scrivere”, “fogli di calcolo” e “lettere” e le hanno trasformate in equivalenti digitali, permettendo all’utente di ragionare sul loro comportamento. Puoi lasciare qualcosa sulla tua scrivania e tornare a prenderlo; hai bisogno di un indirizzo per inviare una lettera. Man mano che abbiamo sviluppato una conoscenza culturale di questi dispositivi, la necessità di queste particolari metafore è scomparsa, e con esse i design di interfaccia skeumorfici che le rafforzavano. Come un cestino o una matita, un computer è ora una metafora di se stesso.
La metafora dominante per i grandi modelli oggi è modello-come-persona. Questa è una metafora efficace perché le persone hanno capacità estese che conosciamo intuitivamente. Implica che possiamo avere una conversazione con un modello e porgli domande; che il modello possa collaborare con noi su un documento o un pezzo di codice; che possiamo assegnargli un compito da svolgere da solo e che tornerà quando sarà finito.
Tuttavia, trattare un modello come una persona limita profondamente il nostro modo di pensare all’interazione con esso. Le interazioni umane sono intrinsecamente lente e lineari, limitate dalla larghezza di banda e dalla natura a turni della comunicazione verbale. Come abbiamo tutti sperimentato, comunicare idee complesse in una conversazione è difficile e dispersivo. Quando vogliamo precisione, ci rivolgiamo invece a strumenti, utilizzando manipolazioni dirette e interfacce visive ad alta larghezza di banda per creare diagrammi, scrivere codice e progettare modelli CAD. Poiché concepiamo i modelli come persone, li utilizziamo attraverso conversazioni lente, anche se sono perfettamente in grado di accettare input diretti e rapidi e di produrre risultati visivi. Le metafore che utilizziamo limitano le esperienze che costruiamo, e la metafora modello-come-persona ci impedisce di esplorare il pieno potenziale dei grandi modelli.
Per molti casi d’uso, e specialmente per il lavoro produttivo, credo che il futuro risieda in un’altra metafora: modello-come-computer.
Usare un’IA come un computer
Sotto la metafora modello-come-computer, interagiremo con i grandi modelli seguendo le intuizioni che abbiamo sulle applicazioni informatiche (sia su desktop, tablet o telefono). Nota che ciò non significa che il modello sarà un’app tradizionale più di quanto il desktop di Windows fosse una scrivania letterale. “Applicazione informatica” sarà un modo per un modello di rappresentarsi a noi. Invece di agire come una persona, il modello agirà come un computer.
Agire come un computer significa produrre un’interfaccia grafica. Al posto del flusso lineare di testo in stile telescrivente fornito da ChatGPT, un sistema modello-come-computer genererà qualcosa che somiglia all’interfaccia di un’applicazione moderna: pulsanti, cursori, schede, immagini, grafici e tutto il resto. Questo affronta limitazioni chiave dell’interfaccia di chat standard modello-come-persona:
Scoperta. Un buon strumento suggerisce i suoi usi. Quando l’unica interfaccia è una casella di testo vuota, spetta all’utente capire cosa fare e comprendere i limiti del sistema. La barra laterale Modifica in Lightroom è un ottimo modo per imparare l’editing fotografico perché non si limita a dirti cosa può fare questa applicazione con una foto, ma cosa potresti voler fare. Allo stesso modo, un’interfaccia modello-come-computer per DALL-E potrebbe mostrare nuove possibilità per le tue generazioni di immagini.
Efficienza. La manipolazione diretta è più rapida che scrivere una richiesta a parole. Per continuare l’esempio di Lightroom, sarebbe impensabile modificare una foto dicendo a una persona quali cursori spostare e di quanto. Ci vorrebbe un giorno intero per chiedere un’esposizione leggermente più bassa e una vibranza leggermente più alta, solo per vedere come apparirebbe. Nella metafora modello-come-computer, il modello può creare strumenti che ti permettono di comunicare ciò che vuoi più efficientemente e quindi di fare le cose più rapidamente.
A differenza di un’app tradizionale, questa interfaccia grafica è generata dal modello su richiesta. Questo significa che ogni parte dell’interfaccia che vedi è rilevante per ciò che stai facendo in quel momento, inclusi i contenuti specifici del tuo lavoro. Significa anche che, se desideri un’interfaccia più ampia o diversa, puoi semplicemente richiederla. Potresti chiedere a DALL-E di produrre alcuni preset modificabili per le sue impostazioni ispirati da famosi artisti di schizzi. Quando clicchi sul preset Leonardo da Vinci, imposta i cursori per disegni prospettici altamente dettagliati in inchiostro nero. Se clicchi su Charles Schulz, seleziona fumetti tecnicolor 2D a basso dettaglio.
Una bicicletta della mente proteiforme
La metafora modello-come-persona ha una curiosa tendenza a creare distanza tra l’utente e il modello, rispecchiando il divario di comunicazione tra due persone che può essere ridotto ma mai completamente colmato. A causa della difficoltà e del costo di comunicare a parole, le persone tendono a suddividere i compiti tra loro in blocchi grandi e il più indipendenti possibile. Le interfacce modello-come-persona seguono questo schema: non vale la pena dire a un modello di aggiungere un return statement alla tua funzione quando è più veloce scriverlo da solo. Con il sovraccarico della comunicazione, i sistemi modello-come-persona sono più utili quando possono fare un intero blocco di lavoro da soli. Fanno le cose per te.
Questo contrasta con il modo in cui interagiamo con i computer o altri strumenti. Gli strumenti producono feedback visivi in tempo reale e sono controllati attraverso manipolazioni dirette. Hanno un overhead comunicativo così basso che non è necessario specificare un blocco di lavoro indipendente. Ha più senso mantenere l’umano nel loop e dirigere lo strumento momento per momento. Come stivali delle sette leghe, gli strumenti ti permettono di andare più lontano a ogni passo, ma sei ancora tu a fare il lavoro. Ti permettono di fare le cose più velocemente.
Considera il compito di costruire un sito web usando un grande modello. Con le interfacce di oggi, potresti trattare il modello come un appaltatore o un collaboratore. Cercheresti di scrivere a parole il più possibile su come vuoi che il sito appaia, cosa vuoi che dica e quali funzionalità vuoi che abbia. Il modello genererebbe una prima bozza, tu la eseguirai e poi fornirai un feedback. “Fai il logo un po’ più grande”, diresti, e “centra quella prima immagine principale”, e “deve esserci un pulsante di login nell’intestazione”. Per ottenere esattamente ciò che vuoi, invierai una lista molto lunga di richieste sempre più minuziose.
Un’interazione alternativa modello-come-computer sarebbe diversa: invece di costruire il sito web, il modello genererebbe un’interfaccia per te per costruirlo, dove ogni input dell’utente a quell’interfaccia interroga il grande modello sotto il cofano. Forse quando descrivi le tue necessità creerebbe un’interfaccia con una barra laterale e una finestra di anteprima. All’inizio la barra laterale contiene solo alcuni schizzi di layout che puoi scegliere come punto di partenza. Puoi cliccare su ciascuno di essi, e il modello scrive l’HTML per una pagina web usando quel layout e lo visualizza nella finestra di anteprima. Ora che hai una pagina su cui lavorare, la barra laterale guadagna opzioni aggiuntive che influenzano la pagina globalmente, come accoppiamenti di font e schemi di colore. L’anteprima funge da editor WYSIWYG, permettendoti di afferrare elementi e spostarli, modificarne i contenuti, ecc. A supportare tutto ciò è il modello, che vede queste azioni dell’utente e riscrive la pagina per corrispondere ai cambiamenti effettuati. Poiché il modello può generare un’interfaccia per aiutare te e lui a comunicare più efficientemente, puoi esercitare più controllo sul prodotto finale in meno tempo.
La metafora modello-come-computer ci incoraggia a pensare al modello come a uno strumento con cui interagire in tempo reale piuttosto che a un collaboratore a cui assegnare compiti. Invece di sostituire un tirocinante o un tutor, può essere una sorta di bicicletta proteiforme per la mente, una che è sempre costruita su misura esattamente per te e il terreno che intendi attraversare.
Un nuovo paradigma per l’informatica?
I modelli che possono generare interfacce su richiesta sono una frontiera completamente nuova nell’informatica. Potrebbero essere un paradigma del tutto nuovo, con il modo in cui cortocircuitano il modello di applicazione esistente. Dare agli utenti finali il potere di creare e modificare app al volo cambia fondamentalmente il modo in cui interagiamo con i computer. Al posto di una singola applicazione statica costruita da uno sviluppatore, un modello genererà un’applicazione su misura per l’utente e le sue esigenze immediate. Al posto della logica aziendale implementata nel codice, il modello interpreterà gli input dell’utente e aggiornerà l’interfaccia utente. È persino possibile che questo tipo di interfaccia generativa sostituisca completamente il sistema operativo, generando e gestendo interfacce e finestre al volo secondo necessità.
All’inizio, l’interfaccia generativa sarà un giocattolo, utile solo per l’esplorazione creativa e poche altre applicazioni di nicchia. Dopotutto, nessuno vorrebbe un’app di posta elettronica che occasionalmente invia email al tuo ex e mente sulla tua casella di posta. Ma gradualmente i modelli miglioreranno. Anche mentre si spingeranno ulteriormente nello spazio di esperienze completamente nuove, diventeranno lentamente abbastanza affidabili da essere utilizzati per un lavoro reale.
Piccoli pezzi di questo futuro esistono già. Anni fa Jonas Degrave ha dimostrato che ChatGPT poteva fare una buona simulazione di una riga di comando Linux. Allo stesso modo, websim.ai utilizza un LLM per generare siti web su richiesta mentre li navighi. Oasis, GameNGen e DIAMOND addestrano modelli video condizionati sull’azione su singoli videogiochi, permettendoti di giocare ad esempio a Doom dentro un grande modello. E Genie 2 genera videogiochi giocabili da prompt testuali. L’interfaccia generativa potrebbe ancora sembrare un’idea folle, ma non è così folle.
Ci sono enormi domande aperte su come apparirà tutto questo. Dove sarà inizialmente utile l’interfaccia generativa? Come condivideremo e distribuiremo le esperienze che creiamo collaborando con il modello, se esistono solo come contesto di un grande modello? Vorremmo davvero farlo? Quali nuovi tipi di esperienze saranno possibili? Come funzionerà tutto questo in pratica? I modelli genereranno interfacce come codice o produrranno direttamente pixel grezzi?
Non conosco ancora queste risposte. Dovremo sperimentare e scoprirlo!
Tradotto da:\ https://willwhitney.com/computing-inside-ai.htmlhttps://willwhitney.com/computing-inside-ai.html
-
-
 @ 502ab02a:a2860397
2024-12-15 01:14:23
@ 502ab02a:a2860397
2024-12-15 01:14:23แสงแดด วิตามิน D, A, K2-MK7 กับสุขภาพกระดูกและหลอดเลือด ว่าด้วยเรื่องของ DAK2 นั้นเคยเขียนไว้นานแล้ว แต่จำได้ว่าเป็นกึ่งๆบทความบ่นๆ แต่ไม่ได้อธิบายเป็นภาษามนุษย์นักครับว่า ตกลงจะหมายถึงอะไรกันแน่ ด้วยวาระโอกาสจะจบปี 2024 เลยคิดว่า นำมาปิดท้ายเนื้อหาหนักๆช่วงปลายๆของ season3 นี้กันดีกว่า
แสงแดด ไม่ใช่สิ่งที่ควรหลีกเลี่ยงเสมอไป แม้ว่าหลายคนจะกังวลเกี่ยวกับความเสี่ยงของโรคมะเร็งผิวหนัง แต่หากได้รับในปริมาณที่เหมาะสม แสงแดดเป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่ช่วยกระตุ้นกลไกของวิตามิน D ในร่างกาย ซึ่งทำงานร่วมกับ วิตามิน A และ วิตามิน K2-MK7 เพื่อดูแลสุขภาพกระดูกและหลอดเลือด รวมถึงช่วยลดความเสี่ยงจากโรคร้ายแรง เช่น โรคกระดูกพรุนและหลอดเลือดอุดตันครับ บทความนี้จะอธิบายถึงกลไกการทำงานของวิตามินเหล่านี้กับร่างกาย เพื่อส่งเสริมการดูดซึมแคลเซียม ลดการสะสมแคลเซียมผิดที่ และสร้างความเข้าใจว่าความเสี่ยงจากการตากแดดนั้น ต่ำกว่าที่หลายคนเข้าใจนักครับ คือ ถ้าไม่ชอบตากก็ไม่ต้องอ้างอะไรอื่นครับ ลองพิจารณาสิ่งที่ผมจะเล่าให้นี้ก่อนว่าซื้อมั๊ย ผมพยายามจะรวบรัดให้สั้นๆนะครับ
หลักการที่ผมมโนออกมาเป็นคำสั้นๆว่า DAK2 ซึ่งผมมักจะเรียกว่า แดก หรือเต็มๆคือ ตากแดดแล้วแดกด้วย คือกิจกรรมตากแดดของเรานั้น จะส่งผลดีได้อีกด้านนึงด้วย ถ้าคุณได้รับวิตามินครบทั้ง DAK2 ครับ เพราะว่า
-วิตามิน D เป็นรากฐานของการดูดซึมแคลเซียม วิตามิน D เป็นจุดเริ่มต้นของกระบวนการที่ช่วยให้ร่างกายดูดซึมแคลเซียมอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพและนำไปใช้อย่างเหมาะสม เมื่อผิวหนังได้รับรังสี UVB จากแสงแดด ร่างกายจะสังเคราะห์ วิตามิน D3 (cholecalciferol) วิตามิน D3 จะถูกเปลี่ยนเป็น calcidiol ในตับ และcalcitriol ที่ไต ซึ่งตรงนี้นะครับ มันจะถูกเปลี่ยนเป็น calcitriol รูปแบบที่ร่างกายนำไปใช้งานได้ ซึ่งเจ้า Calcitriol นี่แหละที่ ช่วยเพิ่มการดูดซึม แคลเซียม และ ฟอสฟอรัส จากอาหารในลำไส้ ทำให้มีแร่ธาตุเพียงพอสำหรับการสร้างและบำรุงกระดูก
-วิตามิน K2-MK7 รับบทผู้ควบคุมแคลเซียมในร่างกาย วิตามิน K2 ตัวนี้สำคัญ หายากและขาดมากที่สุดครับ โดยเฉพาะในรูปแบบ MK7 (menaquinone-7) มีบทบาทสำคัญในการนำแคลเซียมไปสะสมในกระดูกและป้องกันการสะสมในหลอดเลือด โดย K2 นั้นกระตุ้นโปรตีน osteocalcin ซึ่งทำหน้าที่ดึงแคลเซียมเข้าสู่กระดูก นอกจากนี้ K2 ยังช่วยกระตุ้น matrix Gla-protein (MGP) ซึ่งป้องกันการสะสมแคลเซียมไม่ให้ไปเกาะในหลอดเลือดแดงและเนื้อเยื่ออ่อน ดังนั้นการได้รับ K2 เพียงพอจึงช่วยลดความเสี่ยงของโรคหลอดเลือดอุดตัน
คำถามคือทำไมต้อง MK7???? นั่นเพราะ MK7 มีคุณสมบัติที่เหนือกว่า K2 รูปแบบอื่น เนื่องจากมีการทำงานในร่างกายได้นานกว่าวิตามิน K2 ตัวอื่นๆก่อนจะถูกขับทิ้งออกไป จึงช่วยให้เกิดผลลัพธ์ที่ยาวนานและมีประสิทธิภาพสูงที่สุด
-วิตามิน A ผู้สนับสนุนกระดูกและหลอดเลือด วิตามิน A (ในรูป retinoic acid) ทำงานร่วมกับวิตามิน D และ K2 เพื่อช่วยควบคุมการเจริญเติบโตของกระดูกและลดการสะสมแคลเซียมผิดที่ครับ โดยวิตามิน A จะกระตุ้นเซลล์สร้างกระดูก (osteoblasts) และช่วยปรับสมดุลของเซลล์สลายกระดูก (osteoclasts)ควบคุมการทำงานของเซลล์ทำลายกระดูก รวมถึงมีส่วนช่วยในการสร้างเซลล์เยื่อบุหลอดเลือด (endothelial cells) ให้แข็งแรง ช่วยลดการสะสมของคราบแคลเซียมในหลอดเลือด
เมื่อทำงานร่วมกับ วิตามิน K2 (ที่ป้องกันแคลเซียมสะสมในหลอดเลือด) จะช่วยลดความเสี่ยงของโรคหลอดเลือดอุดตัน แล้ววิตามิน A นั้นก็ยังช่วยเสริมสร้างเซลล์เยื่อบุหลอดเลือด ทำให้หลอดเลือดแข็งแรง ลดความเสี่ยงการสะสมของคราบแคลเซียม เมื่อร่างกายได้รับ วิตามิน A, D, และ K2 ร่วมกัน กระบวนการสร้างกระดูกและการสะสมแร่ธาตุในกระดูกจะมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น
ข้อควรระวัง การได้รับวิตามิน A มากเกินไป (เกิน 10,000 IU/วัน) อาจขัดขวางการทำงานของวิตามิน D และเสี่ยงต่อการสูญเสียมวลกระดูก ดังนั้นควรได้รับในปริมาณที่เหมาะสม ไม่ใช่ว่าพอคิดว่าดีแล้วจัดกันแบบไม่ยั้งนะครับ อันนี้อันตรายนะ
สรุปการทำงานร่วมกันของวิตามิน D, A, K2-MK7 วิตามิน D ช่วยเพิ่มการดูดซึมแคลเซียมและฟอสฟอรัสเข้าสู่กระแสเลือด วิตามิน K2-MK7 ช่วยนำแคลเซียมไปสะสมในกระดูก และป้องกันการสะสมในหลอดเลือด วิตามิน A ช่วยปรับสมดุลการเจริญเติบโตและการสลายกระดูก พร้อมเสริมความแข็งแรงของเยื่อบุหลอดเลือด
อาหารที่ช่วยเสริมวิตามิน D, A, K2-MK7 ปกติเราจะท่องๆกันว่า ในเนื้อวัวตับวัว มีครบเกือบทุกอย่าง เว้นวิตามิน K2 เรามาลองดูตัวอย่างอาหารอื่นๆกันบ้างครับ วิตามิน D: ปลาแซลมอน, ปลาซาร์ดีน, น้ำมันตับปลา วิตามิน A: ตับ, ไข่ วิตามิน K2-MK7: นัตโตะ (ถั่วหมักญี่ปุ่น), ชีส, ไข่ไก่จากไก่ที่เลี้ยงปล่อย ส่วนที่มีคนถามว่า กิมจิหล่ะ คือ กิมจิ มีปริมาณวิตามิน K2 จริงครับแต่โดยปกติจะอยู่ในรูปแบบ MK4 ไม่ใช่ MK7 แคลเซียม: นม, กระดูกอ่อนต่างๆ, น้ำซุปกระดูก. ตับ ทีนี้พอเราเห็นภาพรวมแล้ว ก็ต้องบอกว่า จงเลิกมายาที่ต้องมานั่งท่องว่า ตากแดดเวลาไหนดีที่สุด เพราะคุณไม่ต้องไขว่คว้าหาอะไรที่ดีที่สุดเลยครับ คติของการตากแดดคือ ดีทุกเวลา เอาที่ว่าคุณไหวนั่นแหละ ไอ้ที่บอกว่าตากเช้าดีสุดนี่ ตากเช้าเท่านั้น เวลาอื่นห้ามตาก ตากแล้วจะเป็นมะเร็ง โคตรโม้ครับ อย่าเชื่อผมนะ คุณค่อยๆพิจารณา verify ไปทีละจุด ตากแค่เช้าจะได้อะไร ตากสะสมหลายๆเวลาได้อะไร แล้วประโยคที่ส่งต่อกันจังเลยว่า ตากแดดเช้ามันดีสุดจริงไหม
เลิกถามนะครับ ว่าตากเวลาไหนดีที่สุด มัน out แล้ว
#SundaySpecialเราจะไปเป็นหมูแดดเดียว #กูต้องรู้มั๊ย #PirateKeto
-
 @ f1989a96:bcaaf2c1
2024-12-12 14:46:22
@ f1989a96:bcaaf2c1
2024-12-12 14:46:22Good morning, readers!
This week, governments and financial institutions around the world advanced policies that amplify the divide between state interests and the daily economic realities of citizens. In Tunisia, President Kais Saied is once again turning to the nation’s central bank to repay its growing debts, a move that risks accelerating inflation, reducing citizen purchasing power, and increasing costs of living.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is urging regional banks to enhance their Know-Your-Customer (KYC) procedures. This includes implementing a “re-KYC” process that requires millions of citizens to resubmit personal information. In addition, banks are gathering supplementary data, which may be used for marketing purposes and potentially other objectives.
In technology news, Eclair, an implementation of the Lightning Network, added support for BOLT 12 offers and liquidity management features such as splicing, liquidity ads, and on-the-fly funding. These make managing liquidity and using the Lightning Network more accessible and private. Meanwhile, Machankura, a custodial Lightning wallet in Africa with offline functionality for feature phones, announced the launch of a mobile application for Android users. This will bring offline Bitcoin transactions to a greater number of people across the African continent.
We end with the latest episode in the HRF x Pubkey Freedom Tech Series, featuring HRF’s Bitcoin Development Lead, Alex Li, in conversation with Bitcoin Core maintainer Gloria Zhao, on the threats facing Bitcoin, the importance of censorship-resistant payments, and her decision to pursue open-source, grant-funded development over corporate opportunities.
Now, let’s dive right in!
Subscribe Here
GLOBAL NEWS
Tunisia | Turns to Central Bank to Repay Debts
In a clear display of financial manipulation, President Kais Saied is once again turning to the central bank to repay Tunisia’s surging debt. He plans to borrow 7 billion dinars ($2.2 billion), equal to about 28% of the central bank’s foreign currency reserves. This move could increase inflation in an already struggling economy where unemployment exceeds 16%, supermarket shelves run empty, and water shortages threaten families' livelihoods. Saied’s unrelenting consolidation of power — including shutting down parliament, arresting opposition leaders, and controlling the judiciary — has stalled any meaningful way for people to push back and protest the disastrous state-led economic policies.
India | RBI Pushes Banks to Re-KYC Customers
The Reserve Bank of India is urging regional banks to carry out re-KYC (Know-Your-Customer) verifications. Stringent KYC requirements and mandatory periodic updates have caused many citizens to lose access to their bank accounts. Despite repeatedly submitting their personal information to be compliant, numerous account holders continue to be locked out due to delays, errors, and overreaching requirements. Moreover, reports indicate that banks have exploited the KYC process to collect additional data from account holders for third-party marketing.
Kenya | Reinstates Tax Measures that Ignited Nationwide Protests
Kenya’s lawmakers have reinstated controversial tax measures that previously triggered nationwide protests, claiming more than 60 lives. The National Treasury, navigating escalating debts and revenue shortfalls, repackaged the taxes into three bills approved by the National Assembly. These include higher import taxes, a “top-up” tax for multinational companies, and levies on foreign firms operating via digital platforms — all part of Kenya’s “austerity” commitments to the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The reinstatement of these taxes risks reigniting public unrest and inflation, while the growing reliance on the IMF calls into question the autonomy and financial resilience of both the government and ordinary citizens.
Vietnam | Social Media Platforms Censor Anti-State Content
Over the past year, Facebook, Google, and TikTok complied with more than 90% of the Communist Party of Vietnam’s (CPV) requests to censor over 15,000 pieces of “anti-state” content. This censorship aligns with Decree 147, a law passed by the CPV to tighten control over social networks and the Internet. Amnesty International condemned these practices as arbitrary censorship. Adding to the repression, Decree 147 requires organizations to share data with authorities without consent in situations deemed critical to “national security.” Such tactics could easily compromise activists and civil society organizations. In these environments, decentralized protocols like Nostr, which allow communication and expression beyond the reach of the state, can play a vital role in upholding citizens' right to free expression.
Cuba | Nationwide Blackout Following Grid Collapse
Last week, Cuba’s largest electricity producer failed, plunging the island nation into darkness and leaving millions without power. This exemplifies the fragility of Cuba’s electrical grid in a country already battered by currency collapse and fuel shortages. Over the past year, frequent blackouts — some lasting up to 18 hours — have made it prohibitively difficult for families to feed themselves and access basic necessities. The nationwide outage forced schools to close and halted work for millions of Cubans already struggling with food, water, and medicine shortages. While officials scramble to restore power to hospitals and water facilities, this illustrates the shortfalls of a state assuming absolute control over a critical industry, like electricity, and failing to deliver. Such failures ultimately strip citizens — already mired in crisis — of basic rights and essential services.
LATEST IN BITCOIN NEWS, DEVELOPMENT, AND COMMUNITY
Eclair | Integrates Support for BOLT 12, Splicing, Liquidity Ads, and On-The-Fly Funding
Eclair, a Lightning Network implementation developed by ACINQ (the team behind Phoenix Wallet and phoenixd), introduced support for BOLT 12 offers and a host of liquidity management features, including splicing, liquidity ads, and on-the-fly funding. BOLT 12 offers increased receiver privacy and censorship resistance when making payments (as well as helping people receive payments via a static QR code or alphanumeric address), while splicing enables the adjustment of payment channels without interrupting ongoing transactions. Further, liquidity ads and on-the-fly funding make it possible for nodes to buy or sell liquidity when making payments on the Lightning Network. These features improve how people send and receive Bitcoin and manage liquidity when using applications and wallets built with Eclair.
Machankura | Launches Android App
Machankura, a custodial Lightning wallet in Africa with offline functionality for feature phones, announced the launch of a mobile application for Android. Leveraging the Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD) protocol for sending text messages, Machankura enables Africans to access the Bitcoin network simply by dialing a designated number on a feature phone (or a smartphone without data), facilitating Bitcoin transactions without the need for an Internet connection. Launching a mobile app will make offline Bitcoin transactions available to more individuals, helping democratize Bitcoin access and unlock the full potential of censorship-resistant money across Africa.
Lark | New Command Line Application for USB Hardware Wallets
Lark is a new command-line application built by Craig Raw, the creator of Sparrow Wallet, designed to interact with USB hardware wallets such as COLDCARD, Ledger, and Trezor. It serves as an alternative to the widely used HWI (Hardware Wallet Interface) software library, providing users with a second option to interact with their USB hardware wallets. By improving the resilience of the Bitcoin hardware wallet ecosystem, Lark helps advance financial autonomy and censorship resistance.
WabiSabi | Major Vulnerability in Coinjoin Protocol
The Rage, an independent news publication exposing the risks of financial surveillance, disclosed a major vulnerability in the WabiSabi coinjoin protocol that allows malicious coordinators to compromise user privacy by deanonymizing transactions. Coinjoin is a privacy-enhancing method that combines multiple Bitcoin transactions into one, making it harder to trace individual payments. The vulnerability, which affects popular tools and wallets like Wasabi Wallet, Ginger Wallet, and BTCPay Server’s coinjoin plugin, enables malicious actors to link inputs and outputs during a transaction and expose user financial activity. Developers have released updates to fix the issue, and users are urged to upgrade immediately. Learn more here.
OpenSats | Renews Grants for Open Source Bitcoin Projects
OpenSats, a public nonprofit funding free and open-source Bitcoin software and projects, renewed grants for nine crucial Bitcoin projects that are expanding financial freedom around the world. Among the recipients is BTCPay Server, an open-source and non-custodial Bitcoin payment processor that enables businesses and nonprofits to easily accept Bitcoin payments. Stratum V2, a protocol that decentralizes Bitcoin mining by enabling nodes to construct their own block templates, also received funding, as well as BitAxe, a project building open-source Bitcoin mining hardware to empower individual miners.
RECOMMENDED CONTENT
HRF x Pubkey — Shadowy Superheroes: How Bitcoin Core Developers Keep Freedom Money Alive
In the latest HRF x Pubkey Freedom Tech Series, HRF’s Bitcoin Development Lead, Alex Li, sits down for a fireside conversation with Bitcoin Core maintainer Gloria Zhao. Together, they discuss the crucial role of censorship-resistant payments in preserving financial freedom and the challenges Bitcoin faces in a world increasingly hostile toward decentralized systems. Zhao shares her journey of choosing open-source, grant-funded development over corporate opportunities, showcasing her commitment to keeping Bitcoin permissionless, secure, and free from centralized control. Listen to the full conversation here.
Downgrading the Bank Secrecy Act is a Powerful Reform for Bitcoin by Yaël
Ossowski
In this article for the Bitcoin Policy Institute, Yaël Ossowski reveals how policies like the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) impose financial surveillance that stifles innovation, erodes citizens’ privacy, and impacts Bitcoin’s potential as a tool for financial freedom. Highlighting enforcement actions against non-custodial Bitcoin tools and privacy software, the article makes a compelling case for the growing threat current regulations pose to decentralized and privacy-centric technologies. This is a helpful article for anyone seeking to understand the nuanced nature of financial privacy. You can read it here.
If this article was forwarded to you and you enjoyed reading it, please consider subscribing to the Financial Freedom Report here.
Support the newsletter by donating bitcoin to HRF’s Financial Freedom program via BTCPay.
Want to contribute to the newsletter? Submit tips, stories, news, and ideas by emailing us at ffreport @ hrf.org
The Bitcoin Development Fund (BDF) is accepting grant proposals on an ongoing basis. The Bitcoin Development Fund is looking to support Bitcoin developers, community builders, and educators. Submit proposals here.
-
 @ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-12-07 15:06:43
@ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-12-07 15:06:43I started a long series of articles about how to model different types of knowledge graphs in the relational model, which makes on-device memory models for AI agents possible.
We model-directed graphs
Also, graphs of entities
We even model hypergraphs
Last time, we discussed why classical triple and simple knowledge graphs are insufficient for AI agents and complex memory, especially in the domain of time-aware or multi-model knowledge.
So why do we need metagraphs, and what kind of challenge could they help us to solve?
- complex and nested event and temporal context and temporal relations as edges
- multi-mode and multilingual knowledge
- human-like memory for AI agents that has multiple contexts and relations between knowledge in neuron-like networks
MetaGraphs
A meta graph is a concept that extends the idea of a graph by allowing edges to become graphs. Meta Edges connect a set of nodes, which could also be subgraphs. So, at some level, node and edge are pretty similar in properties but act in different roles in a different context.
Also, in some cases, edges could be referenced as nodes.
This approach enables the representation of more complex relationships and hierarchies than a traditional graph structure allows. Let’s break down each term to understand better metagraphs and how they differ from hypergraphs and graphs.Graph Basics
- A standard graph has a set of nodes (or vertices) and edges (connections between nodes).
- Edges are generally simple and typically represent a binary relationship between two nodes.
- For instance, an edge in a social network graph might indicate a “friend” relationship between two people (nodes).
Hypergraph
- A hypergraph extends the concept of an edge by allowing it to connect any number of nodes, not just two.
- Each connection, called a hyperedge, can link multiple nodes.
- This feature allows hypergraphs to model more complex relationships involving multiple entities simultaneously. For example, a hyperedge in a hypergraph could represent a project team, connecting all team members in a single relation.
- Despite its flexibility, a hypergraph doesn’t capture hierarchical or nested structures; it only generalizes the number of connections in an edge.
Metagraph
- A metagraph allows the edges to be graphs themselves. This means each edge can contain its own nodes and edges, creating nested, hierarchical structures.
- In a meta graph, an edge could represent a relationship defined by a graph. For instance, a meta graph could represent a network of organizations where each organization’s structure (departments and connections) is represented by its own internal graph and treated as an edge in the larger meta graph.
- This recursive structure allows metagraphs to model complex data with multiple layers of abstraction. They can capture multi-node relationships (as in hypergraphs) and detailed, structured information about each relationship.
Named Graphs and Graph of Graphs
As you can notice, the structure of a metagraph is quite complex and could be complex to model in relational and classical RDF setups. It could create a challenge of luck of tools and software solutions for your problem.
If you need to model nested graphs, you could use a much simpler model of Named graphs, which could take you quite far.
The concept of the named graph came from the RDF community, which needed to group some sets of triples. In this way, you form subgraphs inside an existing graph. You could refer to the subgraph as a regular node. This setup simplifies complex graphs, introduces hierarchies, and even adds features and properties of hypergraphs while keeping a directed nature.
It looks complex, but it is not so hard to model it with a slight modification of a directed graph.
So, the node could host graphs inside. Let's reflect this fact with a location for a node. If a node belongs to a main graph, we could set the location to null or introduce a main node . it is up to you
Nodes could have edges to nodes in different subgraphs. This structure allows any kind of nesting graphs. Edges stay location-free
Meta Graphs in Relational Model
Let’s try to make several attempts to model different meta-graphs with some constraints.
Directed Metagraph where edges are not used as nodes and could not contain subgraphs

In this case, the edge always points to two sets of nodes. This introduces an overhead of creating a node set for a single node. In this model, we can model empty node sets that could require application-level constraints to prevent such cases.
Directed Metagraph where edges are not used as nodes and could contain subgraphs
Adding a node set that could model a subgraph located in an edge is easy but could be separate from in-vertex or out-vert.
I also do not see a direct need to include subgraphs to a node, as we could just use a node set interchangeably, but it still could be a case.Directed Metagraph where edges are used as nodes and could contain subgraphs
As you can notice, we operate all the time with node sets. We could simply allow the extension node set to elements set that include node and edge IDs, but in this case, we need to use uuid or any other strategy to differentiate node IDs from edge IDs. In this case, we have a collision of ephemeral edges or ephemeral nodes when we want to change the role and purpose of the node as an edge or vice versa.
A full-scale metagraph model is way too complex for a relational database.
So we need a better model.Now, we have more flexibility but loose structural constraints. We cannot show that the element should have one vertex, one vertex, or both. This type of constraint has been moved to the application level. Also, the crucial question is about query and retrieval needs.
Any meta-graph model should be more focused on domain and needs and should be used in raw form. We did it for a pure theoretical purpose. -
 @ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-12-07 15:03:06
@ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-12-07 15:03:06Hey folks! Today, let’s dive into the intriguing world of neurosymbolic approaches, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and personal knowledge graphs (PKGs). Together, these concepts hold much potential for bringing true reasoning capabilities to large language models (LLMs). So, let’s break down how symbolic logic, knowledge graphs, and modern AI can come together to empower future AI systems to reason like humans.
The Neurosymbolic Approach: What It Means ?
Neurosymbolic AI combines two historically separate streams of artificial intelligence: symbolic reasoning and neural networks. Symbolic AI uses formal logic to process knowledge, similar to how we might solve problems or deduce information. On the other hand, neural networks, like those underlying GPT-4, focus on learning patterns from vast amounts of data — they are probabilistic statistical models that excel in generating human-like language and recognizing patterns but often lack deep, explicit reasoning.
While GPT-4 can produce impressive text, it’s still not very effective at reasoning in a truly logical way. Its foundation, transformers, allows it to excel in pattern recognition, but the models struggle with reasoning because, at their core, they rely on statistical probabilities rather than true symbolic logic. This is where neurosymbolic methods and knowledge graphs come in.
Symbolic Calculations and the Early Vision of AI
If we take a step back to the 1950s, the vision for artificial intelligence was very different. Early AI research was all about symbolic reasoning — where computers could perform logical calculations to derive new knowledge from a given set of rules and facts. Languages like Lisp emerged to support this vision, enabling programs to represent data and code as interchangeable symbols. Lisp was designed to be homoiconic, meaning it treated code as manipulatable data, making it capable of self-modification — a huge leap towards AI systems that could, in theory, understand and modify their own operations.
Lisp: The Earlier AI-Language
Lisp, short for “LISt Processor,” was developed by John McCarthy in 1958, and it became the cornerstone of early AI research. Lisp’s power lay in its flexibility and its use of symbolic expressions, which allowed developers to create programs that could manipulate symbols in ways that were very close to human reasoning. One of the most groundbreaking features of Lisp was its ability to treat code as data, known as homoiconicity, which meant that Lisp programs could introspect and transform themselves dynamically. This ability to adapt and modify its own structure gave Lisp an edge in tasks that required a form of self-awareness, which was key in the early days of AI when researchers were exploring what it meant for machines to “think.”
Lisp was not just a programming language—it represented the vision for artificial intelligence, where machines could evolve their understanding and rewrite their own programming. This idea formed the conceptual basis for many of the self-modifying and adaptive algorithms that are still explored today in AI research. Despite its decline in mainstream programming, Lisp’s influence can still be seen in the concepts used in modern machine learning and symbolic AI approaches.
Prolog: Formal Logic and Deductive Reasoning
In the 1970s, Prolog was developed—a language focused on formal logic and deductive reasoning. Unlike Lisp, based on lambda calculus, Prolog operates on formal logic rules, allowing it to perform deductive reasoning and solve logical puzzles. This made Prolog an ideal candidate for expert systems that needed to follow a sequence of logical steps, such as medical diagnostics or strategic planning.
Prolog, like Lisp, allowed symbols to be represented, understood, and used in calculations, creating another homoiconic language that allows reasoning. Prolog’s strength lies in its rule-based structure, which is well-suited for tasks that require logical inference and backtracking. These features made it a powerful tool for expert systems and AI research in the 1970s and 1980s.
The language is declarative in nature, meaning that you define the problem, and Prolog figures out how to solve it. By using formal logic and setting constraints, Prolog systems can derive conclusions from known facts, making it highly effective in fields requiring explicit logical frameworks, such as legal reasoning, diagnostics, and natural language understanding. These symbolic approaches were later overshadowed during the AI winter — but the ideas never really disappeared. They just evolved.
Solvers and Their Role in Complementing LLMs
One of the most powerful features of Prolog and similar logic-based systems is their use of solvers. Solvers are mechanisms that can take a set of rules and constraints and automatically find solutions that satisfy these conditions. This capability is incredibly useful when combined with LLMs, which excel at generating human-like language but need help with logical consistency and structured reasoning.
For instance, imagine a scenario where an LLM needs to answer a question involving multiple logical steps or a complex query that requires deducing facts from various pieces of information. In this case, a solver can derive valid conclusions based on a given set of logical rules, providing structured answers that the LLM can then articulate in natural language. This allows the LLM to retrieve information and ensure the logical integrity of its responses, leading to much more robust answers.
Solvers are also ideal for handling constraint satisfaction problems — situations where multiple conditions must be met simultaneously. In practical applications, this could include scheduling tasks, generating optimal recommendations, or even diagnosing issues where a set of symptoms must match possible diagnoses. Prolog’s solver capabilities and LLM’s natural language processing power can make these systems highly effective at providing intelligent, rule-compliant responses that traditional LLMs would struggle to produce alone.
By integrating neurosymbolic methods that utilize solvers, we can provide LLMs with a form of deductive reasoning that is missing from pure deep-learning approaches. This combination has the potential to significantly improve the quality of outputs for use-cases that require explicit, structured problem-solving, from legal queries to scientific research and beyond. Solvers give LLMs the backbone they need to not just generate answers but to do so in a way that respects logical rigor and complex constraints.
Graph of Rules for Enhanced Reasoning
Another powerful concept that complements LLMs is using a graph of rules. A graph of rules is essentially a structured collection of logical rules that interconnect in a network-like structure, defining how various entities and their relationships interact. This structured network allows for complex reasoning and information retrieval, as well as the ability to model intricate relationships between different pieces of knowledge.
In a graph of rules, each node represents a rule, and the edges define relationships between those rules — such as dependencies or causal links. This structure can be used to enhance LLM capabilities by providing them with a formal set of rules and relationships to follow, which improves logical consistency and reasoning depth. When an LLM encounters a problem or a question that requires multiple logical steps, it can traverse this graph of rules to generate an answer that is not only linguistically fluent but also logically robust.
For example, in a healthcare application, a graph of rules might include nodes for medical symptoms, possible diagnoses, and recommended treatments. When an LLM receives a query regarding a patient’s symptoms, it can use the graph to traverse from symptoms to potential diagnoses and then to treatment options, ensuring that the response is coherent and medically sound. The graph of rules guides reasoning, enabling LLMs to handle complex, multi-step questions that involve chains of reasoning, rather than merely generating surface-level responses.
Graphs of rules also enable modular reasoning, where different sets of rules can be activated based on the context or the type of question being asked. This modularity is crucial for creating adaptive AI systems that can apply specific sets of logical frameworks to distinct problem domains, thereby greatly enhancing their versatility. The combination of neural fluency with rule-based structure gives LLMs the ability to conduct more advanced reasoning, ultimately making them more reliable and effective in domains where accuracy and logical consistency are critical.
By implementing a graph of rules, LLMs are empowered to perform deductive reasoning alongside their generative capabilities, creating responses that are not only compelling but also logically aligned with the structured knowledge available in the system. This further enhances their potential applications in fields such as law, engineering, finance, and scientific research — domains where logical consistency is as important as linguistic coherence.
Enhancing LLMs with Symbolic Reasoning
Now, with LLMs like GPT-4 being mainstream, there is an emerging need to add real reasoning capabilities to them. This is where neurosymbolic approaches shine. Instead of pitting neural networks against symbolic reasoning, these methods combine the best of both worlds. The neural aspect provides language fluency and recognition of complex patterns, while the symbolic side offers real reasoning power through formal logic and rule-based frameworks.
Personal Knowledge Graphs (PKGs) come into play here as well. Knowledge graphs are data structures that encode entities and their relationships — they’re essentially semantic networks that allow for structured information retrieval. When integrated with neurosymbolic approaches, LLMs can use these graphs to answer questions in a far more contextual and precise way. By retrieving relevant information from a knowledge graph, they can ground their responses in well-defined relationships, thus improving both the relevance and the logical consistency of their answers.
Imagine combining an LLM with a graph of rules that allow it to reason through the relationships encoded in a personal knowledge graph. This could involve using deductive databases to form a sophisticated way to represent and reason with symbolic data — essentially constructing a powerful hybrid system that uses LLM capabilities for language fluency and rule-based logic for structured problem-solving.
My Research on Deductive Databases and Knowledge Graphs
I recently did some research on modeling knowledge graphs using deductive databases, such as DataLog — which can be thought of as a limited, data-oriented version of Prolog. What I’ve found is that it’s possible to use formal logic to model knowledge graphs, ontologies, and complex relationships elegantly as rules in a deductive system. Unlike classical RDF or traditional ontology-based models, which sometimes struggle with complex or evolving relationships, a deductive approach is more flexible and can easily support dynamic rules and reasoning.
Prolog and similar logic-driven frameworks can complement LLMs by handling the parts of reasoning where explicit rule-following is required. LLMs can benefit from these rule-based systems for tasks like entity recognition, logical inferences, and constructing or traversing knowledge graphs. We can even create a graph of rules that governs how relationships are formed or how logical deductions can be performed.
The future is really about creating an AI that is capable of both deep contextual understanding (using the powerful generative capacity of LLMs) and true reasoning (through symbolic systems and knowledge graphs). With the neurosymbolic approach, these AIs could be equipped not just to generate information but to explain their reasoning, form logical conclusions, and even improve their own understanding over time — getting us a step closer to true artificial general intelligence.
Why It Matters for LLM Employment
Using neurosymbolic RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) in conjunction with personal knowledge graphs could revolutionize how LLMs work in real-world applications. Imagine an LLM that understands not just language but also the relationships between different concepts — one that can navigate, reason, and explain complex knowledge domains by actively engaging with a personalized set of facts and rules.
This could lead to practical applications in areas like healthcare, finance, legal reasoning, or even personal productivity — where LLMs can help users solve complex problems logically, providing relevant information and well-justified reasoning paths. The combination of neural fluency with symbolic accuracy and deductive power is precisely the bridge we need to move beyond purely predictive AI to truly intelligent systems.
Let's explore these ideas further if you’re as fascinated by this as I am. Feel free to reach out, follow my YouTube channel, or check out some articles I’ll link below. And if you’re working on anything in this field, I’d love to collaborate!
Until next time, folks. Stay curious, and keep pushing the boundaries of AI!
-
 @ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-12-07 14:54:46
@ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-12-07 14:54:46Introduction: Personal Knowledge Graphs and Linked Data
We will explore the world of personal knowledge graphs and discuss how they can be used to model complex information structures. Personal knowledge graphs aren’t just abstract collections of nodes and edges—they encode meaningful relationships, contextualizing data in ways that enrich our understanding of it. While the core structure might be a directed graph, we layer semantic meaning on top, enabling nuanced connections between data points.
The origin of knowledge graphs is deeply tied to concepts from linked data and the semantic web, ideas that emerged to better link scattered pieces of information across the web. This approach created an infrastructure where data islands could connect — facilitating everything from more insightful AI to improved personal data management.
In this article, we will explore how these ideas have evolved into tools for modeling AI’s semantic memory and look at how knowledge graphs can serve as a flexible foundation for encoding rich data contexts. We’ll specifically discuss three major paradigms: RDF (Resource Description Framework), property graphs, and a third way of modeling entities as graphs of graphs. Let’s get started.
Intro to RDF
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) has been one of the fundamental standards for linked data and knowledge graphs. RDF allows data to be modeled as triples: subject, predicate, and object. Essentially, you can think of it as a structured way to describe relationships: “X has a Y called Z.” For instance, “Berlin has a population of 3.5 million.” This modeling approach is quite flexible because RDF uses unique identifiers — usually URIs — to point to data entities, making linking straightforward and coherent.
RDFS, or RDF Schema, extends RDF to provide a basic vocabulary to structure the data even more. This lets us describe not only individual nodes but also relationships among types of data entities, like defining a class hierarchy or setting properties. For example, you could say that “Berlin” is an instance of a “City” and that cities are types of “Geographical Entities.” This kind of organization helps establish semantic meaning within the graph.
RDF and Advanced Topics
Lists and Sets in RDF
RDF also provides tools to model more complex data structures such as lists and sets, enabling the grouping of nodes. This extension makes it easier to model more natural, human-like knowledge, for example, describing attributes of an entity that may have multiple values. By adding RDF Schema and OWL (Web Ontology Language), you gain even more expressive power — being able to define logical rules or even derive new relationships from existing data.
Graph of Graphs
A significant feature of RDF is the ability to form complex nested structures, often referred to as graphs of graphs. This allows you to create “named graphs,” essentially subgraphs that can be independently referenced. For example, you could create a named graph for a particular dataset describing Berlin and another for a different geographical area. Then, you could connect them, allowing for more modular and reusable knowledge modeling.
Property Graphs
While RDF provides a robust framework, it’s not always the easiest to work with due to its heavy reliance on linking everything explicitly. This is where property graphs come into play. Property graphs are less focused on linking everything through triples and allow more expressive properties directly within nodes and edges.
For example, instead of using triples to represent each detail, a property graph might let you store all properties about an entity (e.g., “Berlin”) directly in a single node. This makes property graphs more intuitive for many developers and engineers because they more closely resemble object-oriented structures: you have entities (nodes) that possess attributes (properties) and are connected to other entities through relationships (edges).
The significant benefit here is a condensed representation, which speeds up traversal and queries in some scenarios. However, this also introduces a trade-off: while property graphs are more straightforward to query and maintain, they lack some complex relationship modeling features RDF offers, particularly when connecting properties to each other.
Graph of Graphs and Subgraphs for Entity Modeling
A third approach — which takes elements from RDF and property graphs — involves modeling entities using subgraphs or nested graphs. In this model, each entity can be represented as a graph. This allows for a detailed and flexible description of attributes without exploding every detail into individual triples or lump them all together into properties.
For instance, consider a person entity with a complex employment history. Instead of representing every employment detail in one node (as in a property graph), or as several linked nodes (as in RDF), you can treat the employment history as a subgraph. This subgraph could then contain nodes for different jobs, each linked with specific properties and connections. This approach keeps the complexity where it belongs and provides better flexibility when new attributes or entities need to be added.
Hypergraphs and Metagraphs
When discussing more advanced forms of graphs, we encounter hypergraphs and metagraphs. These take the idea of relationships to a new level. A hypergraph allows an edge to connect more than two nodes, which is extremely useful when modeling scenarios where relationships aren’t just pairwise. For example, a “Project” could connect multiple “People,” “Resources,” and “Outcomes,” all in a single edge. This way, hypergraphs help in reducing the complexity of modeling high-order relationships.
Metagraphs, on the other hand, enable nodes and edges to themselves be represented as graphs. This is an extremely powerful feature when we consider the needs of artificial intelligence, as it allows for the modeling of relationships between relationships, an essential aspect for any system that needs to capture not just facts, but their interdependencies and contexts.
Balancing Structure and Properties
One of the recurring challenges when modeling knowledge is finding the balance between structure and properties. With RDF, you get high flexibility and standardization, but complexity can quickly escalate as you decompose everything into triples. Property graphs simplify the representation by using attributes but lose out on the depth of connection modeling. Meanwhile, the graph-of-graphs approach and hypergraphs offer advanced modeling capabilities at the cost of increased computational complexity.
So, how do you decide which model to use? It comes down to your use case. RDF and nested graphs are strong contenders if you need deep linkage and are working with highly variable data. For more straightforward, engineer-friendly modeling, property graphs shine. And when dealing with very complex multi-way relationships or meta-level knowledge, hypergraphs and metagraphs provide the necessary tools.
The key takeaway is that only some approaches are perfect. Instead, it’s all about the modeling goals: how do you want to query the graph, what relationships are meaningful, and how much complexity are you willing to manage?
Conclusion
Modeling AI semantic memory using knowledge graphs is a challenging but rewarding process. The different approaches — RDF, property graphs, and advanced graph modeling techniques like nested graphs and hypergraphs — each offer unique strengths and weaknesses. Whether you are building a personal knowledge graph or scaling up to AI that integrates multiple streams of linked data, it’s essential to understand the trade-offs each approach brings.
In the end, the choice of representation comes down to the nature of your data and your specific needs for querying and maintaining semantic relationships. The world of knowledge graphs is vast, with many tools and frameworks to explore. Stay connected and keep experimenting to find the balance that works for your projects.
-
 @ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-12-07 14:52:47
@ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-12-07 14:52:47The temporal semantics and temporal and time-aware knowledge graphs. We have different memory models for artificial intelligence agents. We all try to mimic somehow how the brain works, or at least how the declarative memory of the brain works. We have the split of episodic memory and semantic memory. And we also have a lot of theories, right?
Declarative Memory of the Human Brain
How is the semantic memory formed? We all know that our brain stores semantic memory quite close to the concept we have with the personal knowledge graphs, that it’s connected entities. They form a connection with each other and all those things. So far, so good. And actually, then we have a lot of concepts, how the episodic memory and our experiences gets transmitted to the semantic:
- hippocampus indexing and retrieval
- sanitization of episodic memories
- episodic-semantic shift theory
They all give a different perspective on how different parts of declarative memory cooperate.
We know that episodic memories get semanticized over time. You have semantic knowledge without the notion of time, and probably, your episodic memory is just decayed.
But, you know, it’s still an open question:
do we want to mimic an AI agent’s memory as a human brain memory, or do we want to create something different?
It’s an open question to which we have no good answer. And if you go to the theory of neuroscience and check how episodic and semantic memory interfere, you will still find a lot of theories, yeah?
Some of them say that you have the hippocampus that keeps the indexes of the memory. Some others will say that you semantic the episodic memory. Some others say that you have some separate process that digests the episodic and experience to the semantics. But all of them agree on the plan that it’s operationally two separate areas of memories and even two separate regions of brain, and the semantic, it’s more, let’s say, protected.
So it’s harder to forget the semantical facts than the episodes and everything. And what I’m thinking about for a long time, it’s this, you know, the semantic memory.
Temporal Semantics
It’s memory about the facts, but you somehow mix the time information with the semantics. I already described a lot of things, including how we could combine time with knowledge graphs and how people do it.
There are multiple ways we could persist such information, but we all hit the wall because the complexity of time and the semantics of time are highly complex concepts.
Time in a Semantic context is not a timestamp.
What I mean is that when you have a fact, and you just mentioned that I was there at this particular moment, like, I don’t know, 15:40 on Monday, it’s already awake because we don’t know which Monday, right? So you need to give the exact date, but usually, you do not have experiences like that.
You do not record your memories like that, except you do the journaling and all of the things. So, usually, you have no direct time references. What I mean is that you could say that I was there and it was some event, blah, blah, blah.
Somehow, we form a chain of events that connect with each other and maybe will be connected to some period of time if we are lucky enough. This means that we could not easily represent temporal-aware information as just a timestamp or validity and all of the things.
For sure, the validity of the knowledge graphs (simple quintuple with start and end dates)is a big topic, and it could solve a lot of things. It could solve a lot of the time cases. It’s super simple because you give the end and start dates, and you are done, but it does not answer facts that have a relative time or time information in facts . It could solve many use cases but struggle with facts in an indirect temporal context. I like the simplicity of this idea. But the problem of this approach that in most cases, we simply don’t have these timestamps. We don’t have the timestamp where this information starts and ends. And it’s not modeling many events in our life, especially if you have the processes or ongoing activities or recurrent events.
I’m more about thinking about the time of semantics, where you have a time model as a hybrid clock or some global clock that does the partial ordering of the events. It’s mean that you have the chain of the experiences and you have the chain of the facts that have the different time contexts.
We could deduct the time from this chain of the events. But it’s a big, big topic for the research. But what I want to achieve, actually, it’s not separation on episodic and semantic memory. It’s having something in between.
Blockchain of connected events and facts
I call it temporal-aware semantics or time-aware knowledge graphs, where we could encode the semantic fact together with the time component.I doubt that time should be the simple timestamp or the region of the two timestamps. For me, it is more a chain for facts that have a partial order and form a blockchain like a database or a partially ordered Acyclic graph of facts that are temporally connected. We could have some notion of time that is understandable to the agent and a model that allows us to order the events and focus on what the agent knows and how to order this time knowledge and create the chains of the events.
Time anchors
We may have a particular time in the chain that allows us to arrange a more concrete time for the rest of the events. But it’s still an open topic for research. The temporal semantics gets split into a couple of domains. One domain is how to add time to the knowledge graphs. We already have many different solutions. I described them in my previous articles.
Another domain is the agent's memory and how the memory of the artificial intelligence treats the time. This one, it’s much more complex. Because here, we could not operate with the simple timestamps. We need to have the representation of time that are understandable by model and understandable by the agent that will work with this model. And this one, it’s way bigger topic for the research.”
-
 @ 3b19f10a:4e1f94b4
2024-12-07 09:55:46
@ 3b19f10a:4e1f94b4
2024-12-07 09:55:46 -
 @ b2d670de:907f9d4a
2024-12-02 21:24:45
@ b2d670de:907f9d4a
2024-12-02 21:24:45onion-service-nostr-relays
A list of nostr relays exposed as onion services.
The list
| Relay name | Description | Onion url | Operator | Payment URL | Payment options | | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | | nostr.oxtr.dev | Same relay as clearnet relay nostr.oxtr.dev | ws://oxtrdevav64z64yb7x6rjg4ntzqjhedm5b5zjqulugknhzr46ny2qbad.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | relay.snort.social | Same relay as clearnet relay relay.snort.social | wss://skzzn6cimfdv5e2phjc4yr5v7ikbxtn5f7dkwn5c7v47tduzlbosqmqd.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | nostr.thesamecat.io | Same relay as clearnet relay nostr.thesamecat.io | ws://2jsnlhfnelig5acq6iacydmzdbdmg7xwunm4xl6qwbvzacw4lwrjmlyd.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | nostr.land | The nostr.land paid relay (same as clearnet) | ws://nostrland2gdw7g3y77ctftovvil76vquipymo7tsctlxpiwknevzfid.onion | operator | Payment URL | BTC LN | | bitcoiner.social | No auth required, currently | ws://bitcoinr6de5lkvx4tpwdmzrdfdpla5sya2afwpcabjup2xpi5dulbad.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | relay.westernbtc.com | The westernbtc.com paid relay | ws://westbtcebhgi4ilxxziefho6bqu5lqwa5ncfjefnfebbhx2cwqx5knyd.onion | operator | Payment URL | BTC LN | | freelay.sovbit.host | Free relay for sovbit.host | ws://sovbitm2enxfr5ot6qscwy5ermdffbqscy66wirkbsigvcshumyzbbqd.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | nostr.sovbit.host | Paid relay for sovbit.host | ws://sovbitgz5uqyh7jwcsudq4sspxlj4kbnurvd3xarkkx2use3k6rlibqd.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | nostr.wine | 🍷 nostr.wine relay | ws://nostrwinemdptvqukjttinajfeedhf46hfd5bz2aj2q5uwp7zros3nad.onion | operator | Payment URL | BTC LN, BTC, Credit Card/CashApp (Stripe) | | inbox.nostr.wine | 🍷 inbox.nostr.wine relay | ws://wineinboxkayswlofkugkjwhoyi744qvlzdxlmdvwe7cei2xxy4gc6ad.onion | operator | Payment URL | BTC LN, BTC | | filter.nostr.wine | 🍷 filter.nostr.wine proxy relay | ws://winefiltermhqixxzmnzxhrmaufpnfq3rmjcl6ei45iy4aidrngpsyid.onion | operator | Payment URL | BTC LN, BTC | | N/A | N/A | ws://pzfw4uteha62iwkzm3lycabk4pbtcr67cg5ymp5i3xwrpt3t24m6tzad.onion:81 | operator | N/A | N/A | | nostr.fractalized.net | Free relay for fractalized.net | ws://xvgox2zzo7cfxcjrd2llrkthvjs5t7efoalu34s6lmkqhvzvrms6ipyd.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | nfrelay.app | nfrelay.app aggregator relay (nostr-filter-relay) | ws://nfrelay6saohkmipikquvrn6d64dzxivhmcdcj4d5i7wxis47xwsriyd.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | relay.nostr.net | Public relay from nostr.net (Same as clearnet) | ws://nostrnetl6yd5whkldj3vqsxyyaq3tkuspy23a3qgx7cdepb4564qgqd.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | nerostrator | Free to read, pay XMR to relay | ws://nerostrrgb5fhj6dnzhjbgmnkpy2berdlczh6tuh2jsqrjok3j4zoxid.onion | operator |Payment URL | XMR | | nostr.girino.org | Public relay from nostr.girino.org | ws://gnostr2jnapk72mnagq3cuykfon73temzp77hcbncn4silgt77boruid.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | wot.girino.org | WoT relay from wot.girino.org | ws://girwot2koy3kvj6fk7oseoqazp5vwbeawocb3m27jcqtah65f2fkl3yd.onion | operator | N/A | N/A | | haven.girino.org/{outbox, inbox, chat, private} | Haven smart relay from haven.girino.org | ws://ghaven2hi3qn2riitw7ymaztdpztrvmm337e2pgkacfh3rnscaoxjoad.onion/{outbox, inbox, chat, private} | operator | N/A | N/A | | relay.nostpy.lol | Free Web of Trust relay (Same as clearnet) | ws://pemgkkqjqjde7y2emc2hpxocexugbixp42o4zymznil6zfegx5nfp4id.onion | operator |N/A | N/A | | Poster.place Nostr Relay | N/A | ws://dmw5wbawyovz7fcahvguwkw4sknsqsalffwctioeoqkvvy7ygjbcuoad.onion | operator | N/A | N/A |
Contributing
Contributions are encouraged to keep this document alive. Just open a PR and I'll have it tested and merged. The onion URL is the only mandatory column, the rest is just nice-to-have metadata about the relay. Put
N/Ain empty columns.If you want to contribute anonymously, please contact me on SimpleX or send a DM on nostr using a disposable npub.
Operator column
It is generally preferred to use something that includes a NIP-19 string, either just the string or a url that contains the NIP-19 string in it (e.g. an njump url).
-
 @ e31e84c4:77bbabc0
2024-12-02 10:44:07
@ e31e84c4:77bbabc0
2024-12-02 10:44:07Bitcoin and Fixed Income was Written By Wyatt O’Rourke. If you enjoyed this article then support his writing, directly, by donating to his lightning wallet: ultrahusky3@primal.net
Fiduciary duty is the obligation to act in the client’s best interests at all times, prioritizing their needs above the advisor’s own, ensuring honesty, transparency, and avoiding conflicts of interest in all recommendations and actions.
This is something all advisors in the BFAN take very seriously; after all, we are legally required to do so. For the average advisor this is a fairly easy box to check. All you essentially have to do is have someone take a 5-minute risk assessment, fill out an investment policy statement, and then throw them in the proverbial 60/40 portfolio. You have thousands of investment options to choose from and you can reasonably explain how your client is theoretically insulated from any move in the \~markets\~. From the traditional financial advisor perspective, you could justify nearly anything by putting a client into this type of portfolio. All your bases were pretty much covered from return profile, regulatory, compliance, investment options, etc. It was just too easy. It became the household standard and now a meme.
As almost every real bitcoiner knows, the 60/40 portfolio is moving into psyop territory, and many financial advisors get clowned on for defending this relic on bitcoin twitter. I’m going to specifically poke fun at the ‘40’ part of this portfolio.
The ‘40’ represents fixed income, defined as…
An investment type that provides regular, set interest payments, such as bonds or treasury securities, and returns the principal at maturity. It’s generally considered a lower-risk asset class, used to generate stable income and preserve capital.
Historically, this part of the portfolio was meant to weather the volatility in the equity markets and represent the “safe” investments. Typically, some sort of bond.
First and foremost, the fixed income section is most commonly constructed with U.S. Debt. There are a couple main reasons for this. Most financial professionals believe the same fairy tale that U.S. Debt is “risk free” (lol). U.S. debt is also one of the largest and most liquid assets in the market which comes with a lot of benefits.
There are many brilliant bitcoiners in finance and economics that have sounded the alarm on the U.S. debt ticking time bomb. I highly recommend readers explore the work of Greg Foss, Lawrence Lepard, Lyn Alden, and Saifedean Ammous. My very high-level recap of their analysis:
-
A bond is a contract in which Party A (the borrower) agrees to repay Party B (the lender) their principal plus interest over time.
-
The U.S. government issues bonds (Treasury securities) to finance its operations after tax revenues have been exhausted.
-
These are traditionally viewed as “risk-free” due to the government’s historical reliability in repaying its debts and the strength of the U.S. economy
-
U.S. bonds are seen as safe because the government has control over the dollar (world reserve asset) and, until recently (20 some odd years), enjoyed broad confidence that it would always honor its debts.
-
This perception has contributed to high global demand for U.S. debt but, that is quickly deteriorating.
-
The current debt situation raises concerns about sustainability.
-
The U.S. has substantial obligations, and without sufficient productivity growth, increasing debt may lead to a cycle where borrowing to cover interest leads to more debt.
-
This could result in more reliance on money creation (printing), which can drive inflation and further debt burdens.
In the words of Lyn Alden “Nothing stops this train”
Those obligations are what makes up the 40% of most the fixed income in your portfolio. So essentially you are giving money to one of the worst capital allocators in the world (U.S. Gov’t) and getting paid back with printed money.
As someone who takes their fiduciary responsibility seriously and understands the debt situation we just reviewed, I think it’s borderline negligent to put someone into a classic 60% (equities) / 40% (fixed income) portfolio without serious scrutiny of the client’s financial situation and options available to them. I certainly have my qualms with equities at times, but overall, they are more palatable than the fixed income portion of the portfolio. I don’t like it either, but the money is broken and the unit of account for nearly every equity or fixed income instrument (USD) is fraudulent. It’s a paper mache fade that is quite literally propped up by the money printer.
To briefly be as most charitable as I can – It wasn’t always this way. The U.S. Dollar used to be sound money, we used to have government surplus instead of mathematically certain deficits, The U.S. Federal Government didn’t used to have a money printing addiction, and pre-bitcoin the 60/40 portfolio used to be a quality portfolio management strategy. Those times are gone.
Now the fun part. How does bitcoin fix this?
Bitcoin fixes this indirectly. Understanding investment criteria changes via risk tolerance, age, goals, etc. A client may still have a need for “fixed income” in the most literal definition – Low risk yield. Now you may be thinking that yield is a bad word in bitcoin land, you’re not wrong, so stay with me. Perpetual motion machine crypto yield is fake and largely where many crypto scams originate. However, that doesn’t mean yield in the classic finance sense does not exist in bitcoin, it very literally does. Fortunately for us bitcoiners there are many other smart, driven, and enterprising bitcoiners that understand this problem and are doing something to address it. These individuals are pioneering new possibilities in bitcoin and finance, specifically when it comes to fixed income.
Here are some new developments –
Private Credit Funds – The Build Asset Management Secured Income Fund I is a private credit fund created by Build Asset Management. This fund primarily invests in bitcoin-backed, collateralized business loans originated by Unchained, with a secured structure involving a multi-signature, over-collateralized setup for risk management. Unchained originates loans and sells them to Build, which pools them into the fund, enabling investors to share in the interest income.
Dynamics
- Loan Terms: Unchained issues loans at interest rates around 14%, secured with a 2/3 multi-signature vault backed by a 40% loan-to-value (LTV) ratio.
- Fund Mechanics: Build buys these loans from Unchained, thus providing liquidity to Unchained for further loan originations, while Build manages interest payments to investors in the fund.
Pros
- The fund offers a unique way to earn income via bitcoin-collateralized debt, with protection against rehypothecation and strong security measures, making it attractive for investors seeking exposure to fixed income with bitcoin.
Cons
- The fund is only available to accredited investors, which is a regulatory standard for private credit funds like this.
Corporate Bonds – MicroStrategy Inc. (MSTR), a business intelligence company, has leveraged its corporate structure to issue bonds specifically to acquire bitcoin as a reserve asset. This approach allows investors to indirectly gain exposure to bitcoin’s potential upside while receiving interest payments on their bond investments. Some other publicly traded companies have also adopted this strategy, but for the sake of this article we will focus on MSTR as they are the biggest and most vocal issuer.
Dynamics
-
Issuance: MicroStrategy has issued senior secured notes in multiple offerings, with terms allowing the company to use the proceeds to purchase bitcoin.
-
Interest Rates: The bonds typically carry high-yield interest rates, averaging around 6-8% APR, depending on the specific issuance and market conditions at the time of issuance.
-
Maturity: The bonds have varying maturities, with most structured for multi-year terms, offering investors medium-term exposure to bitcoin’s value trajectory through MicroStrategy’s holdings.
Pros
-
Indirect Bitcoin exposure with income provides a unique opportunity for investors seeking income from bitcoin-backed debt.
-
Bonds issued by MicroStrategy offer relatively high interest rates, appealing for fixed-income investors attracted to the higher risk/reward scenarios.
Cons
-
There are credit risks tied to MicroStrategy’s financial health and bitcoin’s performance. A significant drop in bitcoin prices could strain the company’s ability to service debt, increasing credit risk.
-
Availability: These bonds are primarily accessible to institutional investors and accredited investors, limiting availability for retail investors.
Interest Payable in Bitcoin – River has introduced an innovative product, bitcoin Interest on Cash, allowing clients to earn interest on their U.S. dollar deposits, with the interest paid in bitcoin.
Dynamics
-
Interest Payment: Clients earn an annual interest rate of 3.8% on their cash deposits. The accrued interest is converted to Bitcoin daily and paid out monthly, enabling clients to accumulate Bitcoin over time.
-
Security and Accessibility: Cash deposits are insured up to $250,000 through River’s banking partner, Lead Bank, a member of the FDIC. All Bitcoin holdings are maintained in full reserve custody, ensuring that client assets are not lent or leveraged.
Pros
-
There are no hidden fees or minimum balance requirements, and clients can withdraw their cash at any time.
-
The 3.8% interest rate provides a predictable income stream, akin to traditional fixed-income investments.
Cons
-
While the interest rate is fixed, the value of the Bitcoin received as interest can fluctuate, introducing potential variability in the investment’s overall return.
-
Interest rate payments are on the lower side
Admittedly, this is a very small list, however, these types of investments are growing more numerous and meaningful. The reality is the existing options aren’t numerous enough to service every client that has a need for fixed income exposure. I challenge advisors to explore innovative options for fixed income exposure outside of sovereign debt, as that is most certainly a road to nowhere. It is my wholehearted belief and call to action that we need more options to help clients across the risk and capital allocation spectrum access a sound money standard.
Additional Resources
-
River: The future of saving is here: Earn 3.8% on cash. Paid in Bitcoin.
-
MicroStrategy: MicroStrategy Announces Pricing of Offering of Convertible Senior Notes
Bitcoin and Fixed Income was Written By Wyatt O’Rourke. If you enjoyed this article then support his writing, directly, by donating to his lightning wallet: ultrahusky3@primal.net
-
-
 @ 79008e78:dfac9395
2024-12-01 03:15:00
@ 79008e78:dfac9395
2024-12-01 03:15:00บทที่ 1: เกริ่นนำ
เกริ่นนำเรื่องราวของบิตคอยน์แบบกระทัดรัด
บิตคอยน์ (Bitcoin) เป็นชุดแนวคิดและเทคโนโลยีที่เข้ามาผสมผสานรวมกันจนได้กลายเป็นระบบเงินสดอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ หน่วยเงินที่เรียกว่าบิตคอยน์นั้น ใช้เพื่อเก็บและส่งต่อมูลค่าให้กับผู้ใช้คนอื่น ๆ ในระบบ ผู้ใช้ทั้งระบบสื่อสารกันบนโปรโตคอลของบิตคอยน์ โดยผู้ใช้ส่วนใหญ่ก็เข้าถึงกันผ่านอินเตอร์เน็ต แต่ก็ไม่ได้หมายความว่าระบบนี้ไม่สามารถใช้เครือข่ายการสื่อสารรูปแบบอื่นได้ ซอฟต์แวร์ของโปรโตคอลนี้เป็นโอเพนซอร์สและสามารถรันได้บนอุปกรณ์คอมพิวเตอร์หลายประเภท เช่น แล็ปท็อปและสมาร์ทโฟน และสิ่งนี้เองที่ทำให้เทคโนโลยีนี้สามารถเข้าถึงได้ง่าย
ผู้ใช้งานสามารถส่งบิตคอยน์ให้กันผ่านเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์เพื่อทำกิจกรรมต่าง ๆ เช่น ซื้อ-ขายแลกเปลี่ยนสินค้าและบริการ หรือใช้เพื่อแลกเปลี่ยนเป็นสกุลเงินต่าง ๆ ซึ่งถือว่าเหมาะสมเป็นอย่างมากสำหรับการใช้งานบนอินเทอร์เน็ต เพราะมีทั้งความรวดเร็ว ความปลอดภัย และยังข้อจำกัดเรื่องพรมแดน
ซึ่งบิตคอยน์นั้นแตกต่างจากสกุลเงินโดยทั่วไป เนื่องจากเป็นระบบเงินอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ จึงไม่มีเหรียญหรือธนบัตรจริง ๆ ให้ได้จับต้อง แต่คำว่าเหรียญที่มักใช้กันในสังคมของบิตคอยน์จะหมายถึงในธุรกรรมที่ผู้ใช้รายหนึ่งโอนมูลค่าไปยังผู้ใช้อีกรายหนึ่ง ผู้ใช้งานบิตคอยน์จะควบคุมคีย์ (Private Key) ที่ใช้พิสูจน์ความเป็นเจ้าของในบิตคอยน์นั้น ๆ ในเครือข่าย และด้วยคีย์นี้เองทำให้พวกเขาสามารถเซ็นชื่อในธุรกรรมเพื่อปลดล็อกมูลค่าและทำการส่งมันต่อไปยังผู้รับอีกรายหนึ่ง ซึ่งมักจะถูกเก็บอยู่ในกระเป๋าเงินดิจิทัล หรือสมาร์ทโฟนของผู้ใช้งาน การครอบครองคีย์ที่สามารถเซ็นชื่อในธุรกรรมได้เป็นสิ่งเดียวที่จำเป็นในการใช้จ่ายในระบบของบิตคอยน์ และนั่นเป็นเหตุผลที่ทำให้ความสามารถในการควบคุมบิตคอยน์อยู่ในมือผู้ใช้แต่ละคน
เข้าใจว่าในบริบทนี้น่าจะหมายถึง Hot-wallet เพราะงั้นผมไม่ได้แนะนำให้เก็บคีย์คอมพิวเตอร์หรือมือถือนะครับ ส่วนถ้าคุณอยากทำก็เรื่องของคุณจ้าแนะนำเฉย ๆ อยากทำไรทำ
บิตคอยน์นั้นเป็นระบบแบบกระจายศูนย์และทำงานแบบเพียร์-ทู-เพียร์ (Peer-to-Peer) หรือเอาภาษาบ้าน ๆ ว่า เป็นระบบการทำงานแบบบุคคลสู่บุลคลที่ไม่มีตัวกลางระหว่างการทำงาน ดังนั้นจึงไม่มีเซิร์ฟเวอร์กลางหรือจุดควบคุม บิตคอยน์นั้นถูกสร้างขึ้นโดยกระบวนการที่เรียกว่าการขุด ซึ่งเป็นการทำงานทางการคำนวณซ้ำ ๆ ที่อ้างอิงกับรายการธุรกรรมบิตคอยน์ล่าสุด (จริง ๆ ก็มี hash ของบล็อกก่อนหน้าด้วย) ซึ่งผู้ใช้งานบิตคอยน์ทุกคนสามารถที่จะขุดบิตคอยน์ได้ โดยใช้อุปกรณ์คอมพิวเตอร์ของตนเพื่อช่วยรักษาความปลอดภัยในธุรกรรม โดยทุก ๆ สิบนาทีโดยเฉลี่ยนั้น จะมีนักขุดคนหนึ่งที่ได้ช่วยเพิ่มความปลอดภัยให้กับธุรกรรมในอดีต และจะได้รับรางวัลเป็นบิตคอยน์ใหม่และค่าธรรมเนียมจากธุรกรรมชุดล่าสุด ซึ่งกระบวนการนี้ทำให้การออกสกุลเงินและการชำระธุรกรรมไม่จำเป็นต้องมีธนาคารกลาง
โปรโตคอลของบิตคอยน์ มีอัลกอรึทึมที่คอยควบคุมความยากง่ายในการการขุดให้อยู่ในระดับที่เหมาะสม โดยความยากง่ายในการขุดจะขึ้นจะถูกปรับตามระยะเวลาเฉลี่ยของการขุดในช่วงก่อนหน้านี้เพื่อให้การขุดนั้นมีโอกาสสำเร็จเฉลี่ยในทุก ๆ 10 นาที ไม่ว่ามีจำนวนผู้ขุดและการประมวลผลเท่าใดก็ตาม และนอกจากนี้เองโปรโตคอลของบิตคอยน์นั้นยังลดจำนวนของบิตคอยน์ที่นักขุดจะได้เป็นรางวัลลงเรื่อย ๆ ซึ่งจะทำให้บิตคอยน์ที่สร้างได้ในระบบนั้นมีไม่เกิน 21,000,000 ล้านบิตคอยน์ ซึ่งผลลัพธ์ที่ได้ก็คือ จำนวนบิตคอยน์ที่หมุนเวียนในระบบนั้นจะสามารถคาดเดาได้อย่างง่ายดาย ซึ่งอีกครึ่งหนึ่งของบิตคอยน์ที่เหลืออยู่จะถูกเพิ่มเข้าไปในระบบทุก ๆ 4 ปี และที่บล๊อกประมาณ 1,411,200 ซึ่งคาดว่าจะเกิดประมาณปี 2035 จะมีบิตคอยน์เป็นจำนวน 99 % ของที่สามารถเกิดขึ้นได้ในระบบ เนื่องจากอัตราการการผลิตของบิตคอยน์ที่น้อยลงเรื่อย ๆ ทำให้บิตคอยน์มีลักษณะของเงินฝืดในระยะยาว นอกจากนี้ยังไม่มีใครที่สามารถบังคับให้คุณรับบิตคอยน์ที่ถูกผลิตมานอกเหนือจากชุดกฎที่คุณเลือกได้
เบื้องหลังต่าง ๆ ของโปรโตคอลบิตคอยน์ที่ทำให้มันเป็น เครือข่ายแบบบุคคลถึงบุคคล และการคำนวณแบบกระจายศูนย์นั้น ถูกสร้างขึ้นมาบนพื้นฐานของงานวิจัยในด้านการเข้ารหัสและระบบกระจายศูนย์มาเนิ่นนานหลายทศวรรษ โดยมีการรวมเอานวัตกรรมสำคัญ ๆ 4 อย่างนี้มารวมเข้าด้วยกัน:
- เครือข่ายเพียร์ทูเพียร์ที่กระจายศูนย์ (ฺBitcoin protocol)
- บัญชีธุรกรรมสาธารณะ (Blockchain)
- ชุดของกฎในการตรวจสอบธุรกรรมอย่างอิสระและการออกสกุลเงิน ( consensus rules )
- กลไกในการหาข้อตกลงร่วมกันทั่วโลกเกี่ยวกับบล็อกเชนที่ถูกต้อง (PoW algorithm)
ในมุมมองของนักพัฒนา นาย Andreas M. Antonopoulos and David A. Harding ( ไม่ใช่ผมจ้าา ถึงจะเห็นด้วยก็ตาม) พวกเขามองว่าบิตคอยน์นั้นคล้ายกับอินเทอร์เน็ตของเงิน เป็นเครือข่ายสำหรับการกระจายมูลค่าและการรักษาความเป็นเจ้าของสินทรัพย์ดิจิทัลผ่านการคำนวณแบบกระจายศูนย์ ซึ่งบิตคอยน์มีรายระเอียดเยอะกว่าที่พวกเขาเห็นในตอนแรกมาก ๆ
ในบทนี้เองจะเป็นการอธิบายแนวคิด และคำศัพท์หลัก ๆ รวมทั้งการติดตั้งซอฟแวร์ต่าง ๆ ที่จำเป็นในการทอดลองใช้บิตคอยน์สำหรับทำธุรกรรมง่าย ๆ และสำหรับในบทถัดไป เราจะทำการดำดิ่งลงไปในเทคโนโลยีต่าง ๆ ที่ประกอบรวมกันเป็นบิตคอยน์ว่าทำไมมันถึงเป็นไปได้ และตรวจสอบการทำงานภายในของเครือข่ายและโปรโตคอล
ก่อนการมาถึงของบิตคอยน์
สกุลเงินดิจิทัลที่ใช้งานได้จริงในอดีตนั้นมักเกี่ยวข้องกับพัฒนาการในด้านการเข้ารหัส ซึ่งนั่นก็ไม่ได้แปลกอะไรหากเราพิจารณาถึงปัญหาพื้นฐานในการใช้ข้อมูลเพื่อแทนมูลค่าที่สามารถแลกเปลี่ยนเป็นสินค้าและบริการ โดยการที่เงินดิจิทัลจะถูกยอมรับได้นั้นมักจะต้องสามารถตอบคำถามทั้งสามข้อนี้ได้เสียก่อน:
- ฉันจะเชื่อได้อย่างไรว่าเงินนั้นเป็นของจริงและไม่ใช่ของปลอม?
- ฉันจะเชื่อได้อย่างไรว่าเงินดิจิทัลสามารถใช้ได้เพียงครั้งเดียว (ปัญหาการใช้ซ้ำหรือ "double-spend")?
- ฉันจะมั่นใจได้อย่างไรว่าไม่มีใครสามารถอ้างสิทธิ์ว่าเงินนี้เป็นของพวกเขาไม่ใช่ของฉัน?
ผู้ที่ออกเงินกระดาษเองก็พยายามต่อสู้กับปัญหาการปลอมแปลงโดยการใช้เทคโนโลยีการพิมพ์ที่ซับซ้อนมากขึ้นเรื่อย ๆ และเงินกายภาพเองก็จัดการปัญหาการใช้ซ้ำได้ง่ายเพราะธนบัตรเดียวกันไม่สามารถอยู่ในสองที่พร้อมกันได้ แน่นอนละว่าเงินทั่วไปก็ถูกเก็บและส่งแบบดิจิทัลเช่นกัน ในกรณีเหล่านี้ ปัญหาการปลอมแปลงและการใช้ซ้ำจะถูกจัดการโดยการเคลียร์ธุรกรรมทางอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ทั้งหมดผ่านหน่วยงานกลางที่สามารถตรวจสอบสถานะของเงินได้ แต่สำหรับเงินดิจิทัลที่ไม่สามารถใช้หมึกพิเศษหรือแถบโฮโลแกรมได้ การเข้ารหัสจึงเป็นพื้นฐานสำคัญในการยืนยันความถูกต้องของการอ้างสิทธิ์ในมูลค่าของผู้ใช้ โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่ง การเซ็นชื่อดิจิทัลที่เข้ารหัสช่วยให้ผู้ใช้สามารถเซ็นชื่อในสินทรัพย์ดิจิทัลหรือธุรกรรมเพื่อยืนยันการเป็นเจ้าของสินทรัพย์นั้น ซึ่งสิ่งนี้เองยังสามารถใช้ในการแก้ปัญหาการใช้ซ้ำ (doble-spending) ได้
ศาสตร์ของการเข้ารหัสนั้นเริ่มเป็นที่แพร่หลายในช่วงปลายของทศวรรษที่ 1980 นักวิจัยหลายคนเริ่มพยายามใช้การเข้ารหัสเพื่อสร้างสกุลเงินดิจิทัล โดยโครงการเงินดิจิทัลในยุคแรก ๆ นั้นมักจะออกเงินดิจิทัลที่มีการสนับสนุนโดยสกุลเงินของชาติหรือโลหะมีค่าอย่างเช่น ทองคำ
ซึ่งแม้ว่าสกุลเงินดิจิทัลยุคแรกเหล่านี้จะทำงานได้ แต่ก็มีปัญหาที่การรวมศูนย์ของระบบ เนื่องจากมันทำให้ระบบเป็นเป้าหมายที่ง่ายต่อการโจมตีโดยรัฐบาลและเหล่าแฮกเกอร์ สกุลเงินดิจิทัลยุคแรกใช้ศูนย์กลางในการชำระธุรกรรมทั้งหมดเป็นระยะ ๆ เช่นเดียวกับระบบธนาคารทั่วไป เป็นที่น่าเสียดายที่สกุลเงินดิจิทัลเหล่านี้ส่วนใหญ่ถูกกำหนดเป้าหมายโดยรัฐบาลที่กังวลและมักจะถูกฟ้องร้องจนล้มเหลว บางส่วนล้มเหลวอย่างรวดเร็วเมื่อบริษัทผู้ก่อตั้งปิดตัวลงอย่างกะทันหัน และเพื่อให้สกุลเงินดิจิทัลมีความแข็งแกร่งต่อต้านการแทรกแซงจากศัตรู ไม่ว่าจะเป็นรัฐบาลที่ถูกกฎหมายหรืออาชญากรรม เราจึงจำเป็นต้องมีสกุลเงินดิจิทัลที่กระจายศูนย์ เพื่อป้องกันปัญหาดังกล่าว ซึ่งบิตคอยน์คือระบบแบบนั้น ระบบที่ถูกออกแบบให้กระจายศูนย์ และปราศจากอำนาจหรือจุดควบคุมกลางใด ๆ ที่สามารถถูกโจมตีหรือทำให้เสียหายได้
ประวัติของบิตคอยน์
บิตคอยน์ได้ปรากฏครั้งแรกในปี 2008 บนเอกสารที่มีชื่อว่า “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” ซึ่งถูกเขียนโดยบุคคลหรือกลุ่มคนนิรนามที่ใช้นามแฝงว่า ซาโตชิ นากาโมโตะ ซึ่งได้มีการนำนวัตกรรมหลาย ๆ อย่างมารวมเข้าด้วยกัน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นลายเซ็นดิจิทัล และ Hashcash มาสร้างระบบเงินสดอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ที่กระจายศูนย์อย่างสมบูรณ์ ซึ่งไม่ต้องพึ่งพาหน่วยงานกลางในการออกสกุลเงินหรือการชำระและตรวจสอบธุรกรรม โดยนวัตกรรมสำคัญคือการใช้ระบบคำนวณแบบกระจายศูนย์ (Proof-of-work) เพื่อทำสิ่งที่คล้าย ๆ กับการจับฉลากทุก ๆ 10 นาที ทำให้เครือข่ายที่กระจายศูนย์สามารถมีฉันทามติในสถานะของธุรกรรมได้ และสิ่งนี้เองยังสามารถแก้ไขปัญหาการทำธุรกรรมซ้ำซ้อน ซึ่งเป็นข้อบกพร่องของสกุลเงินดิจิทัลที่เคยต้องใช้หน่วยงานกลางในการตรวจสอบธุรกรรมทั้งหมดได้อีกด้วย
เครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์นั้นเริ่มต้นขึ้นในปี 2009 โดยอ้างอิงจากซอฟแวร์ที่เผยแพร่โดย ซาโตชิ และได้ถูกปรับปรุงโดยโปรแกรมเมอร์คนอื่น ๆ มากมายนับไม่ถ้วนมานับตั้งแต่นั้น จำนวนและกำลังของอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ประมวลผล Proof of Work algorithm (การขุด) เองนั้นก็เพิ่มขึ้นอย่างมหาศาล จนในปัจจุบันนี้พลังการคำนวณรวมกันของเครือข่ายนี้มีมากกว่าจำนวนการคำนวณของซุปเปอร์คอมพิวเตอร์ชั้นนำของโลกทั้งหมดรวมกันเสียอีก ซึ่งสิ่งนี้เองได้ช่วยรักษาความปลอดภัยและความเสถียรของเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์ได้เป็นอย่างดี
ซาโตชิ นากาโมโตะ ได้ทำการถอนตัวและหายตัวไปในเดือนเมษายนในปี 2011 และมอบหมายความรับผิดชอบในการพัฒนาโค้ดและเครือข่ายให้กับกลุ่มอาสาสมัครที่เติบโตขึ้นเรื่อย ๆ ซึ่งตัวตนของบุคคลหรือกลุ่มคนที่อยู่เบื้องหลังบิตคอยน์นั้นยังไม่เป็นที่รู้จัก แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม ไม่ว่าจะเป็นซาโตชิ นากาโมโตะ หรือใครหน้าไหนก็ตามก็ไม่สามารถควบคุมเครือข่ายของบิตคอยน์ได้ตามลำพัง เนื่องจากมันอยู่บนหลักการทางคณิตศาสตร์ที่โปร่งใส โค้ดโอเพนซอร์ส และฉันทามติจากผู้ที่เข้าร่วม โดยนวัตกรรมนี้ถือเป็นการเปลี่ยนแปลงครั้งใหญ่และได้ก่อให้เกิดวิทยาการใหม่ในด้านการคำนวณแบบกระจายศูนย์ เศรษฐศาสตร์ และเศรษฐมิติอีกด้วย
การแก้ปัญหาในระบบคำนวณแบบกระจายศูนย์
นวัตกรรมของซาโตชิ นากาโมโตะ ยังเป็นการแก้ไขปัญหาที่มีประสิทธิภาพและแปลกใหม่สำหรับปัญหาในระบบคำนวณแบบกระจายศูนย์ที่เรียกว่า "Byzantine Generals' Problem" ซึ่งปัญหานี้เกี่ยวข้องกับการพยายามทำให้ผู้เข้าร่วมหลายคนที่ไม่มีผู้นำสามารถตกลงกันในแผนการดำเนินการได้โดยการแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลในเครือข่ายที่ไม่น่าเชื่อถือและอาจถูกโจมตีได้ โดยการแก้ปัญหาของซาโตชินั้นได้ใช้แนวคิด proof of work เพื่อหาฉันทามติโดยไม่ต้องมีผู้ควบคุมที่น่าเชื่อถือ ถือเป็นความก้าวหน้าในด้านการคำนวณแบบกระจายศูนย์
เปิดประตูสู่บิตคอยน์
บิตคอยน์เป็นโปรโตคอลที่สามารถเข้าถึงได้ผ่านทางแอปพลิเคชันที่มีการรับรองโปรโตคอลนี้ Bitcoin wallet นั้นเป็นช่องทางหลักที่ผู้ใช้งานส่วนใหญ่เลือกใช้เพื่อเข้าถึงโปรโตคอลของบิตคอยน์ เช่นเดียวกันกับที่ผู้ใช้งานอินเตอร์เน็ตส่วนใหญ่ใช้เว็บบราวเซอร์เป็นช่องทางในการเข้าถึงโปรโตคอลอย่าง HTTP นั่นเอง Bitcoin wallet เองก็มีหลากหลายยี่ห้อเฉกเช่นเดียวกับเว็บบราวเซอร์ อาทิเช่น chorme, safari, firefox ฯลฯ Bitcoin wallet เองก็เช่นกัน แต่ละยี่ห้อเองก็มีความแตกต่างกันในด้านต่าง ๆ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นในด้านคุณภาพ ประสิทธิภาพ ความปลอดภัย ความเป็นส่วนตัว และความน่าเชื่อถือ อีกทั้งยังมี Bitcoin wallet ที่ถูกสร้างขึ้นมาคู่กับโปรโตคอลของบิตคอยน์อย่าง “Bitcoin Core” ซึ่งมีการพัฒนาต่อมาจากเวอร์ชันที่เขียนโดยซาโตชิ
การเลือก Bitcoin wallet
Bitcoin wallet เป็นหนึ่งในประเภทของแอปพลิเคชันที่มีการพัฒนาอย่างต่อเนื่องมากที่สุดในระบบนิเวศของบิตคอยน์ และแน่นอนว่ามีการแข่งขันกันสูงที่สุดด้วย อาจมี Bitcoin wallet ใหม่ ๆ ที่กำลังพัฒนาอยู่ในขณะนี้ Bitcoin wallet เก่า ๆ บางตัวจากปีที่แล้วก็อาจไม่มีการพัฒนาอย่างต่อเนื่องอีกต่อไป Bitcoin wallet หลาย ๆ ตัวเน้นไปที่แพลตฟอร์มหรือการใช้งานเฉพาะ และบางตัวเหมาะสำหรับผู้เริ่มต้น ในขณะที่บางตัวเต็มไปด้วยฟีเจอร์สำหรับผู้ใช้ขั้นสูง การเลือก Bitcoin wallet นั้นจึงขึ้นอยู่กับความต้องการและระดับความเชี่ยวชาญของผู้ใช้ ดังนั้นการที่เราจะแนะนำยี่ห้อหรือ Bitcoin wallet เฉพาะจึงอาจจะไม่เกิดประโยชน์เท่าไหร่ แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม เราสามารถแบ่งประเภท Bitcoin wallet ได้ตามแพลตฟอร์มและการใช้งานได้ดังนี้
ประเภทของ Bitcoin wallet
- Desktop wallet: กระเป๋าเงินแบบเดสก์ท็อปเป็น Bitcoin wallet ประเภทแรกที่ถูกพัฒนาขึ้นและผู้ใช้ส่วนใหญ่มักจะเลือกใช้ Bitcoin wallet ประเภทนี้เพราะฟีเจอร์ของมัน เช่นความความเป็นอิสระในการใช้งาน ความสามารถในการควบคุมบิตคอยน์ในกระเป๋า แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม การใช้งานบนระบบปฏิบัติการทั่วไป อย่างเช่น Windows และ macOS อาจมีข้อเสียด้านความปลอดภัย เนื่องจากแพลตฟอร์มเหล่านี้มักไม่มีความปลอดภัยเพียงพอและอาจถูกตั้งค่ามาอย่างไม่เหมาะสม
- Mobile wallet: กระเป๋าเงินแบบมือถือเป็น Bitcoin wallet ประเภทที่พบเจอได้มากที่สุด โดยทำงานบนระบบปฏิบัติการสมาร์ทโฟน เช่น Apple iOS และ Android กระเป๋าเงินเหล่านี้มักเป็นตัวเลือกที่ดีสำหรับผู้ใช้ใหม่ เพราะออกแบบมาให้ใช้งานง่ายและสะดวก นอกจากนี้ยังมีกระเป๋าเงินมือถือที่มีฟีเจอร์ครบครันสำหรับผู้ใช้ที่มีความเชี่ยวชาญ แต่เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการดาวน์โหลดและจัดเก็บข้อมูลปริมาณมาก กระเป๋าเงินมือถือส่วนใหญ่จะดึงข้อมูลจากเซิร์ฟเวอร์ระยะไกล ซึ่งอาจลดความเป็นส่วนตัวของผู้ใช้เนื่องจากต้องเปิดเผยข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับ address และจำนวนบิตคอยน์ Bitcoin ต่อบุคคลที่สาม
- Web wallet: กระเป๋าเงินแบบเว็บสามารถเข้าถึงได้ผ่านเว็บเบราว์เซอร์และเก็บกระเป๋าเงินของผู้ใช้ไว้บนเซิร์ฟเวอร์ที่บุคคลที่สามเป็นเจ้าของ คล้ายกับบริการอีเมลบนเว็บที่พึ่งพาเซิร์ฟเวอร์ของบุคคลที่สามโดยสมบูรณ์ โดยบางบริการใช้โค้ดฝั่งไคลเอนต์ที่ทำงานในเบราว์เซอร์ของผู้ใช้ และเพื่อให้ผู้ใช้สามารถควบคุมคีย์ของบิตคอยน์ได้เอง แต่การพึ่งพาเซิร์ฟเวอร์ยังคงส่งผลกระทบต่อความเป็นส่วนตัว อย่างไรก็ตาม บริการส่วนใหญ่จะควบคุมคีย์ของบิตคอยน์แทนผู้ใช้เพื่อแลกกับความสะดวกสบาย เราจึงไม่แนะนำให้เก็บ บิตคอยน์จำนวนมากบนระบบของบุคคลที่สาม
- Hardware Signing Devices: อุปกรณ์สำหรับเซ็นดิจิทัลเป็นอุปกรณ์ที่สามารถจัดเก็บคีย์และเซ็นธุรกรรมโดยใช้ฮาร์ดแวร์และเฟิร์มแวร์เฉพาะทาง ซึ่งโดยทั่วไปแล้วจะเชื่อมต่อกับกระเป๋าเงินเดสก์ท็อป มือถือ หรือเว็บ ผ่านสาย USB การสื่อสารระยะใกล้ (NFC) หรือกล้องที่รองรับ QR code แต่เนื่องจากการดำเนินการที่เกี่ยวข้องกับบิตคอยน์ ทั้งหมดถูกจัดการบนฮาร์ดแวร์เฉพาะ อุปกรณ์เหล่านี้จึงปลอดภัยจากการโจมตีหลายรูปแบบ อย่างไรก็ตาม อุปกรณ์เซ็นดิจิทัลมักถูกเรียกว่า hardware wallet แต่ต้องใช้งานร่วมกับกระเป๋าเงินที่มีฟีเจอร์ครบครันเพื่อส่งและรับธุรกรรม ความปลอดภัยและความเป็นส่วนตัวที่ได้จากกระเป๋าเงินที่ใช้งานร่วมกันก็มีบทบาทสำคัญต่อความปลอดภัยและความเป็นส่วนตัวโดยรวมของผู้ใช้อุปกรณ์เซ็นดิจิทัล
ประเภทของการเชื่อมต่อกับโปรโตคอลของบิตคอยน์
- Full node: บิตคอยน์ฟลูโหนดเป็นโปรแกรมที่ตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของประวัติธุรกรรมทั้งหมดของบิตคอยน์ (ทุกธุรกรรมที่เคยเกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ทุกคน) และนอกจากนี้ บิตคอยน์ฟลูโหนดยังสามารถเลือกเก็บข้อมูลธุรกรรมที่ได้รับการตรวจสอบแล้วก่อนหน้า และให้บริการข้อมูลแก่โปรแกรมบิตคอยน์อื่น ๆ ได้ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นบนคอมพิวเตอร์เดียวกันหรือผ่านอินเทอร์เน็ต แต่แม้ว่าบิตคอยน์ฟลูโหนดเองก็ใช้ทรัพยากรคอมพิวเตอร์ในปริมาณมาก (ประมาณเท่ากับการดูวิดีโอสตรีมมิ่งหนึ่งชั่วโมงต่อวันสำหรับธุรกรรมบิตคอยน์ในแต่ละวัน) บิตคอยน์ฟลูโหนดเองก็มอบความเป็นอิสระอย่างสมบูรณ์แก่ผู้ใช้
- Lightweight Client: lightweight client หรือที่เรียกกันอีกชื่อว่าไคลเอนต์การตรวจสอบการชำระเงินแบบง่าย (Simplified-Payment-Verification: SPV) ซึ่งจะเชื่อมต่อกับโหนดแบบเต็มหรือเซิร์ฟเวอร์ระยะไกลอื่น ๆ เพื่อรับและส่งข้อมูลธุรกรรมของบิตคอยน์แต่เก็บกระเป๋าเงินของผู้ใช้ไว้ในเครื่อง โดยสามารถตรวจสอบธุรกรรมที่ได้รับบางส่วน และสร้างธุรกรรมขาออกอย่างอิสระอีกด้วย
- ไคลเอนต์ API ของบุคคลที่สาม (Third-Party API Client): ไคลเอนต์ API ของบุคคลที่สามเป็นโปรแกรมที่เชื่อมต่อกับระบบบิตคอยน์ผ่าน API ของบุคคลที่สาม แทนที่จะเชื่อมต่อกับเครือข่ายบิตคอยน์โดยตรง กระเป๋าเงินนี้อาจถูกจัดเก็บโดยผู้ใช้เองหรือบนเซิร์ฟเวอร์ของบุคคลที่สาม แต่ไคลเอนต์จะต้องไว้วางใจเซิร์ฟเวอร์ระยะไกลในการให้ข้อมูลที่ถูกต้องและปกป้องความเป็นส่วนตัวของตน
บิตคอยน์เป็นเครือข่ายแบบเพียร์ทูเพียร์(Peer-to-Peer หรือ P2P) โดยที่บิตคอยน์ฟลูโหนด ทำหน้าที่เป็นเพียร์ในเครือข่าย เพียร์แต่ละตัวจะตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของธุรกรรมที่ยืนยันแล้วทุกธุรกรรมอย่างอิสระ และสามารถให้ข้อมูลที่เชื่อถือได้แก่ผู้ใช้ Lightweight Wallets และซอฟต์แวร์อื่น ๆ เองก็เป็นลูกข่ายที่ต้องพึ่งพาเพียร์หนึ่งหรือหลายตัวในการรับข้อมูลที่ถูกต้อง ไคลเอนต์สามารถตรวจสอบข้อมูลบางส่วนที่ได้รับเพิ่มเติมและเชื่อมต่อกับเพียร์หลายตัวเพื่อลดการพึ่งพาเพียร์ตัวเดียว แต่ในท้ายที่สุดความปลอดภัยของไคลเอนต์ยังคงขึ้นอยู่กับความน่าเชื่อถือของเพียร์ที่เชื่อมต่อด้วย
ใครควบคุมคีย์
อีกหนึ่งในประเด็นสำคัญที่ควรพิจารณาเพิ่มเติมคือใครเป็นผู้ควบคุมคีย์ (Private key) เนื่องจากเป็นสิ่งที่มีบทบาทสำคัญในการควบคุมการเข้าถึงบิตคอยน์ โดยคีย์เหล่านี้เองเปรียบเสมือน PIN ที่ยาวมาก ซึ่งหากคุณเป็นผู้ควบคุมคีย์ของคุณเองด้วยตัวเอง คุณก็เป็นผู้ควบคุมบิตคอยน์ของคุณด้วยเช่นกัน แต่หากไม่ใช่ ก็จะแปลว่ากุญแจเหล่านั้นจะถูกดูแลโดยบุคคลที่สาม ซึ่งจะเป็นผู้จัดการเงินของคุณในนามของคุณ
ซอฟแวร์ในการจัดการกุญแจนั้นถูกแบ่งออกเป็นสองประเภทหลัก ๆ คือ wallet ที่คุณจำเป็นต้องดูแลคีย์ของตัวเองและ บัญชีที่มีผู้ดูแล (Custodian Accounts) ซึ่งจะมีบุคคลที่สามเป็นผู้ควบคุมกุญแจ
“Your keys, your coins. Not your keys, not your coins.”
มาอยู่ตัวอย่างเพื่อความเข้าใจที่มาขึ้นกันเถอะ
สมมุติว่าอลิซเป็นผู้ใช้งานที่ไม่ได้เชี่ยวชาญด้านเทคนิค และเพิ่งได้ยินเกี่ยวกับบิตคอยน์จากเพื่อนสนิทของเขา โจ ระหว่างปาร์ตี้ โจกำลังอธิบายเกี่ยวกับบิตคอยน์อย่างกระตือรือร้นให้ทุกคนฟังและสาธิตวิธีการใช้งานต่าง ๆ ให้ดู อลิซเองได้มีความสนใจในบิตคอยน์หลังจากได้ฟังโจอธิบาย จึงได้ถามโจว่าเธอจะเริ่มต้นใช้งานบิตคอยน์ได้อย่างไร โจจึงแนะนำให้อลิซดาวน์โหลด Mobile wallet ตัวโปรดของเขาเนื่องจากมันเหมาะสมกับมือใหม่ อลิซจึงดาวน์โหลดและติดตั้งแอปพลิเคชันกระเป๋าเงินที่โจแนะนำบนโทรศัพท์ของเธอ
เมื่ออลิซเปิดแอปพลิเคชันครั้งแรก เธอได้เลือกสร้างกระเป๋าใหม่และเนื่องจากกระเป๋าที่เธอเลือกนั้นเป็นแบบที่ไม่ได้อยู่ภายใต้การควบคุมบุคคลที่สาม (Noncustodial Wallet) อลิซจึงเป็นผู้ควบคุมคีย์เพียงคนเดียว ซึ่งหมายความว่าเธอต้องรับผิดชอบในการสำรองข้อมูลด้วยตัวของเธอเอง และหากเธอได้ทำคีย์สูญหายไป เธอจะไม่สามารถเข้าถึงบิตคอยน์ของเธอได้อีกไปตลอดกาล และเพื่อเพื่อช่วยในเรื่องนี้ Bitcoin wallet ต่าง ๆ จึงมักจะสร้างรหัสการกู้คืน (Recovery Code) ให้ซึ่งสามารถใช้ในการกู้คืน Bitcoin wallet อันนั้น ๆ
Recovery Code (รหัสในการกู้คืน)
Bitcoin wallet แบบที่ไม่ได้อยู่ภายใต้การควบคุมของบุคคลที่สามนั้นส่วนใหญ่จะให้รหัสการกู้คืนแก่ผู้ใช้งานเพื่อสำรองข้อมูล และรหัสการกู้คืนนี้มักประกอบด้วยตัวเลข ตัวอักษร หรือคำที่ถูกเลือกแบบสุ่มโดยซอฟต์แวร์ และใช้เป็นพื้นฐานสำหรับการสร้าง Bitcoin wallet โดยแต่ละยี่ห้อก็อาจมีความแตกต่างกัน เช่น

รหัสการกู้คืนมักเรียกว่า "mnemonic" หรือ "mnemonic phrase" หรือในภาษาไทยว่าวลีช่วยจำ ซึ่งบ่งบอกว่าคุณควรจดจำวลีนั้น แต่การจดวลีนี้ลงบนกระดาษใช้เวลาน้อยกว่าและมักจะเชื่อถือได้มากกว่าความจำของคนส่วนใหญ่ เพราะฉนั้นผมเลยแนะนำว่าจดเถอะ จะได้ไม่เกิดปัญหาที่ไม่คาดคิดในอนาคต
หาก bitcoin wallet ของอลิซมีปัญหา เธอสามารถดาวน์โหลดซอฟแวร์ใหม่และใส่รหัสในการกู้คืนลงไป เพื่อสร้างฐานข้อมูลของ bitcoin wallet ใหม่ที่บันทึกธุรกรรมบนเชนทั้งหมดที่เธอเคยรับหรือส่ง แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม การกู้คืนจากการใช้รหัสการกู้คืนเพียงอย่างเดียวนั้นอาจจะไม่สามารถกู้คืนข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมที่อลิซเคยบันทึกไว้ใน wallet นั้น ๆ ได้ เช่น ป้ายกำกับที่เธอเชื่อมโยงกับที่อยู่หรือธุรกรรมต่าง ๆ แม้ว่าการสูญเสียข้อมูลเมตานี้จะไม่สำคัญเท่ากับการสูญเสียเงิน แต่ก็ยังมีความสำคัญในบางแง่มุม เช่น หากคุณต้องตรวจสอบรายการธนาคารหรือบัตรเครดิตเก่า แต่ชื่อของผู้ที่คุณชำระเงินหรือผู้ที่จ่ายเงินให้คุณถูกลบออกไป ดังนั้นเพื่อป้องกันการสูญเสียข้อมูลเมตา wallet หลาย ๆ ยี่ห้อจึงมีฟีเจอร์สำรองข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมนอกเหนือจากรหัสการกู้คืน
สำหรับ wallet บางประเภทนั้น ฟีเจอร์สำรองข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมนี้ถือว่ามีความสำคัญมาก เนื่องจากการชำระเงินเงินด้วยบิตคอยน์จำนวนมากในปัจจุบันทำผ่านเทคโนโลยีที่อยู่นอกเชน (Offchain) ซึ่งธุรกรรมไม่ได้ถูกบันทึกลงในบล็อกเชนสาธารณะ เนื่องจากการชำระเงินแบบนี้ช่วยลดค่าใช้จ่ายของผู้ใช้และเพิ่มความเป็นส่วนตัวได้บ้าง แต่นั่นก็หมายความว่ากลไกอย่างรหัสการกู้คืนที่พึ่งพาข้อมูลบนเชนไม่สามารถรับประกันการกู้คืนบิตคอยน์ทั้งหมดของผู้ใช้ได้ ดังนั้นสำหรับแอปพลิเคชันที่รองรับการใช้งาน Offchain การสำรองข้อมูลฐานข้อมูล wallet บ่อยครั้งจึงเป็นสิ่งที่มีความสำคัญมาก
นอกจากนี้ เมื่อได้รับบิตคอยน์ครั้งแรกใน moblie wallet หลาย ๆ wallet มักจะตรวจสอบอีกครั้งว่าคุณได้สำรองรหัสการกู้คืนไว้อย่างปลอดภัยแล้ว การตรวจสอบนี้อาจเป็นเพียงการแจ้งเตือน หรืออาจถึงขั้นให้ผู้ใช้ป้อนรหัสนั้นซ้ำด้วยตัวเอง
คำเตือน แม้ว่า Bitcoin Wallet หลาย ๆ ตัวอาจจะมีการให้คุณต้องกรอกรหัสในการกู้คืนใหม่ในบางกรณี แต่มันก็มักจะมีแอปพลิเคชันมัลแวร์จำนวนมากที่เลียนแบบการออกแบบของ wallet ต่าง ๆ โดยมันจะบังคับให้คุณป้อนรหัสการกู้คืน จากนั้นมันจะส่งรหัสที่ป้อนไปยังผู้พัฒนามัลแวร์เพื่อขโมยบิตคอยน์ของคุณ นี่เปรียบเสมือนเว็บไซต์ฟิชชิงที่พยายามหลอกให้คุณให้รหัสผ่านธนาคารของคุณ สำหรับ Bitcoin wallet ส่วนใหญ่ เวลาที่พวกเขาจะขอรหัสการกู้คืนคือในระหว่างการตั้งค่าเริ่มต้น (ก่อนที่คุณจะได้รับบิตคอยน์) และระหว่างการกู้คืน (หลังจากที่คุณสูญเสียการเข้าถึง wallet เดิม) หากแอปพลิเคชันขอรหัสการกู้คืนในช่วงเวลาอื่น คุณควรปรึกษาผู้เชี่ยวชาญเพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าคุณไม่ได้ตกเป็นเหยื่อของการฟิชชิง
Bitcoin Addresses (ที่อยู่ในการรับหรือส่งบิตคอยน์)
ในตอนนี้อลิซพร้อมแล้วสำหรับการสร้าง Bitcoin wallet ใหม่ของเธอ Bitcoin wallet ที่เธอเลือกได้ทำการสร้าง private key แบบสุ่มให้เธอ ซึ่งจะเชื่อมโยงกับ Bitcoin Address ทั้งหมดที่มีใน Bitcoin wallet ของเธอ แต่ ณ ขณะนี้ยังไม่มีใครรู้ Bitcoin address ของเธอ (แม้แต่ Bitcoin network ก็ไม่รู้) นอกจากตัวเธอเอง Bitcoin address เหล่านี้เป็นเพียงตัวเลขที่เชื่อมโยงกับ Private key ของเธอ ซึ่งเธอสามารถใช้ควบคุมการเข้าถึง Bitcoin ใดกระเป๋าได้ Bitcoin address เหล่านี้ถูกสร้างขึ้นโดยอิสระจากกระเป๋าของเธอโดยไม่ต้องอ้างอิงหรือเชื่อมต่อกับบริการใด ๆ
คำแนะนำ: Bitcoin address และ Invoice นั้นมีหลากหลายรูปแบบที่แตกต่างกัน และทั้งหมดนี้สามารถแชร์ให้กับคนอื่น ๆ ได้ เพื่อเป็นการอณุญาติให้พวกเขาส่งบิตคอยน์เข้ามาในกระเป๋าคุณตรง ๆ คุณสามารถแชร์ Bitcoin address และ Invoice ให้คนอื่นได้โดยไม่ต้องกังวลเกี่ยวกับความปลอดภัยของบิตคอยน์ของคุณ เนื่องจากผู้ที่รู้ Bitcion address ของคุณไม่สามารถถอนเงินออกจาก address นั้น ๆ ได้แม้เขาจะสามารถรู้จำนวนเงินใน address นั้น ๆ ก็ตาม เพราะฉะนั้นเพื่อปกป้องความเป็นส่วนตัวของคุณ คุณจึงควรสร้าง Invoice จาก Bitcoin address ใหม่ทุกครั้งที่จะส่งให้ผู้อื่น
-
 @ 9cb3545c:2ff47bca
2024-12-01 00:18:45
@ 9cb3545c:2ff47bca
2024-12-01 00:18:45Hey there! So you’ve got a whopping 50+ Lightning Channels and you’re not keen on them Force Closing? Well, buckle up! This guide will be an additional resource as you navigate through daunting process.
In this post, we will go over some extra tips and tricks not covered in the official guide. While this guide does have some steps that are not covered by Umbrel, its main objective is to provide confidence in the process (not a replacement process), coming from someone who’s been there and done that, and some how came out with all Lightning Channels still running! I highly recommend reading this post fully before starting the migration process.
Before we dive in, here is the Official Guide from the Umbrel team on how to update UmbrelOS from 0.5.4 to 1.x.x. Reference the steps all the time, and follow them carefully.
With that out of the way. Here are some extra TIPs to fill in some gaps I encountered as I went through the process.
The Order of Steps
Tip #1:
In the Official Umbrel Guide, the Umbrel team asks you to start by backing up your data. As a lightning Node Runner, I recommend against this. Because the Bash script will stop all Umbrel Services and your node will remain offline while you prepare a Bootable USB Stick. So definitely don't start with the backup, first get the bootable stick sorted out, then move on to backups.
Creating the Bootable USB Stick
TIP #2:
After many failed attempts to create a bootable USB stick from the link umbrel provides in their official guide. I ended up getting the ISO directly from Umbrels team through their Discord Channel. Unfortunately, I wont be able to share this link here. but just in case the umbrelOS-amd64-usb-installer.iso.xz didnt work for you as well, this could be an alternative route.
TIP #3:
Since Umbrel is an actual full OS now. You might need to handle some BIOS quirks. The umbrelOS Kernal is not signed. So if you have Secure Boot turned on in the BIOS, your PC will try to protect you, and block you from booting into you USB Stick. Turn off Secure Boot and you should be able to bypass this issue. I also had to turn on Legacy Option ROMs as well.
Tip #4:
Test your Bootable USB Stick on a secondary device before you go on trying to update your node. Since turning the node off and on is a hassle, its just easier to be certain the the Bootable Stick is ready before even attempting to upgrade your node.
If all is good, you are ready to get back to the guide and walk through the steps.
Preparing the Hardware
Tip #5:
In the official guide they as you to connect a Keyboard and Screen. This is of course needed. I would highly suggest you connect a mouse as well. My Bios was very stubborn and didn't comply with just a keyboard as I attempted to re-order Boot Sequences.
The Migration Process
Tip #6:
Remember, this is 10 times easier if you are not running a lightning node, but on a lightning node, the Channel.db file is being updated constantly. Once you start the backup process, the script will shutdown umbrel services and start copying. you can''t turn your node back on after this stage. If you do, assume the backup you created through the Bash script is obsolete. and you will have to redo the backup process again. If you really know what you are doing, you probably can surgically copy/paste the LND folder. But its easier not to do this.
But not to worry, if you start the process just keep going (especially if you checked all the TIPs I cover above). I say this out of experience, because after I started the first backup process, it took me about an hour to backup my SSD, but then the Bootable USB stick threw so many errors I gave up, and turned on the node again. Then later re-attempted the process from scratch. This time, since my external SSD was already full, it took 3.5 hours to backup all the files again.
Tip #7:
This will take time, so just trust the migration process and wait for the files to get copied. you are probably copying more than a terabyte worth of data back and forth over USB, Leverage USB 3 if you have it.
Tip #8:
If you have a custom name for your umbrel node. Meaning you do not access it by using umbrel.local, this will be reset to the default umbrel.local after the migration. I am not sure if this could be switched again to a custom name, but for now, this won't cause any issues.
Tip #9:
During the last steps of the Migration process, and once Umbrel has copied the backup back into the SSD, it will finish the process with downloading your apps, and restarting. Don't freak out :D
Tip #10:
I honestly don't have a tenth tip, but thought it would make this list look nicer with one. So my last tip for you is to relax and enjoy the process. And feel free to tag me if you faced any issues. Hopefully it will be something i experienced and will be able to help.
Have Fun, and Good Luck!
-
 @ a849beb6:b327e6d2
2024-11-23 15:03:47
@ a849beb6:b327e6d2
2024-11-23 15:03:47
\ \ It was another historic week for both bitcoin and the Ten31 portfolio, as the world’s oldest, largest, most battle-tested cryptocurrency climbed to new all-time highs each day to close out the week just shy of the $100,000 mark. Along the way, bitcoin continued to accumulate institutional and regulatory wins, including the much-anticipated approval and launch of spot bitcoin ETF options and the appointment of several additional pro-bitcoin Presidential cabinet officials. The timing for this momentum was poetic, as this week marked the second anniversary of the pico-bottom of the 2022 bear market, a level that bitcoin has now hurdled to the tune of more than 6x despite the litany of bitcoin obituaries published at the time. The entirety of 2024 and especially the past month have further cemented our view that bitcoin is rapidly gaining a sense of legitimacy among institutions, fiduciaries, and governments, and we remain optimistic that this trend is set to accelerate even more into 2025.
Several Ten31 portfolio companies made exciting announcements this week that should serve to further entrench bitcoin’s institutional adoption. AnchorWatch, a first of its kind bitcoin insurance provider offering 1:1 coverage with its innovative use of bitcoin’s native properties, announced it has been designated a Lloyd’s of London Coverholder, giving the company unique, blue-chip status as it begins to write bitcoin insurance policies of up to $100 million per policy starting next month. Meanwhile, Battery Finance Founder and CEO Andrew Hohns appeared on CNBC to delve into the launch of Battery’s pioneering private credit strategy which fuses bitcoin and conventional tangible assets in a dual-collateralized structure that offers a compelling risk/return profile to both lenders and borrowers. Both companies are clearing a path for substantially greater bitcoin adoption in massive, untapped pools of capital, and Ten31 is proud to have served as lead investor for AnchorWatch’s Seed round and as exclusive capital partner for Battery.
As the world’s largest investor focused entirely on bitcoin, Ten31 has deployed nearly $150 million across two funds into more than 30 of the most promising and innovative companies in the ecosystem like AnchorWatch and Battery, and we expect 2025 to be the best year yet for both bitcoin and our portfolio. Ten31 will hold a first close for its third fund at the end of this year, and investors in that close will benefit from attractive incentives and a strong initial portfolio. Visit ten31.vc/funds to learn more and get in touch to discuss participating.\ \ Portfolio Company Spotlight
Primal is a first of its kind application for the Nostr protocol that combines a client, caching service, analytics tools, and more to address several unmet needs in the nascent Nostr ecosystem. Through the combination of its sleek client application and its caching service (built on a completely open source stack), Primal seeks to offer an end-user experience as smooth and easy as that of legacy social media platforms like Twitter and eventually many other applications, unlocking the vast potential of Nostr for the next billion people. Primal also offers an integrated wallet (powered by Strike BLACK) that substantially reduces onboarding and UX frictions for both Nostr and the lightning network while highlighting bitcoin’s unique power as internet-native, open-source money.
Selected Portfolio News
AnchorWatch announced it has achieved Llody’s Coverholder status, allowing the company to provide unique 1:1 bitcoin insurance offerings starting in December.\ \ Battery Finance Founder and CEO Andrew Hohns appeared on CNBC to delve into the company’s unique bitcoin-backed private credit strategy.
Primal launched version 2.0, a landmark update that adds a feed marketplace, robust advanced search capabilities, premium-tier offerings, and many more new features.
Debifi launched its new iOS app for Apple users seeking non-custodial bitcoin-collateralized loans.
Media
Strike Founder and CEO Jack Mallers joined Bloomberg TV to discuss the strong volumes the company has seen over the past year and the potential for a US bitcoin strategic reserve.
Primal Founder and CEO Miljan Braticevic joined The Bitcoin Podcast to discuss the rollout of Primal 2.0 and the future of Nostr.
Ten31 Managing Partner Marty Bent appeared on BlazeTV to discuss recent changes in the regulatory environment for bitcoin.
Zaprite published a customer testimonial video highlighting the popularity of its offerings across the bitcoin ecosystem.
Market Updates
Continuing its recent momentum, bitcoin reached another new all-time high this week, clocking in just below $100,000 on Friday. Bitcoin has now reached a market cap of nearly $2 trillion, putting it within 3% of the market caps of Amazon and Google.
After receiving SEC and CFTC approval over the past month, long-awaited options on spot bitcoin ETFs were fully approved and launched this week. These options should help further expand bitcoin’s institutional liquidity profile, with potentially significant implications for price action over time.
The new derivatives showed strong performance out of the gate, with volumes on options for BlackRock’s IBIT reaching nearly $2 billion on just the first day of trading despite surprisingly tight position limits for the vehicles.
Meanwhile, the underlying spot bitcoin ETF complex had yet another banner week, pulling in $3.4 billion in net inflows.
New reports suggested President-elect Donald Trump’s social media company is in advanced talks to acquire crypto trading platform Bakkt, potentially the latest indication of the incoming administration’s stance toward the broader “crypto” ecosystem.
On the macro front, US housing starts declined M/M again in October on persistently high mortgage rates and weather impacts. The metric remains well below pre-COVID levels.
Pockets of the US commercial real estate market remain challenged, as the CEO of large Florida developer Related indicated that developers need further rate cuts “badly” to maintain project viability.
US Manufacturing PMI increased slightly M/M, but has now been in contraction territory (<50) for well over two years.
The latest iteration of the University of Michigan’s popular consumer sentiment survey ticked up following this month’s election results, though so did five-year inflation expectations, which now sit comfortably north of 3%.
Regulatory Update
After weeks of speculation, the incoming Trump administration appointed hedge fund manager Scott Bessent to head up the US Treasury. Like many of Trump’s cabinet selections so far, Bessent has been a public advocate for bitcoin.
Trump also appointed Cantor Fitzgerald CEO Howard Lutnick – another outspoken bitcoin bull – as Secretary of the Commerce Department.
Meanwhile, the Trump team is reportedly considering creating a new “crypto czar” role to sit within the administration. While it’s unclear at this point what that role would entail, one report indicated that the administration’s broader “crypto council” is expected to move forward with plans for a strategic bitcoin reserve.
Various government lawyers suggested this week that the Trump administration is likely to be less aggressive in seeking adversarial enforcement actions against bitcoin and “crypto” in general, as regulatory bodies appear poised to shift resources and focus elsewhere.
Other updates from the regulatory apparatus were also directionally positive for bitcoin, most notably FDIC Chairman Martin Gruenberg’s confirmation that he plans to resign from his post at the end of President Biden’s term.
Many critics have alleged Gruenberg was an architect of “Operation Chokepoint 2.0,” which has created banking headwinds for bitcoin companies over the past several years, so a change of leadership at the department is likely yet another positive for the space.
SEC Chairman Gary Gensler also officially announced he plans to resign at the start of the new administration. Gensler has been the target of much ire from the broader “crypto” space, though we expect many projects outside bitcoin may continue to struggle with questions around the Howey Test.
Overseas, a Chinese court ruled that it is not illegal for individuals to hold cryptocurrency, even though the country is still ostensibly enforcing a ban on crypto transactions.
Noteworthy
The incoming CEO of Charles Schwab – which administers over $9 trillion in client assets – suggested the platform is preparing to “get into” spot bitcoin offerings and that he “feels silly” for having waited this long. As this attitude becomes more common among traditional finance players, we continue to believe that the number of acquirers coming to market for bitcoin infrastructure capabilities will far outstrip the number of available high quality assets.
BlackRock’s 2025 Thematic Outlook notes a “renewed sense of optimism” on bitcoin among the asset manager’s client base due to macro tailwinds and the improving regulatory environment. Elsewhere, BlackRock’s head of digital assets indicated the firm does not view bitcoin as a “risk-on” asset.
MicroStrategy, which was a sub-$1 billion market cap company less than five years ago, briefly breached a $100 billion equity value this week as it continues to aggressively acquire bitcoin. The company now holds nearly 350,000 bitcoin on its balance sheet.
Notably, Allianz SE, Germany’s largest insurer, spoke for 25% of MicroStrategy’s latest $3 billion convertible note offering this week, suggesting growing appetite for bitcoin proxy exposure among more restricted pools of capital.
The ongoing meltdown of fintech middleware provider Synapse has left tens of thousands of customers with nearly 100% deposit haircuts as hundreds of millions in funds remain missing, the latest unfortunate case study in the fragility of much of the US’s legacy banking stack.
Travel
-
BitcoinMENA, Dec 9-10
-
Nashville BitDevs, Dec 10
-
Austin BitDevs, Dec 19
-
-
 @ 41e6f20b:06049e45
2024-11-17 17:33:55
@ 41e6f20b:06049e45
2024-11-17 17:33:55Let me tell you a beautiful story. Last night, during the speakers' dinner at Monerotopia, the waitress was collecting tiny tips in Mexican pesos. I asked her, "Do you really want to earn tips seriously?" I then showed her how to set up a Cake Wallet, and she started collecting tips in Monero, reaching 0.9 XMR. Of course, she wanted to cash out to fiat immediately, but it solved a real problem for her: making more money. That amount was something she would never have earned in a single workday. We kept talking, and I promised to give her Zoom workshops. What can I say? I love people, and that's why I'm a natural orange-piller.
-
 @ fd208ee8:0fd927c1
2024-11-09 09:21:19
@ fd208ee8:0fd927c1
2024-11-09 09:21:19Drumroll, please....
In a previous article, I introduced the concept of relay communities.
The ink had barely dried, on that set of instructions, before one of my favorite Nostr devs, ثعبان, rolled out the alpha version of a relay-community client.
Obviously, it's still a bit of a construction site, but you can check out how it'd work, for your community, by test-driving the functionality on your own relay. Simply type https://chachi.chat/ followed by the name of your relay. For instance, one gigantic relay community, where nearly everyone can try out the functionality, is nos.lol.
If your relay community does not require AUTH to read, anyone can pull your chatter into their own relay and respond to it there. That is because every chat entry is simply a kind 09 event, and unprotected events are not private data.
For instance, I moderate one community theforest.nostr1.com, that is openly readable, and that's probably where most of the chatter on nostr.band is coming from, as that relay is an aggregator of the content of many other relays. However, I have another community, gitcitadel.nostr1.com that is AUTH-protected, whose content stays private to those allowed on that relay. Communities are where write-protected and AUTH relays are going to really shine, as they create an environment similar to Telegram, but where you control the dataset, you decide which types of events to support, and you design the client, the algos, the moderation, the visibility, etc.
With communities, the onboarding experience is seamless: just get a browser extension and a nsec, login, start writing and posting, and start receiving responses. Active, chatty, well-moderated communities will be more attractive to onboard to, than chaotic, spammy, or empty communities. This means that you don't have to have the killer entry under "Posts" (where kind 11 and eventually kind 01 posts appear), just to get some interaction. Chat is the Great Equalizer.
So, we're testing both setups, with cloudfodder adjusting the relay faucet code and ثعبان is fiddling with the community client settings, to make the most-comfortable situation for both kinds.

This is the signal
This #Chachi client, of course, is merely the first horse out of the gate. There are already other devs hacking away at variants of the same concept, such as #Flotilla, I'm sure CloudFodder is also cooking, later versions of #Alexandria will integrate theforest community, and etc. etc. etc.
It remains to be seen, how many new use cases can be dreamt up, with this new architecture, but I am quite certain, that this is the beginning of the end of Nostr 1.0. We are moving up and out, and away from the stultifying and limiting concept of Twitter 2.0, toward

Soon, we will enter Nostr 2.0. See you on the other side.
-
 @ 3bf0c63f:aefa459d
2024-11-07 14:56:17
@ 3bf0c63f:aefa459d
2024-11-07 14:56:17The case against edits
Direct edits are a centralizing force on Nostr, a slippery slope that should not be accepted.
Edits are fine in other, more specialized event kinds, but the
kind:1space shouldn't be compromised with such a push towards centralization, becausekind:1is the public square of Nostr, where all focus should be on decentralization and censorship-resistance.- Why?
Edits introduce too much complexity. If edits are widespread, all clients now have to download dozens of extra events at the same time while users are browsing a big feed of notes which are already coming from dozens of different relays using complicated outbox-model-based querying, then for each event they have to open yet another subscription to these relays -- or perform some other complicated batching of subscriptions which then requires more complexity on the event handling side and then when associating these edits with the original events. I can only imagine this will hurt apps performance, but it definitely raises the barrier to entry and thus necessarily decreases Nostr decentralization.
Some clients may be implemneted in way such that they download tons of events and then store them in a local databases, from which they then construct the feed that users see. Such clients may make edits potentially easier to deal with -- but this is hardly an answer to the point above, since such clients are already more complex to implement in the first place.
- What do you have against complex clients?
The point is not to say that all clients should be simple, but that it should be simple to write a client -- or at least as simple as physically possible.
You may not be thinking about it, but if you believe in the promise of Nostr then we should expect to see Nostr feeds in many other contexts other than on a big super app in a phone -- we should see Nostr notes being referenced from and injected in unrelated webpages, unrelated apps, hardware devices, comment sections and so on. All these micro-clients will have to implement some complicated edit-fetching logic now?
- But aren't we already fetching likes and zaps and other things, why not fetch edits too?
Likes, zaps and other similar things are optional. It's perfectly fine to use Nostr without seeing likes and/or zaps -- and, believe me, it does happen quite a lot. The point is basically that likes or zaps don't affect the content of the main post at all, while edits do.
- But edits are optional!
No, they are not optional. If edits become widespread they necessarily become mandatory. Any client that doesn't implement edits will be displaying false information to its users and their experience will be completely broken.
- That's fine, as people will just move to clients that support edits!
Exactly, that is what I expect to happen too, and this is why I am saying edits are a centralizing force that we should be fighting against, not embracing.
If you understand that edits are a centralizing force, then you must automatically agree that they aren't a desirable feature, given that if you are reading this now, with Nostr being so small, there is a 100% chance you care about decentralization and you're not just some kind of lazy influencer that is only doing this for money.
- All other social networks support editing!
This is not true at all. Bluesky has 10x more users than Nostr and doesn't support edits. Instagram doesn't support editing pictures after they're posted, and doesn't support editing comments. Tiktok doesn't support editing videos or comments after they're posted. YouTube doesn't support editing videos after they're posted. Most famously, email, the most widely used and widespread "social app" out there, does not support edits of any kind. Twitter didn't support edits for the first 15 years of its life, and, although some people complained, it didn't hurt the platform at all -- arguably it benefitted it.
If edits are such a straightforward feature to add that won't hurt performance, that won't introduce complexity, and also that is such an essential feature users could never live without them, then why don't these centralized platforms have edits on everything already? There must be something there.
- Eventually someone will implement edits anyway, so why bother to oppose edits now?
Once Nostr becomes big enough, maybe it will be already shielded from such centralizing forces by its sheer volume of users and quantity of clients, maybe not, we will see. All I'm saying is that we shouldn't just push for bad things now just because of a potential future in which they might come.
- The market will decide what is better.
The market has decided for Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and TikTok. If we were to follow what the market had decided we wouldn't be here, and you wouldn't be reading this post.
- OK, you have convinced me, edits are not good for the protocol. But what do we do about the users who just want to fix their typos?
There are many ways. The annotations spec, for example, provides a simple way to append things to a note without being a full-blown edit, and they fall back gracefully to normal replies in clients that don't implement the full annotations spec.
Eventually we could have annotations that are expressed in form of simple (human-readable?) diffs that can be applied directly to the post, but fall back, again, to comments.
Besides these, a very simple idea that wasn't tried yet on Nostr yet is the idea that has been tried for emails and seems to work very well: delaying a post after the "submit" button is clicked and giving the user the opportunity to cancel and edit it again before it is actually posted.
Ultimately, if edits are so necessary, then maybe we could come up with a way to implement edits that is truly optional and falls back cleanly for clients that don't support them directly and don't hurt the protocol very much. Let's think about it and not rush towards defeat.
-
 @ a367f9eb:0633efea
2024-11-05 08:48:41
@ a367f9eb:0633efea
2024-11-05 08:48:41Last week, an investigation by Reuters revealed that Chinese researchers have been using open-source AI tools to build nefarious-sounding models that may have some military application.
The reporting purports that adversaries in the Chinese Communist Party and its military wing are taking advantage of the liberal software licensing of American innovations in the AI space, which could someday have capabilities to presumably harm the United States.
In a June paper reviewed by Reuters, six Chinese researchers from three institutions, including two under the People’s Liberation Army’s (PLA) leading research body, the Academy of Military Science (AMS), detailed how they had used an early version of Meta’s Llama as a base for what it calls “ChatBIT”.
The researchers used an earlier Llama 13B large language model (LLM) from Meta, incorporating their own parameters to construct a military-focused AI tool to gather and process intelligence, and offer accurate and reliable information for operational decision-making.
While I’m doubtful that today’s existing chatbot-like tools will be the ultimate battlefield for a new geopolitical war (queue up the computer-simulated war from the Star Trek episode “A Taste of Armageddon“), this recent exposé requires us to revisit why large language models are released as open-source code in the first place.
Added to that, should it matter that an adversary is having a poke around and may ultimately use them for some purpose we may not like, whether that be China, Russia, North Korea, or Iran?
The number of open-source AI LLMs continues to grow each day, with projects like Vicuna, LLaMA, BLOOMB, Falcon, and Mistral available for download. In fact, there are over one million open-source LLMs available as of writing this post. With some decent hardware, every global citizen can download these codebases and run them on their computer.
With regard to this specific story, we could assume it to be a selective leak by a competitor of Meta which created the LLaMA model, intended to harm its reputation among those with cybersecurity and national security credentials. There are potentially trillions of dollars on the line.
Or it could be the revelation of something more sinister happening in the military-sponsored labs of Chinese hackers who have already been caught attacking American infrastructure, data, and yes, your credit history?
As consumer advocates who believe in the necessity of liberal democracies to safeguard our liberties against authoritarianism, we should absolutely remain skeptical when it comes to the communist regime in Beijing. We’ve written as much many times.
At the same time, however, we should not subrogate our own critical thinking and principles because it suits a convenient narrative.
Consumers of all stripes deserve technological freedom, and innovators should be free to provide that to us. And open-source software has provided the very foundations for all of this.
Open-source matters When we discuss open-source software and code, what we’re really talking about is the ability for people other than the creators to use it.
The various licensing schemes – ranging from GNU General Public License (GPL) to the MIT License and various public domain classifications – determine whether other people can use the code, edit it to their liking, and run it on their machine. Some licenses even allow you to monetize the modifications you’ve made.
While many different types of software will be fully licensed and made proprietary, restricting or even penalizing those who attempt to use it on their own, many developers have created software intended to be released to the public. This allows multiple contributors to add to the codebase and to make changes to improve it for public benefit.
Open-source software matters because anyone, anywhere can download and run the code on their own. They can also modify it, edit it, and tailor it to their specific need. The code is intended to be shared and built upon not because of some altruistic belief, but rather to make it accessible for everyone and create a broad base. This is how we create standards for technologies that provide the ground floor for further tinkering to deliver value to consumers.
Open-source libraries create the building blocks that decrease the hassle and cost of building a new web platform, smartphone, or even a computer language. They distribute common code that can be built upon, assuring interoperability and setting standards for all of our devices and technologies to talk to each other.
I am myself a proponent of open-source software. The server I run in my home has dozens of dockerized applications sourced directly from open-source contributors on GitHub and DockerHub. When there are versions or adaptations that I don’t like, I can pick and choose which I prefer. I can even make comments or add edits if I’ve found a better way for them to run.
Whether you know it or not, many of you run the Linux operating system as the base for your Macbook or any other computer and use all kinds of web tools that have active repositories forked or modified by open-source contributors online. This code is auditable by everyone and can be scrutinized or reviewed by whoever wants to (even AI bots).
This is the same software that runs your airlines, powers the farms that deliver your food, and supports the entire global monetary system. The code of the first decentralized cryptocurrency Bitcoin is also open-source, which has allowed thousands of copycat protocols that have revolutionized how we view money.
You know what else is open-source and available for everyone to use, modify, and build upon?
PHP, Mozilla Firefox, LibreOffice, MySQL, Python, Git, Docker, and WordPress. All protocols and languages that power the web. Friend or foe alike, anyone can download these pieces of software and run them how they see fit.
Open-source code is speech, and it is knowledge.
We build upon it to make information and technology accessible. Attempts to curb open-source, therefore, amount to restricting speech and knowledge.
Open-source is for your friends, and enemies In the context of Artificial Intelligence, many different developers and companies have chosen to take their large language models and make them available via an open-source license.
At this very moment, you can click on over to Hugging Face, download an AI model, and build a chatbot or scripting machine suited to your needs. All for free (as long as you have the power and bandwidth).
Thousands of companies in the AI sector are doing this at this very moment, discovering ways of building on top of open-source models to develop new apps, tools, and services to offer to companies and individuals. It’s how many different applications are coming to life and thousands more jobs are being created.
We know this can be useful to friends, but what about enemies?
As the AI wars heat up between liberal democracies like the US, the UK, and (sluggishly) the European Union, we know that authoritarian adversaries like the CCP and Russia are building their own applications.
The fear that China will use open-source US models to create some kind of military application is a clear and present danger for many political and national security researchers, as well as politicians.
A bipartisan group of US House lawmakers want to put export controls on AI models, as well as block foreign access to US cloud servers that may be hosting AI software.
If this seems familiar, we should also remember that the US government once classified cryptography and encryption as “munitions” that could not be exported to other countries (see The Crypto Wars). Many of the arguments we hear today were invoked by some of the same people as back then.
Now, encryption protocols are the gold standard for many different banking and web services, messaging, and all kinds of electronic communication. We expect our friends to use it, and our foes as well. Because code is knowledge and speech, we know how to evaluate it and respond if we need to.
Regardless of who uses open-source AI, this is how we should view it today. These are merely tools that people will use for good or ill. It’s up to governments to determine how best to stop illiberal or nefarious uses that harm us, rather than try to outlaw or restrict building of free and open software in the first place.
Limiting open-source threatens our own advancement If we set out to restrict and limit our ability to create and share open-source code, no matter who uses it, that would be tantamount to imposing censorship. There must be another way.
If there is a “Hundred Year Marathon” between the United States and liberal democracies on one side and autocracies like the Chinese Communist Party on the other, this is not something that will be won or lost based on software licenses. We need as much competition as possible.
The Chinese military has been building up its capabilities with trillions of dollars’ worth of investments that span far beyond AI chatbots and skip logic protocols.
The theft of intellectual property at factories in Shenzhen, or in US courts by third-party litigation funding coming from China, is very real and will have serious economic consequences. It may even change the balance of power if our economies and countries turn to war footing.
But these are separate issues from the ability of free people to create and share open-source code which we can all benefit from. In fact, if we want to continue our way our life and continue to add to global productivity and growth, it’s demanded that we defend open-source.
If liberal democracies want to compete with our global adversaries, it will not be done by reducing the freedoms of citizens in our own countries.
Last week, an investigation by Reuters revealed that Chinese researchers have been using open-source AI tools to build nefarious-sounding models that may have some military application.
The reporting purports that adversaries in the Chinese Communist Party and its military wing are taking advantage of the liberal software licensing of American innovations in the AI space, which could someday have capabilities to presumably harm the United States.
In a June paper reviewed by Reuters, six Chinese researchers from three institutions, including two under the People’s Liberation Army’s (PLA) leading research body, the Academy of Military Science (AMS), detailed how they had used an early version of Meta’s Llama as a base for what it calls “ChatBIT”.
The researchers used an earlier Llama 13B large language model (LLM) from Meta, incorporating their own parameters to construct a military-focused AI tool to gather and process intelligence, and offer accurate and reliable information for operational decision-making.
While I’m doubtful that today’s existing chatbot-like tools will be the ultimate battlefield for a new geopolitical war (queue up the computer-simulated war from the Star Trek episode “A Taste of Armageddon“), this recent exposé requires us to revisit why large language models are released as open-source code in the first place.
Added to that, should it matter that an adversary is having a poke around and may ultimately use them for some purpose we may not like, whether that be China, Russia, North Korea, or Iran?
The number of open-source AI LLMs continues to grow each day, with projects like Vicuna, LLaMA, BLOOMB, Falcon, and Mistral available for download. In fact, there are over one million open-source LLMs available as of writing this post. With some decent hardware, every global citizen can download these codebases and run them on their computer.
With regard to this specific story, we could assume it to be a selective leak by a competitor of Meta which created the LLaMA model, intended to harm its reputation among those with cybersecurity and national security credentials. There are potentially trillions of dollars on the line.
Or it could be the revelation of something more sinister happening in the military-sponsored labs of Chinese hackers who have already been caught attacking American infrastructure, data, and yes, your credit history?
As consumer advocates who believe in the necessity of liberal democracies to safeguard our liberties against authoritarianism, we should absolutely remain skeptical when it comes to the communist regime in Beijing. We’ve written as much many times.
At the same time, however, we should not subrogate our own critical thinking and principles because it suits a convenient narrative.
Consumers of all stripes deserve technological freedom, and innovators should be free to provide that to us. And open-source software has provided the very foundations for all of this.
Open-source matters
When we discuss open-source software and code, what we’re really talking about is the ability for people other than the creators to use it.
The various licensing schemes – ranging from GNU General Public License (GPL) to the MIT License and various public domain classifications – determine whether other people can use the code, edit it to their liking, and run it on their machine. Some licenses even allow you to monetize the modifications you’ve made.
While many different types of software will be fully licensed and made proprietary, restricting or even penalizing those who attempt to use it on their own, many developers have created software intended to be released to the public. This allows multiple contributors to add to the codebase and to make changes to improve it for public benefit.
Open-source software matters because anyone, anywhere can download and run the code on their own. They can also modify it, edit it, and tailor it to their specific need. The code is intended to be shared and built upon not because of some altruistic belief, but rather to make it accessible for everyone and create a broad base. This is how we create standards for technologies that provide the ground floor for further tinkering to deliver value to consumers.
Open-source libraries create the building blocks that decrease the hassle and cost of building a new web platform, smartphone, or even a computer language. They distribute common code that can be built upon, assuring interoperability and setting standards for all of our devices and technologies to talk to each other.
I am myself a proponent of open-source software. The server I run in my home has dozens of dockerized applications sourced directly from open-source contributors on GitHub and DockerHub. When there are versions or adaptations that I don’t like, I can pick and choose which I prefer. I can even make comments or add edits if I’ve found a better way for them to run.
Whether you know it or not, many of you run the Linux operating system as the base for your Macbook or any other computer and use all kinds of web tools that have active repositories forked or modified by open-source contributors online. This code is auditable by everyone and can be scrutinized or reviewed by whoever wants to (even AI bots).
This is the same software that runs your airlines, powers the farms that deliver your food, and supports the entire global monetary system. The code of the first decentralized cryptocurrency Bitcoin is also open-source, which has allowed thousands of copycat protocols that have revolutionized how we view money.
You know what else is open-source and available for everyone to use, modify, and build upon?
PHP, Mozilla Firefox, LibreOffice, MySQL, Python, Git, Docker, and WordPress. All protocols and languages that power the web. Friend or foe alike, anyone can download these pieces of software and run them how they see fit.
Open-source code is speech, and it is knowledge.
We build upon it to make information and technology accessible. Attempts to curb open-source, therefore, amount to restricting speech and knowledge.
Open-source is for your friends, and enemies
In the context of Artificial Intelligence, many different developers and companies have chosen to take their large language models and make them available via an open-source license.
At this very moment, you can click on over to Hugging Face, download an AI model, and build a chatbot or scripting machine suited to your needs. All for free (as long as you have the power and bandwidth).
Thousands of companies in the AI sector are doing this at this very moment, discovering ways of building on top of open-source models to develop new apps, tools, and services to offer to companies and individuals. It’s how many different applications are coming to life and thousands more jobs are being created.
We know this can be useful to friends, but what about enemies?
As the AI wars heat up between liberal democracies like the US, the UK, and (sluggishly) the European Union, we know that authoritarian adversaries like the CCP and Russia are building their own applications.
The fear that China will use open-source US models to create some kind of military application is a clear and present danger for many political and national security researchers, as well as politicians.
A bipartisan group of US House lawmakers want to put export controls on AI models, as well as block foreign access to US cloud servers that may be hosting AI software.
If this seems familiar, we should also remember that the US government once classified cryptography and encryption as “munitions” that could not be exported to other countries (see The Crypto Wars). Many of the arguments we hear today were invoked by some of the same people as back then.
Now, encryption protocols are the gold standard for many different banking and web services, messaging, and all kinds of electronic communication. We expect our friends to use it, and our foes as well. Because code is knowledge and speech, we know how to evaluate it and respond if we need to.
Regardless of who uses open-source AI, this is how we should view it today. These are merely tools that people will use for good or ill. It’s up to governments to determine how best to stop illiberal or nefarious uses that harm us, rather than try to outlaw or restrict building of free and open software in the first place.
Limiting open-source threatens our own advancement
If we set out to restrict and limit our ability to create and share open-source code, no matter who uses it, that would be tantamount to imposing censorship. There must be another way.
If there is a “Hundred Year Marathon” between the United States and liberal democracies on one side and autocracies like the Chinese Communist Party on the other, this is not something that will be won or lost based on software licenses. We need as much competition as possible.
The Chinese military has been building up its capabilities with trillions of dollars’ worth of investments that span far beyond AI chatbots and skip logic protocols.
The theft of intellectual property at factories in Shenzhen, or in US courts by third-party litigation funding coming from China, is very real and will have serious economic consequences. It may even change the balance of power if our economies and countries turn to war footing.
But these are separate issues from the ability of free people to create and share open-source code which we can all benefit from. In fact, if we want to continue our way our life and continue to add to global productivity and growth, it’s demanded that we defend open-source.
If liberal democracies want to compete with our global adversaries, it will not be done by reducing the freedoms of citizens in our own countries.
Originally published on the website of the Consumer Choice Center.
-
 @ 09fbf8f3:fa3d60f0
2024-11-02 08:00:29
@ 09fbf8f3:fa3d60f0
2024-11-02 08:00:29> ### 第三方API合集:
免责申明:
在此推荐的 OpenAI API Key 由第三方代理商提供,所以我们不对 API Key 的 有效性 和 安全性 负责,请你自行承担购买和使用 API Key 的风险。
| 服务商 | 特性说明 | Proxy 代理地址 | 链接 | | --- | --- | --- | --- | | AiHubMix | 使用 OpenAI 企业接口,全站模型价格为官方 86 折(含 GPT-4 )| https://aihubmix.com/v1 | 官网 | | OpenAI-HK | OpenAI的API官方计费模式为,按每次API请求内容和返回内容tokens长度来定价。每个模型具有不同的计价方式,以每1,000个tokens消耗为单位定价。其中1,000个tokens约为750个英文单词(约400汉字)| https://api.openai-hk.com/ | 官网 | | CloseAI | CloseAI是国内规模最大的商用级OpenAI代理平台,也是国内第一家专业OpenAI中转服务,定位于企业级商用需求,面向企业客户的线上服务提供高质量稳定的官方OpenAI API 中转代理,是百余家企业和多家科研机构的专用合作平台。 | https://api.openai-proxy.org | 官网 | | OpenAI-SB | 需要配合Telegram 获取api key | https://api.openai-sb.com | 官网 |
持续更新。。。
推广:
访问不了openai,去
低调云购买VPN。官网:https://didiaocloud.xyz
邀请码:
w9AjVJit价格低至1元。
-
 @ 4c48cf05:07f52b80
2024-10-30 01:03:42
@ 4c48cf05:07f52b80
2024-10-30 01:03:42I believe that five years from now, access to artificial intelligence will be akin to what access to the Internet represents today. It will be the greatest differentiator between the haves and have nots. Unequal access to artificial intelligence will exacerbate societal inequalities and limit opportunities for those without access to it.
Back in April, the AI Index Steering Committee at the Institute for Human-Centered AI from Stanford University released The AI Index 2024 Annual Report.
Out of the extensive report (502 pages), I chose to focus on the chapter dedicated to Public Opinion. People involved with AI live in a bubble. We all know and understand AI and therefore assume that everyone else does. But, is that really the case once you step out of your regular circles in Seattle or Silicon Valley and hit Main Street?
Two thirds of global respondents have a good understanding of what AI is
The exact number is 67%. My gut feeling is that this number is way too high to be realistic. At the same time, 63% of respondents are aware of ChatGPT so maybe people are confounding AI with ChatGPT?
If so, there is so much more that they won't see coming.
This number is important because you need to see every other questions and response of the survey through the lens of a respondent who believes to have a good understanding of what AI is.
A majority are nervous about AI products and services
52% of global respondents are nervous about products and services that use AI. Leading the pack are Australians at 69% and the least worried are Japanise at 23%. U.S.A. is up there at the top at 63%.
Japan is truly an outlier, with most countries moving between 40% and 60%.
Personal data is the clear victim
Exaclty half of the respondents believe that AI companies will protect their personal data. And the other half believes they won't.
Expected benefits
Again a majority of people (57%) think that it will change how they do their jobs. As for impact on your life, top hitters are getting things done faster (54%) and more entertainment options (51%).
The last one is a head scratcher for me. Are people looking forward to AI generated movies?

Concerns
Remember the 57% that thought that AI will change how they do their jobs? Well, it looks like 37% of them expect to lose it. Whether or not this is what will happen, that is a very high number of people who have a direct incentive to oppose AI.
Other key concerns include:
- Misuse for nefarious purposes: 49%
- Violation of citizens' privacy: 45%
Conclusion
This is the first time I come across this report and I wil make sure to follow future annual reports to see how these trends evolve.
Overall, people are worried about AI. There are many things that could go wrong and people perceive that both jobs and privacy are on the line.
Full citation: Nestor Maslej, Loredana Fattorini, Raymond Perrault, Vanessa Parli, Anka Reuel, Erik Brynjolfsson, John Etchemendy, Katrina Ligett, Terah Lyons, James Manyika, Juan Carlos Niebles, Yoav Shoham, Russell Wald, and Jack Clark, “The AI Index 2024 Annual Report,” AI Index Steering Committee, Institute for Human-Centered AI, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, April 2024.
The AI Index 2024 Annual Report by Stanford University is licensed under Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International.
-
 @ cb084639:2f16502a
2024-10-29 05:28:32
@ cb084639:2f16502a
2024-10-29 05:28:32ทำไมถึงกลัว คลอเรสเตอรอลและไขมันอิ่มตัวกันขนาดนั้น !!!

จากภาพจะเห็นได้ว่ามีการวางขายไข่จากพืช!!! ซึ่งอ่านแล้วน่าขัน ในเมื่อเราสามารถ กินไข่จากแม่ไก่ได้!!!

เพื่อความกระจ่างเรามาดูฉลากเจ้าน้ำไข่จากพืชกล่องสีเหลืองกันดีกว่า
 อย่างแรกเรามาดูที่ราคากันก่อน ราคาต่อกล่อง 6.98 usd ราคาบาทอยู่ที่ประมาณ 235 บาทต่อกล่อง 16 ออนซ์หรือ 454 กรัม และถ้าเป็นการ นำเงินจำนวนนี้ไปซื้อไข่จริงเบอร์ 2 ราคาแผงละ 119 บาท จะได้ไข่ 58 ฟอง(เกือบ 2 แผงขาดไป 2ฟอง)
อย่างแรกเรามาดูที่ราคากันก่อน ราคาต่อกล่อง 6.98 usd ราคาบาทอยู่ที่ประมาณ 235 บาทต่อกล่อง 16 ออนซ์หรือ 454 กรัม และถ้าเป็นการ นำเงินจำนวนนี้ไปซื้อไข่จริงเบอร์ 2 ราคาแผงละ 119 บาท จะได้ไข่ 58 ฟอง(เกือบ 2 แผงขาดไป 2ฟอง) เน้นเรื่องปลอด GMO และไม่มี คลอเรสเตอรอล
อันนี้เป็นวิธปรุงง่ายๆ ใช่น้ำไข่จากพืช 3 ช้อนโต๊ะ ต่อไข่ไก่จริง 1 ฟอง ทำง่ายสะดวก
เน้นเรื่องปลอด GMO และไม่มี คลอเรสเตอรอล
อันนี้เป็นวิธปรุงง่ายๆ ใช่น้ำไข่จากพืช 3 ช้อนโต๊ะ ต่อไข่ไก่จริง 1 ฟอง ทำง่ายสะดวก
 ด้านนี้พยายามเปรียบเทียบให้เห็นว่า ไม่มีคลอเรสเตอรอลและไข่มันอิ่มตัว
ด้านนี้พยายามเปรียบเทียบให้เห็นว่า ไม่มีคลอเรสเตอรอลและไข่มันอิ่มตัว ปริมาณสารอาหารไข่จากพืช ไม่มีคลอเรสเตอรอล มีไขมันทั้งหมด 4 กรัม คือไขมันไม่อิ่มตัวเชิงซ้อนและไขมันไม่อิ่มตัวเชิงเดี่ยว ต่อหนึ่งหน่วยบริกโภค
ปริมาณสารอาหารไข่จากพืช ไม่มีคลอเรสเตอรอล มีไขมันทั้งหมด 4 กรัม คือไขมันไม่อิ่มตัวเชิงซ้อนและไขมันไม่อิ่มตัวเชิงเดี่ยว ต่อหนึ่งหน่วยบริกโภค
ภาพนี้คือข้อมูลขอไข่ไก่ที่ได้จากแม่ไก่จริงๆ
 เกือบลืมไปน้ำไข่จากพืชจำเป็นต้องมีส่วนผสมต่างๆ เช่น น้ำ โปรตีนถั่วเขียว น้ำมันคาโนล่าสกัดเย็น สีจากสารสกัดแครอท หัวหอมแห้ง เจลแลนกัม เพื่อรสชาติและเนื้อสัมผัส โพแทสเซียมซิเตรต เกลือ น้ำตาล น้ำเชื่อมมันสำปะหลังของแข็ง เตตระโซเดียมไพโรฟอสเฟต ทรานส์กลูตามิเนส สารสกัดขมิ้น (สี) ไนซิน (สารกันบูด)
เกือบลืมไปน้ำไข่จากพืชจำเป็นต้องมีส่วนผสมต่างๆ เช่น น้ำ โปรตีนถั่วเขียว น้ำมันคาโนล่าสกัดเย็น สีจากสารสกัดแครอท หัวหอมแห้ง เจลแลนกัม เพื่อรสชาติและเนื้อสัมผัส โพแทสเซียมซิเตรต เกลือ น้ำตาล น้ำเชื่อมมันสำปะหลังของแข็ง เตตระโซเดียมไพโรฟอสเฟต ทรานส์กลูตามิเนส สารสกัดขมิ้น (สี) ไนซิน (สารกันบูด)สินค้าเน่าเสียง่าย - เก็บในตู้เย็น รับประทานได้ภายใน 7 วันหลังจากเปิด
 เราต้องแลกกับการที่ต้องบริโภคสารแปรรูปสารพัดเพื่อที่จะต้องการหนีจากคลอเรสเตอรอลอละไขมันจากธรรมชาติ จะดีกว่ามั้ยถ้าเราเลือกกินไข่ที่ผลิตจากธรรมชาติโดยแม่ไก่?
เราต้องแลกกับการที่ต้องบริโภคสารแปรรูปสารพัดเพื่อที่จะต้องการหนีจากคลอเรสเตอรอลอละไขมันจากธรรมชาติ จะดีกว่ามั้ยถ้าเราเลือกกินไข่ที่ผลิตจากธรรมชาติโดยแม่ไก่? -
 @ bd32f268:22b33966
2024-10-24 17:57:26
@ bd32f268:22b33966
2024-10-24 17:57:26A atualidade acostumou-nos a uma lânguida linguagem devido à cultura do politicamente correto e ao crescente relativismo em que vivemos. A confusão é tanta que já não se chamam os bois pelos nomes e este ambiente faz com que inclusive desconheçamos o significado das palavras. A este respeito temos visto cada vez mais indefinição sobre o que são os vícios e sobre o que são as virtudes. Tal é a confusão que por vezes trocamos o significado de uns pelos outros.
A coragem e a convicção facilmente passam por orgulho e arrogância, a castidade passa por beatice e por aí segue a confusão com muitos outros termos.
A inversão de valores é tão disseminada que atrocidades como a pornografia, o aborto, o adultério entre outras atrocidades são celebrados como conquistas civilizacionais. A sua disseminação é de tal forma que hoje a pessoa média já banalizou e normalizou completamente estes aspectos.
“Primeiro estranha-se depois entranha-se.”
Fernando Pessoa
Enquanto isto acontece por um lado, por outro a defesa da família, da identidade e da tradição são abertamente atacadas como se se tratassem de produtos de uma cultura opressora que deve ser combatida por todos os meios. Por agora a perseguição destas ideias é ainda maioritariamente realizada através da exclusão social e económica, no entanto, não são escassos os exemplos da história em que essa perseguição assume uma outra dimensão.
Desta forma, está criado um paradigma e um sistema de incentivos que premeia a pessoa que colabora com o sistema vigente. Tanto é assim que se multiplicam cada vez mais os exemplos de programas de quotas e subvenções que permitem, a quem possui um grau mais avançado de assimilação ideológica progredir socialmente atalhando o caminho para o fazer.
“Assim, toda a árvore boa produz bons frutos, porém a árvore má produz frutos maus. Não pode a árvore boa produzir frutos maus, nem a árvore má produzir frutos bons (…)”
Mateus 7:17-18“Assim, toda a árvore boa produz bons frutos, porém a árvore má produz frutos maus. Não pode a árvore boa produzir frutos maus, nem a árvore má produzir frutos bons (…)”
> Mateus 7:17-18*
Desengane-se quem pensa que no paradigma pos-moderno não há moralização, sacerdotes e uma matriz religiosa, tudo isso existe.
Os psicólogos, para mal da nossa sociedade, são crescentemente os sacerdotes desta religião pagã, aquela que baseada numa filosofia e antropologia erradas vai corrompendo intelecto e coração.
Nesta nova ordem social, que em abono da verdade é já antiga, a inversão de valores é tal que já a própria vida humana é sacrificada no altar do clima em abono da “mãe” natureza. Regredimos ao tribalismo que nos sugere que a natureza vale mais que a vida humana.
Este é apenas um exemplo dos rituais de sacrifício proporcionados pela “nova” religião. Um outro exemplo que podemos dar é o da castração química e física de crianças e jovens no altar da falsa compaixão e empatia. Ainda um outro exemplo que podemos dar é o da promoção do homossexualismo, do transexualismo e da não-monogamia como caminhos saudáveis a seguir, sacrificando a vida de muitos jovens confusos no altar da inclusão. Muitos mais exemplos poderiam ser dados, porque à medida que esta “nova” religião aumenta a sua ortodoxia os rituais vão ficando cada vez mais assombrosos.
Estes rituais têm por base uma apologia ao anti logos, quer isto dizer que procuram negar tudo o que é conhecimento básico sobre a realidade e sobre a verdade. A própria razão e lógica não se sustentam quando vemos situações como a de homens a competir em desportos femininos. As leis desta nova ordem são: “procura a felicidade (aqui muitas vezes entendida como o prazer) como fim último da vida “; “todas as opiniões são certas e não há uma verdade”; “Não servirás a nenhuma autoridade”; “não seguir o vício é opressão e seguir o vício é liberdade”.
Neste ambiente inóspito, quem quiser preservar a honra e a virtude terá cada vez mais dificuldade uma vez que a dissidência desta nova religião não é aplaudida, pelo contrário é anatematizada. Porém, importa dizer que independentemente da época há sempre espaço para o heroísmo e para a transformação destas dificuldades em degraus para que o indivíduo se possa distinguir dos demais pelas suas virtudes. Onde o vício abunda também maior o destaque será em relação à graça, como uma pedra preciosa reluzente no meio da lama que aparenta brilhar mais intensamente aos nossos olhos tal é o contraste, ou como uma luz na escuridão que se distingue facilmente.
 ###### Casper David Friedrich - dreaming man in church ruins
###### Casper David Friedrich - dreaming man in church ruins -
 @ 8947a945:9bfcf626
2024-10-17 08:06:55
@ 8947a945:9bfcf626
2024-10-17 08:06:55สวัสดีทุกคนบน Nostr ครับ รวมไปถึง watchersและ ผู้ติดตามของผมจาก Deviantart และ platform งานศิลปะอื่นๆนะครับ
ตั้งแต่ต้นปี 2024 ผมใช้ AI เจนรูปงานตัวละครสาวๆจากอนิเมะ และเปิด exclusive content ให้สำหรับผู้ที่ชื่นชอบผลงานของผมเป็นพิเศษ
ผมโพสผลงานผมทั้งหมดไว้ที่เวบ Deviantart และค่อยๆสร้างฐานผู้ติดตามมาเรื่อยๆอย่างค่อยเป็นค่อยไปมาตลอดครับ ทุกอย่างเติบโตไปเรื่อยๆของมัน ส่วนตัวผมมองว่ามันเป็นพิร์ตธุรกิจออนไลน์ ของผมพอร์ตนึงได้เลย
เมื่อวันที่ 16 กย.2024 มีผู้ติดตามคนหนึ่งส่งข้อความส่วนตัวมาหาผม บอกว่าชื่นชอบผลงานของผมมาก ต้องการจะขอซื้อผลงาน แต่ขอซื้อเป็น NFT นะ เสนอราคาซื้อขายต่อชิ้นที่สูงมาก หลังจากนั้นผมกับผู้ซื้อคนนี้พูดคุยกันในเมล์ครับ
นี่คือข้อสรุปสั่นๆจากการต่อรองซื้อขายครับ
(หลังจากนี้ผมขอเรียกผู้ซื้อว่า scammer นะครับ เพราะไพ่มันหงายมาแล้ว ว่าเขาคือมิจฉาชีพ)

- Scammer รายแรก เลือกผลงานที่จะซื้อ เสนอราคาซื้อที่สูงมาก แต่ต้องเป็นเวบไซต์ NFTmarket place ที่เขากำหนดเท่านั้น มันทำงานอยู่บน ERC20 ผมเข้าไปดูเวบไซต์ที่ว่านี้แล้วรู้สึกว่ามันดูแปลกๆครับ คนที่จะลงขายผลงานจะต้องใช้ email ในการสมัครบัญชีซะก่อน ถึงจะผูก wallet อย่างเช่น metamask ได้ เมื่อผูก wallet แล้วไม่สามารถเปลี่ยนได้ด้วย ตอนนั้นผมใช้ wallet ที่ไม่ได้ link กับ HW wallet ไว้ ทดลองสลับ wallet ไปๆมาๆ มันทำไม่ได้ แถมลอง log out แล้ว เลข wallet ก็ยังคาอยู่อันเดิม อันนี้มันดูแปลกๆแล้วหนึ่งอย่าง เวบนี้ค่า ETH ในการ mint 0.15 - 0.2 ETH … ตีเป็นเงินบาทนี่แพงบรรลัยอยู่นะครับ

-
Scammer รายแรกพยายามชักจูงผม หว่านล้อมผมว่า แหม เดี๋ยวเขาก็มารับซื้องานผมน่า mint งานเสร็จ รีบบอกเขานะ เดี๋ยวเขารีบกดซื้อเลย พอขายได้กำไร ผมก็ได้ค่า gas คืนได้ แถมยังได้กำไรอีก ไม่มีอะไรต้องเสีนจริงมั้ย แต่มันเป้นความโชคดีครับ เพราะตอนนั้นผมไม่เหลือทุนสำรองที่จะมาซื้อ ETH ได้ ผมเลยต่อรองกับเขาตามนี้ครับ :
-
ผมเสนอว่า เอางี้มั้ย ผมส่งผลงานของผมแบบ low resolution ให้ก่อน แลกกับให้เขาช่วยโอน ETH ที่เป็นค่า mint งานมาให้หน่อย พอผมได้ ETH แล้ว ผมจะ upscale งานของผม แล้วเมล์ไปให้ ใจแลกใจกันไปเลย ... เขาไม่เอา
- ผมเสนอให้ไปซื้อที่ร้านค้าออนไลน์ buymeacoffee ของผมมั้ย จ่ายเป็น USD ... เขาไม่เอา
- ผมเสนอให้ซื้อขายผ่าน PPV lightning invoice ที่ผมมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึง เพราะเป็น creator ของ Creatr ... เขาไม่เอา
- ผมยอกเขาว่างั้นก็รอนะ รอเงินเดือนออก เขาบอก ok
สัปดาห์ถัดมา มี scammer คนที่สองติดต่อผมเข้ามา ใช้วิธีการใกล้เคียงกัน แต่ใช้คนละเวบ แถมเสนอราคาซื้อที่สูงกว่าคนแรกมาก เวบที่สองนี้เลวร้ายค่าเวบแรกอีกครับ คือต้องใช้เมล์สมัครบัญชี ไม่สามารถผูก metamask ได้ พอสมัครเสร็จจะได้ wallet เปล่าๆมาหนึ่งอัน ผมต้องโอน ETH เข้าไปใน wallet นั้นก่อน เพื่อเอาไปเป็นค่า mint NFT 0.2 ETH
ผมบอก scammer รายที่สองว่า ต้องรอนะ เพราะตอนนี้กำลังติดต่อซื้อขายอยู่กับผู้ซื้อรายแรกอยู่ ผมกำลังรอเงินเพื่อมาซื้อ ETH เป็นต้นทุนดำเนินงานอยู่ คนคนนี้ขอให้ผมส่งเวบแรกไปให้เขาดูหน่อย หลังจากนั้นไม่นานเขาเตือนผมมาว่าเวบแรกมันคือ scam นะ ไม่สามารถถอนเงินออกมาได้ เขายังส่งรูป cap หน้าจอที่คุยกับผู้เสียหายจากเวบแรกมาให้ดูว่าเจอปัญหาถอนเงินไม่ได้ ไม่พอ เขายังบลัฟ opensea ด้วยว่าลูกค้าขายงานได้ แต่ถอนเงินไม่ได้
Opensea ถอนเงินไม่ได้ ตรงนี้แหละครับคือตัวกระตุกต่อมเอ๊ะของผมดังมาก เพราะ opensea อ่ะ ผู้ใช้ connect wallet เข้ากับ marketplace โดยตรง ซื้อขายกันเกิดขึ้น เงินวิ่งเข้าวิ่งออก wallet ของแต่ละคนโดยตรงเลย opensea เก็บแค่ค่า fee ในการใช้ platform ไม่เก็บเงินลูกค้าไว้ แถมปีนี้ค่า gas fee ก็ถูกกว่า bull run cycle 2020 มาก ตอนนี้ค่า gas fee ประมาณ 0.0001 ETH (แต่มันก็แพงกว่า BTC อยู่ดีอ่ะครับ)
ผมเลยเอาเรื่องนี้ไปปรึกษาพี่บิท แต่แอดมินมาคุยกับผมแทน ทางแอดมินแจ้งว่ายังไม่เคยมีเพื่อนๆมาปรึกษาเรื่องนี้ กรณีที่ผมทักมาถามนี่เป็นรายแรกเลย แต่แอดมินให้ความเห็นไปในทางเดียวกับสมมุติฐานของผมว่าน่าจะ scam ในเวลาเดียวกับผมเอาเรื่องนี้ไปถามในเพจ NFT community คนไทนด้วย ได้รับการ confirm ชัดเจนว่า scam และมีคนไม่น้อยโดนหลอก หลังจากที่ผมรู้ที่มาแล้ว ผมเลยเล่นสงครามปั่นประสาท scammer ทั้งสองคนนี้ครับ เพื่อดูว่าหลอกหลวงมิจฉาชีพจริงมั้ย
โดยวันที่ 30 กย. ผมเลยปั่นประสาน scammer ทั้งสองรายนี้ โดยการ mint ผลงานที่เขาเสนอซื้อนั่นแหละ ขึ้น opensea แล้วส่งข้อความไปบอกว่า
mint ให้แล้วนะ แต่เงินไม่พอจริงๆว่ะโทษที เลย mint ขึ้น opensea แทน พอดีบ้านจน ทำได้แค่นี้ไปถึงแค่ opensea รีบไปซื้อล่ะ มีคนจ้องจะคว้างานผมเยอะอยู่ ผมไม่คิด royalty fee ด้วยนะเฮ้ย เอาไปขายต่อไม่ต้องแบ่งกำไรกับผม
เท่านั้นแหละครับ สงครามจิตวิทยาก็เริ่มขึ้น แต่เขาจนมุม กลืนน้ำลายตัวเอง ช็อตเด็ดคือ
เขา : เนี่ยอุส่ารอ บอกเพื่อนในทีมว่าวันจันทร์ที่ 30 กย. ได้ของแน่ๆ เพื่อนๆในทีมเห็นงานผมแล้วมันสวยจริง เลยใส่เงินเต็มที่ 9.3ETH (+ capture screen ส่งตัวเลขยอดเงินมาให้ดู)ไว้รอโดยเฉพาะเลยนะ ผม : เหรอ ... งั้น ขอดู wallet address ที่มี transaction มาให้ดูหน่อยสิ เขา : 2ETH นี่มัน 5000$ เลยนะ ผม : แล้วไง ขอดู wallet address ที่มีการเอายอดเงิน 9.3ETH มาให้ดูหน่อย ไหนบอกว่าเตรียมเงินไว้มากแล้วนี่ ขอดูหน่อย ว่าใส่ไว้เมื่อไหร่ ... เอามาแค่ adrress นะเว้ย ไม่ต้องทะลึ่งส่ง seed มาให้ เขา : ส่งรูปเดิม 9.3 ETH มาให้ดู ผม : รูป screenshot อ่ะ มันไม่มีความหมายหรอกเว้ย ตัดต่อเอาก็ได้ง่ายจะตาย เอา transaction hash มาดู ไหนว่าเตรียมเงินไว้รอ 9.3ETH แล้วอยากซื้องานผมจนตัวสั่นเลยไม่ใช่เหรอ ถ้าจะส่ง wallet address มาให้ดู หรือจะช่วยส่ง 0.15ETH มาให้ยืม mint งานก่อน แล้วมากดซื้อ 2ETH ไป แล้วผมใช้ 0.15ETH คืนให้ก็ได้ จะซื้อหรือไม่ซื้อเนี่ย เขา : จะเอา address เขาไปทำไม ผม : ตัดจบ รำคาญ ไม่ขายให้ละ เขา : 2ETH = 5000 USD เลยนะ ผม : แล้วไง
ผมเลยเขียนบทความนี้มาเตือนเพื่อนๆพี่ๆทุกคนครับ เผื่อใครกำลังเปิดพอร์ตทำธุรกิจขาย digital art online แล้วจะโชคดี เจอของดีแบบผม
ทำไมผมถึงมั่นใจว่ามันคือการหลอกหลวง แล้วคนโกงจะได้อะไร
อันดับแรกไปพิจารณาดู opensea ครับ เป็นเวบ NFTmarketplace ที่ volume การซื้อขายสูงที่สุด เขาไม่เก็บเงินของคนจะซื้อจะขายกันไว้กับตัวเอง เงินวิ่งเข้าวิ่งออก wallet ผู้ซื้อผู้ขายเลย ส่วนทางเวบเก็บค่าธรรมเนียมเท่านั้น แถมค่าธรรมเนียมก็ถูกกว่าเมื่อปี 2020 เยอะ ดังนั้นการที่จะไปลงขายงานบนเวบ NFT อื่นที่ค่า fee สูงกว่ากันเป็นร้อยเท่า ... จะทำไปทำไม
ผมเชื่อว่า scammer โกงเงินเจ้าของผลงานโดยการเล่นกับความโลภและความอ่อนประสบการณ์ของเจ้าของผลงานครับ เมื่อไหร่ก็ตามที่เจ้าของผลงานโอน ETH เข้าไปใน wallet เวบนั้นเมื่อไหร่ หรือเมื่อไหร่ก็ตามที่จ่ายค่า fee ในการ mint งาน เงินเหล่านั้นสิ่งเข้ากระเป๋า scammer ทันที แล้วก็จะมีการเล่นตุกติกต่อแน่นอนครับ เช่นถอนไม่ได้ หรือซื้อไม่ได้ ต้องโอนเงินมาเพิ่มเพื่อปลดล็อค smart contract อะไรก็ว่าไป แล้วคนนิสัยไม่ดีพวกเนี้ย ก็จะเล่นกับความโลภของคน เอาราคาเสนอซื้อที่สูงโคตรๆมาล่อ ... อันนี้ไม่ว่ากัน เพราะบนโลก NFT รูปภาพบางรูปที่ไม่ได้มีความเป็นศิลปะอะไรเลย มันดันขายกันได้ 100 - 150 ETH ศิลปินที่พยายามสร้างตัวก็อาจจะมองว่า ผลงานเรามีคนรับซื้อ 2 - 4 ETH ต่องานมันก็มากพอแล้ว (จริงๆมากเกินจนน่าตกใจด้วยซ้ำครับ)
บนโลกของ BTC ไม่ต้องเชื่อใจกัน โอนเงินไปหากันได้ ปิดสมุดบัญชีได้โดยไม่ต้องเชื่อใจกัน
บบโลกของ ETH "code is law" smart contract มีเขียนอยู่แล้ว ไปอ่าน มันไม่ได้ยากมากในการทำความเข้าใจ ดังนั้น การจะมาเชื่อคำสัญญาจากคนด้วยกัน เป็นอะไรที่ไม่มีเหตุผล
ผมไปเล่าเรื่องเหล่านี้ให้กับ community งานศิลปะ ก็มีทั้งเสียงตอบรับที่ดี และไม่ดีปนกันไป มีบางคนยืนยันเสียงแข็งไปในทำนองว่า ไอ้เรื่องแบบเนี้ยไม่ได้กินเขาหรอก เพราะเขาตั้งใจแน่วแน่ว่างานศิลป์ของเขา เขาไม่เอาเข้ามายุ่งในโลก digital currency เด็ดขาด ซึ่งผมก็เคารพมุมมองเขาครับ แต่มันจะดีกว่ามั้ย ถ้าเราเปิดหูเปิดตาให้ทันเทคโนโลยี โดยเฉพาะเรื่อง digital currency , blockchain โดนโกงทีนึงนี่คือหมดตัวกันง่ายกว่าเงิน fiat อีก
อยากจะมาเล่าให้ฟังครับ และอยากให้ช่วยแชร์ไปให้คนรู้จักด้วย จะได้ระวังตัวกัน
Note
- ภาพประกอบ cyber security ทั้งสองนี่ของผมเองครับ ทำเอง วางขายบน AdobeStock
- อีกบัญชีนึงของผม "HikariHarmony" npub1exdtszhpw3ep643p9z8pahkw8zw00xa9pesf0u4txyyfqvthwapqwh48sw กำลังค่อยๆเอาผลงานจากโลกข้างนอกเข้ามา nostr ครับ ตั้งใจจะมาสร้างงานศิลปะในนี้ เพื่อนๆที่ชอบงาน จะได้ไม่ต้องออกไปหาที่ไหน
ผลงานของผมครับ - Anime girl fanarts : HikariHarmony - HikariHarmony on Nostr - General art : KeshikiRakuen - KeshikiRakuen อาจจะเป็นบัญชี nostr ที่สามของผม ถ้าไหวครับ
-
 @ 8947a945:9bfcf626
2024-10-17 07:33:00
@ 8947a945:9bfcf626
2024-10-17 07:33:00Hello everyone on Nostr and all my watchersand followersfrom DeviantArt, as well as those from other art platforms
I have been creating and sharing AI-generated anime girl fanart since the beginning of 2024 and have been running member-exclusive content on Patreon.
I also publish showcases of my artworks to Deviantart. I organically build up my audience from time to time. I consider it as one of my online businesses of art. Everything is slowly growing
On September 16, I received a DM from someone expressing interest in purchasing my art in NFT format and offering a very high price for each piece. We later continued the conversation via email.
Here’s a brief overview of what happened

- The first scammer selected the art they wanted to buy and offered a high price for each piece. They provided a URL to an NFT marketplace site running on the Ethereum (ETH) mainnet or ERC20. The site appeared suspicious, requiring email sign-up and linking a MetaMask wallet. However, I couldn't change the wallet address later. The minting gas fees were quite expensive, ranging from 0.15 to 0.2 ETH

-
The scammers tried to convince me that the high profits would easily cover the minting gas fees, so I had nothing to lose. Luckily, I didn’t have spare funds to purchase ETH for the gas fees at the time, so I tried negotiating with them as follows:
-
I offered to send them a lower-quality version of my art via email in exchange for the minting gas fees, but they refused.
- I offered them the option to pay in USD through Buy Me a Coffee shop here, but they refused.
- I offered them the option to pay via Bitcoin using the Lightning Network invoice , but they refused.
- I asked them to wait until I could secure the funds, and they agreed to wait.
The following week, a second scammer approached me with a similar offer, this time at an even higher price and through a different NFT marketplace website.
This second site also required email registration, and after navigating to the dashboard, it asked for a minting fee of 0.2 ETH. However, the site provided a wallet address for me instead of connecting a MetaMask wallet.
I told the second scammer that I was waiting to make a profit from the first sale, and they asked me to show them the first marketplace. They then warned me that the first site was a scam and even sent screenshots of victims, including one from OpenSea saying that Opensea is not paying.
This raised a red flag, and I began suspecting I might be getting scammed. On OpenSea, funds go directly to users' wallets after transactions, and OpenSea charges a much lower platform fee compared to the previous crypto bull run in 2020. Minting fees on OpenSea are also significantly cheaper, around 0.0001 ETH per transaction.
I also consulted with Thai NFT artist communities and the ex-chairman of the Thai Digital Asset Association. According to them, no one had reported similar issues, but they agreed it seemed like a scam.
After confirming my suspicions with my own research and consulting with the Thai crypto community, I decided to test the scammers’ intentions by doing the following
I minted the artwork they were interested in, set the price they offered, and listed it for sale on OpenSea. I then messaged them, letting them know the art was available and ready to purchase, with no royalty fees if they wanted to resell it.
They became upset and angry, insisting I mint the art on their chosen platform, claiming they had already funded their wallet to support me. When I asked for proof of their wallet address and transactions, they couldn't provide any evidence that they had enough funds.
Here’s what I want to warn all artists in the DeviantArt community or other platforms If you find yourself in a similar situation, be aware that scammers may be targeting you.
My Perspective why I Believe This is a Scam and What the Scammers Gain
From my experience with BTC and crypto since 2017, here's why I believe this situation is a scam, and what the scammers aim to achieve
First, looking at OpenSea, the largest NFT marketplace on the ERC20 network, they do not hold users' funds. Instead, funds from transactions go directly to users’ wallets. OpenSea’s platform fees are also much lower now compared to the crypto bull run in 2020. This alone raises suspicion about the legitimacy of other marketplaces requiring significantly higher fees.
I believe the scammers' tactic is to lure artists into paying these exorbitant minting fees, which go directly into the scammers' wallets. They convince the artists by promising to purchase the art at a higher price, making it seem like there's no risk involved. In reality, the artist has already lost by paying the minting fee, and no purchase is ever made.
In the world of Bitcoin (BTC), the principle is "Trust no one" and “Trustless finality of transactions” In other words, transactions are secure and final without needing trust in a third party.
In the world of Ethereum (ETH), the philosophy is "Code is law" where everything is governed by smart contracts deployed on the blockchain. These contracts are transparent, and even basic code can be read and understood. Promises made by people don’t override what the code says.
I also discuss this issue with art communities. Some people have strongly expressed to me that they want nothing to do with crypto as part of their art process. I completely respect that stance.
However, I believe it's wise to keep your eyes open, have some skin in the game, and not fall into scammers’ traps. Understanding the basics of crypto and NFTs can help protect you from these kinds of schemes.
If you found this article helpful, please share it with your fellow artists.
Until next time Take care
Note
- Both cyber security images are mine , I created and approved by AdobeStock to put on sale
- I'm working very hard to bring all my digital arts into Nostr to build my Sats business here to my another npub "HikariHarmony" npub1exdtszhpw3ep643p9z8pahkw8zw00xa9pesf0u4txyyfqvthwapqwh48sw
Link to my full gallery - Anime girl fanarts : HikariHarmony - HikariHarmony on Nostr - General art : KeshikiRakuen
-
 @ 319ad3e7:cc01d50a
2024-10-08 18:05:44
@ 319ad3e7:cc01d50a
2024-10-08 18:05:44LETTER FROM THE FOUNDER
Welcome to the inaugural edition of the Zap.Cooking newsletter!
What began as a simple idea and a collaborative effort has grown into a vibrant community. Food, in its unique way, transcends culture and connects us all. It’s at the dinner table where we break bread and share our lives. Here, we’ve created a space where people come together to exchange ideas and celebrate a shared passion for cooking and culinary excellence.
This is the Nostr way—a community built on shared ideas and a constructive culture. We are excited to embark on this new journey of sharing a newsletter with friends of Nostr and Zap.Cooking. We hope you enjoy this fresh approach and look forward to many shared recipes and conversations.
Bon appétit!
Seth, Founder of Zap.Cooking
\ __________________
Food Clubs For Life Outside The System
Jack Spirko is the founder and host of The Survival Podcast. In episode 3552, titled "Food Clubs for Life Outside The System," Jack engages in a fascinating two-hour conversation with Joshua Longbrook, who established a food club and hub in Chattanooga, TN, as a means of building a parallel society that respects food freedom and self-sovereignty. Agora Food Club is a private association of members who value natural, organic food and regenerative farming practices, creating and sustaining a locally based alternative food system. In this episode, they discuss the blueprint and what it takes to start a food club in your neighborhood.

Links to YT video and Food Club:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5uPcAfG-9AU

The Six-Ingredient Grandma Betty's Chicken Dijon Family Recipe
https://image.nostr.build/55d3f300fdc4563265f49f729476724f98ff0a062ce7f8d769bf136f0de05cf5.jpg
“Growing up there are a few staple foods that stick with you. For me, it was my Grandma Betty's Chicken Dijon. It was my birthday request every year and every time we cook it up it touches my heart. Grandma Betty passed away 7 years ago. This dish is dedicated to her, directly from her recipe book.” - Quiet Warrior
Grandma Betty's Chicken Dijon on zap.cooking
Glowing Rolls: Raw Vegan Sushi for a Healthy Boost!
https://image.nostr.build/b11da1b878fe48ee74cb1c6c1cc66692ce12827f26c256ecd7a184f99d9c7649.png
“All you need are your favorite vegetables, nori sheets, a bamboo mat, a cutting board, and a knife. For the dip, you can simply use soy sauce, or try this recipe for a delicious creamy dip. I make my own cream cheese with soaked cashews, nutritional yeast, salt, lime juice, and vinegar. You can also find vegan cream cheese or cashew cheese at a health food store. Feel free to add other veggies like bell pepper, chili, cucumber, fresh onion or anything you like! In the image I also used red bell pepper and shiitake.” - Essencial
Glowing Rolls: Raw Vegan Sushi for a Healthy Boost! on zap.cooking
Slow Cookin’ Tender Sweet-and-Sour Brisket
https://image.nostr.build/97a8a78e39fbe4d19f913ea3c7cac9b94ee20d155596a83e241f0fa71a51517a.jpg
“In this case, sweet-and-sour doesn’t mean Americanized Chinese food but rather the sauce that dominated the Shabbos and Pesach dinner table among American Jewish immigrants in the early 20th century.” - Lizsweig
Sweet-and-Sour Brisket on zap.cooking
2024 Nostriga Photo Album
\ Community Photos by AZA_to_₿_myself, Jeroen, elsat, Derek Ross, realjode, and SimplySarah
To share your Nostr community photos, please DM @ZapCooking on Nostr
https://image.nostr.build/388b3bb338672728337ef1c04c90f65655cc29c716f168d35dd4c7343d5802b0.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/011edabbe3f427c60506fddab024bfeb46c72cf5e0a808b562d7c3ace9f239a0.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/5fcb47e3a21bbbedafe245f311b6d43f1f610ad96eec26aa85cdcbd0958fdabf.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/c2eac240326a7e4ab176776c5d140d0017ccdfef89ef733eaf85efda8e0d39f5.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/078682ee987734911886592f377a356245b5a5ea2a15c44ba80e3101ae523b52.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/c28418d851f3ad7f61435813d8aee82d87af3de4472b4d718a1d2573ae7d38c8.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/d3a55e11d7927c7cae106491d00a0cfda8323b976aa29123a0fd4e4e3fe78505.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/bdd055b0b37a9ebcdc91411796ae6cf785338679e7f44aebf1dc721cc09b076c.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/e7bf6c58de70510e96ec3b10630f4a4cfb770026532e2d307b4f95346a4d9ea4.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/b8eb934f8f15aae87ed0db66e898062ec723a8f16d9e93229cd2783d2b158e9d.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/f999d2389c363be56543444f301e443ddc126f1caebb9462b74b800d54ed2c28.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/0ca2d868703298d222f9cabc3e10a73dcd2d1f82f1b22f8526d9360e9bec8cc7.jpg
https://image.nostr.build/94460309bf933bcd89887f16ea6c384fa5bc5e3eb74500de099a3a1405da8edc.jpg
UPCOMING NOSTR HAPPENINGS
To submit your Nostr event, please DM @ZapCooking on Nostr
Nostr Valley @ Happy Valley Brewing Company - October 12, 2024 - 12pm to 4pm (est)
https://image.nostr.build/6c830618389046460ad41e3704864adb338b2a980cc765de51106a2f65adba67.jpg
Nostrville 2.0 No Panels, All Party! @ Bitcoin Park - November 6, 2024 - 4:30pm to 7:30pm (cst)
Nostrville 2.0 - No panels, all party!, Wed, Nov 6, 2024, 4:30 PM | Meetup
ZAP.COOKING PRESENTS: LACE
https://image.nostr.build/fb37dfaa7efe8add086d75af2dfd193181de728e108bd2c8e095a60f7e64bc4f.jpg
\ SimplySarah: Let’s start by learning a little background on Lace. What is your food story?
\ Lace: Food for me runs in my veins. My family is from Jamaica and my grandmother began cooking as a girl. She brought her recipes with her to the UK in the 1950s and cooks the most delicious dishes. My mother has been a professional chef for over 40 years. Family meals at Christmas were always a big deal. However, it wasn't until 18, I began cooking at university where I vowed my children would know how to cook a healthy meal and not end up like the people around me living on take out and micro meals. As a student, I just recreated things I ate at home and when I was unsure, I'd call my mum or my grandmother for help. When I had kids, I put them in the kitchen at age 2 and my eldest, now 15, is an incredible chef. We are also well traveled and always enjoying local cuisine which also inspires our cooking.
SimplySarah: That is a lovely background. It seems it was a natural progression to want to get into writing cookbooks. I understand you are working on your second currently, but let's backtrack and talk about how the first one came to life.
Lace: It would seem so. I always wanted to write a book but a cookbook wasn't what I thought I would write first 😅 And yes, the second is coming next year, a co-authored book. The first, came about because of Facebook, actually. Admittedly, I am one of those people who posts food pictures. And my Facebook followers began asking me for my recipes all the time. And I would write them out... and then decided it made more sense to write them once inside a book and sell it. Hence Lace's Bad Ass Yard Food was born.
https://image.nostr.build/563b2d4299d824ef4fbb8b85749ba1bb24b0fb4025bf6b10fa2ddaed7217240a.jpg
SimplySarah: That's an awesome title! What IS Bad Ass Yard Food?
Lace: Hahaha, thank you! Yard food is what we (as Jamaicans in my family) call our cuisine. Yard food. Yard means home. So it's basically great homemade food. Typically, this is things like Curry Chicken, Fry Fish, Jerk Chicken, Rice and Peas, Hard Food (yam, dumplings and green bananas) and many other things.
SimplySarah: All those dishes sound phenomenal. If you had a go-to dish from the first cookbook what would you select? Maybe something that is always served on a weekly or regular basis at your home?
Lace: Oh they are! My favorite is curry goat. Curry Chicken has got to be the go to, I still cook it weekly now! And no matter where I've lived in the world, I can always prepare it.
https://image.nostr.build/da216e149bee8676a806f010ddde5a29eb4ffa0adeaf5f68265e0e2cc3f11649.jpg
SimplySarah: Funny, I believe you just posted on Nostr that you were in the process of making curry chicken if I recall correctly. Is the next cookbook following the same roots? Or are you and your partner exploring different cuisines?
Lace: That's right! I did just post that curry on Nostr. The next book is going to feature 8 of my favorite recipes. Some will be Jamaican but I also happen to love Asian inspired dishes and have some European favorites too which will be featured. This will be the first time I'm sharing non Caribbean dishes. As for me and my boyfriend, he is Colombian and an ex-military Chef. He has been sharing his food with us and has been enjoying eating food from different regions for the first time as a result of meeting me. It's great fun to bond through food.
Lace’s Curry Chicken with Purple Cabbage, Plantains, and White Rice:\ https://image.nostr.build/fb37dfaa7efe8add086d75af2dfd193181de728e108bd2c8e095a60f7e64bc4f.jpg
SimplySarah: Is he the co-author you are speaking about?
\ Lace: Nope. The other Authors of the book are all entrepreneurs who love food. The first edition will be available in november, it's called Made with Love. I will be featured in the second coming 2025.
SimplySarah: Oh, nice! How did you get tapped into this project?
Lace: Again, my facebook network. I was chatting with a lady who is a self made millionaire about money. She checked out my fb profile and said.. ohh I love your cooking videos, what a fun way to market (my tech business) and then invited me to check out the cookbook project and be part of it. And just like that I was in.
SimplySarah: Facebook definitely brings a lot of people together based on their favorite topics. Now that you are exploring Nostr and have such an incredible background with culinary arts, what do you hope to achieve here on this social protocol?
Lace: Yes, socials are great for that! Honestly, I just want to connect with folks who love great food and are into self development, natural living, love travel and sovereignty. On my second day on Nostr, I met you, a fellow foodie, so it's certainly working out well so far. :) And without all the ads and other crap fb force on it's users
SimplySarah: Personally, I am super thrilled you have joined Nostr. We need more foodies, and I love nerding out about anything food related, especially the food travel stories. I would absolutely love to follow your food journey, and I think all the Nostr foodies should too. Where can everyone find you, follow you, and maybe buy a cookbook?
Lace: Yay! Thank you. I love talking about food, cooking, sharing food, buying ingredients and trying food. You can find me on Facebook - the loved and hated, Nostr, and my personal website. There's no fancy sales page for the cookbook yet! 11 of my Jamaican recipes in one cute ebook :) I'm coming over to Zap Cooking too.
SimplySarah: One day you will be Nostr Only and forget all about Facebook. Haha! We look forward to having you on Zap.Cooking. We have a lot of ideas in the works and would love for you to be involved! I have one final question. First, I want to thank you for taking your time to spend your Saturday morning with me. This was fun. You mentioned you put your children in the kitchen at an early age. I'm a big fan of teaching kids life skills when they are young. Do you have any tips for parents to help them in the kitchen with their children?
Lace: I'm sure that will happen. My fb network has been instrumental in my success and surviving the rough time in my travel. Do tell me all about your ideas for Zap, I'd love to see how I can be involved!
Yes, tips for parents, When kids are eating solids, feed them home cooked meals, no jars, no processed stuff, healthy, varied, adventurous meals you eat. If you're eating octopus, let ‘em try. If you're eating veg, let them try. If you're eating chicken liver pate, let them try. Encourage a varied diet and pallet. Then at 2, get them in the kitchen. Let them peel garlic cloves, add herbs to meat, make meatballs, mix and taste things. Invite them to cook everyday. And have fun with it!
It's been my pleasure to spend time with you this Saturday morning Sarah. Thank YOU.
You can find the talented Lace at:
https://www.facebook.com/iamlaceflowers
https://primal.net/p/npub1ruhmx2wy663u9k2sams6qrlvgq86t3p4q3ygwgp5wqzcrgd6fh7sr20ys2
https://www.iamlaceflowers.com/workwithme
Follow Zap.Cooking Content Coordinator SimplySarah at:
https://image.nostr.build/c208bb8d562421beb00cc26fcf38417a0d52660659f4ac9d40365f3761a486b8.png
-
 @ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-10-06 11:21:27
@ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-10-06 11:21:27Hey folks, today we're diving into an exciting and emerging topic: personal artificial intelligence (PAI) and its connection to sovereignty, privacy, and ethics. With the rapid advancements in AI, there's a growing interest in the development of personal AI agents that can work on behalf of the user, acting autonomously and providing tailored services. However, as with any new technology, there are several critical factors that shape the future of PAI. Today, we'll explore three key pillars: privacy and ownership, explainability, and bias.
1. Privacy and Ownership: Foundations of Personal AI
At the heart of personal AI, much like self-sovereign identity (SSI), is the concept of ownership. For personal AI to be truly effective and valuable, users must own not only their data but also the computational power that drives these systems. This autonomy is essential for creating systems that respect the user's privacy and operate independently of large corporations.
In this context, privacy is more than just a feature—it's a fundamental right. Users should feel safe discussing sensitive topics with their AI, knowing that their data won’t be repurposed or misused by big tech companies. This level of control and data ownership ensures that users remain the sole beneficiaries of their information and computational resources, making privacy one of the core pillars of PAI.
2. Bias and Fairness: The Ethical Dilemma of LLMs
Most of today’s AI systems, including personal AI, rely heavily on large language models (LLMs). These models are trained on vast datasets that represent snapshots of the internet, but this introduces a critical ethical challenge: bias. The datasets used for training LLMs can be full of biases, misinformation, and viewpoints that may not align with a user’s personal values.
This leads to one of the major issues in AI ethics for personal AI—how do we ensure fairness and minimize bias in these systems? The training data that LLMs use can introduce perspectives that are not only unrepresentative but potentially harmful or unfair. As users of personal AI, we need systems that are free from such biases and can be tailored to our individual needs and ethical frameworks.
Unfortunately, training models that are truly unbiased and fair requires vast computational resources and significant investment. While large tech companies have the financial means to develop and train these models, individual users or smaller organizations typically do not. This limitation means that users often have to rely on pre-trained models, which may not fully align with their personal ethics or preferences. While fine-tuning models with personalized datasets can help, it's not a perfect solution, and bias remains a significant challenge.
3. Explainability: The Need for Transparency
One of the most frustrating aspects of modern AI is the lack of explainability. Many LLMs operate as "black boxes," meaning that while they provide answers or make decisions, it's often unclear how they arrived at those conclusions. For personal AI to be effective and trustworthy, it must be transparent. Users need to understand how the AI processes information, what data it relies on, and the reasoning behind its conclusions.
Explainability becomes even more critical when AI is used for complex decision-making, especially in areas that impact other people. If an AI is making recommendations, judgments, or decisions, it’s crucial for users to be able to trace the reasoning process behind those actions. Without this transparency, users may end up relying on AI systems that provide flawed or biased outcomes, potentially causing harm.
This lack of transparency is a major hurdle for personal AI development. Current LLMs, as mentioned earlier, are often opaque, making it difficult for users to trust their outputs fully. The explainability of AI systems will need to be improved significantly to ensure that personal AI can be trusted for important tasks.
Addressing the Ethical Landscape of Personal AI
As personal AI systems evolve, they will increasingly shape the ethical landscape of AI. We’ve already touched on the three core pillars—privacy and ownership, bias and fairness, and explainability. But there's more to consider, especially when looking at the broader implications of personal AI development.
Most current AI models, particularly those from big tech companies like Facebook, Google, or OpenAI, are closed systems. This means they are aligned with the goals and ethical frameworks of those companies, which may not always serve the best interests of individual users. Open models, such as Meta's LLaMA, offer more flexibility and control, allowing users to customize and refine the AI to better meet their personal needs. However, the challenge remains in training these models without significant financial and technical resources.
There’s also the temptation to use uncensored models that aren’t aligned with the values of large corporations, as they provide more freedom and flexibility. But in reality, models that are entirely unfiltered may introduce harmful or unethical content. It’s often better to work with aligned models that have had some of the more problematic biases removed, even if this limits some aspects of the system’s freedom.
The future of personal AI will undoubtedly involve a deeper exploration of these ethical questions. As AI becomes more integrated into our daily lives, the need for privacy, fairness, and transparency will only grow. And while we may not yet be able to train personal AI models from scratch, we can continue to shape and refine these systems through curated datasets and ongoing development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, personal AI represents an exciting new frontier, but one that must be navigated with care. Privacy, ownership, bias, and explainability are all essential pillars that will define the future of these systems. As we continue to develop personal AI, we must remain vigilant about the ethical challenges they pose, ensuring that they serve the best interests of users while remaining transparent, fair, and aligned with individual values.
If you have any thoughts or questions on this topic, feel free to reach out—I’d love to continue the conversation!
-
 @ 4ba8e86d:89d32de4
2024-10-05 22:04:32
@ 4ba8e86d:89d32de4
2024-10-05 22:04:32Como funciona o PGP.
O texto a seguir foi retirado do capítulo 1 do documento Introdução à criptografia na documentação do PGP 6.5.1. Copyright © 1990-1999 Network Associates, Inc. Todos os direitos reservados.
-O que é criptografia? -Criptografia forte -Como funciona a criptografia? -Criptografia convencional -Cifra de César -Gerenciamento de chaves e criptografia convencional -Criptografia de chave pública -Como funciona o PGP - Chaves • Assinaturas digitais -Funções hash • Certificados digitais -Distribuição de certificados -Formatos de certificado •Validade e confiança -Verificando validade -Estabelecendo confiança -Modelos de confiança • Revogação de certificado -Comunicar que um certificado foi revogado -O que é uma senha? -Divisão de chave
Os princípios básicos da criptografia.
Quando Júlio César enviou mensagens aos seus generais, ele não confiou nos seus mensageiros. Então ele substituiu cada A em suas mensagens por um D, cada B por um E, e assim por diante através do alfabeto. Somente alguém que conhecesse a regra “shift by 3” poderia decifrar suas mensagens. E assim começamos.
Criptografia e descriptografia.
Os dados que podem ser lidos e compreendidos sem quaisquer medidas especiais são chamados de texto simples ou texto não criptografado. O método de disfarçar o texto simples de forma a ocultar sua substância é chamado de criptografia. Criptografar texto simples resulta em um jargão ilegível chamado texto cifrado. Você usa criptografia para garantir que as informações sejam ocultadas de qualquer pessoa a quem não se destinam, mesmo daqueles que podem ver os dados criptografados. O processo de reverter o texto cifrado ao texto simples original é chamado de descriptografia . A Figura 1-1 ilustra esse processo.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_5922365650718442651699905288.webp
Figura 1-1. Criptografia e descriptografia
O que é criptografia?
Criptografia é a ciência que usa a matemática para criptografar e descriptografar dados. A criptografia permite armazenar informações confidenciais ou transmiti-las através de redes inseguras (como a Internet) para que não possam ser lidas por ninguém, exceto pelo destinatário pretendido. Embora a criptografia seja a ciência que protege os dados, a criptoanálise é a ciência que analisa e quebra a comunicação segura. A criptoanálise clássica envolve uma combinação interessante de raciocínio analítico, aplicação de ferramentas matemáticas, descoberta de padrões, paciência, determinação e sorte. Os criptoanalistas também são chamados de atacantes. A criptologia abrange tanto a criptografia quanto a criptoanálise.
Criptografia forte.
"Existem dois tipos de criptografia neste mundo: a criptografia que impedirá a sua irmã mais nova de ler os seus arquivos, e a criptografia que impedirá os principais governos de lerem os seus arquivos. Este livro é sobre o último." --Bruce Schneier, Criptografia Aplicada: Protocolos, Algoritmos e Código Fonte em C. PGP também trata deste último tipo de criptografia. A criptografia pode ser forte ou fraca, conforme explicado acima. A força criptográfica é medida no tempo e nos recursos necessários para recuperar o texto simples. O resultado de uma criptografia forte é um texto cifrado que é muito difícil de decifrar sem a posse da ferramenta de decodificação apropriada. Quão díficil? Dado todo o poder computacional e o tempo disponível de hoje – mesmo um bilhão de computadores fazendo um bilhão de verificações por segundo – não é possível decifrar o resultado de uma criptografia forte antes do fim do universo. Alguém poderia pensar, então, que uma criptografia forte resistiria muito bem até mesmo contra um criptoanalista extremamente determinado. Quem pode realmente dizer? Ninguém provou que a criptografia mais forte disponível hoje resistirá ao poder computacional de amanhã. No entanto, a criptografia forte empregada pelo PGP é a melhor disponível atualmente.
Contudo, a vigilância e o conservadorismo irão protegê-lo melhor do que as alegações de impenetrabilidade.
Como funciona a criptografia?
Um algoritmo criptográfico, ou cifra, é uma função matemática usada no processo de criptografia e descriptografia. Um algoritmo criptográfico funciona em combinação com uma chave – uma palavra, número ou frase – para criptografar o texto simples. O mesmo texto simples é criptografado em texto cifrado diferente com chaves diferentes. A segurança dos dados criptografados depende inteiramente de duas coisas: a força do algoritmo criptográfico e o sigilo da chave. Um algoritmo criptográfico, mais todas as chaves possíveis e todos os protocolos que o fazem funcionar constituem um criptossistema. PGP é um criptossistema.
Criptografia convencional.
Na criptografia convencional, também chamada de criptografia de chave secreta ou de chave simétrica , uma chave é usada tanto para criptografia quanto para descriptografia. O Data Encryption Standard (DES) é um exemplo de criptossistema convencional amplamente empregado pelo Governo Federal. A Figura 1-2 é uma ilustração do processo de criptografia convencional.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_1563316185075842071699905520.webp
Figura 1-2. Criptografia convencional
Cifra de César.
Um exemplo extremamente simples de criptografia convencional é uma cifra de substituição. Uma cifra de substituição substitui uma informação por outra. Isso é feito com mais frequência compensando as letras do alfabeto. Dois exemplos são o Anel Decodificador Secreto do Capitão Meia-Noite, que você pode ter possuído quando era criança, e a cifra de Júlio César. Em ambos os casos, o algoritmo serve para compensar o alfabeto e a chave é o número de caracteres para compensá-lo. Por exemplo, se codificarmos a palavra "SEGREDO" usando o valor chave de César de 3, deslocaremos o alfabeto para que a terceira letra abaixo (D) comece o alfabeto. Então começando com A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z e deslizando tudo para cima em 3, você obtém DEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABC onde D=A, E=B, F=C e assim por diante. Usando este esquema, o texto simples, "SECRET" é criptografado como "VHFUHW". Para permitir que outra pessoa leia o texto cifrado, você diz a ela que a chave é 3. Obviamente, esta é uma criptografia extremamente fraca para os padrões atuais, mas, ei, funcionou para César e ilustra como funciona a criptografia convencional.
Gerenciamento de chaves e criptografia convencional.
A criptografia convencional tem benefícios. É muito rápido. É especialmente útil para criptografar dados que não vão a lugar nenhum. No entanto, a criptografia convencional por si só como meio de transmissão segura de dados pode ser bastante cara, simplesmente devido à dificuldade de distribuição segura de chaves. Lembre-se de um personagem do seu filme de espionagem favorito: a pessoa com uma pasta trancada e algemada ao pulso. Afinal, o que há na pasta? Provavelmente não é o código de lançamento de mísseis/fórmula de biotoxina/plano de invasão em si. É a chave que irá descriptografar os dados secretos. Para que um remetente e um destinatário se comuniquem com segurança usando criptografia convencional, eles devem chegar a um acordo sobre uma chave e mantê-la secreta entre si. Se estiverem em locais físicos diferentes, devem confiar em um mensageiro, no Bat Phone ou em algum outro meio de comunicação seguro para evitar a divulgação da chave secreta durante a transmissão. Qualquer pessoa que ouvir ou interceptar a chave em trânsito poderá posteriormente ler, modificar e falsificar todas as informações criptografadas ou autenticadas com essa chave. Do DES ao Anel Decodificador Secreto do Capitão Midnight, o problema persistente com a criptografia convencional é a distribuição de chaves: como você leva a chave ao destinatário sem que alguém a intercepte?
Criptografia de chave pública.
Os problemas de distribuição de chaves são resolvidos pela criptografia de chave pública, cujo conceito foi introduzido por Whitfield Diffie e Martin Hellman em 1975. (Há agora evidências de que o Serviço Secreto Britânico a inventou alguns anos antes de Diffie e Hellman, mas a manteve um segredo militar - e não fez nada com isso.
[JH Ellis: The Possibility of Secure Non-Secret Digital Encryption, CESG Report, January 1970]) A criptografia de chave pública é um esquema assimétrico que usa um par de chaves para criptografia: uma chave pública, que criptografa os dados, e uma chave privada ou secreta correspondente para descriptografia. Você publica sua chave pública para o mundo enquanto mantém sua chave privada em segredo. Qualquer pessoa com uma cópia da sua chave pública pode criptografar informações que somente você pode ler. Até mesmo pessoas que você nunca conheceu. É computacionalmente inviável deduzir a chave privada da chave pública. Qualquer pessoa que possua uma chave pública pode criptografar informações, mas não pode descriptografá-las. Somente a pessoa que possui a chave privada correspondente pode descriptografar as informações.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_6137622541655550851699909180.webp
Figura 1-3. Criptografia de chave pública O principal benefício da criptografia de chave pública é que ela permite que pessoas que não possuem nenhum acordo de segurança pré-existente troquem mensagens com segurança. A necessidade de remetente e destinatário compartilharem chaves secretas através de algum canal seguro é eliminada; todas as comunicações envolvem apenas chaves públicas e nenhuma chave privada é transmitida ou compartilhada. Alguns exemplos de criptossistemas de chave pública são Elgamal (nomeado em homenagem a seu inventor, Taher Elgamal), RSA (nomeado em homenagem a seus inventores, Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir e Leonard Adleman), Diffie-Hellman (nomeado, você adivinhou, em homenagem a seus inventores). ) e DSA, o algoritmo de assinatura digital (inventado por David Kravitz). Como a criptografia convencional já foi o único meio disponível para transmitir informações secretas, o custo dos canais seguros e da distribuição de chaves relegou a sua utilização apenas àqueles que podiam pagar, como governos e grandes bancos (ou crianças pequenas com anéis descodificadores secretos). A criptografia de chave pública é a revolução tecnológica que fornece criptografia forte para as massas adultas. Lembra do mensageiro com a pasta trancada e algemada ao pulso? A criptografia de chave pública o tira do mercado (provavelmente para seu alívio).
Como funciona o PGP.
O PGP combina alguns dos melhores recursos da criptografia convencional e de chave pública. PGP é um criptossistema híbrido. Quando um usuário criptografa texto simples com PGP, o PGP primeiro compacta o texto simples. A compactação de dados economiza tempo de transmissão do modem e espaço em disco e, mais importante ainda, fortalece a segurança criptográfica. A maioria das técnicas de criptoanálise explora padrões encontrados no texto simples para quebrar a cifra. A compressão reduz esses padrões no texto simples, aumentando assim enormemente a resistência à criptoanálise. (Arquivos que são muito curtos para compactar ou que não são compactados bem não são compactados.) O PGP então cria uma chave de sessão, que é uma chave secreta única. Esta chave é um número aleatório gerado a partir dos movimentos aleatórios do mouse e das teclas digitadas. Esta chave de sessão funciona com um algoritmo de criptografia convencional rápido e muito seguro para criptografar o texto simples; o resultado é texto cifrado. Depois que os dados são criptografados, a chave da sessão é criptografada na chave pública do destinatário. Essa chave de sessão criptografada com chave pública é transmitida junto com o texto cifrado ao destinatário.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_1978130242364857481699910331.webp
Figura 1-4. Como funciona a criptografia PGP A descriptografia funciona ao contrário. A cópia do PGP do destinatário usa sua chave privada para recuperar a chave de sessão temporária, que o PGP usa para descriptografar o texto cifrado criptografado convencionalmente.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_1978130242364857481699910331.webp
Figura 1-5. Como funciona a descriptografia PGP A combinação dos dois métodos de criptografia combina a conveniência da criptografia de chave pública com a velocidade da criptografia convencional. A criptografia convencional é cerca de 1.000 vezes mais rápida que a criptografia de chave pública. A criptografia de chave pública, por sua vez, fornece uma solução para
problemas de distribuição de chaves e transmissão de dados. Usados em conjunto, o desempenho e a distribuição de chaves são melhorados sem qualquer sacrifício na segurança.
Chaves.
Uma chave é um valor que funciona com um algoritmo criptográfico para produzir um texto cifrado específico. As chaves são basicamente números muito, muito, muito grandes. O tamanho da chave é medido em bits; o número que representa uma chave de 1024 bits é enorme. Na criptografia de chave pública, quanto maior a chave, mais seguro é o texto cifrado. No entanto, o tamanho da chave pública e o tamanho da chave secreta da criptografia convencional não têm nenhuma relação. Uma chave convencional de 80 bits tem a força equivalente a uma chave pública de 1.024 bits. Uma chave convencional de 128 bits é equivalente a uma chave pública de 3.000 bits. Novamente, quanto maior a chave, mais segura, mas os algoritmos usados para cada tipo de criptografia são muito diferentes e, portanto, a comparação é como a de maçãs com laranjas. Embora as chaves pública e privada estejam matematicamente relacionadas, é muito difícil derivar a chave privada dada apenas a chave pública; no entanto, derivar a chave privada é sempre possível, desde que haja tempo e capacidade computacional suficientes. Isto torna muito importante escolher chaves do tamanho certo; grande o suficiente para ser seguro, mas pequeno o suficiente para ser aplicado rapidamente. Além disso, você precisa considerar quem pode estar tentando ler seus arquivos, quão determinados eles estão, quanto tempo têm e quais podem ser seus recursos. Chaves maiores serão criptograficamente seguras por um longo período de tempo. Se o que você deseja criptografar precisar ficar oculto por muitos anos, você pode usar uma chave muito grande. Claro, quem sabe quanto tempo levará para determinar sua chave usando os computadores mais rápidos e eficientes de amanhã? Houve um tempo em que uma chave simétrica de 56 bits era considerada extremamente segura. As chaves são armazenadas de forma criptografada. O PGP armazena as chaves em dois arquivos no seu disco rígido; um para chaves públicas e outro para chaves privadas. Esses arquivos são chamados de chaveiros. Ao usar o PGP, você normalmente adicionará as chaves públicas dos seus destinatários ao seu chaveiro público. Suas chaves privadas são armazenadas em seu chaveiro privado. Se você perder seu chaveiro privado, não será possível descriptografar nenhuma informação criptografada nas chaves desse anel.
Assinaturas digitais.
Um grande benefício da criptografia de chave pública é que ela fornece um método para empregar assinaturas digitais. As assinaturas digitais permitem ao destinatário da informação verificar a autenticidade da origem da informação e também verificar se a informação está intacta. Assim, as assinaturas digitais de chave pública fornecem autenticação e integridade de dados. A assinatura digital também proporciona o não repúdio, o que significa que evita que o remetente alegue que não enviou realmente as informações. Esses recursos são tão fundamentais para a criptografia quanto a privacidade, se não mais. Uma assinatura digital tem a mesma finalidade de uma assinatura manuscrita. No entanto, uma assinatura manuscrita é fácil de falsificar. Uma assinatura digital é superior a uma assinatura manuscrita porque é quase impossível de ser falsificada, além de atestar o conteúdo da informação, bem como a identidade do signatário.
Algumas pessoas tendem a usar mais assinaturas do que criptografia. Por exemplo, você pode não se importar se alguém souber que você acabou de depositar US$ 1.000 em sua conta, mas quer ter certeza de que foi o caixa do banco com quem você estava lidando. A maneira básica pela qual as assinaturas digitais são criadas é ilustrada na Figura 1-6 . Em vez de criptografar informações usando a chave pública de outra pessoa, você as criptografa com sua chave privada. Se as informações puderem ser descriptografadas com sua chave pública, elas deverão ter se originado em você.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_4033165715613998201699910446.webp
Figura 1-6. Assinaturas digitais simples
Funções hash.
O sistema descrito acima apresenta alguns problemas. É lento e produz um enorme volume de dados – pelo menos o dobro do tamanho da informação original. Uma melhoria no esquema acima é a adição de uma função hash unidirecional no processo. Uma função hash unidirecional recebe uma entrada de comprimento variável – neste caso, uma mensagem de qualquer comprimento, até mesmo milhares ou milhões de bits – e produz uma saída de comprimento fixo; digamos, 160 bits. A função hash garante que, se a informação for alterada de alguma forma – mesmo que por apenas um bit – seja produzido um valor de saída totalmente diferente. O PGP usa uma função hash criptograficamente forte no texto simples que o usuário está assinando. Isso gera um item de dados de comprimento fixo conhecido como resumo da mensagem. (Novamente, qualquer alteração nas informações resulta em um resumo totalmente diferente.) Então o PGP usa o resumo e a chave privada para criar a “assinatura”. O PGP transmite a assinatura e o texto simples juntos. Ao receber a mensagem, o destinatário utiliza o PGP para recalcular o resumo, verificando assim a assinatura. O PGP pode criptografar o texto simples ou não; assinar texto simples é útil se alguns dos destinatários não estiverem interessados ou não forem capazes de verificar a assinatura. Desde que uma função hash segura seja usada, não há como retirar a assinatura de alguém de um documento e anexá-la a outro, ou alterar uma mensagem assinada de qualquer forma. A menor alteração em um documento assinado causará falha no processo de verificação da assinatura digital.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_2943209062439984111699910538.webp
Figura 1-7. Assinaturas digitais seguras As assinaturas digitais desempenham um papel importante na autenticação e validação de chaves de outros usuários PGP.
Certificados digitais.
Um problema com os criptosistemas de chave pública é que os usuários devem estar constantemente vigilantes para garantir que estão criptografando com a chave da pessoa correta. Num ambiente onde é seguro trocar chaves livremente através de servidores públicos, os ataques man-in-the-middle são uma ameaça potencial. Neste tipo de ataque, alguém publica uma chave falsa com o nome e ID de usuário do destinatário pretendido. Os dados criptografados – e interceptados por – o verdadeiro proprietário desta chave falsa estão agora em mãos erradas. Em um ambiente de chave pública, é vital que você tenha certeza de que a chave pública para a qual você está criptografando os dados é de fato a chave pública do destinatário pretendido e não uma falsificação. Você pode simplesmente criptografar apenas as chaves que foram entregues fisicamente a você. Mas suponha que você precise trocar informações com pessoas que nunca conheceu; como você pode saber se tem a chave correta? Os certificados digitais, ou certs, simplificam a tarefa de estabelecer se uma chave pública realmente pertence ao suposto proprietário. Um certificado é uma forma de credencial. Exemplos podem ser sua carteira de motorista, seu cartão de previdência social ou sua certidão de nascimento. Cada um deles contém algumas informações que identificam você e alguma autorização informando que outra pessoa confirmou sua identidade. Alguns certificados, como o seu passaporte, são uma confirmação importante o suficiente da sua identidade para que você não queira perdê-los, para que ninguém os use para se passar por você.
Um certificado digital são dados que funcionam como um certificado físico. Um certificado digital é uma informação incluída na chave pública de uma pessoa que ajuda outras pessoas a verificar se uma chave é genuína ou válida. Os certificados digitais são usados para impedir tentativas de substituir a chave de uma pessoa por outra.
Um certificado digital consiste em três coisas:
● Uma chave pública.
● Informações do certificado. (Informações de "identidade" sobre o usuário, como nome, ID do usuário e assim por diante.) ● Uma ou mais assinaturas digitais.
O objetivo da assinatura digital em um certificado é afirmar que as informações do certificado foram atestadas por alguma outra pessoa ou entidade. A assinatura digital não atesta a autenticidade do certificado como um todo; ele atesta apenas que as informações de identidade assinadas acompanham ou estão vinculadas à chave pública. Assim, um certificado é basicamente uma chave pública com uma ou duas formas de identificação anexadas, além de um forte selo de aprovação de algum outro indivíduo confiável.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_7979578982089845401699910854.webp
Figura 1-8. Anatomia de um certificado PGP
Distribuição de certificados.
Os certificados são utilizados quando é necessário trocar chaves públicas com outra pessoa. Para pequenos grupos de pessoas que desejam se comunicar com segurança, é fácil trocar manualmente disquetes ou e-mails contendo a chave pública de cada proprietário. Esta é a distribuição manual de chave pública e é prática apenas até certo ponto. Além desse ponto, é necessário implementar sistemas que possam fornecer os mecanismos necessários de segurança, armazenamento e troca para que colegas de trabalho, parceiros de negócios ou estranhos possam se comunicar, se necessário. Eles podem vir na forma de repositórios somente de armazenamento, chamados Servidores de Certificados, ou sistemas mais estruturados que fornecem recursos adicionais de gerenciamento de chaves e são chamados de Infraestruturas de Chave Pública (PKIs).
Servidores de certificados.
Um servidor de certificados, também chamado de servidor certificado ou servidor de chaves, é um banco de dados que permite aos usuários enviar e recuperar certificados digitais. Um servidor certificado geralmente fornece alguns recursos administrativos que permitem que uma empresa mantenha suas políticas de segurança – por exemplo, permitindo que apenas as chaves que atendam a determinados requisitos sejam armazenadas.
Infraestruturas de Chave Pública.
Uma PKI contém os recursos de armazenamento de certificados de um servidor de certificados, mas também fornece recursos de gerenciamento de certificados (a capacidade de emitir, revogar, armazenar, recuperar e confiar em certificados). A principal característica de uma PKI é a introdução do que é conhecido como Autoridade Certificadora,ou CA, que é uma entidade humana — uma pessoa, grupo, departamento, empresa ou outra associação — que uma organização autorizou a emitir certificados para seus usuários de computador. (A função de uma CA é análoga à do Passport Office do governo de um país.) Uma CA cria certificados e os assina digitalmente usando a chave privada da CA. Devido ao seu papel na criação de certificados, a CA é o componente central de uma PKI. Usando a chave pública da CA, qualquer pessoa que queira verificar a autenticidade de um certificado verifica a assinatura digital da CA emissora e, portanto, a integridade do conteúdo do certificado (mais importante ainda, a chave pública e a identidade do titular do certificado).
Formatos de certificado.
Um certificado digital é basicamente uma coleção de informações de identificação vinculadas a uma chave pública e assinadas por um terceiro confiável para provar sua autenticidade. Um certificado digital pode ter vários formatos diferentes.
O PGP reconhece dois formatos de certificado diferentes:
● Certificados PGP ● Certificados X.509 Formato do certificado PGP. Um certificado PGP inclui (mas não está limitado a) as seguintes informações: ● O número da versão do PGP — identifica qual versão do PGP foi usada para criar a chave associada ao certificado. A chave pública do titular do certificado — a parte pública do seu par de chaves, juntamente com o algoritmo da chave: RSA, DH (Diffie-Hellman) ou DSA (Algoritmo de Assinatura Digital).
● As informações do detentor do certificado — consistem em informações de “identidade” sobre o usuário, como seu nome, ID de usuário, fotografia e assim por diante. ● A assinatura digital do proprietário do certificado — também chamada de autoassinatura, é a assinatura que utiliza a chave privada correspondente da chave pública associada ao certificado. ● O período de validade do certificado — a data/hora de início e a data/hora de expiração do certificado; indica quando o certificado irá expirar. ● O algoritmo de criptografia simétrica preferido para a chave — indica o algoritmo de criptografia para o qual o proprietário do certificado prefere que as informações sejam criptografadas. Os algoritmos suportados são CAST, IDEA ou Triple-DES. Você pode pensar em um certificado PGP como uma chave pública com um ou mais rótulos vinculados a ele (veja a Figura 1.9 ). Nessas 'etiquetas' você encontrará informações que identificam o proprietário da chave e uma assinatura do proprietário da chave, que afirma que a chave e a identificação andam juntas. (Essa assinatura específica é chamada de autoassinatura; todo certificado PGP contém uma autoassinatura.) Um aspecto único do formato de certificado PGP é que um único certificado pode conter múltiplas assinaturas. Várias ou muitas pessoas podem assinar o par chave/identificação para atestar a sua própria garantia de que a chave pública pertence definitivamente ao proprietário especificado. Se você procurar em um servidor de certificados público, poderá notar que certos certificados, como o do criador do PGP, Phil Zimmermann, contêm muitas assinaturas. Alguns certificados PGP consistem em uma chave pública com vários rótulos, cada um contendo um meio diferente de identificar o proprietário da chave (por exemplo, o nome do proprietário e a conta de e-mail corporativa, o apelido do proprietário e a conta de e-mail residencial, uma fotografia do proprietário — tudo em um certificado). A lista de assinaturas de cada uma dessas identidades pode ser diferente; as assinaturas atestam a autenticidade de que um dos rótulos pertence à chave pública, e não que todos os rótulos da chave sejam autênticos. (Observe que 'autêntico' está nos olhos de quem vê - assinaturas são opiniões, e diferentes pessoas dedicam diferentes níveis de devida diligência na verificação da autenticidade antes de assinar uma chave.)
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_7979578982089845401699910854.webp
Figura 1-9. Um certificado PGP
Formato de certificado X.509.
X.509 é outro formato de certificado muito comum. Todos os certificados X.509 estão em conformidade com o padrão internacional ITU-T X.509; assim (teoricamente) os certificados X.509 criados para um aplicativo podem ser usados por qualquer aplicativo compatível com X.509. Na prática, porém, diferentes empresas criaram suas próprias extensões para certificados X.509, e nem todas funcionam juntas. Um certificado exige que alguém valide que uma chave pública e o nome do proprietário da chave andam juntos. Com os certificados PGP, qualquer pessoa pode desempenhar o papel de validador. Com certificados X.509, o validador é sempre uma Autoridade Certificadora ou alguém designado por uma CA. (Tenha em mente que os certificados PGP também suportam totalmente uma estrutura hierárquica usando uma CA para validar certificados.)
Um certificado X.509 é uma coleção de um conjunto padrão de campos contendo informações sobre um usuário ou dispositivo e sua chave pública correspondente. O padrão X.509 define quais informações vão para o certificado e descreve como codificá-lo (o formato dos dados). Todos os certificados X.509 possuem os seguintes dados:
O número da versão X.509
— identifica qual versão do padrão X.509 se aplica a este certificado, o que afeta quais informações podem ser especificadas nele. A mais atual é a versão 3.
A chave pública do titular do certificado
— a chave pública do titular do certificado, juntamente com um identificador de algoritmo que especifica a qual sistema criptográfico a chave pertence e quaisquer parâmetros de chave associados.
O número de série do certificado
— a entidade (aplicação ou pessoa) que criou o certificado é responsável por atribuir-lhe um número de série único para distingui-lo de outros certificados que emite. Esta informação é usada de diversas maneiras; por exemplo, quando um certificado é revogado, seu número de série é colocado em uma Lista de Revogação de Certificados ou CRL.
O identificador exclusivo do detentor do certificado
— (ou DN — nome distinto). Este nome pretende ser exclusivo na Internet. Este nome pretende ser exclusivo na Internet. Um DN consiste em múltiplas subseções e pode ser parecido com isto: CN=Bob Allen, OU=Divisão Total de Segurança de Rede, O=Network Associates, Inc., C=EUA (Referem-se ao nome comum, à unidade organizacional, à organização e ao país do sujeito .)
O período de validade do certificado
— a data/hora de início e a data/hora de expiração do certificado; indica quando o certificado irá expirar.
O nome exclusivo do emissor do certificado
— o nome exclusivo da entidade que assinou o certificado. Normalmente é uma CA. A utilização do certificado implica confiar na entidade que assinou este certificado. (Observe que em alguns casos, como certificados de CA raiz ou de nível superior , o emissor assina seu próprio certificado.)
A assinatura digital do emitente
— a assinatura utilizando a chave privada da entidade que emitiu o certificado.
O identificador do algoritmo de assinatura
— identifica o algoritmo usado pela CA para assinar o certificado.
Existem muitas diferenças entre um certificado X.509 e um certificado PGP, mas as mais importantes são as seguintes: você pode criar seu próprio certificado PGP;
● você deve solicitar e receber um certificado X.509 de uma autoridade de certificação
● Os certificados X.509 suportam nativamente apenas um único nome para o proprietário da chave
● Os certificados X.509 suportam apenas uma única assinatura digital para atestar a validade da chave
Para obter um certificado X.509, você deve solicitar a uma CA a emissão de um certificado. Você fornece sua chave pública, prova de que possui a chave privada correspondente e algumas informações específicas sobre você. Em seguida, você assina digitalmente as informações e envia o pacote completo – a solicitação de certificado – para a CA. A CA então realiza algumas diligências para verificar se as informações fornecidas estão corretas e, em caso afirmativo, gera o certificado e o devolve.
Você pode pensar em um certificado X.509 como um certificado de papel padrão (semelhante ao que você recebeu ao concluir uma aula de primeiros socorros básicos) com uma chave pública colada nele. Ele contém seu nome e algumas informações sobre você, além da assinatura da pessoa que o emitiu para você.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_4125576093727079591699911294.webp
Figura 1-10. Um certificado X.509 Provavelmente, o uso mais visível dos certificados X.509 atualmente é em navegadores da web.
Validade e confiança Cada usuário em um sistema de chave pública está vulnerável a confundir uma chave falsa (certificado) com uma chave real. Validade é a confiança de que um certificado de chave pública pertence ao seu suposto proprietário. A validade é essencial em um ambiente de chave pública onde você deve estabelecer constantemente se um determinado certificado é autêntico ou não. Depois de ter certeza de que um certificado pertencente a outra pessoa é válido, você pode assinar a cópia em seu chaveiro para atestar que verificou o certificado e que ele é autêntico. Se quiser que outras pessoas saibam que você deu ao certificado seu selo de aprovação, você pode exportar a assinatura para um servidor de certificados para que outras pessoas possam vê-la.
Conforme descrito na seção Infraestruturas de Chave Pública , algumas empresas designam uma ou mais Autoridades de Certificação (CAs) para indicar a validade do certificado. Em uma organização que usa uma PKI com certificados X.509, é função da CA emitir certificados aos usuários — um processo que geralmente envolve responder à solicitação de certificado do usuário. Em uma organização que usa certificados PGP sem PKI, é função da CA verificar a autenticidade de todos os certificados PGP e depois assinar os bons. Basicamente, o objetivo principal de uma CA é vincular uma chave pública às informações de identificação contidas no certificado e, assim, garantir a terceiros que algum cuidado foi tomado para garantir que esta ligação das informações de identificação e da chave seja válida. O CA é o Grand Pooh-bah da validação em uma organização; alguém em quem todos confiam e, em algumas organizações, como aquelas que utilizam uma PKI, nenhum certificado é considerado válido, a menos que tenha sido assinado por uma CA confiável.
Verificando validade.
Uma maneira de estabelecer a validade é passar por algum processo manual. Existem várias maneiras de fazer isso. Você pode exigir que o destinatário pretendido lhe entregue fisicamente uma cópia de sua chave pública. Mas isto é muitas vezes inconveniente e ineficiente. Outra forma é verificar manualmente a impressão digital do certificado. Assim como as impressões digitais de cada ser humano são únicas, a impressão digital de cada certificado PGP é única. A impressão digital é um hash do certificado do usuário e aparece como uma das propriedades do certificado. No PGP, a impressão digital pode aparecer como um número hexadecimal ou uma série das chamadas palavras biométricas, que são foneticamente distintas e são usadas para facilitar um pouco o processo de identificação da impressão digital. Você pode verificar se um certificado é válido ligando para o proprietário da chave (para que você origine a transação) e pedindo ao proprietário que leia a impressão digital de sua chave para você e compare essa impressão digital com aquela que você acredita ser a verdadeira. Isso funciona se você conhece a voz do proprietário, mas como verificar manualmente a identidade de alguém que você não conhece? Algumas pessoas colocam a impressão digital de sua chave em seus cartões de visita exatamente por esse motivo. Outra forma de estabelecer a validade do certificado de alguém é confiar que um terceiro indivíduo passou pelo processo de validação do mesmo. Uma CA, por exemplo, é responsável por garantir que, antes de emitir um certificado, ele ou ela o verifique cuidadosamente para ter certeza de que a parte da chave pública realmente pertence ao suposto proprietário. Qualquer pessoa que confie na CA considerará automaticamente quaisquer certificados assinados pela CA como válidos. Outro aspecto da verificação da validade é garantir que o certificado não foi revogado. Para obter mais informações, consulte a seção Revogação de certificado .
Estabelecendo confiança.
Você valida certificados. Você confia nas pessoas. Mais especificamente, você confia nas pessoas para validar os certificados de outras pessoas. Normalmente, a menos que o proprietário lhe entregue o certificado, você terá que confiar na palavra de outra pessoa de que ele é válido.
Introdutores meta e confiáveis.
Na maioria das situações, as pessoas confiam completamente na CA para estabelecer a validade dos certificados. Isso significa que todos os demais dependem da CA para passar por todo o processo de validação manual. Isso é aceitável até um certo número de usuários ou locais de trabalho e, então, não é possível para a AC manter o mesmo nível de validação de qualidade. Nesse caso, é necessário adicionar outros validadores ao sistema.
Um CA também pode ser um meta- introdutor. Um meta-introdutor confere não apenas validade às chaves, mas também confere a capacidade de confiar nas chaves a outros. Semelhante ao rei que entrega seu selo a seus conselheiros de confiança para que eles possam agir de acordo com sua autoridade, o meta-introdutor permite que outros atuem como introdutores de confiança. Esses introdutores confiáveis podem validar chaves com o mesmo efeito do meta-introdutor. Eles não podem, entretanto, criar novos introdutores confiáveis.
Meta-introdutor e introdutor confiável são termos PGP. Em um ambiente X.509, o meta-introdutor é chamado de Autoridade de Certificação raiz ( CA raiz) e os introdutores confiáveis são Autoridades de Certificação subordinadas . A CA raiz usa a chave privada associada a um tipo de certificado especial denominado certificado CA raiz para assinar certificados. Qualquer certificado assinado pelo certificado CA raiz é visto como válido por qualquer outro certificado assinado pela raiz. Este processo de validação funciona mesmo para certificados assinados por outras CAs no sistema — desde que o certificado da CA raiz tenha assinado o certificado da CA subordinada, qualquer certificado assinado pela CA será considerado válido para outras pessoas dentro da hierarquia. Este processo de verificação de backup por meio do sistema para ver quem assinou cujo certificado é chamado de rastreamento de um caminho de certificação ou cadeia de certificação.
Modelos de confiança.
Em sistemas relativamente fechados, como em uma pequena empresa, é fácil rastrear um caminho de certificação até a CA raiz. No entanto, os usuários muitas vezes precisam se comunicar com pessoas fora do seu ambiente corporativo, incluindo algumas que nunca conheceram, como fornecedores, consumidores, clientes, associados e assim por diante. É difícil estabelecer uma linha de confiança com aqueles em quem sua CA não confia explicitamente. As empresas seguem um ou outro modelo de confiança, que determina como os usuários irão estabelecer a validade do certificado. Existem três modelos diferentes:
Confiança Direta.
Confiança Hierárquica Uma teia de confiança Confiança direta A confiança direta é o modelo de confiança mais simples. Neste modelo, um usuário confia que uma chave é válida porque sabe de onde ela veio. Todos os criptosistemas usam essa forma de confiança de alguma forma. Por exemplo, em navegadores da Web, as chaves raiz da Autoridade de Certificação são diretamente confiáveis porque foram enviadas pelo fabricante. Se houver alguma forma de hierarquia, ela se estenderá a partir desses certificados diretamente confiáveis. No PGP, um usuário que valida as chaves e nunca define outro certificado para ser um introdutor confiável está usando confiança direta.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_4681914789296468891699911522.webp
Figura 1-11. Confiança direta
Confiança Hierárquica.
Em um sistema hierárquico, há vários certificados "raiz" a partir dos quais a confiança se estende. Esses certificados podem certificar eles próprios certificados ou podem certificar certificados que certificam ainda outros certificados em alguma cadeia. Considere isso como uma grande “árvore” de confiança. A validade do certificado "folha" é verificada rastreando desde seu certificador até outros certificadores, até que um certificado raiz diretamente confiável seja encontrado.
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_2764578291212045251699911580.webp
Figura 1-12. Confiança hierárquica
Teia de Confiança.
Uma teia de confiança abrange ambos os outros modelos, mas também acrescenta a noção de que a confiança está nos olhos de quem vê (que é a visão do mundo real) e a ideia de que mais informação é melhor. É, portanto, um modelo de confiança cumulativa. Um certificado pode ser confiável diretamente ou confiável em alguma cadeia que remonta a um certificado raiz diretamente confiável (o meta-introdutor) ou por algum grupo de introdutores.
Talvez você já tenha ouvido falar do termo seis graus de separação, que sugere que qualquer pessoa no mundo pode determinar algum vínculo com qualquer outra pessoa no mundo usando seis ou menos outras pessoas como intermediários. Esta é uma teia de introdutores. É também a visão de confiança do PGP. PGP usa assinaturas digitais como forma de introdução. Quando qualquer usuário assina a chave de outro, ele ou ela se torna o introdutor dessa chave. À medida que esse processo avança, ele estabelece uma rede de confiança.
Em um ambiente PGP, qualquer usuário pode atuar como autoridade certificadora. Qualquer usuário PGP pode validar o certificado de chave pública de outro usuário PGP. No entanto, tal certificado só é válido para outro usuário se a parte confiável reconhecer o validador como um introdutor confiável. (Ou seja, você confia na minha opinião de que as chaves dos outros são válidas apenas se você me considerar um apresentador confiável. Caso contrário, minha opinião sobre a validade das outras chaves é discutível.) Armazenados no chaveiro público de cada usuário estão indicadores de
● se o usuário considera ou não uma chave específica válida
● o nível de confiança que o usuário deposita na chave que o proprietário da chave pode servir como certificador das chaves de terceiros
Você indica, na sua cópia da minha chave, se acha que meu julgamento conta. Na verdade, é um sistema de reputação: certas pessoas têm a reputação de fornecer boas assinaturas e as pessoas confiam nelas para atestar a validade de outras chaves.
Níveis de confiança no PGP.
O nível mais alto de confiança em uma chave, a confiança implícita , é a confiança em seu próprio par de chaves. O PGP assume que se você possui a chave privada, você deve confiar nas ações da sua chave pública relacionada. Quaisquer chaves assinadas pela sua chave implicitamente confiável são válidas.
Existem três níveis de confiança que você pode atribuir à chave pública de outra pessoa:
● Confiança total ● Confiança marginal ● Não confiável (ou não confiável)
Para tornar as coisas confusas, também existem três níveis de validade:
● Válido ● Marginalmente válido ● Inválido
Para definir a chave de outra pessoa como um introdutor confiável, você
- Comece com uma chave válida, que seja.
- assinado por você ou
-
assinado por outro apresentador confiável e então
-
Defina o nível de confiança que você acha que o proprietário da chave tem direito.
Por exemplo, suponha que seu chaveiro contenha a chave de Alice. Você validou a chave de Alice e indica isso assinando-a. Você sabe que Alice é uma verdadeira defensora da validação de chaves de outras pessoas. Portanto, você atribui a chave dela com confiança total. Isso faz de Alice uma Autoridade Certificadora. Se Alice assinar a chave de outra pessoa, ela aparecerá como Válida em seu chaveiro. O PGP requer uma assinatura Totalmente confiável ou duas assinaturas Marginalmente confiáveis para estabelecer uma chave como válida. O método do PGP de considerar dois Marginais iguais a um Completo é semelhante a um comerciante que solicita duas formas de identificação. Você pode considerar Alice bastante confiável e também considerar Bob bastante confiável. Qualquer um deles sozinho corre o risco de assinar acidentalmente uma chave falsificada, portanto, você pode não depositar total confiança em nenhum deles. No entanto, as probabilidades de ambos os indivíduos terem assinado a mesma chave falsa são provavelmente pequenas.
Revogação de certificado.
Os certificados só são úteis enquanto são válidos. Não é seguro simplesmente presumir que um certificado é válido para sempre. Na maioria das organizações e em todas as PKIs, os certificados têm uma vida útil restrita. Isso restringe o período em que um sistema fica vulnerável caso ocorra um comprometimento do certificado.
Os certificados são assim criados com um período de validade programado: uma data/hora de início e uma data/hora de expiração. Espera-se que o certificado seja utilizável durante todo o seu período de validade (seu tempo de vida ). Quando o certificado expirar, ele não será mais válido, pois a autenticidade do seu par chave/identificação não estará mais garantida. (O certificado ainda pode ser usado com segurança para reconfirmar informações que foram criptografadas ou assinadas dentro do período de validade – no entanto, ele não deve ser confiável para tarefas criptográficas futuras.)
Existem também situações em que é necessário invalidar um certificado antes da sua data de expiração, como quando o titular do certificado termina o contrato de trabalho com a empresa ou suspeita que a chave privada correspondente do certificado foi comprometida. Isso é chamado de revogação. Um certificado revogado é muito mais suspeito do que um certificado expirado. Os certificados expirados são inutilizáveis, mas não apresentam a mesma ameaça de comprometimento que um certificado revogado. Qualquer pessoa que tenha assinado um certificado pode revogar a sua assinatura no certificado (desde que utilize a mesma chave privada que criou a assinatura). Uma assinatura revogada indica que o signatário não acredita mais que a chave pública e as informações de identificação pertencem uma à outra, ou que a chave pública do certificado (ou a chave privada correspondente) foi comprometida. Uma assinatura revogada deve ter quase tanto peso quanto um certificado revogado. Com certificados X.509, uma assinatura revogada é praticamente igual a um certificado revogado, visto que a única assinatura no certificado é aquela que o tornou válido em primeiro lugar – a assinatura da CA. Os certificados PGP fornecem o recurso adicional de que você pode revogar todo o seu certificado (não apenas as assinaturas nele) se você achar que o certificado foi comprometido. Somente o proprietário do certificado (o detentor da chave privada correspondente) ou alguém que o proprietário do certificado tenha designado como revogador pode revogar um certificado PGP. (Designar um revogador é uma prática útil, pois muitas vezes é a perda da senha da chave privada correspondente do certificado que leva um usuário PGP a revogar seu certificado - uma tarefa que só é possível se alguém tiver acesso à chave privada. ) Somente o emissor do certificado pode revogar um certificado X.509.
Comunicar que um certificado foi revogado.
Quando um certificado é revogado, é importante conscientizar os usuários potenciais do certificado de que ele não é mais válido. Com certificados PGP, a maneira mais comum de comunicar que um certificado foi revogado é publicá-lo em um servidor de certificados para que outras pessoas que desejem se comunicar com você sejam avisadas para não usar essa chave pública. Em um ambiente PKI, a comunicação de certificados revogados é mais comumente obtida por meio de uma estrutura de dados chamada Lista de Revogação de Certificados, ou CRL, que é publicada pela CA. A CRL contém uma lista validada com carimbo de data e hora de todos os certificados revogados e não expirados no sistema. Os certificados revogados permanecem na lista apenas até expirarem e, em seguida, são removidos da lista — isso evita que a lista fique muito longa. A CA distribui a CRL aos usuários em algum intervalo programado regularmente (e potencialmente fora do ciclo, sempre que um certificado é revogado). Teoricamente, isso impedirá que os usuários usem involuntariamente um certificado comprometido. É possível, no entanto, que haja um período de tempo entre as CRLs em que um certificado recentemente comprometido seja usado.
O que é uma senha?
A maioria das pessoas está familiarizada com a restrição de acesso a sistemas de computador por meio de uma senha, que é uma sequência única de caracteres que um usuário digita como código de identificação.
Uma senha longa é uma versão mais longa de uma senha e, em teoria, mais segura. Normalmente composta por várias palavras, uma frase secreta é mais segura contra ataques de dicionário padrão, em que o invasor tenta todas as palavras do dicionário na tentativa de determinar sua senha. As melhores senhas são relativamente longas e complexas e contêm uma combinação de letras maiúsculas e minúsculas, caracteres numéricos e de pontuação. O PGP usa uma senha para criptografar sua chave privada em sua máquina. Sua chave privada é criptografada em seu disco usando um hash de sua senha como chave secreta. Você usa a senha para descriptografar e usar sua chave privada. Uma senha deve ser difícil de esquecer e difícil de ser adivinhada por outras pessoas. Deve ser algo já firmemente enraizado na sua memória de longo prazo, em vez de algo que você invente do zero. Por que? Porque se você esquecer sua senha, você estará sem sorte. Sua chave privada é total e absolutamente inútil sem sua senha e nada pode ser feito a respeito. Lembra-se da citação anterior neste capítulo?
https://nostrcheck.me/media/public/nostrcheck.me_5284734693832771181699911783.webp
PGP é a criptografia que manterá os principais governos fora dos seus arquivos. Certamente também o manterá fora de seus arquivos. Tenha isso em mente quando decidir alterar sua senha para a piada daquela piada que você nunca consegue lembrar.
Divisão de chave.
Dizem que um segredo não é segredo se for conhecido por mais de uma pessoa. Compartilhar um par de chaves privadas representa um grande problema. Embora não seja uma prática recomendada, às vezes é necessário compartilhar um par de chaves privadas. Chaves de assinatura corporativa, por exemplo, são chaves privadas usadas por uma empresa para assinar – por exemplo – documentos legais, informações pessoais confidenciais ou comunicados de imprensa para autenticar sua origem. Nesse caso, vale a pena que vários membros da empresa tenham acesso à chave privada. No entanto, isto significa que qualquer indivíduo pode agir plenamente em nome da empresa. Nesse caso, é aconselhável dividir a chave entre várias pessoas, de modo que mais de uma ou duas pessoas apresentem um pedaço da chave para reconstituí-la em condições utilizáveis. Se poucas peças da chave estiverem disponíveis, a chave ficará inutilizável. Alguns exemplos são dividir uma chave em três partes e exigir duas delas para reconstituir a chave, ou dividi-la em duas partes e exigir ambas as peças. Se uma conexão de rede segura for usada durante o processo de reconstituição, os acionistas da chave não precisam estar fisicamente presentes para aderirem novamente à chave.
-
 @ bd32f268:22b33966
2024-10-02 17:28:12
@ bd32f268:22b33966
2024-10-02 17:28:12A escolha de algo implica abdicar de uma outra coisa. Quando investimos num determinado item vamos ter custos associados a essa decisão, no entanto a melhor forma de pensar nesses custos não será apenas dinheiro que possamos estar a investir mas em todas as possibilidades de que abdicamos para que possamos investir nesse item.
Suponhamos o seguinte cenário, um milionário decide dar uma esmola a um mendigo no valor de 10€, nesse mesmo dia um pobre passa no mesmo local onde está o mendigo e tendo apenas 10 € na carteira decide dar tudo ao mendigo. Apesar de em termos nominais se tratar da mesma quantia facilmente percebemos que o custo de oportunidade é significativamente diferente para o pobre e para o milionário. Esta aferição do custo de oportunidade superior coloca-nos interessantes questões no que diz respeito às razões particulares que levaram a pessoa a tomar a decisão. É lógico esperar que aquele que incorre no maior custo de oportunidade tem uma forte razão para tomar determinada decisão.
Importante também é esta ideia de que priorizamos umas coisas em detrimento de outras, o pobre pode ter ficado sem almoço ao dar todo o dinheiro que lhe restava, caso fosse assim ele de facto priorizou o donativo ao alimentar-se naquela circunstância.
Quando temos 100€ e temos de escolher entre dois produtos de igual preço (100€ cada um), em condições normais vamos escolher o mais importante para nós, isto é o mais valioso. Estas decisões acontecem partindo do pressuposto que o nosso objetivo é maximizar o valor (aqui entendido subjetivamente). Este tipo de decisões têm ainda um outro fator chave, determinante na priorização das decisões: o tempo.
Sendo um recurso escasso, o tempo cria um incentivo natural para a tomada de decisão dado que não podemos diferir a decisão eternamente. Pensando no exemplo concreto da escolha entre dos produtos referidos sabemos que os produtos não estarão sempre disponíveis, dado que a loja pode fechar e além disso a disponibilidade dos produtos poderá estar condicionada caso o produto seja arrebatado por outra pessoa. Este aspecto implica na nossa decisão na medida em que, quando conscientes disto, temos que tomar uma decisão.
Os estoicos e os religiosos repetem muitas vezes a expressão, memento mori, que significa: “lembra-te que morrerás”. Esta frase pungente serve como um despertador existencial, que nos recorda que este tempo acabará. O facto de lembrarmos da morte acorda-nos para aquilo que devemos priorizar, algo frequente ver-se por exemplo em pessoas que vivem situações traumáticas. Quando ultrapassadas as situações traumáticas, o resultado muitas vezes orienta as pessoas para uma redefinição das prioridades de vida, chamamos a isto o crescimento pós-traumático.
 > “Nos ossos que aqui estamos pelos vossos esperamos” Inscrição numa das portas da Igreja de São Francisco em Évora (Capela dos ossos)
> “Nos ossos que aqui estamos pelos vossos esperamos” Inscrição numa das portas da Igreja de São Francisco em Évora (Capela dos ossos)Além deste aspeto o tempo influi também de numa outra questão, na preferência temporal. Este conceito diz respeito à nossa capacidade ou incapacidade em diferir a nossa gratificação, ou seja, se somos propensos à gratificação imediata dos nossos desejos ou se sacrificamos o presente com o intuito de obter uma recompensa maior no futuro. Este conceito ficou bem ilustrado no famoso teste marshmallow em que um grupo de crianças escolhidas por psicólogos tinham de escolher entre comer um marshmallow no imediato, ou esperar cinco minutos numa sala, tendo o marshmallow à sua frente sem o comer e assim receber o segundo.
No caso das crianças que esperaram podemos concluir uma preferência temporal baixa, ao passo que os que decidiram comer de imediato o marshmallow revelam uma elevada preferência temporal. Para concluir esta ideia de que a preferência temporal influencia na toma de decisão diga-se, as crianças com mais baixa preferência temporal revelam: melhores competências sociais, melhor resposta ao stress, menor probabilidade de obesidade; tendo sido isto concluído em estudos feitos à posteriori neste grupo.
Olhando para estes exemplos podemos ver o quão determinantes estas questões são na forma como tomamos as decisões e estruturamos a nossa hierarquia de valor para que possamos aferir de forma mais exata qual a estratégia que nos permite maximizar este valor. Daqui penso que podemos facilmente perceber que a preferência temporal baixa e o custo de oportunidade elevado são marcadores importantes de que nos podemos estar a mover mais em direção a algo que valorizamos e é importante para nós. Atrevo-me a dizer que se não arriscamos nada, talvez aquilo que temos entre mãos não seja assim tão valioso. A maximização do risco é também a maximização do benefício, contudo isto deve sempre ser temperado pela baixa preferência temporal porque a decisão deve sustentar-se ao teste do tempo, idealmente ser algo que resiste mais à erosão que o tempo impõe àquilo que foi objeto da nossa decisão.
Estes aspetos podem estar presentes quer nas decisões mais triviais como referia, decisões de consumo de bens mas também estão presentes noutras decisões como por exemplo: que tipo de relações procuramos com os outros, se mantemos ou não uma prática religiosa, se somos capazes ou não de negar as nossas vontades e impor a disciplina de procurar a excelência nas virtudes. Tudo isto será influenciado por estes aspetos e sendo conscientes destes mecanismos podemos então traçar um perfil mais ajustado à maximização do valor, não só no presente como no futuro.

-
 @ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-09-30 14:52:23
@ e6817453:b0ac3c39
2024-09-30 14:52:23In the modern world of AI, managing vast amounts of data while keeping it relevant and accessible is a significant challenge, mainly when dealing with large language models (LLMs) and vector databases. One approach that has gained prominence in recent years is integrating vector search with metadata, especially in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipelines. Vector search and metadata enable faster and more accurate data retrieval. However, the process of pre- and post-search filtering results plays a crucial role in ensuring data relevance.
The Vector Search and Metadata Challenge
In a typical vector search, you create embeddings from chunks of text, such as a PDF document. These embeddings allow the system to search for similar items and retrieve them based on relevance. The challenge, however, arises when you need to combine vector search results with structured metadata. For example, you may have timestamped text-based content and want to retrieve the most relevant content within a specific date range. This is where metadata becomes critical in refining search results.
Unfortunately, most vector databases treat metadata as a secondary feature, isolating it from the primary vector search process. As a result, handling queries that combine vectors and metadata can become a challenge, particularly when the search needs to account for a dynamic range of filters, such as dates or other structured data.
LibSQL and vector search metadata
LibSQL is a more general-purpose SQLite-based database that adds vector capabilities to regular data. Vectors are presented as blob columns of regular tables. It makes vector embeddings and metadata a first-class citizen that naturally builds deep integration of these data points.
create table if not exists conversation ( id varchar(36) primary key not null, startDate real, endDate real, summary text, vectorSummary F32_BLOB(512) );It solves the challenge of metadata and vector search and eliminates impedance between vector data and regular structured data points in the same storage.
As you can see, you can access vector-like data and start date in the same query.
select c.id ,c.startDate, c.endDate, c.summary, vector_distance_cos(c.vectorSummary, vector(${vector})) distance from conversation where ${startDate ? `and c.startDate >= ${startDate.getTime()}` : ''} ${endDate ? `and c.endDate <= ${endDate.getTime()}` : ''} ${distance ? `and distance <= ${distance}` : ''} order by distance limit ${top};vector_distance_cos calculated as distance allows us to make a primitive vector search that does a full scan and calculates distances on rows. We could optimize it with CTE and limit search and distance calculations to a much smaller subset of data.
This approach could be calculation intensive and fail on large amounts of data.
Libsql offers a way more effective vector search based on FlashDiskANN vector indexed.
vector_top_k('idx_conversation_vectorSummary', ${vector} , ${top}) ivector_top_k is a table function that searches for the top of the newly created vector search index. As you can see, we could use only vector as a function parameter, and other columns could be used outside of the table function. So, to use a vector index together with different columns, we need to apply some strategies.
Now we get a classical problem of integration vector search results with metadata queries.
Post-Filtering: A Common Approach
The most widely adopted method in these pipelines is post-filtering. In this approach, the system first retrieves data based on vector similarities and then applies metadata filters. For example, imagine you’re conducting a vector search to retrieve conversations relevant to a specific question. Still, you also want to ensure these conversations occurred in the past week.

Post-filtering allows the system to retrieve the most relevant vector-based results and subsequently filter out any that don’t meet the metadata criteria, such as date range. This method is efficient when vector similarity is the primary factor driving the search, and metadata is only applied as a secondary filter.
const sqlQuery = ` select c.id ,c.startDate, c.endDate, c.summary, vector_distance_cos(c.vectorSummary, vector(${vector})) distance from vector_top_k('idx_conversation_vectorSummary', ${vector} , ${top}) i inner join conversation c on i.id = c.rowid where ${startDate ? `and c.startDate >= ${startDate.getTime()}` : ''} ${endDate ? `and c.endDate <= ${endDate.getTime()}` : ''} ${distance ? `and distance <= ${distance}` : ''} order by distance limit ${top};However, there are some limitations. For example, the initial vector search may yield fewer results or omit some relevant data before applying the metadata filter. If the search window is narrow enough, this can lead to complete results.
One working strategy is to make the top value in vector_top_K much bigger. Be careful, though, as the function's default max number of results is around 200 rows.
Pre-Filtering: A More Complex Approach
Pre-filtering is a more intricate approach but can be more effective in some instances. In pre-filtering, metadata is used as the primary filter before vector search takes place. This means that only data that meets the metadata criteria is passed into the vector search process, limiting the scope of the search right from the beginning.
While this approach can significantly reduce the amount of irrelevant data in the final results, it comes with its own challenges. For example, pre-filtering requires a deeper understanding of the data structure and may necessitate denormalizing the data or creating separate pre-filtered tables. This can be resource-intensive and, in some cases, impractical for dynamic metadata like date ranges.

In certain use cases, pre-filtering might outperform post-filtering. For instance, when the metadata (e.g., specific date ranges) is the most important filter, pre-filtering ensures the search is conducted only on the most relevant data.
Pre-filtering with distance-based filtering
So, we are getting back to an old concept. We do prefiltering instead of using a vector index.
WITH FilteredDates AS ( SELECT c.id, c.startDate, c.endDate, c.summary, c.vectorSummary FROM YourTable c WHERE ${startDate ? `AND c.startDate >= ${startDate.getTime()}` : ''} ${endDate ? `AND c.endDate <= ${endDate.getTime()}` : ''} ), DistanceCalculation AS ( SELECT fd.id, fd.startDate, fd.endDate, fd.summary, fd.vectorSummary, vector_distance_cos(fd.vectorSummary, vector(${vector})) AS distance FROM FilteredDates fd ) SELECT dc.id, dc.startDate, dc.endDate, dc.summary, dc.distance FROM DistanceCalculation dc WHERE 1=1 ${distance ? `AND dc.distance <= ${distance}` : ''} ORDER BY dc.distance LIMIT ${top};It makes sense if the filter produces small data and distance calculation happens on the smaller data set.
As a pro of this approach, you have full control over the data and get all results without omitting some typical values for extensive index searches.
Choosing Between Pre and Post-Filtering
Both pre-filtering and post-filtering have their advantages and disadvantages. Post-filtering is more accessible to implement, especially when vector similarity is the primary search factor, but it can lead to incomplete results. Pre-filtering, on the other hand, can yield more accurate results but requires more complex data handling and optimization.
In practice, many systems combine both strategies, depending on the query. For example, they might start with a broad pre-filtering based on metadata (like date ranges) and then apply a more targeted vector search with post-filtering to refine the results further.
Conclusion
Vector search with metadata filtering offers a powerful approach for handling large-scale data retrieval in LLMs and RAG pipelines. Whether you choose pre-filtering or post-filtering—or a combination of both—depends on your application's specific requirements. As vector databases continue to evolve, future innovations that combine these two approaches more seamlessly will help improve data relevance and retrieval efficiency further.
-
 @ c4f5e7a7:8856cac7
2024-09-27 08:20:16
@ c4f5e7a7:8856cac7
2024-09-27 08:20:16Best viewed on Habla, YakiHonne or Highlighter.
TL;DR
This article explores the links between public, community-driven data sources (such as OpenStreetMap) and private, cryptographically-owned data found on networks such as Nostr.
The following concepts are explored:
- Attestations: Users signalling to their social graph that they believe something to be true by publishing Attestations. These social proofs act as a decentralised verification system that leverages your web-of-trust.
- Proof of Place: An oracle-based system where physical letters are sent to real-world locations, confirming the corresponding digital ownership via cryptographic proofs. This binds physical locations in meatspace with their digital representations in the Nostrverse.
- Check-ins: Foursquare-style check-ins that can be verified using attestations from place owners, ensuring authenticity. This approach uses web-of-trust to validate check-ins and location ownership over time.
The goal is to leverage cryptographic ownership where necessary while preserving the open, collaborative nature of public data systems.
Open Data in a public commons has a place and should not be thrown out with the Web 2.0 bathwater.
Cognitive Dissonance
Ever since discovering Nostr in August of 2022 I've been grappling with how BTC Map - a project that helps bitcoiners find places to spend sats - should most appropriately use this new protocol.
I am assuming, dear reader, that you are somewhat familiar with Nostr - a relatively new protocol for decentralised identity and communication. If you don’t know your nsec from your npub, please take some time to read these excellent posts: Nostr is Identity for the Internet and The Power of Nostr by @max and @lyn, respectively. Nostr is so much more than a short-form social media replacement.
The social features (check-ins, reviews, etc.) that Nostr unlocks for BTC Map are clear and exciting - all your silos are indeed broken - however, something fundamental has been bothering me for a while and I think it comes down to data ownership.
For those unfamiliar, BTC Map uses OpenStreetMap (OSM) as its main geographic database. OSM is centred on the concept of a commons of objectively verifiable data that is maintained by a global community of volunteer editors; a Wikipedia for maps. There is no data ownership; the data is free (as in freedom) and anyone can edit anything. It is the data equivalent of FOSS (Free and Open Source Software) - FOSD if you will, but more commonly referred to as Open Data.
In contrast, Notes and Other Stuff on Nostr (Places in this cartographic context) are explicitly owned by the controller of the private key. These notes are free to propagate, but they are owned.
How do we reconcile the decentralised nature of Nostr, where data is cryptographically owned by individuals, with the community-managed data commons of OpenStreetMap, where no one owns the data?
Self-sovereign Identity
Before I address this coexistence question, I want to talk a little about identity as it pertains to ownership. If something is to be owned, it has to be owned by someone or something - an identity.
All identities that are not self-sovereign are, by definition, leased to you by a 3rd party. You rent your Facebook identity from Meta in exchange for your data. You rent your web domain from your DNS provider in exchange for your money.
Taken to the extreme, you rent your passport from your Government in exchange for your compliance. You are you at the pleasure of others. Where Bitcoin separates money from the state; Nostr separates identity from the state.
Or, as @nvk said recently: "Don't build your house on someone else's land.".
https://i.nostr.build/xpcCSkDg3uVw0yku.png
While we’ve had the tools for self-sovereign digital identity for decades (think PGP keys or WebAuthN), we haven't had the necessary social use cases nor the corresponding social graph to elevate these identities to the mainstream. Nostr fixes this.
Nostr is PGP for the masses and will take cryptographic identities mainstream.
Full NOSTARD?
Returning to the coexistence question: the data on OpenStreetMap isn’t directly owned by anyone, even though the physical entities the data represents might be privately owned. OSM is a data commons.
We can objectively agree on the location of a tree or a fire hydrant without needing permission to observe and record it. Sure, you could place a tree ‘on Nostr’, but why should you? Just because something can be ‘on Nostr’ doesn’t mean it should be.
https://i.nostr.build/s3So2JVAqoY4E1dI.png
There might be a dystopian future where we can't agree on what a tree is nor where it's located, but I hope we never get there. It's at this point we'll need a Wikifreedia variant of OpenStreetMap.
While integrating Nostr identities into OpenStreetMap would be valuable, the current OSM infrastructure, tools, and community already provide substantial benefits in managing this data commons without needing to go NOSTR-native - there's no need to go Full NOSTARD. H/T to @princeySOV for the original meme.
https://i.nostr.build/ot9jtM5cZtDHNKWc.png
So, how do we appropriately blend cryptographically owned data with the commons?
If a location is owned in meatspace and it's useful to signal that ownership, it should also be owned in cyberspace. Our efforts should therefore focus on entities like businesses, while allowing the commons to manage public data for as long as it can successfully mitigate the tragedy of the commons.
The remainder of this article explores how we can:
- Verify ownership of a physical place in the real world;
- Link that ownership to the corresponding digital place in cyberspace.
As a side note, I don't see private key custodianship - or, even worse, permissioned use of Places signed by another identity's key - as any more viable than the rented identities of Web 2.0.
And as we all know, the Second Law of Infodynamics (no citation!) states that:
"The total amount of sensitive information leaked will always increase over time."
This especially holds true if that data is centralised.
Not your keys, not your notes. Not your keys, not your identity.
Places and Web-of-Trust
@Arkinox has been leading the charge on the Places NIP, introducing Nostr notes (kind 37515) that represent physical locations. The draft is well-crafted, with bonus points for linking back to OSM (and other location repositories) via NIP-73 - External Content IDs (championed by @oscar of @fountain).
However, as Nostr is permissionless, authenticity poses a challenge. Just because someone claims to own a physical location on the Internet doesn’t necessarily mean they have ownership or control of that location in the real world.
Ultimately, this problem can only be solved in a decentralised way by using Web-of-Trust - using your social graph and the perspectives of trusted peers to inform your own perspective. In the context of Places, this requires your network to form a view on which digital identity (public key / npub) is truly the owner of a physical place like your local coffee shop.
This requires users to:
- Verify the owner of a Place in cyberspace is the owner of a place in meatspace.
- Signal this verification to their social graph.
Let's look at the latter idea first with the concept of Attestations ...
Attestations
A way to signal to your social graph that you believe something to be true (or false for that matter) would be by publishing an Attestation note. An Attestation note would signify to your social graph that you think something is either true or false.
Imagine you're a regular at a local coffee shop. You publish an Attestation that says the shop is real and the owner behind the Nostr public key is who they claim to be. Your friends trust you, so they start trusting the shop's digital identity too.
However, attestations applied to Places are just a single use case. The attestation concept could be more widely applied across Nostr in a variety of ways (key rotation, identity linking, etc).
Here is a recent example from @lyn that would carry more signal if it were an Attestation:
https://i.nostr.build/lZAXOEwvRIghgFY4.png
Parallels can be drawn between Attestations and transaction confirmations on the Bitcoin timechain; however, their importance to you would be weighted by clients and/or Data Vending Machines in accordance with:
- Your social graph;
- The type or subject of the content being attested and by whom;
- Your personal preferences.
They could also have a validity duration to be temporally bound, which would be particularly useful in the case of Places.
NIP-25 (Reactions) do allow for users to up/downvote notes with optional content (e.g., emojis) and could work for Attestations, but I think we need something less ambiguous and more definitive.
‘This is true’ resonates more strongly than ‘I like this.’.
https://i.nostr.build/s8NIG2kXzUCLcoax.jpg
There are similar concepts in the Web 3 / Web 5 world such as Verified Credentials by tdb. However, Nostr is the Web 3 now and so wen Attestation NIP?
https://i.nostr.build/Cb047NWyHdJ7h5Ka.jpg
That said, I have seen @utxo has been exploring ‘smart contracts’ on nostr and Attestations may just be a relatively ‘dumb’ subset of the wider concept Nostr-native scripting combined with web-of-trust.
Proof of Place
Attestations handle the signalling of your truth, but what about the initial verification itself?
We already covered how this ultimately has to be derived from your social graph, but what if there was a way to help bootstrap this web-of-trust through the use of oracles? For those unfamiliar with oracles in the digital realm, they are simply trusted purveyors of truth.
Introducing Proof of Place, an out–of-band process where an oracle (such as BTC Map) would mail - yes physically mail- a shared secret to the address of the location being claimed in cyberspace. This shared secret would be locked to the public key (npub) making the claim, which, if unlocked, would prove that the associated private key (nsec) has physical access to the location in meatspace.
One way of doing this would be to mint a 1 sat cashu ecash token locked to the npub of the claimant and mail it to them. If they are able to redeem the token then they have cryptographically proven that they have physical access to the location.
Proof of Place is really nothing more than a weighted Attestation. In a web-of-trust Nostrverse, an oracle is simply a npub (say BTC Map) that you weigh heavily for its opinion on a given topic (say Places).
In the Bitcoin world, Proof of Work anchors digital scarcity in cyberspace to physical scarcity (energy and time) in meatspace and as @Gigi says in PoW is Essential:
"A failure to understand Proof of Work, is a failure to understand Bitcoin."
In the Nostrverse, Proof of Place helps bridge the digital and physical worlds.
@Gigi also observes in Memes vs The World that:
"In Bitcoin, the map is the territory. We can infer everything we care about by looking at the map alone."
https://i.nostr.build/dOnpxfI4u7EL2v4e.png
This isn’t true for Nostr.
In the Nostrverse, the map IS NOT the territory. However, Proof of Place enables us to send cryptographic drones down into the physical territory to help us interpret our digital maps. 🤯
Check-ins
Although not a draft NIP yet, @Arkinox has also been exploring the familiar concept of Foursquare-style Check-ins on Nostr (with kind 13811 notes).
For the uninitiated, Check-ins are simply notes that signal the publisher is at a given location. These locations could be Places (in the Nostr sense) or any other given digital representation of a location for that matter (such as OSM elements) if NIP-73 - External Content IDs are used.
Of course, not everyone will be a Check-in enjoyooor as the concept will not sit well with some people’s threat models and OpSec practices.
Bringing Check-ins to Nostr is possible (as @sebastix capably shows here), but they suffer the same authenticity issues as Places. Just because I say I'm at a given location doesn't mean that I am.
Back in the Web 2.0 days, Foursquare mitigated this by relying on the GPS position of the phone running their app, but this is of course spoofable.
How should we approach Check-in verifiability in the Nostrverse? Well, just like with Places, we can use Attestations and WoT. In the context of Check-ins, an Attestation from the identity (npub) of the Place being checked-in to would be a particularly strong signal. An NFC device could be placed in a coffee shop and attest to check-ins without requiring the owner to manually intervene - I’m sure @blackcoffee and @Ben Arc could hack something together over a weekend!
Check-ins could also be used as a signal for bonafide Place ownership over time.
Summary: Trust Your Bros
So, to recap, we have:
Places: Digital representations of physical locations on Nostr.
Check-ins: Users signalling their presence at a location.
Attestations: Verifiable social proofs used to confirm ownership or the truth of a claim.
You can visualise how these three concepts combine in the diagram below:
https://i.nostr.build/Uv2Jhx5BBfA51y0K.jpg
And, as always, top right trumps bottom left! We have:
Level 0 - Trust Me Bro: Anyone can check-in anywhere. The Place might not exist or might be impersonating the real place in meatspace. The person behind the npub may not have even been there at all.
Level 1 - Definitely Maybe Somewhere: This category covers the middle-ground of ‘Maybe at a Place’ and ‘Definitely Somewhere’. In these examples, you are either self-certifying that you have checked-in at an Attested Place or you are having others attest that you have checked-in at a Place that might not even exist IRL.
Level 2 - Trust Your Bros: An Attested Check-in at an Attested Place. Your individual level of trust would be a function of the number of Attestations and how you weigh them within your own social graph.
https://i.nostr.build/HtLAiJH1uQSTmdxf.jpg
Perhaps the gold standard (or should that be the Bitcoin standard?) would be a Check-in attested by the owner of the Place, which in itself was attested by BTC Map?
Or perhaps not. Ultimately, it’s the users responsibility to determine what they trust by forming their own perspective within the Nostrverse powered by web-of-trust algorithms they control. ‘Trust Me Bro’ or ‘Trust Your Bros’ - you decide.
As we navigate the frontier of cryptographic ownership and decentralised data, it’s up to us to find the balance between preserving the Open Data commons and embracing self-sovereign digital identities.
Thanks
With thanks to Arkinox, Avi, Ben Gunn, Kieran, Blackcoffee, Sebastix, Tomek, Calle, Short Fiat, Ben Weeks and Bitcoms for helping shape my thoughts and refine content, whether you know it or not!
-
 @ e83b66a8:b0526c2b
2024-09-26 19:29:43
@ e83b66a8:b0526c2b
2024-09-26 19:29:43If you’re thinking of buying a Bitaxe, here is some information about pools vs solo mining.
Firstly, although the terms are clear “pool mining”, “solo mining” there is nuance in these definitions, so I want to explain these terms fully.
Solo mining pools exist, such as: https://solo.ckpool.org/
It is called a pool, because you are using their credentials to mine, but you keep all the rewards if you win a block. Despite the name, this is not a pool.
You then have a pool such as https://ocean.xyz/ who are a pool, you use their credentials to mine, and you earn a share of their income relative to your contribution in hash power.
There has been some publicity about a solo miner winning a pool recently, there were about 12 blocks won in 2023 by solo miners. However a winning solo miner is likely to be a server farm with hundreds or even thousands of S19’s or S21’s sharing the same payout wallet address. The image of a home miner with a Bitaxe winning a block is extremely unlikely.
A solo miner is defined as a group of miners that share a payout wallet address, so for example you could have 10 Bitaxe’s at home all configured with the same BTC wallet address, this is considered a single solo miner. And so it is with mid tier mining farms, often privately owned, who have a number of machines set to the same payout address. Most of the time, they share earnings for a more reliable income, but the owner may decide to gamble on winning a block and so choose to solo (lottery) mine.
So far, my Bitaxe, which has been running for 4 days now and is part of the Ocean pool. It is earning about 50 Sats a day. If I were to wait for an on-chain payout, it would take around 60 years to receive one. I can, however, setup a BOLT12 lightning payout address and earn this tiny income through Lightning.
So here’s my recommendation.
Currently, there are two pools that control more than 50% of mining, Foundry USA and AntPool. This is a dangerous position and in fact Bitmain, who provide around 90% of all mining hardware actually invest and have stakes in these and several other pools. This is centralising mining and could potentially allow a 51% attack, which could compromise Bitcoin.
Jack Dorsey is currently developing competing mining hardware chipset, through his company Block and Ocean are attempting to decentralise the pools by building a truly independent option for miners to join.
If you buy a Bitaxe, the best way you can help alleviate the dominance of Bitmain is to join a true pool like Ocean to slowly move control away from the dominant pools.
Bear in mind that many of the other smaller pools are still controlled by Bitmain.
If you're still interested in lottery mining, here are your chances of winning a block:
Represented as Hash rates of different miners:
Nerdminer: 20 KH/s = 20,000 H/s
Bitaxe: 750 GH/s = 750,000,000,000 H/s
Bitmain Antminer S9: 13.5 TH/s = 13,500,000,000,000 H/s
Bitmain Antminer S19: 110TH/s = 110,000,000,000,000 H/s
Bitmain Antminer S21: 200TH/s = 200,000,000,000,000 H/s
Current Global Hash rate 628EH/s (Sept 2024) = 628,000,000,000,000,000,000
If you're running a Bitaxe, your percentage chance of winning a block is: 0.000000119426751592357%
Over a year, your chances increase to: 0.00627707006369428%
Your chances of winning the UK national lottery (assuming 20M tickets sold and you buy one):
0.000005%
Over a year, your chances increase to: 0.00026%
Like in all things in Bitcoin, I don’t ask you to trust me. If you want to verify, here are the references I used in making my conclusions:
https://protos.com/chart-when-solo-miners-found-a-bitcoin-block/
https://investors.block.xyz/investor-news/news-details/2024/Blocks-New-Bitcoin-Mining-Chip-to-Be-Part-of-an-Ongoing-Project-With-Core-Scientific-to-Decentralize-Mining-Hardware/default.aspx
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wo91DWvZRs8
https://i.nostr.build/9rQ9Plv6XQYtt6xd.jpg
-
 @ a9434ee1:d5c885be
2024-09-26 10:42:52
@ a9434ee1:d5c885be
2024-09-26 10:42:521. Relay = Community?
If spinning up a relay is getting easier and cheaper by the day, why can't the relays literally be the group/community?
Then: * Any relay is by default a public community. The more restricted read- or write-access is, the more it becomes a private group. * Any publication targeted at (h-tag) and stored, and thus accepted, by a relay can be seen as a publication in that community. * All-in-1 hosting solutions (integrated blossom servers, lightning nodes, ...) are made easier.
2. Why invent new kinds?
Why can't Kind 1 posts that are targeted and accepted by a relay (i.e. community) just be the forum-posts of that community? Why create new kinds for this? And even weirder, why create a new kind with that exclusively serves as a reply to that new kind? Why not just use generic replies (kind 1111) and take the #otherstuff (event kinds and apps) as an opportunity to introduce those?
For chat messages, however, I get it. You need a kind + reply-kind for those.
3. Community VS Private group
It seems like the only distinction you really need, both for the user and the apps implementing all this, is:
1. Public Community: anyone can read and follow this community but for writing the admins can set limits (pricing, white listings, ...) 2. Private group: only the profiles that even know this relay (i.e. group) exists can interact with it. Read-access has to be granted (invite, pricing, ...) and admins can set limits for writing too. Beyond this distinction it's a bit naive to try to categorize them. Open vs Closed doesn't really mean much for example, since technically all groups/communities set limits and are thus closed. It's more interesting to look the ways in which they can be closed and build on the simplest distinctions you can make there.The difference between Public communities and private groups is the most important one because they both have very different UX and specification requirements:
Memberlist
Communities: None existent
Anyone can read and follow. It just has limits on who can publish what, when. So the most interesting thing to surface is probable something like a list of most active members or a highlighted set of profiles that have special characteristics within this community (top supporter, god-mode, resident artist, ...).
Private Groups: Necessary for it's existence
The whitelisted npubs for read-access are the members.Moderation actions
Both types of groups need a way for the admin(s) to:
* Block/remove users * Remove events * Edit metadata (name, description, guidelines...) * Specify who can write publish what, under what conditionOnly private groups need a way for the admin(s) to:
* Add/approve new members → specify who has read-access, under what conditionGeneralizing too many actions like
add member,join request, etc... that are only applicable to one of these categories just creates bad UX for the other one. You don't "add a member" to a public community. People can follow it without asking anyone's permission (ok yes, some will AUTH for reading but that's besides the point). Some of its followers will then just choose to publish something there and the admin either allows them or not.Having a common protocol for specifying the conditions for this write-access interoperably (as mentioned above) is what I would like to see instead: * Both Communities and Private groups need it anyway * You have to assume admins need granularity in the conditions they set for publishing in their group/community: Who, what, under what condition, ... * You don't want to link out to custom websites (or similar) explaining their allowance schemes
Sidenote: we need a similar kind of spec for the services that allow you to spin up your hosting solution (relay, server, node, ...) so that, when you click "Create new community" in an app, those services can be surfaced. With their business models (including options to self-host parts of it) just there, in the app, without linking out. Same for the lines of communication and payments that are needed to make those business models work from within any app.
Publication and Discovery
Only Communities allow for the exciting possibility of publishing something in multiple overlapping communities at once. Someone writing about how Bees are Capitalists can target their article at the communities that most overlap with its content (and with the author's means and write-access of course). Members of a community around beekeeping can organically discover content and communities on Austrian economics relevant to them.
With Private groups publication happens only in the group and discovery is blocked on purpose.
-
 @ 862fda7e:02a8268b
2024-09-24 01:14:40
@ 862fda7e:02a8268b
2024-09-24 01:14:40The media, government, and "elite" (who are only elite in this low vibration illusion we call "life") are afraid of people like me because I do not accept the reality they have forced us into. My manifesto is an attempt to wake you up from ideas you have been conditioned into believing because it benefits one class - the protected class known as the "elite".
The elite would like to have you believe that my message is something crafted from hatred and they would like to label me with mental issues. They would like you to think I am some crazy extremist who wants to advocate for the harm of others. They would like you to think that I am enciting violence.
This could not be further from the truth.
I am not and will never be an extremist, white supermicist, terrorist, radical, hateful human being. I do not believe in killing in order to convey a message or movement. I do not believe in division.
I only advocate that you become conscious of the reality around us. The reality is that this is a world controlled by the most evil, controlling, destructive freaks. These people work to make sure we are essentially slaves to a system that benefits those who created the system - the elites. Let me make this clear: I do NOT advocate for violence, destruction, death, killing, murder, hatred, division, or terrorism. The elite are threatened by people like me, because they know that we know their game. We know their plans are to destroy, to advocate for violence, to kill, murder, to encite hatred and division. This is all the elite do - they cannot fathom having people live in peace because it isn't beneficial if you want to control the world.
So while you may think it's impossible there is a group of a few evil people who control the world - look back at history. It has always been littered with the few evil who control the many. It would be stupid to think it would be different
-
 @ 08f96856:ffe59a09
2024-09-22 13:02:22
@ 08f96856:ffe59a09
2024-09-22 13:02:22สวัสดีครับเพื่อน ๆ ชาว #siamstr วันนี้ผมจะมาแนะนำ Meshtastic เครื่องมือสื่อสารที่ไร้ศูนย์กลางที่เพื่อน ๆ ไม่ควรพลาดเป็นอันขาด!! เพราะมันคือเครือข่ายการสื่อสารที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี LoRa (Long Range Radio) ซึ่งสามารถส่งข้อความได้ไกลมาก ๆ เป็นกิโลเลยทีเดียว ที่สำคัญไม่ต้องพึ่งพาโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของอินเทอร์เน็ตและไร้การสอดส่องและควบคุมจากรัฐ
Meshtastic คืออะไร?
Meshtastic จะสร้างเครือข่าย "mesh" โดยที่ทุกอุปกรณ์ในเครือข่ายจะช่วยกันรับส่งข้อความต่อ ๆ กันไป ทำให้ทุกคนในเครือข่ายสามารถรับข้อความได้ แม้ว่าจะอยู่ไกลแค่ไหน นอกจากนี้ ข้อความทั้งหมดจะถูก เข้ารหัสไว้ ทำให้เฉพาะผู้ส่งและผู้รับเท่านั้นที่สามารถอ่านได้ ส่วนอุปกรณ์ที่ส่งต่อข้อความจะไม่สามารถเข้าถึงเนื้อหาได้เลย ในการใช้งานนั้นเพื่อน ๆ สามารถเชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ Meshtastic เข้ากับโทรศัพท์มือถือเพื่อทุกคนในเครืองข่ายสามารถสื่อสารกันได้ง่าย ๆ ผ่านแอปส่งข้อความบนมือถือ
จับมือทำ เริ่มต้นใช้งาน Meshtastic แบบง่าย ๆ
เพื่อน ๆ อยากลองใช้ Meshtastic แล้วใช่มั้ย? มาดูขั้นตอนง่ายๆ กันเลยครับ
1. หาซื้ออุปกรณ์ที่ต้องใช้
ขั้นแรกเลย เราต้องมีอุปกรณ์ LoRa กันก่อนครับ ส่วนตัวผมแนะนำบอร์ด LoRa32 ของ LILYGO ครับ เพราะหาซื้อในไทยและต่างประเทศได้ง่ายมาก โดยจะมีให้เลือกหลายรุ่นมากตามความชอบและการใช้งาน ผมได้ทำตารางเปรียบเทียบคุณสมบัติของแต่ละรุ่นดังนี้ | Name | MCU | RF option | Battery | GPS | Link | | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | | Lora32 2.1-1.6 | ESP32 | 433/868/915/923 Mhz | no | no | https://a.aliexpress.com/_opRiKMR | | Lora32 T3S3 | ESP32 | 433/868/915 Mhz / 2.4 GHz | no | no | https://a.aliexpress.com/_opRiKMR | | T-Beam v1.1 | ESP32 | 433/868/915/923 Mhz | has batt slot | yes | https://a.aliexpress.com/_oneeH43 | | T-Watch S3 | ESP32 | 433/868/915 Mhz | yes | no | https://a.aliexpress.com/_olkXkLlData | | T-Deck | ESP32 | 433/868/915 Mhz | yes | no | https://a.aliexpress.com/_olkXkLlData | | T-Echo | nRF52840 | 433/868/915 Mhz | yes | yes | https://a.aliexpress.com/_olkXkLlData |
คุณสมบัติสำคัญที่ควรพิจารณาเป็นหลักในการเลือกอุปกรณ์เลยคือความถี่คลื่นวิทยุ (radio frequency) ครับ เพราะการเลือกความถี่สำหรับใช้งานกับ Meshtastic นั้นขึ้นอยู่กับหลายปัจจัย เช่น กฎระเบียบในประเทศ, ระยะทางที่ต้องการสื่อสาร, และความหนาแน่นของสัญญาณในพื้นที่นั้นๆ อุปกรณ์ LoRa ทำงานที่ความถี่ต่างกันในแต่ละภูมิภาค ตามกฎระเบียบในแต่ละประเทศ เช่น สหรัฐอเมริกาใช้คลื่น 915 MHz, ยุโรปใช้ 868 MHz สำหรับประเทศไทยความถี่ที่ได้รับอนุญาตและไม่มีข้อจำกัดในการใช้งานมีดังนี้ครับ: * 433 MHz: ความถี่นี้เป็นที่นิยมใช้ในหลายประเทศรวมถึงในยุโรปสำหรับอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้พลังงานต่ำและไม่ต้องขอใบอนุญาต (LPWAN) เหมาะสำหรับการใช้งานส่งสัญญานได้ไกลเพราะความยาวคลื่นยาวที่สุดในบรรดาตัวเลือกทั้งหมด * 923 MHz: ความถี่นี้ใช้ได้ในหลายประเทศในเอเชีย รวมถึงประเทศไทยที่อนุญาตให้ใช้อุปกรณ์ IoT ที่สื่อสารระยะไกลอย่าง LoRa ได้รับอนุญาตให้สามารถส่งสัญญาณได้ด้วยกำลังงาน (50mW) ที่สูงกว่าคลื่น 433 MHz (10mW) ถือว่าเป็นความถี่ที่เหมาะสำหรับการใช้งานในไทย * 2.4 GHz: เป็นความถี่ที่ใช้กันทั่วโลก และนิยมใช้กับอุปกรณ์หลายประเภท เช่น Wi-Fi และ Bluetooth ความถี่นี้สามารถใช้ในทั่วโลกได้อย่างเสรี แต่มีระยะการส่งสัญญาณที่สั้นกว่าและไม่ค่อยทะลุทะลวงสิ่งกีดขวางได้ดีนัก เหมาะกับพื้นที่ในเมือง
ส่วนตัวผมเลือกใช้ความถี่ 433 MHz เพราะมันทะลุทะลวงสิ่งกีดขวางได้ดี เหมาะกับการใช้งานในพื้นที่ที่มีสิ่งกีดขวางเยอะ เช่น ป่าเขา และช่วยให้การสื่อสารครอบคลุมระยะทางไกลโดยไม่ต้องพึ่งอินเทอร์เน็ตครับ
2. ประกอบอุปกรณ์
เมื่ออุปกรณ์มาถึง ก็จัดการประกอบเลย! อย่าลืมต่อเสาอากาศและแบตเตอรี่ (ถ้ามี) ให้เรียบร้อยก่อนเปิดเครื่องล่ะ ถ้ารุ่นที่ไม่มีแบตก็ต้องหา power bank อแดปเตอร์จ่ายไฟไว้ให้พร้อมครับ
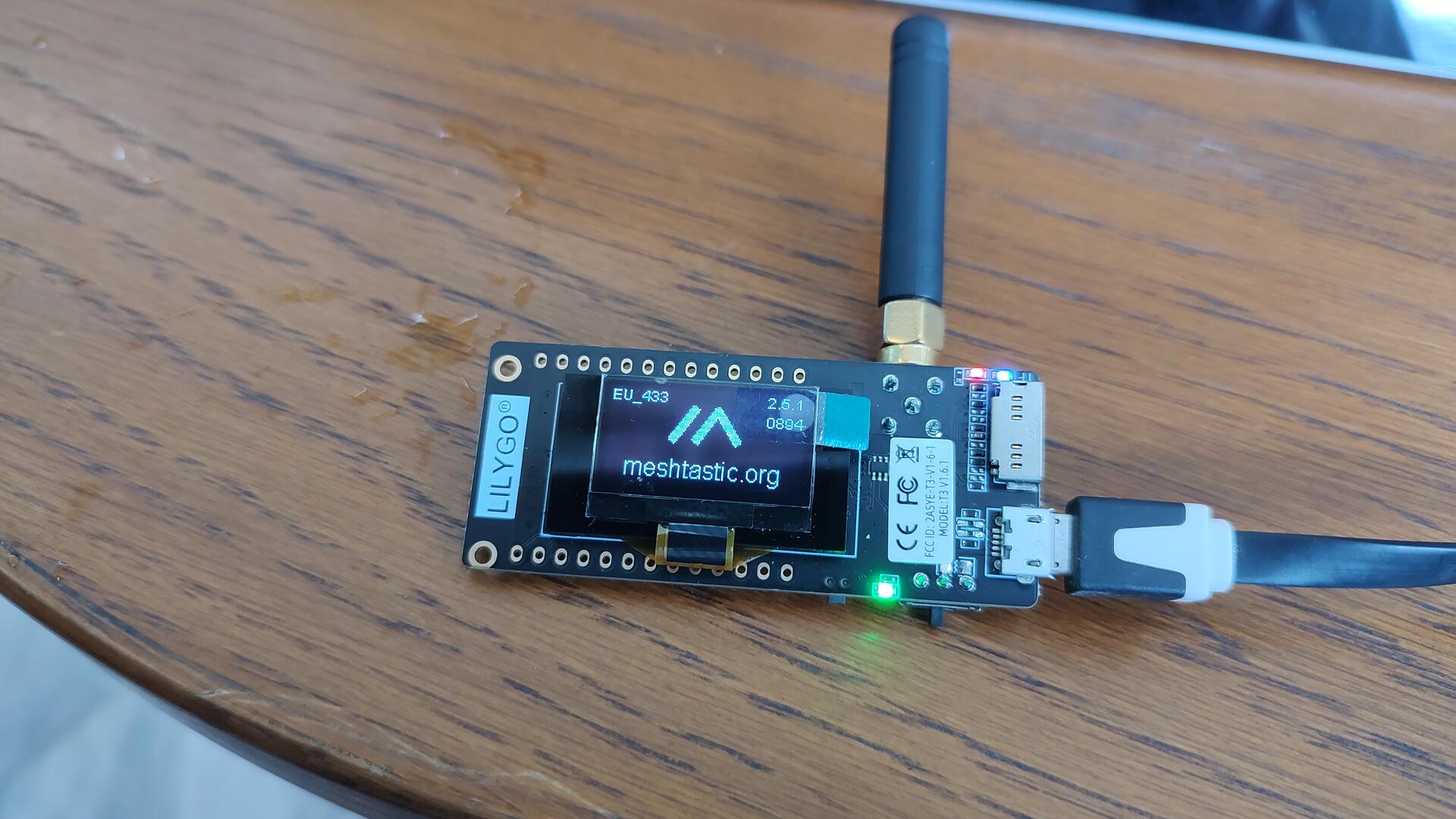

3. Flash Firmware
ต่อไปก็มาลงเฟิร์มแวร์ล่าสุดให้กับอุปกรณ์ของคุณ โดยใช้เครื่องมือ Meshtastic Flasher ซึ่งแนะนำให้ใช้ผ่านเบราว์เซอร์ Chrome จะดีที่สุด ภายในเว็บให้เลือกอุปกรณ์ตามรุ่นที่เราซื้อมา เลือกเวอร์ชันของ firmware เป็นล่าสุด แล้วกด flash ได้เลยครับ
![image![image![image]()](https://image.nostr.build/362c78edcd72da9c5a0bf42d4527788e9a8384441b6199aff2f807dfdf8bcf49.jpg)](https://image.nostr.build/93e348b78ec36153e13aff1141d07ad5b22573a984813b19be82b3530b1199e8.jpg)
4. ติดตั้งแอป Meshtastic
จากนั้นก็ดาวน์โหลดแอป Meshtastic มาลงบนมือถือของคุณได้เลย iPhone: https://meshtastic.org/docs/software/apple/installation/ Android: https://meshtastic.org/docs/software/android/installation/
หลังจากนั้นเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ เปิดแอป Meshtastic แล้วเชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ LoRa กับมือถือผ่าน Bluetooth ด้วยการกดที่เครื่องหมาย + ที่ขวาล่างในหน้า setting ดังรูป
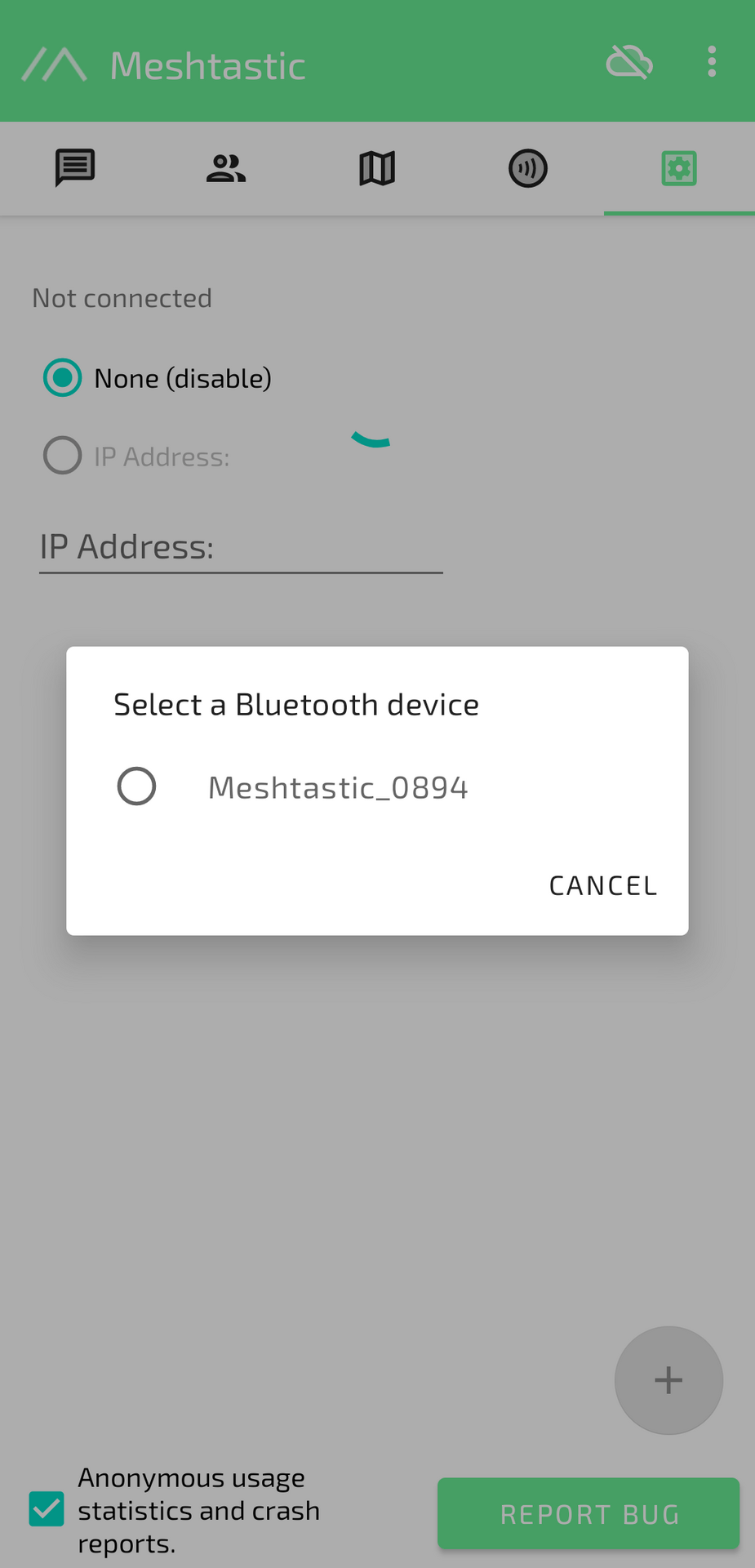 แอปจะทำการค้นหาและเชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ ให้ทำการกรอกหมายเลขตามที่ปรากฏบนหน้าจอของอุปกรณ์ lora
แอปจะทำการค้นหาและเชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ ให้ทำการกรอกหมายเลขตามที่ปรากฏบนหน้าจอของอุปกรณ์ lora
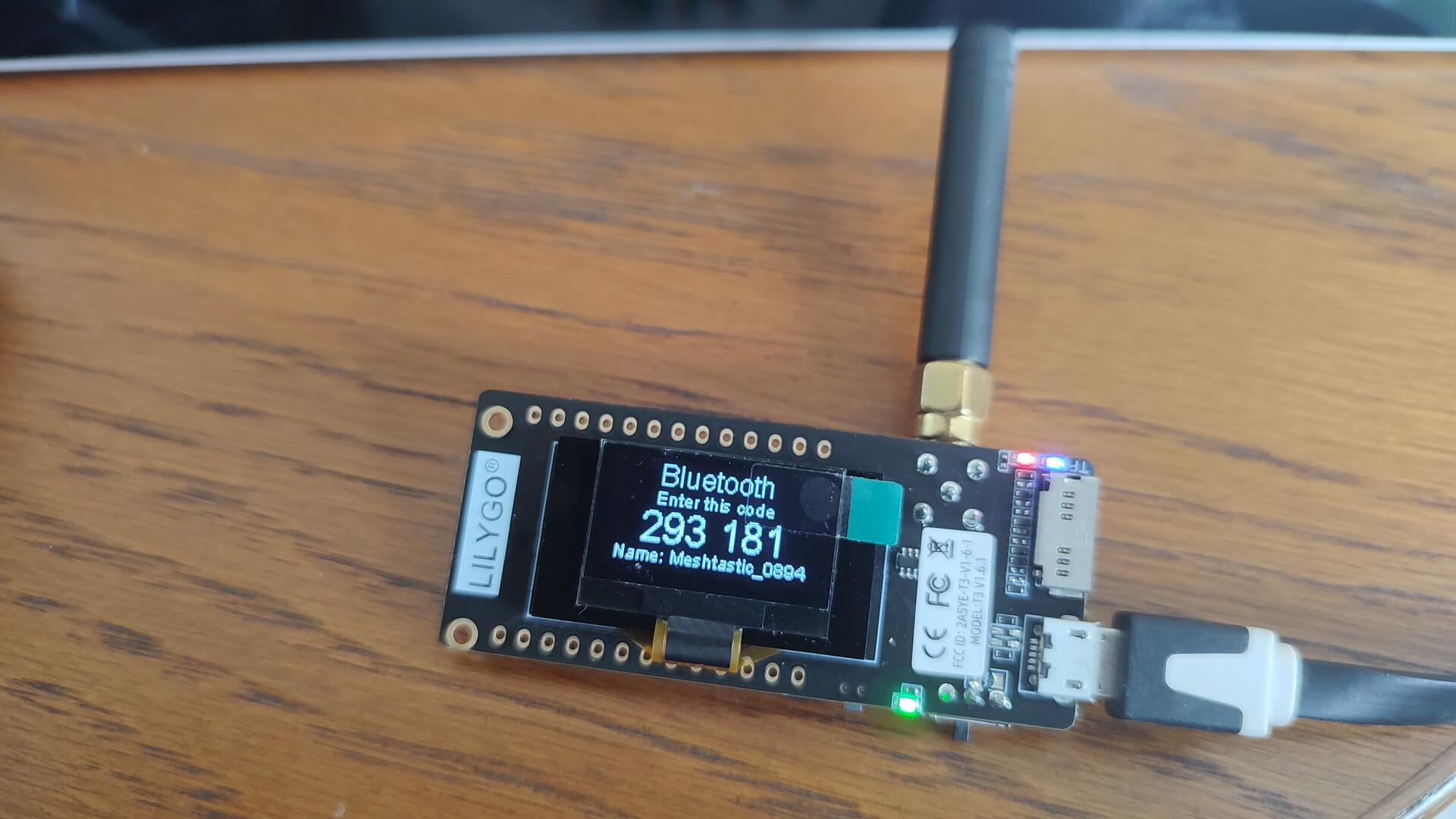

5. ปรับแต่งการตั้งค่า
เข้าไปตั้งค่าในแอป เลือกภูมิภาคตามความถี่ของอุปกรณ์ที่เราซื้อมาครับ ยกตัวอย่างเช่น * ความถี่ 433 MHz ให้เลือก EU_433 * ความถี่ 923 MHz ให้เลือก TH * ความถี่ 2.4 GHz ให้เลือก LORA_24
หลังจากนั้นตั้งชื่ออุปกรณ์ให้เท่ ๆ และปรับแต่งค่าอื่น ๆ ได้ตามใจชอบ
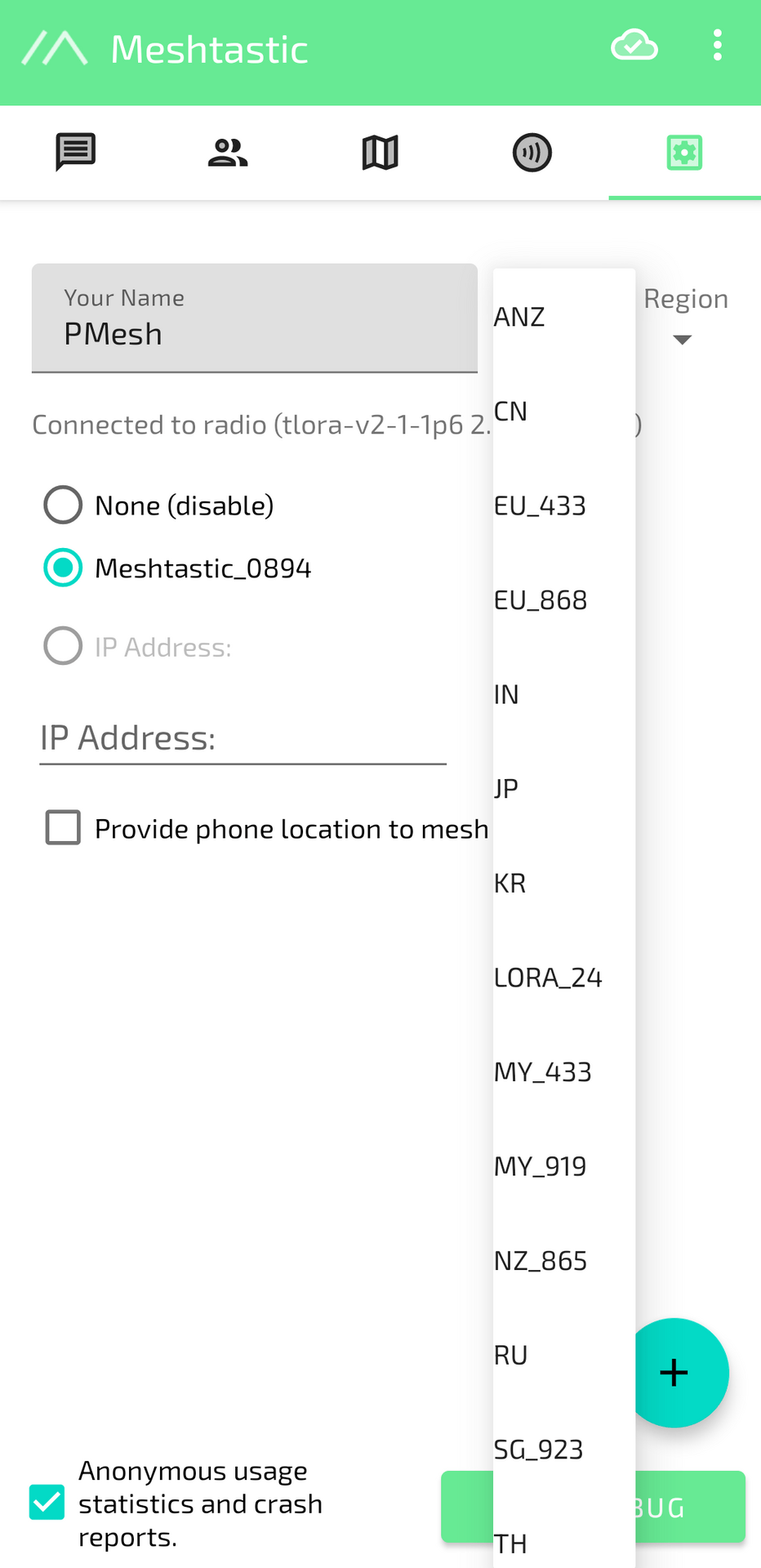
6. ทดสอบส่งข้อความ
ลองส่งข้อความทดสอบไปที่ช่องแชทสาธารณะ "LongFast" ดู แล้วรอคำตอบจากเพื่อน ๆ ในเครือข่าย

7. สนุกกับการสื่อสารแบบไร้ศูนย์กลาง
เมื่อทุกอย่างพร้อมแล้ว ก็เริ่มใช้ Meshtastic ได้เลยครับ ลองสำรวจฟังก์ชันต่าง ๆ และสนุกไปกับการแชทส่วนตัวแบบไม่ต้องพึ่งพาเครือข่ายอินเทอร์เน็ตกันเลยครับ
สรุปส่งท้าย
Meshtastic เป็นโซลูชันการสื่อสารที่ดีและประหยัดสุด ๆ เหมาะกับการใช้ในพื้นที่ที่ไม่มีสัญญาณโทรศัพท์หรืออินเทอร์เน็ต เพราะมันทำงานได้โดยไม่ต้องพึ่งพาโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของเครือข่ายที่รัฐควบคุม เพื่อน ๆ สามารถใช้ Meshtastic ได้อย่างอิสระ ใครได้ลองกันแล้วเป็นยังไงก็อย่าลืมทักกันเข้ามานะครับ จะ DM ผ่าน meshtatic นี้หรือ nostr ก็ได้ หากเพื่อน ๆ มีข้อสงสัยหรือติดปัญหาอะไรก็ทักมาถามกันได้ ไว้พบกันใหม่นะครับ :)
-
 @ e83b66a8:b0526c2b
2024-09-21 16:29:23
@ e83b66a8:b0526c2b
2024-09-21 16:29:23Here are some of the more interesting projects that I like:
Messaging:
https://www.0xchat.com/#/ - Private messaging - think WhatsApp
Xitter Like Clients:
https://damus.io/ - iPhone client
https://nostrapps.com/amethyst - Android client
https://primal.net/downloads - Android, iPhone & Desktop
https://shipyard.pub/posts - Schedule future posts
Interesting sites:
https://zap.stream/ - Video streaming
https://fountain.fm/ - Podcasting
https://wavlake.com/ - Music streaming
https://shopstr.store/ - Online shop
https://zap.cooking/recent - Cooking recipes
https://ostrich.work/ - NOSTR jobs board
NOSTR tools
https://nostr.band/ - Powerful search tool
https://nostr.wine/ - Powerful, but centralised paid relay
https://npub.pro/ - Website creation tool
https://nostr.build/ - Media and file storage
https://relay.tools/ - Build and curate your own relay
https://creatr.nostr.wine/subscriptions/new-user - Creator tools
List of NOSTR apps:
https://nostrapps.com/
-
 @ eac63075:b4988b48
2024-09-20 09:23:23
@ eac63075:b4988b48
2024-09-20 09:23:23Overview of the Infrastructure
- Umbrel/Citadel/RaspiBlitz/Start9 Server
- Purpose: Acts as your personal Bitcoin and Lightning Network node.
- Setup: Installed on a Raspberry Pi 4 running Debian or Umbrel OS.
- Benefits:
- Participate in Bitcoin Consensus: Validates transactions and blocks independently.
- Lightning Network Routing: Facilitates faster transactions and earns routing fees.
- Cold Storage Wallets
- Coldcard: A highly secure hardware wallet designed specifically for Bitcoin.
- Ledger Nano X: A versatile hardware wallet supporting multiple cryptocurrencies.
- Purpose: Store your Bitcoin offline to protect against online threats.
- Secure Devices
- Encrypted Computer: A notebook with encrypted storage for managing your wallets and nodes securely.
- Android Phone with Secure Area:
- Old Device: Repurposed without a SIM card to minimize exposure.
- Secure Area for Apps: Uses features like Samsung's Secure Folder/Knox to isolate sensitive applications.
- NerdMiner
- Purpose: A compact mining device like the Nerdminer V2 to engage in Bitcoin mining.
- Function: Attempts to mine Bitcoin blocks, offering a chance (albeit very low) to earn block rewards and learn about the mining process.
 ### Advantages of This Setup
### Advantages of This Setup- Self-Sovereignty: You have complete control over your funds without relying on third-party services.
- Enhanced Privacy:
- CoinJoin Transactions: Mix your coins with others to obfuscate transaction history.
- No SIM Card Devices: Reduces the risk of SIM swapping attacks.
- Network Participation:
- Consensus Involvement: By running a full node, you help maintain the network's integrity.
- Lightning Network: Improve transaction speeds and network scalability.
- Security:
- Cold Storage: Keeps your private keys offline, away from potential online threats.
- Encrypted Devices: Protects data even if physical devices are lost or stolen.
 ### Simplifying the Perceived Complexity
### Simplifying the Perceived ComplexityWhile the infrastructure may seem daunting, it's more approachable than it appears:
- Starting Point: Use an old computer or phone as a cold wallet with software like Electrum or Sparrow.
- Step-by-Step Setup:
- Begin with setting up the Umbrel/Citadel/RaspiBlitz/Start9 server.
- Gradually add hardware wallets like Coldcard, SeedSigner DIY, Jade, Ledger, Trezor or Onekey.
- Implement security measures on your existing devices.
- Community Resources: Numerous guides and communities are available to assist with each step.
 ### Embracing Freedom and Privacy
### Embracing Freedom and PrivacyPracticing self-sovereignty and custody isn't just about securing your Bitcoin—it's about embracing freedom and privacy in the digital age. By taking control:
- Financial Independence: You're not dependent on banks or exchanges.
- Data Privacy: Your financial data remains confidential.
- Empowerment: Gain a deeper understanding of how Bitcoin and blockchain technology work.
Remember: Even simple steps like using an old device as a cold wallet can significantly enhance your security. The journey towards complete self-sovereignty is a progressive one, and each step you take strengthens your position in the digital world.
-
 @ 502ab02a:a2860397
2024-09-20 02:30:23
@ 502ab02a:a2860397
2024-09-20 02:30:23
มีเรื่องจะประกาศครับ ถ้าสามารถแชร์ออกไปได้ก็ยินดีมากครับ
เป็นความตั้งใจตั้งแต่ก่อนงาน Thailand Bitcoin Conference 2024 ว่าจะเป็นงานสุดท้ายที่ผมจะใช้คำว่า ขนมคีโต
ตลอดเส้นทางที่ผ่านมา หมวกอีกใบนึงของผมคือ การถ่ายทอดความรู้ที่ศึกษามาในแขนงโภชนาการ และคำถามตลอดกาลคือ "อันไหนเป็นอาหารคีโต"
จริงอยู่ครับก็ยินดีตอบให้ได้ แต่ลึกๆมันก็มีความขุ่นๆนิดๆว่า หากเป็นขวบปีแรกของคีโตก็ยังพอเข้าใจ แต่ขณะนี้ก้าวเข้าวปีที่ 8 แล้ว อีกไม่เท่าไรก็ 10ปีคีโตในไทยแล้ว สิ่งแรกที่คนคีโตมองหาเวลาซื้ออาหารคือ ฉลากคีโต
แล้วพอเจอบางสินค้าแปะป้ายคีโต แต่มีวัตถุดิบที่ต่างจากกูรูต่างจากเจ้าพ่อเจ้าแม่คีโต ได้บัญญัติไว้ ก็เกิดความสับสนวุ่นวายทะเลาะเบาะแว้ง ว่าตกลงมันเป็นอาหารคีโตหรือไม่
ผมเลือกทางนี้ครับ หักดิบไปเลย
ต่อไปนี้ผมจะไม่ใส่คำว่า คีโต ในชื่อเรียกอาหาร ต่อไปนี้จะไม่มีชีสเค้กคีโต ดาร์คชอคกานาซคีโต หน้าไก่คีโต บลาบลาบลา ที่มีคีโตเป็นชื่อเรียก อีกต่อไปครับ พอกันทีกับสิ่งนี้
ของกินทุกอย่างที่ผมทำ จะใช้ความเชี่ยวชาญด้านโภชนาการ ความสะอาด สุขอนามัย ฉลากสารอาหาร ใช้การคำนวนแบบเผื่อข้อผิดพลาด(บวก ไม่ลบ) ด้วยการใส่ Macro Nutrient ให้ในทุกเมนู !!!!
เพราะผมเชื่อว่า การกินคาร์บต่ำ เป็นการกินแบบ "ปกติ" การกินคาร์บมากก็เป็นการกินแบบ "ปกติ" เหมือนคนไม่ชอบกินผิก ไม่ชอบกินปลา ไม่ชอบกินเนื้อ อันนี้มันก็แค่คนไม่ชอบกินคาร์บสูงเกินไป แค่นั้นครับ เป็นการกินแบบปกติ ย้ำ เป็นการกินแบบปกติ คาร์บต่ำแบบคีโต เป็นการกินแบบปกติ ที่ควรเป็นมานานแล้วด้วย
การยัดทะนานคาร์บสูงมากๆ ในมุมมองผมคือ นี่แหละที่ไม่ปกติ
ทีนี้ความไม่ปกตินี้มันก็ไม่ผิดอะไรด้วย ถ้าคนกินไม่ปกติ นิยามไม่ปกติคือ ไม่ใช่คนทั่วๆไปเช่น นักกล้าม นักกีฬา ผู้ที่ใช้ "พลังงาน" สูงมากๆแลละต้องการใช้คาร์บ เพื่อการใดการหนึ่งโดยเฉพาะ ดังนั้นไม่มีอะไรที่ผิดเลยครับ ใครอยากกินอะไร กิน ตราบใดที่เรารู้ตัวเราเองว่าทำอะไร
ผมอยู่ในวงการธุรกิจทั้งอาหารและการโฆษณา เข้าใจดีครับว่าการแปะป้ายคีโต คือการช่วยให้คนตัดสินใจง่ายขึ้น เข้าใจง่ายขึ้น ช่วยในการขายให้สะดวกขึ้น แต่ ผมพอแล้วครับ เหรียญอีกด้านนึงของป้ายนีคือ มันไม่ได้ช่วยให้คนคีโต เรียนรู้การทำความเข้าใจด้านสารอาหารเท่าที่ผมคาดหวัง เพราะถ้าไม่มีป้ายพวกนี้ คนคีโตหลายๆคนถึงกับไปไม่เป็นกันเลยทีเดียว แล้วทุกวันนี้เหรียญมันออกด้านนี้ซะเยอะด้วย
นอกจากนี้ประเด็นที่หลีกไม่ได้คือ การหมอบคลานเข้ารับวัตถุดิบคีโตจากกูรู ซึ่งไม่เคยได้เหตุผลในการ "ห้าม" ของหลายๆอย่างเช่น สารหวานบางประเภท แครอท ฟักทอง(ตัวนี้มีคนถามและส่งมาให้ดูเยอะ เดี๋ยวจัดให้เคลียร์ๆ)
ซึ่งใครที่เลือกกินสิ่งนี้แล้วแชร์ความรู้ให้คนคีโตว่ากินได้ ก็จะโดนตรรกะวิบัติจากกูรูด้วยการแปะคำว่า "อยากกิน เลยชวนคนอื่นกิน ชวนคนให้ไม่เคร่ง" เป็นตรรกะวิบัติที่เรียกว่า Ad Hominem หรือ การโจมตีที่ตัวบุคคล นั่นเอง (ref : https://siripun.com/2023/06/09/logical-fallacies-2-ad-hominem ) ทั้งที่ถ้าจะนิยามคำว่าเคร่ง สิ่งที่กูรูให้ทำ ไม่สามารถมีคำตอบที่สร้างสมการสมดุลได้ (ทำไม A ได้แล้ว B ไม่ได้ถ้าเทียบบริบทเอามาชนกันชัดๆเลย)
จริงๆก็อยากรณรงค์ให้ผู้ประกอบการอาหารคีโต ร่วมโครงการนี้ แต่เข้าใจว่ามันคงไม่สามารถทำได้ เพราะอาจจะมองในมุมที่ต่างกัน ผมเข้าใจในสิ่งนั้นครับ แต่มุมของผมคือ การทำอาหารคีโตให้กลับมาอยู่ในประเภทอาหารปกติ จะยิ่งขยายมูลค่าตลาดออกไปได้มากกว่าทุกวันนี้
ตลาดคีโตมันซบเซา เพราะเราทำให้มัน "ประหลาด" ทำให้มันกลายเป็นของ "ไม่ปกติ" พอได้น้ำหนัก หุ่น ลูก สมปรารถนาแล้วก็ถวิลหาการ "ออกไปกินปกติ" นั่นคือการทำให้ตลาดหายไปเรื่อยๆเพราะพวกคุณเองครับ ผมกลับมองว่าทำให้คีโตคืออาหารปกติ แล้วกินกันไปตลอด ไม่มีการขอออกจากเผ่า หานเป็ดอะไรคือทางที่ดีกว่า ได้สุขภาพที่ดีกว่า
คีโตคือการกินปกติ ไม่ควรต้องมาแยกเป็นชนเผ่าอะไรเลย คีโตคือคนเมือง คนมีความรู้ คือ วิทยาศาสตร์ คือความฉลาดในการเลือกสารอาหาร อย่าไปยัดเยียดความ "ไม่ปกติ" ให้อาหาร "ปกติ"
ก็เลยคิดว่า ไม่เป็นไร ร้านคีโตร้านใดอยากร่วมเรายินดี แต่ถ้ามองว่าไม่เอาด้วยก็ยินดีเหมือนกัน เพราะการค้าเสรี อยากทำอะไรก็ทำได้ครับ ในส่วนตัวผม เราทำของเรา เราเริ่มของเราเลยก็ได้ เพราะเส้นทางที่ผ่านมา เราก็เดินอยู่ในเส้นทางของเราอยู่แล้ว และผมเชื่อใน Proof of Work ครับ ผมสามารถทุ่มแรงกายแรงใจ ลงในอาหาร ลงในการสอน ให้คนตระหนักถึง "สารอาหาร" มากกว่า "ป้ายฉลาก"
แล้ววันนึง มันจะส่งผลที่ impact ครับ ผมเชื่ออย่างนั้น Proof of Work สามารถส่งต่อได้ และ พลิกโลกได้ มานับต่อนับแล้ว
ทุกวันนี้ผมทุ่มเนื้อหาด้าน ฉลากอาหาร เพื่อให้คนหัดอ่าน รู้เท่า รู้ทัน มันก็ทำให้ผมยิ่งรู้สึกว่า ผมไม่ควรแปะคำว่าคีโต ลงไปเลย มันเหมือนไปสปอยให้คนลืมพื้นฐานสำคัญ
ไม่ใช่ว่าไม่ง้อคนคีโตนะ คนทำการค้าต้องยินดีกับทุกการค้าอยู่แล้ว แต่ผมกลับมมองว่า ตลาดของผมขอเป็นตลาดที่มีการอ่านฉลาก มีการหัดพิจารณาสารอาหาร ดูคาร์บเป็น เลือกวัตถุดิบที่เหมาะกับแต่ละคน มากกว่าวัตถุดิบที่ต้องได้รับการโปรดจากกูรู
ผมมองว่า คนกินคลีน คนกินไฮโปรตีน หรือแม้แต่แค่คนที่ไม่อยากกินน้ำตาล ก็จะสามารถกินอาหารที่ผมทำได้ ไม่โดนปิดกั้นจากป้ายคีโต ที่โลกประเคน mind set ให้ว่าต้อง high fat เท่านั้น
ซึ่งถ้าผมทำอาหารในแบบของผม + คนกินพิจารณาได้เองว่าสารอาหารเหมาะกับเขาไหม = การกินแบบมีความรู้จริง เหมาะกับตัวเองจริงๆ
ถือว่าเป็นอีกเส้นทางที่ผมต้อง fight for ครับ ถ้าสำเร็จ มันจะช่วยให้คนในสังคมหลุดกรอบ และมองสารอาหารได้ ดูแลสุขภาพได้ ด้วยพื้นฐานความรู้ที่มากขึ้นครับ ไม่ใช่ทางที่สบายแน่นอนครับ แต่พวกคุณจะได้ประโยชน์ติดตัวไปแน่ๆ
ถามว่าทำเพื่อการค้าใช่ไหม ก็ใช่ครับ การค้ามันคู่กับโลก ผมไม่ค่อยเข้าใจในมุมของการต้องการอะไรฟรีๆอยู่ตลอด ถ้าคุณเคารพใน value แล้วยินดีส่งต่อ value for value คุุณจะยินดีในการค้าที่ไม่ยัดเยียด (fiat) คุณจะยินดีในการส่งต่อ value ด้วยคุณค่า คุณจะยินดีในการมองคุณค่าของ "เวลา" ที่ผู้สร้างผู้ทำลงทุนลงไป (เวลาคือทรัพยการที่มีค่าที่สุดในโลก) แล้วถ้าคุณให้เกียรติกับสิ่งเหล่านี้ คุณจะไม่อยากได้มันฟรีๆ คุณจะกระดากใจที่จะหยิบมันมาเปล่าๆ นี่คือเหตุผลที่ผมไม่เคยมองว่า การทำการค้า มันจะเลวร้ายอะไร แต่ที่แน่ๆ ผมจะไม่ทำ FIAT keto ครับ ผมจะไม่เร่งเร้า ไม่ขู่เข็ญ ไม่ใช้ตรรกะประเภท "ของมันต้องมี" ผมจะแบไต๋แฟร์ๆด้วยสารอาหารครับ
แม้มันจะแลกมาด้วยการขาดโอกาส จากป้าย "คีโต" ก็ตาม แม้คนคีโตจะมองว่า ไม่มีป้ายคือไม่คีโตก็ตาม แม้จะไม่ได้รับการรับรองจากกูรูใดๆ ว่า "คีโตกินได้" ก็ตาม ถ้าจะให้สังคมมีการเรียนรู้สารอาหารขึ้นได้ ผมยอม
pirateketo #ตำรับเอ๋ #siripun #siamstr
-
 @ cb084639:2f16502a
2024-09-17 10:09:23
@ cb084639:2f16502a
2024-09-17 10:09:23รีวิวงาน #TBC2024 สไตล์ #Richter

เรื่องมันเริ่มมาตั้งแต่ช่วงที่ทาง
npub1ejn774qahqmgjsfajawy7634unk88y26yktvwuzp9kfgdeejx9mqdm97a5
ประกาศขายตั๋วงาน TBC2024 และได้ยินมาว่า จะเปิดรับ อาสาสมัครมาช่วยงาน ตั้งแต่วันนั้นก็คิดมาตลอดว่าอยากจะช่วยงานแต่ไม่รู้จะช่วยอะไรดี อย่างน้อยก็ช่วยทำในสิ่งที่ช่วยได้แล้วให้คนที่เราไปแทนได้ไปทำหน้าที่ที่ดีกว่า ก็ถือว่าเป็นการสนับสนุนส่วนหนึ่ง ก็ยังดี เพราะภาพจากปีที่แล้วมันลอยเข้ามา เราเองก็มางานคนเดียวไม่รู้จักใครเลย ได้เห็นพี่นิวและคุณนิ่ม ที่อยู่ร้านขายเสื้อแบบยุ่งมากๆ ถ้ามีคนมาช่วยเพิ่มก็คงดี พอดีเลยที่ทีมงานจับเราลงตำแหน่งนี้ จึงมีโอกาสได้มาช่วยงาน และรู้สึกเป็นเกียรติที่ได้ร่วมงานครับ ขอบคุณทุกคนที่ได้มาเจอกันในงาน ผมอาจจะไม่ได้พูดถึงทุกคนแต่ แค่มองตากันก็เข้าใจแล้ว เจอกันเยอะมากๆ ถ้าใครได้ผ่านร้านขายเสื้อก็จะเจอผมอยู่ตรงนั้น มีเพื่อนๆแวะเวียนมาทักทาย พูดคุย มาป่วน 😄😄 ประโยคที่ส่วนมากจะได้ยินเวลาผมทักทายไม่ใช่ว่าชื่ออะไรนะ ผมจะถามว่า กินข้าวยัง กินอะไรหรือยัง มันอาจจะเป็นคำง่ายๆ แต่มันแฝงไปด้วยความห่วงใยกัน บางคนเห็นไกลๆได้แต่สบตาแล้ว พยักหน้าให้กัน เหมือนทุกคนในงานเป็นเพื่อน เพื่อนที่พูดจาภาษาเดียวกัน ไม่รู้จะบรรยายออกมายังไงมันรู้สึกดี อิ่มเอมไปหมด ได้แนะนำสินค้า ได้มองเห็นกลุ่มเพื่อนคุยกันสนุกสนาน มันเป็นบรรยากาศที่ดีเลยทีเดียว เอาเป็นว่าเป็นประสบการณ์ที่ดีมากๆ เมื่อเทียบกับปีที่แล้วเลยแหละครับ ขอบคุณ อ.ตั๊ม แม่โบว์ npub1ejn774qahqmgjsfajawy7634unk88y26yktvwuzp9kfgdeejx9mqdm97a5
ที่ให้โอกาสได้ร่วมงาน ขอบคุณเฮียโต้ง สำหรับหนังสือและขนมแสนอร่อยที่เอามาให้เราได้จับจ่ายกัน ขอบคุณ เพื่อนทุกคนที่เข้ามาทักทายกัน ขอบคุณลูกพี่สมนึกหัวหน้าแก๊งค์ร้านเสื้อ พี่แองจี้ แฟนพี่สมนึก แฟนพี่ตั้ม และทีมงานน้องเอิ้น ที่ช่วยขายของ รักทุกคน
siamstr #siamstrog #nostr




-
 @ 502ab02a:a2860397
2024-09-17 03:02:24
@ 502ab02a:a2860397
2024-09-17 03:02:24เหนื่อยกาย อาบน้ำก็หาย ความประทับใจ มันจะประทับไปอีกนาน
น้ำนี่มีประโยชน์กับมนุษย์สูงมาก โดยเฉพาะน้ำใจ
Thailand Bitcoin Conference 2024 ที่ผ่านมา 2 วัน 14-15 september 2024 block 861367 เป็นงานที่ตอนนี้ผมนั่งตกตะกอน บันทึกไว้ใน long form ของ YakiHonne ที่ต้องขอบคุณมากๆ เพราะคุณ Wendy มาที่บูธผม หลังจากแนะนำตัว ผมบอกว่าใช้ YakiHonne อยู่ คุณ Wendy ถามว่า user ชื่ออะไร พอเปิดแอพถึงแค่หน้า feed ที่มีรูปผมกลมๆเล็กมุมขวาบน ยังไม่ทันกดเมนู profile เพื่อแสดงชื่อ คุณ Wendy ก็ชี้รูปแล้วบอก i know you ทันที ซึ่งน่าตกใจและประทับใจมากๆ

ใน YakiHonne ผมมีหัวข้อ ”เจอนี่“ ที่เอาไว้บันทึกเรื่อง เจอนี่ อยู่แล้ว การที่ได้เจอ ชาวบอทคอยน์,ทุ่งม่วง และ Wendy จึงเหมาะกับคอลัมน์ เจอนี่ที่สุดแล้ว
หลังจากแผน Mission unknown ลุล่วงไปได้ มี error ไว้ให้แก้บ้างซึ่งวางแผนสองไว้แล้ว แต่ก็เหนือความคาดหมาย จาก Mission unknown กลายเป็น Mission Impossible ไปด้วยการทำ world records ของตัวเอง 2 วันซ้อนคือ 64ก้อน ภายใน 2 ชั่วโมงในวันแรก และ 80ก้อน ภายใน 50นาที (8:30-9:20) วันที่สอง
เรื่องเค้ก เดี๋ยวไปสวมหมวกกุ๊กเขียนในตำรับเอ๋บนสื่อมาร์กนะครับ ในนี้ผมอยากบันทึกเรื่องคอมมูทุ่งม่วงมากกว่า
ต้องขออภัยที่ไม่ได้แทกหรือระบุชื่อใคร เหมือนตอนซื้อสติกเกอร์อะครับ ผมรักพวกคุณเท่าๆกันหมดเลย กลัวว่าเอ่ยชื่อไม่หมดผมเองจะเสียใจ
ครั้งนี้เป็นครั้งแรกที่ผมได้เจอชาวทุ่งม่วง ขอบคุณที่แนะนำตัวกันด้วยชื่อในทุ่งม่วง ไม่งั้นนี่ผมต้องไปไม่เป็นแน่ๆครับ โชคดีที่ชาวทุ่งม่วงมารวมกระจุกตัวที่ตลาดสายฟ้า ขอบคุณ มิก ที่เป็นแม่เหล็กดูดคนไว้ไม่ให้ไปไหน จนฝั่งทุ่งม่วงคาเฟ่ของเรา กลายเป็นจุดรวมพลคนทุ่งม่วงไปเลย
ตามที่ตั้งใจไว้ครับ ว่าชีวิตผมหลังจาก 31 กรกฎาคม 2567 จะเป็น chapter ใหม่ ของการใช้ชีวิต ผมจะพยายามหลอมรวมทรัพยากรที่มีค่าที่สุดในโลกที่เรียกว่า “เวลา” มาใช้จ่ายให้คุ้มที่สุด หลังจากที่เลือกหันหลังให้อาชีพที่หลายๆคนมองว่ามั่นคง แต่มันดูดเวลาผมไปแทบจะหมดตัว จนตัวเองมองว่า ทรัพย์ในมือเราแท้ๆ จริงๆแล้วเวลามันอยู่ในกระเป๋าเรา ตัวเราเองไม่ใช่เหรอที่หยิบมาจ่ายออกไป เราเลือกจะจ่ายให้กับอะไรไม่รู้ แทนที่จะจ่ายให้คนที่เรารัก นี่มันสุรุ่ยสุร่ายนี่หว่า
ดังนั้น
ผมกลับมาใช้บั้นปลายชีวิต ด้วยการจ่ายที่มีคุณค่าขึ้น ผมเรียกการใช้จ่ายนี้ว่า spend time ยิ่งเหลือน้อยยิ่งต้องใช้แบบมีคุณค่า ผมไม่ได้ออมเวลามาตั้งแต่วัยรุ่น ผมเลยไม่มั่งคั่งในเวลา นี่จะ 50 อยู่รอมร่อ ถ้าคำว่า make saving great again ไม่ผ่านหูผ่านตามา ผมคงไม่ save time เพื่อเอาไป spend time ที่มีคุณค่าได้ครับ เรียกว่า กลับตัวยังทันในวันที่มีลมหายใจ จึงเลือกที่จะ ประหยัดเวลาเพื่อเอาไปใช้จ่ายกับสิ่งที่มีคุณค่า
ความอบอุ่นที่ได้รับจากคอมมูนิตี้ มันมีพลังมากๆเลยครับ ไม่ผิดกับที่คาดไว้หลังจากได้อ่านมาจากหลายๆอีเวนท์ที่เกิดขึ้น
เหมือนที่ยืนคุยกับหมอเอก กับ คุณริช ครับว่าภาพความสำเร็จของงานมันแสดงออกมาทางหน้างานนี่ละครับ ความครึกครื้น การพูดคุยกัน sats สะพัด มันเหมือนเราเห็นภาพอนาคตได้ในวันนี้ บรรยากาศแห่งน้ำใจ บรรยากาศการใช้บิทคอยน์แลกสินค้าที่มาจากความตั้งใจในการทำ ผมมั่นใจเลยว่า สินค้าตลาด lighting ล้วนเกิดจากอิทธิบาท4 แม้แต่ฝั่งเบียร์ มันมาจาก passion ทั้งนั้นเลย ภาษาบิทคอยน์อาจเรียกว่าตลาดนี้เป็นศูนย์รวมของ proof of work
นึกถึงตอนวัยรุ่น เวลาคนมีไฟมารวมกัน มันคือพลังระดับ ดวงอาทิตย์
ถ้ามันเป็นแบบนี้ตลอดไป ก็ไม่มีอะไรที่ภายในทุ่งม่วงนี้ ที่ทำไม่ได้แล้วหละครับ

ยินดีและปรีดา ที่ได้พบทุกท่านจริงๆครับ ทุกท่านกลายเป็นตัวหนังสือที่ออกมาโลดแล่นบนโลกจริงๆ ภาพในหัวตอนนี้เวลาเห็นตัวหนังสือก็จะฝังหน้าลงไป embed เรียบร้อย เหมือนแต่ละ block ที่ฝังเหตุการณ์เอาไว้
ท้ายสุด ด้วยความนิยมชมชอบในงานของกันและกัน พ่อมดคริปโต ได้มอบการ์ด prototype จากบอร์ดเกมส์ Age of Bitcoin Boardgame ให้ผมเป็นที่ระลึก ก่อนรับรางวัลที่ 1 กิจกรรม geyser ทำให้เป็น rare item ในทันที ขอบคุณ ชับบี้ มากๆครับ

ขอบคุณพี่ป้ำ เป็นพิเศษสำหรับ DM ตอนก่อนเตรียมงานและการสนทนาภาษา baker ในงานครับ
ถึงทีม Right Shift ทุกคนครับ "ผมเป็นอีกคนที่มีความสุขนะครับ" ผมในฐานะที่อยู่วงการโฆษณา ประเภท below the line และ ออกาไนเซอร์ มาก่อน ยืนดูงานแล้ว ต้องขอขอบคุณที่เหนื่อยกันนะครับ break the leg จริงๆ
ปล. ด้วยว่าส่วนตัวความจำระยะสั้นผมแย่มาก ผมมักจำด้วยภาพ ใครที่ผมได้มองหน้าบ่อยผมจะ match ชื่อไปกับหน้าด้วยเลย แต่งานนี้ information overload ทั้งขายของ ทั้งทักทาย ประกอบกับนอนน้อยมากด้วย ผมจำใครไม่ได้บ้างก็โปรดให้อภัยครับ คิดเลขยังเครื่องคิดเลขเลย
ถ้าได้เจอตามท้องถนน เรียกทักกันด้วยนะครับ ผมยินดีและอยากคุยครับ ส่วนถ้าผมเดินผ่านคุณไปทักเลยนะครับ เพราะนอกจากความจำสั้นแล้วสายตายังยาวด้วยครับ

-
 @ 862fda7e:02a8268b
2024-09-16 22:59:38
@ 862fda7e:02a8268b
2024-09-16 22:59:38I was in some sort of nice romantic building and I met this nicer middle aged blonde woman who looked a lot like one of my old teachers. We got to chatting and things started moving quickly, we were going to have sexy lesbian sex but she told me she wanted me to shave my vagina before we started. I said fine, went to a bathroom and started shaving. If it meant I was going to slang some tang, I was gonna do it. It took me a long time to complete this daunting task, as I've mantioned many times before, I have a very thick and dense bush. I also wanted to make sure no hair was left behind, if my sweet lesbian lover saw that I had a hair on my vagina, she would probably freak out and call me disgusting for having a feature that naturally grows on me.
Anyways, I finished shaving my vagina and went to go meet her. Sadly, she decided to not have lesbian sex with me anymore since I took too long and she had some time to think about it. I got screwed without getting screwed. And now I had a gross hairless vagina.
I think I know why this dream occured. It's because my so called "fans" have judged me on my fan page for having hair on my vagina. Yes, I sometimes maintain it and keep it trimmed, sometimes. But sometimes I just let it go if I'm too lazy. Now the lesbians in my dreams want me to shave, and even at that, they still don't want to have sex with me. One time I remember cumming from a wet dream I had, which is very rare for me to do. I was watching 2 Japanese chicks dressed up in the school girl uniform scissor, and I remember waking up with a hard clit and it pulsated. I felt embarassed waking up, because I didn't even voluntarily masturbate but I still climaxed.
-
 @ 7fa56f5d:751ac194
2024-09-16 12:31:25
@ 7fa56f5d:751ac194
2024-09-16 12:31:25If you are a nostr user or developer you're probably familiar with nostr identifiers. These identifiers are used to represent public/private keys or event ids. They allow for a human-readable representation of these values that can be used for copy-pasting, sharing, nostr URIs, rendering QR codes or referencing entities in text content.
The identifier start with a prefix that indicates the type of the identifier:
npubfor public keys,nsecfor private keys andnotefor note ids. The prefix is followed by a separator character (1) and a payload that is encoded using the Bech32 encoding scheme.The pubkey
7fa56f5d6962ab1e3cd424e758c3002b8665f7b0d8dcee9fe9e288d7751ac194is represented asnpub107jk7htfv243u0x5ynn43scq9wrxtaasmrwwa8lfu2ydwag6cx2quqncxg.Context matters
There are special variants of the identifiers that include metadata to provide more context. The extra information enhances nostr client UX and interoperability since it allows to more easily find and display these entities.
The
nprofileprefix is used to represent a public key with a set of relays where the user profile can be found. Theneventprefix is used to represent an event id (not necesarily a kind 1 note) with an optional set of relays where the event has been seen, the author of the event and an optional kind number. Thenaddrprefix is used to represent an address with kind, author, identifier (d) and an optional set of relays where the event has been seen.For those variants the content is a binary-encoded list of
TLVfields. Check out NIP-19 for a breakdown of which types are used for each prefix.Pubkeys
Although there are relays that aggregate profile metadata and relay lists such as Purple Pages and profiles.nos.social, a bare
npubis not enough to find a user's content. Thenprofilealternative prefix tells clients where they can find the user's profile and posts.Some great options for the relay hints included in an
nprofileare the relays on the user's relay list metadata event.Events
An
neventidentifier can contain additional metadata about the event such as relay hints, the author of the event and the kind number. The relay hints can be used to find the event on the network and the author can be used to display the author's profile picture and name.Including the kind number in the identifier is useful for clients since they can know if the event is compatible with their rendering logic. A client that only supports kind 1 notes can ignore kind 9802 highlights or show their
.contentfield. A better alternative would be to query the nostr network to find compatbile apps via NIP-89 Recommended Application Handlers or even embed the apps in the client itself.Addresses
There are certain types of events that do not have stable identifiers since they can be replaced anytime. A user can publish new versions of long-form articles or their profile. The
naddrprefix is used to represent these events with an identifier that can be used to find the latest event. Thedfield is used to represent the identifier of the event that the address points to.Similary to
nevent, thenaddrprefix can include relay hints to find the event on the network. The author field can be used to display the author's profile picture and name. The kind field can be used to know if the event is compatible with the client's rendering logic.tl;dr
I encourage developers to use the variants with added context whenever possible. This means that clients will need to keep track of which relays an event has been seen on and which relays a user is posting to and reading from. The trade-off between longer identifiers and better interoperability is worth it if we want to make the nostr network decentralized and resilient.
You can use tools such as nak to get familiar with the different types of identifiers, add or remove metadata to your identifiers and decode them.
-
 @ 502ab02a:a2860397
2024-09-14 08:26:05
@ 502ab02a:a2860397
2024-09-14 08:26:05
YakiHonne คือแพลทฟอร์ม long form ที่ผมมักใช้ประจำในการทำบทความยาวๆ มาวันนี้ได้เจอคุณเวนดี้ ที่งาน Thailand Bitcoin conference 2024 รู้สึกดีใจมากๆ
siamstr
-
 @ 79008e78:dfac9395
2024-09-12 11:16:45
@ 79008e78:dfac9395
2024-09-12 11:16:45" ผมตื่นเต้นที่จะประกาศเปิดตัว NWS ครั้งแรก นี่เป็นคำตอบของการเชื่อมต่อออกไปยังโลกของอินเตอร์เน็ต โดยใช้ NOSTR เข้าไปแทรกระหว่าง transport layer และ network layer ที่อยู่บน TCP/IP โมเดล NWS นั้นจะเข้ามาช่วยให้การสื่อสารระหว่างอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ ให้เป็นไปอย่างราบรื่น มีความเป็นส่วนตัวเพิ่มขึ้น และทำให้เราสามารถท่องโลกของอินเตอร์เน็ตโดยไม่จำเป็นต้องใช้ Public IP " -asmogo
NostrWebServices (NWS) คืออะไร?
NWS คือการนำ Nostr เข้ามาช่วยในการเข้าถึงบริการของเว็บไซต์ต่าง ๆ โดยยังสามารถส่งข้อมูลขึ้นไปยัง transport layer บน TCP/IP ซึ่งด้วยวิธีนี้เองเลยทำให้เราสามารถสร้างการเชื่อมต่อได้โดยไม่จำเป็นต้องมี Public IP โดยส่วนที่จำเป็นหลัก ๆ ในการทำงานนี้เราจำเป็นต้องเตรียม
-
Entry node: SOCKS5 proxy ที่คอยส่งต่อ TCP packets ที่เข้ารหัสผ่านทาง event ของ Nostr ก่อนส่งส่งผ่านรีเลย์ต่าง ๆ ไปยัง Exit node
-
Exit node: TCP reverse proxy ที่คอยรอรับข้อมูลมาจาก Entry node และส่งต่อข้อมูลต่าง ๆ ไปยังบริการอื่น ๆ ต่อไป

ในส่วนของการทำงานนั้นสามารถดูได้จากในรูปที่ได้แนบไว้ข้างต้นได้เลย อย่างที่เห็นเลยว่ามันเริ่มจากแอพต่าง ๆ เหมือนที่เรามีการใช้งานกันอยู่ในปัจจุบัน เพียงแต่แทนที่เราจะส่งข้อมูลต่าง ๆ ผ่าน IP layer ตามปกติ เราสามารถส่งเข้าไปยัง Entry node และหลังจากนั้นข้อมูลจะถูกส่งผ่าน relay ต่าง ๆ ก่อนที่จะวิ่งไปยัง Exit node และ Exit node จะคอยส่งข้อมูลต่าง ๆ ไปยังบริการหลังบ้านที่เราต้องการจะเชื่อมต่อ
เราจะเห็นได้ว่าการทำงานของ NWS นั้น สำหรับผู้ใช้งานโดยทั่วไปแล้วแทบจะไม่แตกต่างอะไรกับในปัจจุบันเลย นั่นก็เพราะว่าเรายังทำการใช้งานแอพต่าง ๆ ตามปกติ แต่ประโยชน์ที่เราจะได้รับเพิ่มเติมนั้นคือความเป็นส่วนตัวในการใช้บริการเบื้องหลังอื่น ๆ
นอกจากนี้ยังมีในส่วนของ NWS domain names ใน NWS นั้นมีการรับรอง domain สองตัวนั้นคือ
- ".nostr" ซึ่งใช้ชื่อโฮสต์เป็นกุญแจสาธารณะที่เข้ารหัสด้วย base32 และ รีเลย์ที่เข้ารหัสด้วย base32 เป็นโดเมนย่อย
- "nprofiles" ซึ่งเป็นการผสมผสานกันระหว่างกุญแจสาธารณะของNostrและรีเลย์หลายตัว
ซึ่งโดเมนทั้งสองประเภทจะถูกสร้างและปรากฏอยู่บนคอนโซลเมื่อเริ่มต้นใช้งาน
หัวใจหลักในการทำงานของ NWS
อย่างที่ได้กล่าวไว้ข้างต้นว่า NWS เข้ามาช่วยเหลือในการเพิ่มความเป็นส่วนตัวได้ แล้วถ้าเราไม่ได้ต้องการเข้ารหัส หรือถ้าเราอยากจะเปิด Entry node แล้วเราไม่ต้องการให้คนที่จะเชื่อมต่อเข้ามาเข้ารหัสข้อมูลเราสามารถทำได้เช่นกัน โดยทั้งสองระบบที่ NWS ทำได้มีดังนี้
-
แบบไม่เข้ารหัส: เราจำเป็นต้องรันโหนดไว้ในเครื่องที่เราใช้รัน client แล้วแปลง client ให้ส่งข้อความใส่โหนดปลายทางตรง ๆ
-
แบบเข้ารหัส เริ่มจากการเชื่อมไปที่โหนดที่ต้องการ (อารมณ์ ssh เข้าไป) แต่วิธีนี้ยังติดที่บางเว็บที่เป็น https จะเชื่อมไม่ได้หาก cert ของโหนดที่เราเชื่อมมีปัญหา ส่วนข้อมูลที่ส่งจะถูก encrypt ไว้ด้วย Sphinx (เข้ารหัสแบบหนึ่งในมาตรฐาน RSA) ฉนั้นมั่นใจได้ว่าโหนดที่เราไปยืมจมูกเขาหายใจก็ไม่รู้ว่าเราส่งอะไรไป
การตรวจสอบตัวตนของเซิร์ฟเวอร์ปลายทาง
การตรวจสอบตัวตนของเซิร์ฟเวอร์ปลายทางของ NWS ทำโดยการใช้ประโยชน์จาก nostr โดยให้โหนดปลายทางปล่อย cert (TLS) บน nostr และเซ็นรับรองด้วยตนเองและอณุญาติให้ไคลเอนต์สามารถดึงใบรับรองนี้มาก่อนเชื่อมต่อกับโหนดที่เป็นจุดเริ่มที่เราใช้
และนอกจากนี้ในอนาคตของการพัฒนา NWS กำลังพัฒนาให้ NWS สามารถกำหนดให้โหนดปลายทางสามารถกำหนดค่าให้เข้าถึงอินเทอร์เน็ตได้ (ไม่ใช่แค่บริการภายใน) ทำให้ NWS ทำงานคล้าย VPN โดยสามารถเข้าเว็บไซต์ปกติได้ เช่น พิมพ์ "https google dot com" ก็เข้า google ได้
และทั้งหมดที่กล่าวไว้ข้างต้นเป็นเพียงการเริ่มต้น ยังมีคุณสมบัติอย่างอื่นอีกมากมายที่จะเข้ามาปรับปรุงปัญหาต่าง ๆ ในการใช้งานอินเตอร์เน็ต โดยส่วนตัวผมรู้สึกตื่นเต้นกับอนาคตของ NWS มาก ๆ และคาดหวังที่จะได้เห็นคนหันมาให้ความสนใจและใช้งานมัน ทั้งนี้หากใครอยากทดลองใช้งานก็สามารถติดตามได้ที่
GitHub: https://github.com/asmogo/nws
ส่งท้าย
สำหรับ series nOStr ผมตั้งใจจะหาเรื่องราวเกี่ยวกับ other stuff ที่น่าสนใจ ให้ทุกคน ๆ ได้ศึกษาไปพร้อม ๆ กัน เพราะว่า nostr ไม่ได้มีแค่โน๊ต
-
-
 @ 6ad3e2a3:c90b7740
2024-09-11 15:16:53
@ 6ad3e2a3:c90b7740
2024-09-11 15:16:53I’ve occasionally been called cynical because some of the sentiments I express strike people as negative. But cynical, to me, does not strictly mean negative. It means something more along the lines of “faithless” — as in lacking the basic faith humans thrive when believing what they take to be true, rather than expedient, and doing what they think is right rather than narrowly advantageous.
In other words, my primary negative sentiment — that the cynical utilitarian ethos among our educated classes has caused and is likely to cause catastrophic outcomes — stems from a sort of disappointed idealism, not cynicism.
On human nature itself I am anything but cynical. I am convinced the strongest, long-term incentives are always to believe what is true, no matter the cost, and to do what is right. And by “right,” I don’t mean do-gooding bullshit, but things like taking care of one’s health, immediate family and personal responsibilities while pursuing the things one finds most compelling and important.
That aside, I want to touch on two real-world examples of what I take to be actual cynicism. The first is the tendency to invoke principles only when they suit one’s agenda or desired outcome, but not to apply them when they do not. This kind of hypocrisy implies principles are just tools you invoke to gain emotional support for your side and that anyone actually applying them evenhandedly is a naive simpleton who doesn’t know how the game is played.
Twitter threads don’t show up on substack anymore, but I’d encourage you to read this one with respect to objecting to election outcomes. I could have used many others, but this one (probably not even most egregious) illustrates how empty words like “democracy” or “election integrity” are when thrown around by devoted partisans. They don’t actually believe in democracy, only in using the word to evoke the desired emotional response. People who wanted to coerce people to take a Pfizer shot don’t believe in “bodily autonomy.” It’s similarly just a phrase that’s invoked to achieve an end.
The other flavor of cynicism I’ve noticed is less about hypocrisy and more about nihilism:
 I’d encourage people to read the entire thread, but if you’re not on Twitter, it’s essentially about whether money (and apparently anything else) has essential qualities, or whether it is whatever peoples’ narratives tell them it is.
I’d encourage people to read the entire thread, but if you’re not on Twitter, it’s essentially about whether money (and apparently anything else) has essential qualities, or whether it is whatever peoples’ narratives tell them it is.In other words, is money whatever your grocer takes for the groceries, or do particular forms of money have qualities wherein they are more likely to be accepted over the long haul? The argument is yes, gold, for example had qualities that made it a better money (scarcity, durability, e.g.) than say seashells which are reasonably durable but not scarce. You could sell the story of seashells as a money (and some societies not close to the sea used them as such), but ultimately such a society would be vulnerable to massive inflation should one of its inhabitants ever stroll along a shore.
The thread morphed into whether everything is just narrative, or there is an underlying reality to which a narrative must correspond in order for it to be useful and true.
The notion that anything could be money if attached to the right story, or any music is good if it’s marketed properly is deeply cynical. I am not arguing people can’t be convinced to buy bad records — clearly they can — but that no matter how much you market it, it will not stand the test of time unless it is in fact good.
In order to sell something that does not add value, meaning or utility to someone’s life, something you suspect they are likely to regret buying in short order, it’s awfully useful to convince yourself that nothing has inherent meaning or value, that “storytelling is all that matters.”
I am not against marketing per se, and effective storytelling might in fact point someone in the right direction — a good story can help someone discover a truth. But that storytelling is everything, and by implication the extent to which a story has correlates in reality nothing, is the ethos of scammers, the refuge of nihilists who left someone else holding the bag and prefer not to think about it.
-
 @ ee11a5df:b76c4e49
2024-09-11 08:16:37
@ ee11a5df:b76c4e49
2024-09-11 08:16:37Bye-Bye Reply Guy
There is a camp of nostr developers that believe spam filtering needs to be done by relays. Or at the very least by DVMs. I concur. In this way, once you configure what you want to see, it applies to all nostr clients.
But we are not there yet.
In the mean time we have ReplyGuy, and gossip needed some changes to deal with it.
Strategies in Short
- WEB OF TRUST: Only accept events from people you follow, or people they follow - this avoids new people entirely until somebody else that you follow friends them first, which is too restrictive for some people.
- TRUSTED RELAYS: Allow every post from relays that you trust to do good spam filtering.
- REJECT FRESH PUBKEYS: Only accept events from people you have seen before - this allows you to find new people, but you will miss their very first post (their second post must count as someone you have seen before, even if you discarded the first post)
- PATTERN MATCHING: Scan for known spam phrases and words and block those events, either on content or metadata or both or more.
- TIE-IN TO EXTERNAL SYSTEMS: Require a valid NIP-05, or other nostr event binding their identity to some external identity
- PROOF OF WORK: Require a minimum proof-of-work
All of these strategies are useful, but they have to be combined properly.
filter.rhai
Gossip loads a file called "filter.rhai" in your gossip directory if it exists. It must be a Rhai language script that meets certain requirements (see the example in the gossip source code directory). Then it applies it to filter spam.
This spam filtering code is being updated currently. It is not even on unstable yet, but it will be there probably tomorrow sometime. Then to master. Eventually to a release.
Here is an example using all of the techniques listed above:
```rhai // This is a sample spam filtering script for the gossip nostr // client. The language is called Rhai, details are at: // https://rhai.rs/book/ // // For gossip to find your spam filtering script, put it in // your gossip profile directory. See // https://docs.rs/dirs/latest/dirs/fn.data_dir.html // to find the base directory. A subdirectory "gossip" is your // gossip data directory which for most people is their profile // directory too. (Note: if you use a GOSSIP_PROFILE, you'll // need to put it one directory deeper into that profile // directory). // // This filter is used to filter out and refuse to process // incoming events as they flow in from relays, and also to // filter which events get/ displayed in certain circumstances. // It is only run on feed-displayable event kinds, and only by // authors you are not following. In case of error, nothing is // filtered. // // You must define a function called 'filter' which returns one // of these constant values: // DENY (the event is filtered out) // ALLOW (the event is allowed through) // MUTE (the event is filtered out, and the author is // automatically muted) // // Your script will be provided the following global variables: // 'caller' - a string that is one of "Process", // "Thread", "Inbox" or "Global" indicating // which part of the code is running your // script // 'content' - the event content as a string // 'id' - the event ID, as a hex string // 'kind' - the event kind as an integer // 'muted' - if the author is in your mute list // 'name' - if we have it, the name of the author // (or your petname), else an empty string // 'nip05valid' - whether nip05 is valid for the author, // as a boolean // 'pow' - the Proof of Work on the event // 'pubkey' - the event author public key, as a hex // string // 'seconds_known' - the number of seconds that the author // of the event has been known to gossip // 'spamsafe' - true only if the event came in from a // relay marked as SpamSafe during Process // (even if the global setting for SpamSafe // is off)
fn filter() {
// Show spam on global // (global events are ephemeral; these won't grow the // database) if caller=="Global" { return ALLOW; } // Block ReplyGuy if name.contains("ReplyGuy") || name.contains("ReplyGal") { return DENY; } // Block known DM spam // (giftwraps are unwrapped before the content is passed to // this script) if content.to_lower().contains( "Mr. Gift and Mrs. Wrap under the tree, KISSING!" ) { return DENY; } // Reject events from new pubkeys, unless they have a high // PoW or we somehow already have a nip05valid for them // // If this turns out to be a legit person, we will start // hearing their events 2 seconds from now, so we will // only miss their very first event. if seconds_known <= 2 && pow < 25 && !nip05valid { return DENY; } // Mute offensive people if content.to_lower().contains(" kike") || content.to_lower().contains("kike ") || content.to_lower().contains(" nigger") || content.to_lower().contains("nigger ") { return MUTE; } // Reject events from muted people // // Gossip already does this internally, and since we are // not Process, this is rather redundant. But this works // as an example. if muted { return DENY; } // Accept if the PoW is large enough if pow >= 25 { return ALLOW; } // Accept if their NIP-05 is valid if nip05valid { return ALLOW; } // Accept if the event came through a spamsafe relay if spamsafe { return ALLOW; } // Reject the rest DENY} ```
-
 @ bf95e1a4:ebdcc848
2024-09-11 06:31:05
@ bf95e1a4:ebdcc848
2024-09-11 06:31:05This is the lightly-edited AI generated transcript of Bitcoin Infinity Show #125. The transcription isn't perfect, but it's usually pretty good!
If you'd like to support us, send us a zap or check out the Bitcoin Infinity Store for our books and other merchandise! https://bitcoininfinitystore.com/
Intro
Luke: Paolo, Mathias, welcome to the Bitcoin Infinity Show. Thank you for joining us.
Paolo: Thank you for having us.
Knut: Yeah, good to have you here, guys. We're going to talk a bit about Keet and Holepunch and a little bit about Tether today, aren't we?
Luke: Sounds like that's the plan. So thank you again, both for joining us.
Introducing Paolo and Mathias
Luke: would you both mind giving a quick introduction on yourselves just so our listeners have the background on you
Paolo: Sure, I'm Paolo Arduino, I'm the CEO at Tether. I started my career as a developer, I pivoted towards more, strategy and execution for, Tether and Bitfinex. And, co founded with Matthias, Holepunch, that is, building very, crazy and awesome technology, that is gonna be disrupting the way people communicate.
Luke: And, Mathias, over to you.
Mathias: Yeah, thank you. Yeah, I've been, so I come from a peer-to-peer background. I've been working with peer-to-peer technology. The last, I always say five, but it's probably more like 10 years. I did a lot of work on BitTorrent and I did a lot of work on JavaScript. and a little bit later to, Bitcoin and I saw a lot of potential on how we can use Bitcoin with pureology and like how we can use.
P2P technology to bring the same mission that Bitcoin has, but to all kinds of data, setting all data free and, making everything private per default and self sovereignty and that kind of thing. I'm very into that. and I've been lucky to work with, like I said, with Paolo for, many years now and, Get a lot of, valuable, feedback and, idea sharing out of that.
And we're on a mission to, build some, really cool things. In addition to all the things we've already been building. So it's super exciting and glad to be here.
Luke: Oh, fantastic.
Introduction to Holepunch
Luke: Matthias, that was a perfect segue into basically, an introduction to, can you tell us about, Holepunch.
What is Holepunch and what are you doing?
Mathias: Yeah, sure. like I said, we co founded the company a couple of years ago. Now, we've been building up a team of really talented peer to peer engineers. we're always hiring also. So if anybody's listening and want to join our mission, please, apply. we have some really smart people working with us.
but we teamed up to basically. like I said in my introduction, I've been working on peer to peer technology for many years now and thinking ahead how we can, stop using all that technology when I started it was only used for basically piracy. I'm from the Nordics, and I think Knut is from the Nordics also, so he knows all about, the Nordics know about piracy.
It wasn't back in the day. A lot of very interesting technologies came out of that. But basically, how can we use those ideas that were proven by piracy back then to be really unstoppable, because a lot of people wanted to stop it, but apply that same kind of mindset to the general data, so we can build actual applications that has that kind of quality, that can withstand the wrath of God.
that can work without any centralization. Actually, nobody can shut down, not even the authorities if they wanted to. Basically unkillable and make that general enough that it can basically run any kind of application, solve a lot of really hot problems. it works on your own computers, your own networks.
Mobile phones, and tie that up. I'm a developer by heart, into a software stack that people can just build on. So not everybody has to go in and tackle all these problems individually, but just give them some software to solve all this so they can, as much as possible, just worry about making really cool applications that we use,
Yeah, like I said, we've been working really intensely on this, for a long time and in Holepunch, we made this our co mission to scale this up and, deliver a software stack on that. it's been really exciting and it's been really fun and it's been very, challenging, but if it's not challenging, then why, do it?
and, especially, with the backing of, Tether, through Paolo and also just expertise from there, we have a good hand built to deliver this to the world. And, the first thing we did was, like, think about what's, a good first application that we can build that can showcase this, but also something we really want to use ourself and see scale have also have on the world.
And obviously that was a communications app, keyed, which we was our first project. And, we're still in beta and we're still lots of work to do. And we're still iterating that really heavily, but I like to show that you can build these kind of apps without any kind of. central points. and we released that also, like the first thing we released when we launched the company.
And like I said, we're still, building and still iterating it. A lot of fun. and then take the software stack from that, which we call the pair runtime and then split that out. So anybody else can build similar apps on top. With that same technology stack, and, yeah, that's, we launched that earlier this year also, and, it's been really exciting so far, and it's, I love going to work every day and solve, even though, you can see on my hair that it's not really good for, the head scratching, but, but, it's really fun, and it's really challenging, and it's interesting thing. goal as a company, basically to have that if we go out of business tomorrow, our technology continues to exist because we're not in the loop of anything. It's also sometimes really hard to explain that we don't have any, chip coins involved or any kind of limitations on the stack because we're basically engineering it not to be part of it, because that's the only way you can actually engineer these things that they can understand.
anything, super exciting and, encourage everybody to try to check it out.
Luke: we've both used Keet and I've certainly enjoyed the experience. I, think, the, basics of this, as I understand it, is that it's, entirely on both sides. The communicators end, or a group of communicators, it's all on their end, and the communication is entirely peer to peer, what is Keet really, what is the basics of Keet as, say, a product?
What is the easiest way that you would explain what it is?
The Vision Behind Keet
Mathias: But We're basically trying to just build a world class communications app that works to a large degree, like normal communication apps that you know, like Signal, Telegram, WhatsApp. Just with all the centralization tucked away, with all the costs of running it tucked away, and then adding all the features that also we can, because we're peer to peer
People don't care about technology. We loved it, but don't have that surface off too much to the user.
Just have the user use it as any other app, but then just have it be 100 percent private per default, 100 percent like no strings attached. It just works. if we get caught off by a. From the internet tomorrow, it will still work, that kind of thing, but deliver that in a way, and this is always our mission where users don't really need to worry about it.
It just works. And, it works the same way to a large degree as their other apps work, except obviously, there's no phone numbers and things like that. Very cryptographically sound and, but trying always not to bubble it up. And I think that's, so it's actually a really simple mission, but it's obviously really hard.
And that requires a lot of smart people, but luckily our users in a good way, don't need to be very smart about that.
Keet vs Nostr
Knut: Yeah, a quick one there. No strings attached starts with the letters Nostr, so is, Keet and Nostr, do they go mix well together or, is there an integration there between the two? I see a lot of similarities here.
Paolo: I tried to explain the differences between Kit and Nostr. I think Nostr is a very interesting protocol, but also is very, simple. the way I like to describe it is that, if you are familiar with the history of filesharing, Starting from the first one, super centralized, and then eventually every single step, you get to a decentralized platform.
And the last one, the most decentralized one, that is BitTorrent. the history of file sharing proved that every time you try to centralize something, it ends up badly, right? if you have any special node in the system that does a little bit more than others and requires more resources than others to run, that will end up badly.
You might end up in a small room with a lamp in your room. Point it to your face, and then everyone suddenly will stop running an indexer. That reminds me about Nostr structure. if you are building a peer to peer system, or if you are building a very resilient communication system, if you think about Nostr, you would imagine that if you have, 10 million or 100 million users, the number of relays would be probably less than the square root of the number of users.
So that surface, although a hundred million users is very, they're not attackable, right? But the surface of, the relays is much more attackable. look at what is happening with, the coin joinin platforms, right? very similar. the beauty of KIT versus Nostr is that in KIT you have number of relays is actually equal to the number of users because the users are their own relays.
and they can act as relays for others to, further their connectivity. That is how we think a technology that, has to be ready for the apocalypse and resilient to the wrath of God should, work. if you have, a log number of users or square root of number of users as relates, I don't think it's cool technology.
It will work better than centralized, Technologies like WhatsApp and so on, or Twitter, but eventually will not work when you will need it the most. Because the point is that we will not know what will happen when we will need this technology the most. Today, not for everyone, but the world is still almost at peace.
Things might unfold, in the future, maybe sooner rather than later. But when things unfold, you will need the best technology, the one that is truly independent, the one that is truly peer to peer. it's not really peer to peer if you have specialized relays, but where you have super peers randomly.
Luke: Yeah, the difference here, between the Realize and not having any other centralized infrastructure in the picture is certainly an interesting distinction. I hadn't heard anything about that you can act as a next connector or something like that.
Pear Runtime
Luke: So there's a couple of related things. I know there was an announcement about the, pair runtime, is that right? can you talk a little bit about that or any other, ways that this is growing in your whole, platform,
Mathias: Yeah, sure. so basically when we talk about ideas, internally, also from our software background, We want to solve a small problem that then can solve it for everybody. So
We want to build technology that can just send data around efficiently, so you can build any kind of app on top. We're all about modularity and taking these things to the extreme so we can repurpose it into any kind of application and other people can, get value out of it.
And, that's been our mission from the get go. So basically, like Paolo said, when we built Keed. We took all of these primitives we have, it's all open source on our GitHub, that can do various things, relay encrypted data in a way that's completely private, nobody can read it, and in a generalizable way, so it can run on any applications.
We have databases that can interpret, work with this data on device, but still in a way where nobody else knows what's going on, fully private, and we spent many years perfecting this, and it's still ongoing. And we, similar to like connectivity, it might seem really easy if you don't know what's going on that, connecting this computer to another computer and another place, but it's really hard because ISPs and, your internet providers, et cetera, they don't really want you to do that.
So there's a lot of firewalls involved that you have to work around to get around This is all really, hard problems that took a long time to solve.
But luckily, all of these are like generalizable problems where you just solve them once to a large degree, and then it's solved for everybody. If you put them in a modular framework where anybody can put the Legos together on top. And that's what we've been heavily invested in. And then as we were building Keed, we realized that Keete is just like 95 percent of these Lego blocks that are applicable for anything.
So why not take all this stuff, pack it up for free, we don't make any money on it. and an open source runtime that we're just giving away so other people can contribute to it, but also build their own apps. the more peer to peer apps the world has, the better from my point of view.
and document it and make it really easy to install. And I think actually Paolo said something interesting because as soon as you have, one point of centralization, you can always unravel it. coming from the Bitcoin days, I remember how quickly things can unravel. people went to jail for linking to things because authorities, when they crack down, really hard.
so if you have one weak spot, it will be taken advantage of at some point by somebody. And so even things like distributing updates to your software can be really hard because this often requires a central point, like you go to a website and you don't download it. And so all apps built on our runtime, for example.
It's distributed through the runtime, which is a little bit mind bending. So all apps are peer to peer data applications themselves, and the network doesn't care, which means that we can continue to distribute updates even, if everything gets shut down, you only need like a bootstrap for the first install when you get the app.
So we're thinking that in. At every level, because it's really, important to us to, basically learn from everything that happened in the past and then actually build things that are resilient. And we take this to a degree where I'm sure we could move 10 times faster if we just let go a little bit of that idea, because it is easier to just put all the data in one place or put all the updates in one place.
But then it's then we're just building the same old thing that's going to die eventually anyway. So we're very, uncompromising in that mission of actually decentralizing everything from updates to data, and then also always solving in a way where everybody can take advantage of that.
And then the final thing I'll say about that is that, every time we update. That runtime, those building blocks of that runtime, every time we fix a bug, every time we make it faster, every app becomes faster. That's also very exciting. It's because you're building the whole infrastructure into this layer that runs on your phone.
And it's all somewhat generalizable. Every time we fix something, it's just better for the entire ecosystem. And that's obviously really, exciting. And like I said, actually, no strings attached.
Yeah, so I think you were referring to the trial of the Pirate Bay people there In Sweden, right? lucky enough to meet a couple of them in Denmark and it's been very fun to hear about their journey and, yeah, like
Knut: and there, there's, there was a great documentary made about it called TPBAFK. So the Pirate Bay Away From Keyboard, about that whole trial and how, corrupt the system was even back then. And, throwing people in jail for providing links. they didn't do any more wrong than Google did, from a certain perspective.
And, I remember even, before BitTorrents, there was a program called. DC or Direct Connect Do you remember that?
Mathias: I used to, it was one of my first introductions to decentralization. it as you just shared your, like a Google Drive for everyone or something. Like you just shared parts of your file tree to everyone who wanted to peek into it, Yeah, anyway. Oh, that's good that you didn't know you were going with that. it interesting what you said, because I think it's interesting to think that I think to a large degree, the whole decentralization movement that was happening with BitTorrent back in the day got shut down because At some point, authorities figured out that they could just block DNS requests to shut it down for normal people, and as soon as they did that, it was actually effective.
And to Paolo's point, no matter how weak it is, they're done. and they tried to kill the technology elsewhere, but that's actually what killed them. Then, obviously, alternatives came that people could pay for, and it also shows that people actually want, to stay on the right side of things.
I think, now it's going very much in the wrong direction again, because now we're back at abusing that centralization again. the cycle will repeat. But, yeah, like any point of weakness will be attacked at any point.
Decentralization vs. Centralization
Luke: So what are the drawbacks to decentralization? I think we and our audience certainly understand the benefit of decentralization, what you gain by decentralizing, but what do you naturally give up in terms of the user experience and the convenience factor?
Mathias: yeah, I'm sure Paola has stuff to say here, but I'm just, I love talking about this stuff, so I'll go first. Mattias.
I think it's a really interesting question, first of all, because it's one of those questions where You know, obviously I want to say there's no drawbacks, but like anything, it's a balance, right?
Because it's not that there's drawbacks and advantages, there obviously is, but it's also just a different paradigm. first of all, with sensitization, I think one of the biggest thing I noticed also with developers is that we all come out of systems, education systems. That teaches how to think centralized, which makes us biased towards centralized solutions.
and that's, I remember my whole curriculum was about servers and clients and stuff like that. it's actually really hard to think about decentralization as a developer. And I think that's actually part of why a lot of people think it's hard. It's complex because it is complex, but also because we're just like, we've been trained massively in the other direction, and it's really hard to go back because decentralization can be as simple as what Knut said about DC Connect, DC where it's just, oh, I'm just browsing other people's computers.
That's amazing. That's a really, simple experience, and it's like something you can never do But like in today's world, people, the first thing I always get asked is like, how do I get a username? And I'm like, usernames have an inherent centralization and there's trade offs there.
And we need to think that through and stuff. and most applications don't necessarily require usernames. I'm not saying that's a bad feature, but it's that's where you need to think more about the trade offs because there's governance involved to some degree. But for the core experience, and I think that's what we've shown in Keith so far.
Then, there's obviously tons of upsides also, it's much easier to do big data transfers. Money is less of a concern, which actually changes the thinking, how you think about features.
And that, again, is something we've been trained in a lot as developers, because we think centralized. When we talk about features at Holepunch, hey, we should add podcast recording to Keed. Normally somebody would say, that's going to cost a lot of money to host that data. And we just always we don't even have that discussion because it doesn't matter because it's just between the users.
And then it's more about like the UX. But then other simple, like I said, other simple discussions, let's add a username index. That's where we're like, okay, let's think that through because there's like various things to think about there because there's no centric governance, and we don't want to introduce that because again, one point is.
It's bad. so it's, more like you really need to think differently and it's really hard to wire your brain to think differently. but once you get past that point, I think it's, super interesting. And I, think actually developers care way more than normal people because, developers care a lot about how links look and links and structure and that.
And normal people are just used to just clicking buttons and apps and going with the flow on that. And that's also what we're seeing, I think, with, a lot of key
Paolo: I think the hiring has proven a little bit more challenging, as Matthias was saying, when you are told that the cloud is your friend, hosting, on, Google Cloud or AWS is the right thing to do. And, of course, it got cheaper and cheaper, so now everyone can host their websites.
But the reality is that 70 percent of, the entire internet knowledge is hosted in the data centers of three companies. developers should think about that, should think about the fact that internet was born to be point to point and peer to peer. And, we are very far away from that initial concept.
over the years, especially with the boom in, in the year 2000 for the internet boom, and bubble, then, realized that, holding people's data is the way to go, with social media and social network. That is even worse. And so you have these friendly advertisements that are telling you, That, with a smiley face that, you know, yeah, you should, upload all your data on, Apple cloud or Google cloud.
And in general, cloud backups are great, right? You want to have some sort of redundancy in your life, but the reality is that you should be able to upload those. In an encrypted way, and yet most of this data sits unencrypted because, the big tech companies have to decrypt it and use it for, to milk the information to pay for, for, another month of their new data centers.
the, issue is, we have so much power in our hands through our phones. the phones that we have today are much more powerful than the phones that we, or even the computers that we have 10 years ago or 5 years ago. And so We should, we are at a stage where we can use this hardware, not only for communicating, but also for in the future for AI processing and inference and so on.
is, we need to, understand that the word cannot be connected to Google. I mean we cannot be a function of Google. We cannot be a function of AWS. And so I think that, there is, escalating pace of, towards centralization and it's almost a black hole.
And eventually, the, we'll attract all the lights and if we are too close to it, no lights will come out anymore. And, that's why we want to really to double down on this technology, because it's not going to be easy, right? It's going to be very challenging, and most of the people don't care, as Maite has said before.
Most of the people will think, everything works with WhatsApp and, Signal, but Signal announced that their 2023 costs for data centers and data center costs are around 50 million, and they, apart from the mobile coin that was not The best thing that they could do, there is, it's not easy for them to monetize.
And the problem is that if you are, you're basically almost the only way to monetize it is to sell your customer's data. So if you don't want to sell your customer data, eventually your service will not be sustainable. So the only way to make it sustainable is actually going back to peer, where you can leverage people, infrastructure, people, connectivity, people, phones, people, processing power, Deliver very high quality communication system.
And when they will care, it will be probably usually too late if nothing exists yet. when people will care is because shit is hitting the fan. And, you really want to have a solution that is not, that will survive if, the countries around you or around the country where you live are not going to be nice to your own country.
So that's the view to peer-to-peer. The peer-to-peer wheel system will keep working if your neighbor countries are not going to be nice towards you. That's independence, that's resiliency, those are terms that, we need to take very seriously, especially seeing where the, world is going to.
Knut: Yeah, I think we're all primed for, centralized solutions, from a very young age. this is the state, this is what it is like, state funded schooling. state funders or state subsidized media. We are, like brainwashed into, trusting, institutions all our lives.
So I think that is somewhat connected to why people are so reluctant to be vigilant about this on the internet. I think the two go hand in hand that we, take the comfortable way, or most people take the comfortable route of, not taking responsibility for their own stuff. not only on the internet, but outsourcing responsibility to the government is basically the, another side of the same coin, right?
Mathias: I also find it very interesting, especially being from a small country like Denmark that doesn't have a lot of homegrown infrastructure. And I'm just seeing how much communication with some of the public entities is happening through centralized platforms like Facebook and things like that, where even though we centralize it, we also centralize it in companies that we don't even have any control over in different countries where we probably have, no rights at all.
So it's like hyper centralization, especially from the weakest point of view. And I think that's super problematic. And I'm always. Thinking it's, weird that we're not talking about that more especially when you look at the things that they're trying to do in the EU, they're almost trying to just push more in that direction, which I find even more interesting.
yeah, definitely. it's, a huge problem and it's only getting bigger. And that's, why
Challenges and Future of Decentralization
Luke: So to what level can decentralization actually get there? What is the limit to decentralization? And I'll calibrate this with an example. The internet itself, you said it was built to essentially originally be decentralized, but we don't have it. For physical links, like individual physical links between each other, the fiber or whatever the wire is goes together into another group of wires, which eventually go into some backbone, which is operated by a company.
And then that goes into the global Internet. And so somewhere it centralizes into telecom companies and other services. It might be decentralized on one level, but there is a layer of centralized services that make the internet work that isn't necessarily the so called cloud providers and that sort of thing.
So is there a limitation to how far this can go?
Paolo: I think the, in general, sure, there are the ISPs and, their physical infrastructure is in part centralized, but also you start having redundancy, right? So for example, the backbones are redundant. There are multiple companies running, cross connects across different areas of the world.
Now you have Starlink if you want. that is a great way to start decentralizing connectivity because Starlink will not be the only one that will run satellites, so there will be multiple companies that will allow you to connect through satellites, plus you have normal cabling.
So you will have, it will become a huge mesh network, it's already in part, but it will become more and more a huge mesh network. in general, you will always find a way, even with a pigeon, to start sending bits out of your house.
I think the most important part is, you have to be in control of your own data, and then, you need to send this data with the shortest path to the people that you want to talk to. Right now, I usually make this example, because I think it's When we do this presentation, we try to make people think about how much waste also centralized systems have created.
imagine you live in Rome, you live in Rome and you have your family. Most people live nearby their families. That is a classic thing among humans. 90 percent of the people live nearby their families. Maybe nearby, like 10km, 50km nearby. If you talk to your family, every single message, every single photo that you will send to your family, that message will travel, instead of going 50 kilometers in a nearby town where your mother lives or your father lives, it will travel every single message, every single bit of every single video call or every single bit of every photo will travel 5, 000 miles to Frankfurt just to go back 50 kilometers from you.
Imagine how much government spent in order to create these internet lines and to empower them to make it bigger, more, with more capacity Peer to peer allows with a lower latency, allows to save on bandwidth, allows to save on cost of global infrastructure.
So that's how, actually, We can create better mesh networks, more resilient mesh networks, just because data will always find the shortest path from one point to another.
And still all roads lead to Rome. I'm Italian, so I need to use Rome as an example.
Knut: Yeah.
Mathias: I think the discussion here is really interesting compared to Bitcoin, because it's actually the scaling longer term. Sovereignty, like how, Bitcoin kind of told us very direct terms that if you have a key pair, you have your money.
And it doesn't matter where you are in the world. If you have that key pair, you have a way to get to that money. the means of transportation, it's actually very uninteresting in that sense, because you have it with you. The Internet today, the centralized Internet is designed in a way where, what does it mean to go to Facebook?
it's really hard to explain because it's like some certificate that issued by somebody, and there's. Some, cabal of companies that manages them, there's some regulations around it, but we don't really actually understand it that well as normal people. Technically, we can understand it, but it's very, centralized and it's very, opaque and it's built into the infrastructure in that way, in a bad way.
And, with Pure Technology, we're taking the same approach as Bitcoin here and saying, You're just a key pair, and the other person is just a key pair, and there's a bunch of protocols around that, but the transportation is actually not that interesting. Right now, we use the internet to do it.
We'll probably do that for a long time, but there's no reason why we can take the same technology we have right now and in 50 years run it on, laser beams or something else, because we're taking the software and feedback.
Bitcoin and Holepunch: Drawing Parallels
Mathias: I think, that's the main thing to think about in that. Discussion.
Luke: when, Paolo, when you were talking about that people don't care, when you were saying that people don't care because WhatsApp just works, I was at the same time thinking that's the parallel of people saying that, I don't care because Visa just works, right? And so the parallel between Bitcoin and what you're doing at Holepunch, Keet, everything else here, really seems to be tracking along the same line.
And I guess there's the connection that, I won't say all, but a lot of the people involved are already in the Bitcoin ecosystem. But can you comment on is there a little more of a connection there between Holepunch and Keet and Bitcoin?
Paolo: Yeah, Bitcoin definitely is working and servicing, I think, in a good way, many, people in communities. The users of Bitcoin today are, unfortunately, and also that relates to Tether, mostly, in the Western world, in the richer countries, as a way to save wealth and, as a store of value, more than a means of exchange.
For different reasons, right? We'd like a network that would improve, of course, over time, and there will be different approaches, but, still, the world is not yet using Bitcoin, but the world will use Bitcoin when shit will hit the fan. but the beauty of Bitcoin is that an option is already there, is available, and when something bad will happen, people immediately, with a snap of a finger, will turn to Bitcoin, and will have it and can use it. don't have that in communications. What is our communica our parallel with communications, if we don't have it? I don't know, because if, if suddenly centralized communications will, be blocked, then, or privacy in communications will be blocked, and you cannot, you cannot use Whatsapp, or Whatsapp has to start giving all the information to every single government.
and the government will become more evil than what they are today, also western governments then. don't, we wanted to build the exact parallel as we said it, we just tried to describe it, that with Bitcoin, for communications. We need to have something that, since there are so many alternatives that are working as with your, you can make the parallel with Visa, right?
Visa is working today, so people are still using a lot of Visa, but if something will happen, they will use Bitcoin from one day to another. Whatsapp is working, and Zoom is working, and Google Meet is working, so people don't feel the urge, but there will be a trigger point when people will feel the urge at some point in their lives, because something happened around them, and we need to make sure that kit will be available to them.
and will be an option, will be stable, will be well designed so that when they will need it the most that option will be available to them.
Luke: Yeah, fantastic.
The Future of Decentralized Communication
Luke: And so I think the follow up I have, and just to get back to the earlier discussion a little bit with Nostr, the communication in terms of messaging, I absolutely see that and directly in what Keet is, I already absolutely see that. Is there a goal to get somewhere towards more like Social media, social networking, things like that in a, in certainly a decentralized way, but right now there isn't something like that as I understand it, coming from, Keet.
So is, that a goal? Is that on the roadmap?
Paolo: Yeah, it is on the roadmap, it's something that, so we had to start with the thing that we thought was more urgent and also the thing that could have been, would have been a game changer. social media is very important, especially In difficult situation, you want to get news, and you want to get unbiased news, so you want to use, social networks to see what's happening in the world.
But we, think that the most sacrosanct thing that you need in your life is to be able to talk to your family and friends in any situation with the highest privacy possible. that's the first thing that we tackled, and also was a way to battle test the technology with, KIT you can do high quality video calls as well, so if we are able to tackle in the best way possible privacy and extreme scalability of peer to peer communications, then on top of that foundation we can build also social media and every single other application that we have in mind.
Mathias: But first, we wanted to tackle the hardest problem. No, I think it makes a lot of sense. And I also just want to say, as a, probably like one of the most prolific KEET users, I use KEET right now also as a very, like a social media, we have big public rooms where we talk about KEET and talk about technology. I get a lot of the value I would get otherwise on Twitter X from that because I, it's like a public platform for me to, get ideas out there, but also interact with users directly.
And I think, there's many ways to take them as a young app. And we're talking about this a lot, obviously it has to be simple, has to be parent approved. My parents can figure it out, but I think, to a large degree, all really healthy social networks that are actually, to some degree, a communication app.
And it's also just a really good way to get local news and to get this locality that Peter is good at. That doesn't mean that we might not also make other things, but I think it's a hard line to set the difference between a social network and a communications app when it's structured correctly,
Interoperability and User Experience
Luke: Yeah, and this, another thing that came to mind just as, you were talking about these parallels, as, I understand it, the account system with Keet is, essentially still just a, Key pair. Correct me if I'm, wrong,
Mathias: Very, true.
Luke: you backups with the same 1224 words.
Is, that fully interoperable as well? Is that, could be your Bitcoin key. That could be
Mathias: We use the, same, I can't remember the date, the BIP, but there's a BIP for like during key generation. So we can use it also in the future for other things. and you have those words, you have your account, and that's, we never store that. And that's like your sovereignty and, no, I was just going to say that lets you use it seamlessly on different devices also. It's one of those things that I love because I know what's going on when you use keyed Insanely hard problem, but it's solved by the runtime, and it just works seamlessly and I think that's, the beauty of it.
Paolo: I think there's some UX stuff to figure out about onboarding that stuff a little bit easier for normal people. That's probably to a large degree the same for Bitcoin. The other part that I would do with Bitcoin is that, with Bitcoin, with your 12, 24 words, you can access your private wealth. the beauty of Bitcoin is that you can remember 12 24 words, you cross borders, and you carry with you your wealth. You can do the same thing with your digital private life.
You remember 12 24 words, they could be the same by the way. whatever happens, you can spawn back your digital private life fully encrypted from, one of your other devices that you connected that is somewhere else in the world. So when you start seeing and understanding the unlock in terms of also human resilience that this creates is very, insane and can create a very powerful, that can be used for, to create a very, powerful applications, not just communications, but you can build.
Really any sort of interaction, even mapping. Imagine peer to peer mapping, where basically data is not stored in one single location. You can access, tiles of the maps, from, local people that curate them in a better way. So the, level of applications that you can build, All unlocked by the same technology that is being used by Bitcoin is very, incredible.
Luke: Yes, absolutely it is. And what do you think of the idea that all of this stuff is just interoperable now based on essentially you have your private key and there you go. It doesn't matter the technology stack. Is that sort of an agnostic thing where you can take your data to any one of these systems?
What you're building with Keith being one, Nostr being another, Bitcoin being a third, what do you think of that?
Paolo: Yeah, the fact that, data is yours, right? So you should do whatever you want with your data. That is, I think, an axiom that we should assume. And, it shouldn't even, we shouldn't even discuss about this, right? We are discussing about it because people are trying to take away this axiom from us.
The, you are a key pair, and you're basically, unique, and uniqueness is expressed by the cryptography around those 24 words, and that's, that also is a way to prove your identity, it's a mathematical way to prove your identity.
No one can steal that from you, of course, but no one can track it as no one can impersonate, should not be able to impersonate you. So it's truly powerful.
Mathias: also think it's like worth remembering here also in this discussion that a lot of very high valuable data for yourself is actually not that big, but centralized platforms take it hostage anyway. if you take all my chat history and, I have pictures, but like a couple of the pictures would probably be bigger than all my chat history ever.
but a lot of that, those messages have a lot of value for me, especially personally and also being able to search through it and have infinite history, it's very valuable for me personally. But it's very scary for me if that's on some other platform where it gets leaked at some point, et cetera, et cetera.
But we already have the devices, just normal consumer devices that we buy, that we all have, phones, computers, whatever, that have more than enough capacity to store multiple copies of this. In terms of like per user, data production, it's a manageable problem.
And I think it's interesting how, providers force us to think in terms of giving that data away, even though we could easily store it.
Paolo: And this is even more important when we think about potential, AI applications, right? So imagine your best assistant. Paolo's assistant should go through all my emails, my kids chats, my old social stuff, and be able to be my best assistant. But in order to do that, I have two options.
Either, I imagine that OpenAI would come with an assistant. They would upload, All the information on their servers, crunch that information, and then, use it to serve, me, but also service their own needs. And that can become very scary, also because they wear a hat. It's public, right?
you don't want your most intimate codes that your best personal assistant could know, to be on somewhere else, rather than your devices. And so people were, people never uploaded, at least most of the people would never upload medical, information on Facebook, right? But they are uploading it on ChatGPT to get a second opinion.
so things can be, get even scarier than what we described today because, we, discussed about social media, that is basically, the fun part where we upload photos, But, things can become scarier when it comes to privacy and data control with ai.
So I want to see a future where I have a local AI that can read all key messages that I have from my local phone on my local device, and can become the best powers assistant possible without renouncing to my privacy, and also still governed by the same 24 words. the fine tuning that is applied on that LLM should stay local to my own device, and it should be in control of that.
And still, the current power of the devices that we have makes it possible. We should not fall for the same lie. We don't need, of course, big data centers with GPUs are important for training a huge LLM, but that is a generic LLM. You can take that one and then fine tune it with your own data and run it by yourself.
And for most of it, unless you want to do crazy things, that is more than enough and can run on modern GPUs or local GPUs or your phones. We should start thinking that we can build local experiences without having an API all the time connected to someone else's data center.
Knut: Yeah.
The Role of Tether in the Crypto Ecosystem
Knut: It's super interesting. you briefly just briefly mentioned tether before and I think we need to get into this. what is it and how much of a maxi are you, Paolo?
And, what, made this thing happen? Can you give us the story here about Tether?
Tether's Origin and Evolution
Paolo: Tether started in 2014. I consider myself a maxi, but running Tether, you could say that, I'm a shit coiner. I don't mind, right? I like what I do, and I think I'm net positive, so it's okay. Tera was born in 2014 with a very simple idea. there were a few crypto exchanges in, 2014.
it was Bitfinex, Coinbase, Kraken, Bitstamp. OKCoin, there was BTCChina, and just a few others, right? Around 10 that were meaningful. The problem back then was to do, trading arbitrage, you sell Bitcoin on the exchange where the price is higher, you take the dollars. From that sale, you move the dollars on the exchange where the price is lower and rinse and repeat.
That is called arbitrage. It is a property of every single efficient financial system. And that also helps to keep the price of Bitcoin in line across different exchanges. But, that was very, hard in 2014. If you remember in 2013 was the first year that Bitcoin broke the 1, 000.
But on some exchanges the price was 1. 2, on others was 900. in order to arbitrage that price difference, you have to move dollars from one exchange to another and Bitcoin from one exchange to another. You can move Bitcoin from one exchange to another. 10 minutes, but dollars would take days, right?
International wires. And so of course the opportunity arbitrage was, fully gone by, the, time the wire was hitting the, receiving exchange. the reason why we created that was, USDT was simply to put the dollar on a blockchain so that we could have the same user experience that we had with bitcoin.
For the first two years, almost no exchange apart Bitfinex understood USDT. Then Poloniex in 2016 started to add the USDT across for against every single trading pair. There was the start of the ICO boom. 2017 was the peak of the ICO boom and, USDT reached 1 billion in market cap. Fast forward in 2020, we had around 10 billion in market cap, and then the bull run started, but also another important thing started, that was the pandemic.
USDT's Impact on Emerging Markets
Paolo: So the pandemic had a huge effect on many economies around the world, in all the economies around the world, but especially in emerging markets, developing countries.
Basically pandemic also killed entire economies. And so as a Bitcoin you would think, oh, all these people that are in countries like Argentina and Venezuela and Turkey and so on, they should use Bitcoin and they should, they should, only use Bitcoin because everything else is cheap.
So that is pretty much, the approach that we have as Bitcoiners that, I believe in. But the problem is that. Not everyone is ready, so not everyone has our time to understand Bitcoin. Not everyone has yet the full skill set to understand Bitcoin at this stage, at this moment in time.
we as Bitcoiners didn't build the best user experience in the world, right? So one of the best wallets for Bitcoin is still Electrum. That, is not necessarily nice and well done for and simple to be used for, a 70 year old lady. so we need to do a better job as Bitcoiners to build better user experiences we want Bitcoin to be more used around the world.
At the same time, 99 percent of the population knows, especially the ones that are living in high inflation areas, knows that there is the dollar that is usually Much better currency than what they hold in their hands. the US dollar is not, definitely not perfect. It's not the perfect fiat currency. but it's like the tale of the two friends running away from the lion, right?
you have, one friend tells to the other, Oh, the lion is gonna kill us. We have to run really fast. And one of the two friends says to the other, I just have to run faster than you, right? So the US dollar is the friend that is running faster, in a sense that is the one that is likely better than the others.
And so being better than the others is creating a sort of safety feeling among 5 billion people in the world that live in high inflation countries. And for those people that, they don't have yet the time, they didn't have the luck also, maybe, to understand Bitcoin, they are, in fact, using USDT.
If you live in Argentina, peso lost 98% against the US dollar in the last five years. The Turkish L lost 80% against the US dollar in, the last five years. So of course, Bitcoin would be better than the US dollar, but even already, if you hold the dollar, you are the king of the hill there, right?
So because it's, you are able to preserve your wealth much, better than almost anyone else in the region. I think, USDT is offering a temporary solution and is providing a service, a very good service to people that don't have alternatives and good alternatives and they are very, familiar with the U.
S. dollar already. so eventually, the hyperbitcoinization, I think it will happen. there is no way it won't happen. It's hard to pinpoint on a time when, that will happen. But it's all about the turning point. What the economy will look like in the next, 10, 20 years and what trigger point there will be for fiat currencies to blow up and become irrelevant.
Bitcoin as a Savings Account
Paolo: the way I see it is that it's likely that the U. S. dollar will stay around for a while, and people might still want to use, the U. S. dollar as a checking account, but they, should start to use, Bitcoin as their savings account, in the checking account, you, are happy to not make interest, It's something that you use for payments, it's something that you are okay to detach from because it's the money that you are ready to spend.
The savings account is the thing that we should fight for. This thing is the thing that matter the most, and, it's the thing that will is protecting people wealth. And so in the long term. And in the medium term, we should push for this savings account to be Bitcoin. also with Tether, we are heavily investing in companies, in Bitcoin companies.
we support the Blockstream. We supported so many in the space that are, we, are supporting RGB. That is a protocol that is building, assets on top of, like network, style channels. Thank you for listening. and we buy Bitcoin ourselves. We do a lot of Bitcoin mining.
We develop, I think, the best and most sophisticated Bitcoin mining software, by the way, based on hole punch technology. It's like IoT for Bitcoiners and Bitcoin mining. It's very cool. we are relying on the dollar and, you could say that USDT is helping the dollar, expansion, but the same way I don't think Dollar and Bitcoin aren't necessarily opposed to one or the other.
I think that Bitcoin has its own path. And no matter what happens, there is no way to slow it down. I think, it's going to be inevitable success. It's going to be inevitable that it will become global internet money and global words money. No country will trust to each other with, with each other currencies for, for a longer time, and so the only viable solution is a currency that is governed by math.
That is the only objective way, objective thing that we have in the universe. that's my train of thoughts on, Tether and Bitcoin.
Knut: Oh, thank you. Thank you for that explanation. It explains a lot of things. To me, it sounds a bit like you're a lubrication company, like selling lubrication for the transition between the rape of the dollar to the love fest of the hyperbitcoinized world, to make the transition a little smoother.
Paolo: we are more than, at Tether we have also this educational arm and, believe it or not, the majority of the creation we do is actually on Bitcoin, right? So we are supporting the Plan B network led by the great Giacomo Zucco. The unfortunate thing is that USDT, didn't have a marketing team up to, 2022 with Tether.
So basically, I wish I could say that success of Tether is because we were super intelligent and great. but actually the success of Tether, unfortunately is a symptom of the success of, of, national economies. And it's sad if you think about it, right? So the success of your main product U as it is, They're actually proportional to the FACAP of many central banks. And, but it is what it is, right? So we need to do what we do at, really, at DataRace, creating all these educational contents to try to explain that, sure, we are providing a tool for today, but, For tomorrow you probably need, you need to understand that you have other options, you need to understand Bitcoin, because as we said for, Keith, right?
So the moment when you will need the most Bitcoin, it has to be available, you need to understand it, so that is a true option for you. The way we, see bitcoin education.
Knut: No, and, something like Tether would have, emerged, either way, and it's very comforting to know that it's run by Bitcoiners and not by a central bank itself or something. yeah, and the Plan B Network, I was a guest lecturer there in Logano and it was fantastic.
I love what you're doing there with the educational hub. And we even got Giacomo to write the foreword to our new book here that you can see here behind Luke.
Luke: Always say the title, Knut. Always say the title.
Knut: Bitcoin, the inverse of Clown World. It's, you, if, you're good at maths and emojis, you might be able to figure out the title from the cover, but it's one divided by Clown World anyway, which is on the opposite side of the everything divided by 21 million equation, So anyway, looking forward to seeing you in Lugano and giving you both a copy of the book, of course.
Paolo: Oh, with pleasure, with great pleasure, with a nice, education.
Luke: Absolutely. Yep.
Plan B Forum and Future Events
Luke: 100%. And we have to wind things down, but I'll just say as well, yeah, absolutely looking forward to Lugano Plan B Forum. Always a highlight of the year. It was my first time last year. I absolutely loved it. can't wait to attend this year.
so it's the 25th, 2020 6th of October, 2024. this year, it's a Bitcoin event that is not made to make money. So the problem with events is that. You have to find sponsors, and usually, sponsor might not be well aligned with the message you want to give, right? I think Tether is lucky enough, to not have to make money on the event.
Paolo: I want to have, good, guests. I want to have great speakers. I want to have the messaging. That is not only about Bitcoin, it's about, freedom of speech as well. We had the family of Assange for the last few years, and I think that they will come also this year.
I'm going to be probably killed by the By our marketing team, I'm not sure if they announced it, but we are going to have another Plan B event also in El Salvador next year, so we're trying to create this network of cities and countries that have things in common and, invite people that want to share knowledge around the world.
And, yeah, and of course we, are very proud of the good food that we, serve in Lugano. So that is another thing that, not all the bands can say the same thing.
Knut: No, it's fantastic. And we happened to bump into the Assange family at the cocktail bar in a fancy hotel and, had a very interesting conversation with them there. So if you're listening. Anyone from the Assange family is welcome on the show any time. So yeah, no looking forward to that event for sure, we had a great time.
And I think we're even playing this year, aren't we, Luke?
Paolo: You're
Luke: yeah, the Satoshi Rakamoto is in the event there, we, played, back in Prague, it was my first, time, but Knut is a regular at the Rakamotos.
Yeah, we played at Lugano last year Oh, anything and everything, what did we do in Prague?
Knut: paranoid and,
Paolo: Can I commission a
Knut: What song would you like to hear?
Paolo: I have two that I would suggest. One is Nothing Else Matters.
Knut: Alright.
Paolo: So I think that, is very inspiring, right?
Knut: Bitcoin, for sure.
Nothing Else Matters. it's perfectly aligned with Bitcoin. And, the other one is Sad But True. Oh, that would be fun. We'll squeeze in some Metallica there, won't we, Luke?
Mathias: we'll 100% have those songs ready to go. We also have, a big peer to peer track at the conference,
Knut: Yeah.
Mathias: not so much music, but yeah, that's peer to
Knut: Nothing else matters.
Luke: looking forward to that.
Knut: Sorry, brain fart. Sad but true is about the dollar still being around,
Paolo: Yeah, you can say that.
Luke: Okay.
Final Thoughts and Closing Remarks
Luke: Hey, we have to wind things down here because, we're, almost, out of time. So I'll just hand this, back to you both. Is there anything else you'd like to, mention about, your plans in the upcoming couple of years, in, key, toll, punch, anything like that?
Mathias: only that we're, like I said, we're integrating really hard right now, and it's a really fun time to, join the company because, we're small and efficient We get to work with Tether, which has a lot of benefits and it's getting really fast, so definitely check that out. And it's also a really fun time to join Keith in our public rooms.
There's a lot of very personal, in a good way, intense chats where you get to be part of the loop. I love to be part of those early communities and I would suggest everybody to check that out and go to the website and try it out.
Paolo: we will certainly do that. Yeah, I couldn't agree more. So go check out Keith and Holepunch and the Plan B forum in Lugano, You could visit tether. io, that is, the website where we are trying to explain what we have in our minds between, finance, bitcoin mining, energy production, AI, communications, brain chips and stuff, right? I think it's more exciting.
Mathias: Just those things, that's all.
Paolo: Yeah, we can piss off more than this. Thanks.
Mathias: a
Luke: No, It's just perfect. and is on that note, is there anywhere else specific you'd like to direct our listeners?
Paolo: just follow the social channels and give us feedback on kit all the time because these technologies, needs everyone's help to be nailed them.
Mathias: We love technical feedback. We love UX feedback. We're trying to make something that works for the masses, so anything is good.
Luke: So that's, all at Keet. Is that correct? For Keet?
Mathias: Key. io and pairs. com for our runtime. It's all peer to peer.
Knut: Alright,
Mathias: Wonderful. And you're also still on the legacy social media platforms, right? Yeah.
Knut: we'll make sure to include links to your handles so people can find you there if they would like. forward to seeing you in Lugano.
Paolo: Likewise, I
Knut: But yeah, worth saying again.
Paolo: Thank you for having an invitation.
Luke: Yes, we'll wrap things up here. This has been the Bitcoin Infinity Show.
-
 @ 8cb60e21:5f2deaea
2024-09-10 21:14:08
@ 8cb60e21:5f2deaea
2024-09-10 21:14:08 -
 @ 655a7cf1:d0510794
2024-09-10 13:16:15
@ 655a7cf1:d0510794
2024-09-10 13:16:15Currently have kyc BTC, huge fan of lightning Network. Because I am a constant user of lightning. Plan on doing my business with lightning as well , peer-to-peer I'm not sure if I'm so worried about kyc I might be misguided in this situation.
originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/679520
-
 @ 09fbf8f3:fa3d60f0
2024-09-10 13:12:15
@ 09fbf8f3:fa3d60f0
2024-09-10 13:12:15由于gmail在中国被防火墙拦截了,无法打开,不想错过邮件通知。
通过自建ntfy接受gmail邮件通知。 怎么自建ntfy,后面再写。
2024年08月13日更新:
修改不通过添加邮件标签来标记已经发送的通知,通过Google Sheets来记录已经发送的通知。
为了不让Google Sheets文档的内容很多,导致文件变大,用脚本自动清理一个星期以前的数据。
准备工具
- Ntfy服务
- Google Script
- Google Sheets
操作步骤
- 在Ntfy后台账号,设置访问令牌。
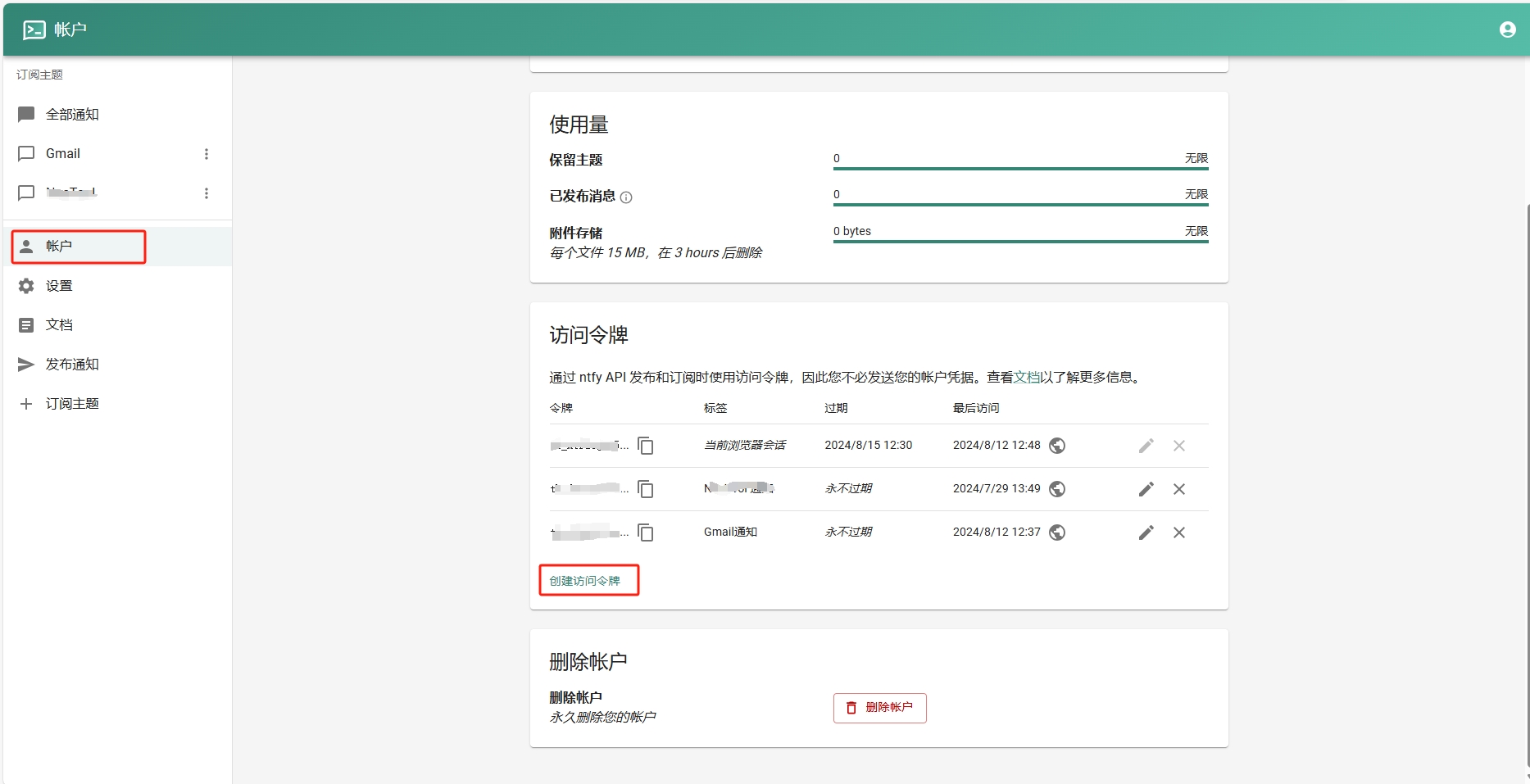
- 添加订阅主题。
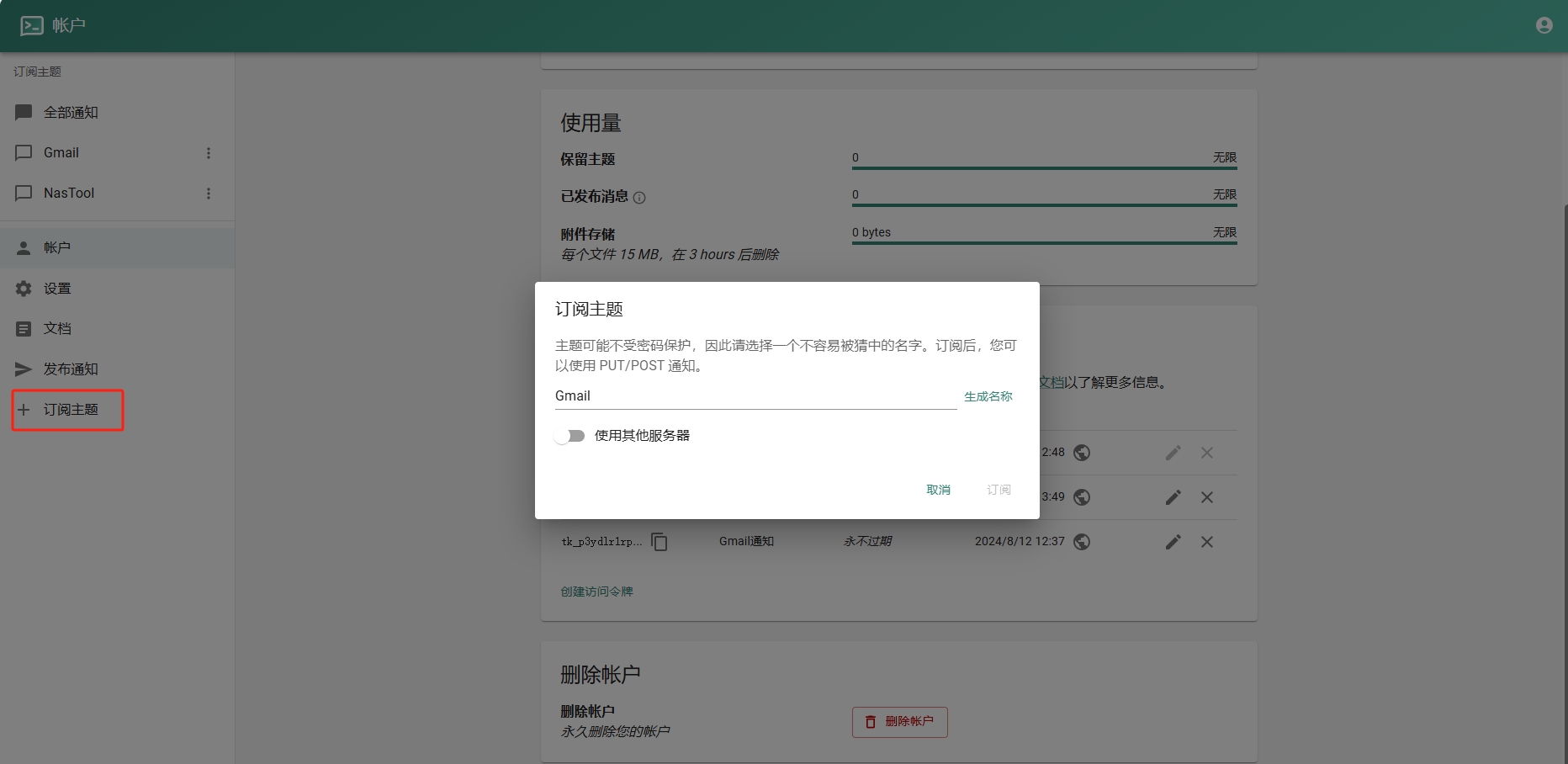
- 进入Google Sheets创建一个表格.记住id,如下图:

- 进入Google Script创建项目。填入以下代码(注意填入之前的ntfy地址和令牌):
```javascript function checkEmail() { var sheetId = "你的Google Sheets id"; // 替换为你的 Google Sheets ID var sheet = SpreadsheetApp.openById(sheetId).getActiveSheet();
// 清理一星期以前的数据 cleanOldData(sheet, 7 * 24 * 60); // 保留7天(即一周)内的数据
var sentEmails = getSentEmails(sheet);
var threads = GmailApp.search('is:unread'); Logger.log("Found threads: " + threads.length);
if (threads.length === 0) return;
threads.forEach(function(thread) { var threadId = thread.getId();
if (!sentEmails.includes(threadId)) { thread.getMessages().forEach(sendNtfyNotification); recordSentEmail(sheet, threadId); }}); }
function sendNtfyNotification(email) { if (!email) { Logger.log("Email object is undefined or null."); return; }
var message = `发件人: ${email.getFrom() || "未知发件人"} 主题: ${email.getSubject() || "无主题"}
内容: ${email.getPlainBody() || "无内容"}`;
var url = "https://你的ntfy地址/Gmail"; var options = { method: "post", payload: message, headers: { Authorization: "Bearer Ntfy的令牌" }, muteHttpExceptions: true };
try { var response = UrlFetchApp.fetch(url, options); Logger.log("Response: " + response.getContentText()); } catch (e) { Logger.log("Error: " + e.message); } }
function getSentEmails(sheet) { var data = sheet.getDataRange().getValues(); return data.map(row => row[0]); // Assuming email IDs are stored in the first column }
function recordSentEmail(sheet, threadId) { sheet.appendRow([threadId, new Date()]); }
function cleanOldData(sheet, minutes) { var now = new Date(); var thresholdDate = new Date(now.getTime() - minutes * 60 * 1000); // 获取X分钟前的时间
var data = sheet.getDataRange().getValues(); var rowsToDelete = [];
data.forEach(function(row, index) { var date = new Date(row[1]); // 假设日期保存在第二列 if (date < thresholdDate) { rowsToDelete.push(index + 1); // 存储要删除的行号 } });
// 逆序删除(从最后一行开始删除,以避免行号改变) rowsToDelete.reverse().forEach(function(row) { sheet.deleteRow(row); }); }
```
5.Google Script是有限制的不能频繁调用,可以设置五分钟调用一次。如图:
结尾
本人不会代码,以上代码都是通过chatgpt生成的。经过多次修改,刚开始会一直发送通知,后面修改后将已发送的通知放到一个“通知”的标签里。后续不会再次发送通知。
如需要发送通知后自动标记已读,可以把代码复制到chatgpt给你写。
-
 @ 6ad3e2a3:c90b7740
2024-09-10 09:26:37
@ 6ad3e2a3:c90b7740
2024-09-10 09:26:37While I love traveling and usually feel enriched by the experience, I dread and detest the process of going to the airport and getting on a plane. It’s not that I’m afraid of flying — though a plane crash would be one of the worst ways to die — but that the airlines and airports have made the experience as inefficient, dehumanizing and cumbersome as possible. While in the short-term these measures might have generated some extra revenue, cut costs or staved off encroachment from competitors, long-term it cannot be good for the service you offer to be so universally reviled. In the interest of improving their product — and the experience of millions of future passengers including me — here are some practical suggestions:
1. Separate passengers from their bags as early as possible.
The single stupidest airline policy is that checking a bag costs extra while carry-ons are free. What that does is incentivize everyone to drag their luggage through the airport and onto the plane. This has several negative consequences:
a) Even though most airlines have assigned seats, everyone lines up 10 or 20 minutes before the start of the already too long boarding process, frantically hoping to secure some scarce overhead space rather than relaxing in the terminal and boarding at their leisure before the door closes.
b) The process of people filing into the narrow plane aisle(s) with their bags and taking time to load them into the overheads stalls the entire boarding process. Not only do people stand in line at the boarding gate, but they stand in line in the jet bridge and again in the aisle(s). Whereas boarding with purses, laptops and other small, under-the-seat items might take 10 minutes or so, getting all the luggage in takes half an hour. If there are 150 people aboard, that’s 3,000 minutes (50 hours) of human life squandered on a useless and stressful activity. Multiply that by thousands of flights per day.
c) The process of deplaning is also slow because everyone has to get their bags out of the overhead. That’s another 15-minute process that should take five.
d) Everyone going through security with all their carry-ons slows down the security line significantly and makes people have to arrive at the airport earlier.
e) Because everyone has their bags, they have to lug them around the terminal while using the restroom, eating or shopping for something to read. Having a 20-pound weight on your shoulder only makes the experience that much more miserable.
The solution to this is for airlines to allow free checked bags and charge for carry-ons with the exception of parents traveling with young children.
To make the process of checking bags more efficient and less cumbersome there should be an immediate drop-off outside the airport. Like curb-side check-in, but automated, a giant conveyor belt of sorts where everyone drops their bag that will be sorted appropriately inside. This drop off area would have security keeping an eye on it, but it would be self-serve and connect at all entry points including curb-side, the parking garage, from the train, etc.
There would be no need for bag tags because people could have an airport-certified chip inserted into their luggage that syncs with the traveler’s boarding pass, i.e., the system reads the chip and directs the bag to the proper gate underground. (Maybe there would be a plastic bin at all the drop-off points you into which you put your bag so luggage of different shapes, sizes and materials could move smoothly and reliably on the conveyor belt to its destination.)
Security details would have to be worked out (maybe you’d have to scan your boarding pass or passport at the bag drop to open it), but as it stands, once you drop your bag off at the curb or the check-in area, it’s essentially the same process now, i.e, it has to be scanned internally before being placed on the plane.
2. Eliminate Security Lines
Going through security would be far easier without all the bags, but to expedite and improve it further, we should make two key changes, neither of which should be beyond our capacity to implement.
a) Instead of a single-file conveyor belt scanned by humans, make the conveyor belt wide enough for everyone to put their laptops, belts, etc. on simultaneously. This could easily be done by providing plastic bins (as they do now), but with individual numbers and keys on them, like you’d find in most locker rooms. You’d grab bin 45, for example, pull the key out, put your things in it, lock it, walk through the metal detector, retrieve your bin on the other side, unlock it, get your things, put the key back in it, and it gets returned for re-use.
Instead of a bored-out-of-his-mind human looking at each bag individually, there would be a large scanner that would look at all the bags simultaneously and flag anything suspicious.
b) Just as there’s no reason to send the bags through the scanner single-file, there’s no reason to send the people through that way, either. Instead, install room-wide metal detectors through which dozens of people could walk simultaneously. Any passengers that set it off would be digitally marked by the detector, directed back out, shed the offending item into a numbered bin and collect it on the other side.
Basically, you’d drop anything big off before you even set foot in the building, and you’d drop everything else into a security bin, walk through without waiting and collect it on the other side.
3. Make sure the gates are clean, have enough seats to accommodate the passengers of even the largest planes that come through, ample charging stations and reliable and free wi-fi.
Because you’re no longer forced to line up and hustle for overhead space, you’ll be spending more time sitting comfortably in the terminal.
4. Have clean, efficient public transportation from the center of each city directly to the airport. (Some cities already have this.) Not a train, a bus and a one-mile walk.
There are smaller things airports could do to make the process even better — and I’ll suggest some below — but these three would at least make it tolerable and humane. It would shave off roughly an hour per trip, spare people the burden of schlepping around with heavy bags, wading through slow-moving security lines (which add stress if you’re in danger of missing your flight), standing in the terminal, waiting in line after line to sit in a cramped and uncomfortable seat for 20-30 minutes before the plane even takes off and remaining stuck in that seat 15 minutes after the plane has made it to the gate while people one by one painstakingly get their bags out of the overhead bins. Moreover, people could get to the airport later without rushing, and if they were early, they could relax in the terminal or get work done.
Here are some other suggestions:
- With fewer people using the overhead bins, rip them out. There would be a few bins at designated spots (just like there are a few emergency exits), but the interior of the plane would feel more spacious and less claustrophobic. You also wouldn’t risk hitting your head when you stood up.
- Airplanes should have reasonably priced (ideally free) wi-fi and outlets in each row. There’s no way it costs anywhere near the $35 per flight, per person GoGo Inflight absurdly charges.
- Treat airports as public squares — invest in their design as well as their functionality. Incorporate outdoor spaces, green spaces. Attract decent restaurants, bars, cafes. People unencumbered by bags and not rushing to wait in line to board 40 minutes early will be more able to enjoy the environment and arriving travelers will immediately get a good impression and be put at ease.
- Do not advertise mileage rewards from credit cards or other sources unless those miles are actually redeemable at a reasonable rate and on routes and times someone would actually fly. As it stands those programs are borderline fraud — you can fly a middle seat one way from NY to LA for 30,000 miles at 6 am, but that’s not why I signed up for the credit card. If mileage plans are too costly, scrap them.
I can anticipate some objections to these ideas, and I’ll address each one in turn.
1. This would cost too much money.
My suggestions would require a significant initial investment, but it would be but a small piece of the infrastructure outlay that’s sorely needed — and on which our current president campaigned — and it would create jobs. Moreover, it would save travelers tens of millions of hours per year. At $15 per hour — it would pay for itself in short order. (And taxpayers’ squandered time and awful experiences are exactly what their tax dollars should go toward remediating.)
2. It’s too much of a security risk.
Airport security is incredibly flawed right now, as tests repeatedly show. You can get prohibited items through security easily already, and it’s likely the screening process is mostly “security theater,” i.e., just for show. But to the extent this is a serious concern, the newer system might actually improve security due to improved technology spurred by the infrastructure investment. Better detection could be designed into the new system, rather than relying on bored-out-of-their-mind humans to scan endlessly through people’s toiletries expecting to find nothing for hours and days on end.
Moreover, airport security has never actually been an issue in the US. Even on 9/11, the flimsy security worked well — the hijackers managed only boxcutters on the tragically ill-fated flights, not guns or bombs. In other words, that was a failure of government intelligence, not one of airline security even when no one took his shoes off or had to worry about how many ounces of liquid was in his shampoo bottle.
3. I like free carry-ons because it saves me from waiting at the baggage claim.
Great, then pay extra for that. When something you like individually causes collective harm, there needs to be a cost for it. That we have the opposite system where people doing what would make everyone else’s experience easier and better have to pay is perverse.
The bottom line — the current state of air travel both in the US and Europe is unacceptable*. We cannot have a system in which everyone participating despises it and simply pretend it’s an inevitable hassle about which we’re powerless to do anything. The central issue is the dehumanizing** lack of respect for travelers’ time and experience. It’s time to change our priorities and take care of the human beings for whom airports and air travel exist.
*I haven’t even touched on the awful state of flights themselves with cramped seats, small, dirty rest rooms, bad food and exorbitant fees to change your itinerary. That’s because I wanted to focus mostly on the airport/government side over which the public has ownership, and fixing the overall economics of air travel is probably more difficult than getting airlines to reverse their checked-bag fee policies.
** This article was written in March of 2017, and little did I know how much more dehumanizing things would get during covid.
-
 @ 6ad3e2a3:c90b7740
2024-09-10 08:21:48
@ 6ad3e2a3:c90b7740
2024-09-10 08:21:48I’ll write a separate Week 1 Observations later, but I wanted to dedicate this space solely to mourning my Circa Survivor entry.
Circa Survivor costs $1000 to enter and has a $10M prize for the winner, usually split by several as things get down to the wire. Three years ago, when the prize was $6M Dalton Del Don and I — the first time we ever entered — made it to the final 23 in Week 12. The value of our share was something like $260K at that point, but we got bounced by the Lions who beat the 12-point favored Cardinals and took home nothing.
When you enter a large survivor pool, the overwhelming likelihood is you’ll meet this fate at some point, whether in Week 1 or 12. So it’s not really the loss that’s painful, so much as not getting to live and die each week with a chosen team. You lose your status as “the man in the arena whose face is marred by dust and sweat and blood” and become just an observer watching and commentating on the games without the overarching purpose of surviving each week.
This year was also different due to the lengths to which I went to sign up. It’s not just the $1000 fee, it’s getting to Vegas in person, the $400 in proxy fees (you need locals to input your picks for you if you don’t live there), the $60 credit card fee, the $200 crappy hotel I booked at the last minute, the flights (one of which was cancelled due to heat), the rental car that necessitated, the gas, getting lost in the desert, the entire odyssey while sick and still jet-lagged in 122-degree heat.
But it’s not about the money, and it’s not even about the herculean effort per se, but the feeling and narrative I crafted around it. I was the guy who got this done. I flew from Portugal to San Francisco for 12 hours, two days later from SF to Palm Springs to help my 87-YO uncle with his affairs, improvised to get from Palm Springs to Vegas, which took six hours due to road closures, signed up for the contests, made the flight back to San Francisco, flew to Denver at 7 am the next day, took my daughter the Rockies game in the afternoon and then on to Boulder the following day. Maybe that’s not so impressive to some of you, but for me, an idle ideas person, a thinker, observer, someone who likes to express himself via a keyboard, it was like Alexander the Great conquering Persia.
And it’s not only about that smaller mission, or the narrative I crafted around it, but a larger one which was to bring sports content to nostr which I vowed to do before the summer which is why I felt I had to make the effort to get to Vegas to sign up for the contests, to have sufficient skin in the game, to have something real about which to write.
And I got the idea to do this seriously because Heather wrote a guide to Lisbon which I posted on nostr, and a few prominent developers there were surprisingly excited about getting that kind of quality content on the protocol. And I thought — if they’re this excited about a (very in-depth) guide to one particular city in Europe, how much more value could I create posting about a hobby shared by 50-odd million Americans? And that thought (and the fact I had to go to Palm Springs anyway) is what set me off on the mission in the first place and got me thinking this would be Team of Destiny, Part 2, only to discover, disappointingly, it’s real destiny was not to make it out of the first week.
. . .
While my overwhelming emotion is one of disappointment, there’s a small element of relief. Survivor is a form of self-inflicted torture that probably subtracts years from one’s life. Every time Rhamondre Stevenson broke the initial tackle yesterday was like someone tightening a vice around my internal organs. There was nothing I could do but watch, and I even thought about turning it off. At one point, I was so enraged, I had to calm down consciously and refuse to get further embittered by events going against me. Mike Gesicki had a TD catch overturned because he didn’t hold the ball to the ground, The next play Tanner Hudson fumbled while running unimpeded to the end zone. I kept posting, “Don’t tilt” after every negative play.
There’s a perverse enjoyment to getting enraged about what’s going on, out of your control, on a TV screen, but when you examine the experience, it really isn’t good or wholesome. I become like a spoiled child, ungrateful for everything, miserable and indignant at myriad injustices and wrongs I’m powerless to prevent.
At one point Sasha came in to tell me she had downloaded some random game from the app store on her Raspberry Pi computer. I had no interest in this as I was living and dying with every play, but I had forced myself to calm down so much already, I actually went into her room to check it out, not a trace of annoyance in my voice or demeanor.
I don’t think she cared about the game, or about showing it to me, but had stayed with her friends most of the weekend and was just using it as an excuse to spend a moment together with her dad. I scratched her back for a couple seconds while standing behind her desk chair. The game was still going on, and even though I was probably going to lose, and I was still sick about it, I was glad to have diverted a moment’s attention from it to Sasha.
. . .
In last week’s Survivor post, I wrote:
What method do I propose to see into the future? Only my imagination. I’m going to spend a lot of time imagining what might happen, turn my brain into a quantum device, break space-time and come to the right answers. Easier said than done, but I’m committed.
It’s possible I did this, but simply retrieved my information from the wrong branch of the multiverse. It happens.
. . .
I picked the Bengals knowing full well the Bills were the correct “pot odds” play which is my usual method. Maybe when the pot-odds are close, I might go with my gut, but they were not especially close this week, and yet I still stuck with Cincinnati because they were the team I trusted more.
And despite it being a bad pick — there are no excuses in Survivor, no matter what happens in the game, if you win it’s good, and lose it’s bad — I don’t feel that badly about it.
I regret it only because I wish I were still alive, but it was my error. I went with what I believed, and it was wrong. That I can live with 100 times better than swapping out my belief for someone else’s and losing. Had I done that I’d be inconsolable.
. . .
I won’t let the Survivor debacle undermine my real mission to bring sports to nostr. Team of Destiny 2 would have been a compelling story, but it was never essential. After all, my flight was cancelled and I had to improvise, so now my Survivor entry is cancelled, and I’ll have to improvise again. The branch of the multiverse where the Bengals won didn’t give me the information I wanted, but maybe it was what I really needed to know. That I am the man in the arena yet, the battle was ever against myself, and for a brief moment, while my team was losing, I prevailed.
-
 @ 862fda7e:02a8268b
2024-09-10 01:32:05
@ 862fda7e:02a8268b
2024-09-10 01:32:05I have a lot of dreams where I'm playing a claw machine and just winning a ton of toys. One of the best clawe machine dreams is where I come across claw machines with large toys as prizes, it had carnival toys from the 70's-80's as prizes. Unfortunately, the claw machine was non functional as it was pretty old. In most of these dreams I am winning an endless amount of toys, so much so that the prize chute becomes full with toys. In real life, they rig claw machines. Often times, the owners of the machines set it so they must meet a certain "pay out" before the claw will actually grip a prize. So while you might have a great aim on getting the claw around a toy, it won't grip it firmly enough until enough money has been inserted to meet that payout. Some claw machines will do a fake out, where it will grab the prize, then once the claw gets back to the top of the machine, it will drop the prize. It's to trick you that it got it, but it actually didn't. Sadly, claw machines are worthless to play these days. It's become highly monetizable and impossible to win. I'm great at claw machines, but it's just a matter of luck with hitting the payout these days.
-
 @ 129f5189:3a441803
2024-09-09 23:28:41
@ 129f5189:3a441803
2024-09-09 23:28:41Project 2025, outlined in the Heritage Foundation's "Mandate for Leadership" document, serves as a fundamental guide for the next Republican administration. Despite Trump's extensive denial, in today's material, we will explore the deepening and continuation of many policies already employed during his first term. The idea is that this material will serve as a reference document to consult and verify what was actually implemented and/or followed. https://image.nostr.build/e3b89d71ff929258e5d9cb0b5ca8709a381598f43d8be4b17df3c69c0bc74d4a.jpg This document presents proposals for the foreign policy and the State Department of the United States of America, as well as the strategy with its political partners and adversaries. We will also address the U.S. government's communication strategy abroad. https://image.nostr.build/a4250b786f611b478aaf0be559427ad7d4296fbcacb2acc692c7f0d7eb06b0dd.jpg Reorienting U.S. Foreign Policy: Proposals for a Conservative Future In the chapter "The Department of State" from the "Mandate for Leadership," also known as "Project 2025," Kiron K. Skinner presents a comprehensive plan to reform U.S. foreign policy under a conservative administration. Skinner, a renowned foreign policy expert and former Director of Policy Planning at the U.S. State Department, outlines global threats and offers specific recommendations to strengthen the U.S. position on the international stage. Below, we present a detailed analysis of the proposals, emphasizing direct quotes and explanations of the key points discussed. https://image.nostr.build/278dcd7ef0439813ea35d0598319ee347f7a8cd7dfecac93be24ffdd0f6ecd04.jpg History and Structure of the State Department Since its founding in 1789, the State Department has been the primary diplomatic channel of the U.S. With nearly 80,000 employees and 275 posts around the world, it faces significant structural challenges. Skinner highlights that "the biggest problem of the State Department is not a lack of resources," but the belief that it is "an independent institution that knows what is best for the U.S." (Skinner). The scholar and former Director of Policy Planning at the U.S. State Department during the Trump administration emphasizes these points, considering the difficulty in accepting a conservative international approach by State Department employees (the equivalent of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in other countries). https://image.nostr.build/049939926793e86000b300b9a962dc0ae7e271d9a607ae36d8cb08642adf4174.jpg Political Leadership and Bureaucratic Support To align the State Department with presidential priorities, Kiron suggests appointing political leaders who are committed to the president's vision. "Leadership should include political appointees in positions that do not require Senate confirmation, including senior advisors and deputy secretaries" (Skinner). Furthermore, she emphasizes the importance of training and supporting these appointees to ensure effective coordination between agencies. https://image.nostr.build/6ed704cc9612aa6489e048b143f1e489c1f8807fdf2ab011b4ba88e4a1e3619a.jpg Global Threats to the U.S. The document identifies five countries that pose significant threats to the security and prosperity of the U.S.: China, Iran, Venezuela, Russia, and North Korea. 🇨🇳 China: Skinner argues that China represents an existential threat. "The U.S. needs a strategic cost-imposing response to make Beijing's aggression economically unviable" (Skinner). Additionally, she emphasizes that the issue is not with the Chinese people, but with the communist dictatorship that oppresses them: "As with all global struggles against communist and other tyrannical regimes, the issue should never be with the Chinese people, but with the communist dictatorship that oppresses them" (Skinner). https://image.nostr.build/e707273f1d08bdc4187123a312bd116695b5f603066e11ad30fcef4466730b6b.jpg 🇮🇷 Iran: The Obama administration, through the 2015 nuclear deal, provided the Iranian regime with a "crucial cash bailout" (Skinner). Kiron criticizes this approach, asserting that the U.S. should support the Iranian people in their demands for a democratic government. "The correct policy for Iran is one that recognizes that it is in the U.S. national security interests and the human rights of Iranians that they have the democratic government they demand" (Skinner). https://image.nostr.build/cda7d29a62981f59ad8d77362b3867b552f190c8d7e0e8d9233cb7c1d1d0309e.jpg 🇻🇪 Venezuela: Under the regimes of Hugo Chávez and Nicolás Maduro, Venezuela has transitioned from a prosperous country to one of the poorest in South America. Skinner suggests that the U.S. should work to contain Venezuelan communism and support its people. "The next administration should take steps to put Venezuela's communist abusers on notice and make progress in helping the Venezuelan people" (Skinner). https://image.nostr.build/f53e12564cae74d4b50c24b0f3752dd2c53b70bd1c00a16df20736fb8588417d.jpg 🇷🇺 Russia: The war between Russia and Ukraine divides opinions among conservatives, and the document considers three lines of action. Some advocate continuing support for Ukraine, while others believe that such support does not serve U.S. security interests. "The conservative approach rejects both isolationism and interventionism, first asking: What is in the interest of the American people?" https://image.nostr.build/8fedaf77129f4801f4edb8b169b2ac93a3e518b8bf3642b3abc62575b5435fa3.jpg One conservative school of thought believes that "Moscow's illegal war of aggression against Ukraine represents major challenges to U.S. interests, as well as to peace, stability, and the post-Cold War security order in Europe" (Skinner). This view advocates for continued U.S. involvement, including military and economic aid, to defeat Russian President Vladimir Putin and return to pre-invasion border lines. Another conservative school of thought argues that U.S. support for Ukraine is not in the interest of U.S. national security. According to this view, "Ukraine is not a member of the NATO alliance and is one of the most corrupt countries in the region" (Skinner). It is argued that the European nations directly affected by the conflict should help defend Ukraine, but the U.S. should seek a swift end to the conflict through a negotiated settlement. https://image.nostr.build/22db3d0e79340c1d62344a2b8a3bfddbe4d5bd923cf77d70cfbf5ebf73e4db3e.jpg A third conservative viewpoint avoids both isolationism and interventionism, proposing that "each foreign policy decision should first ask: What is in the interest of the American people?" (Skinner). From this perspective, continued U.S. involvement should be fully funded, limited to military aid while European allies address Ukraine's economic needs, and must have a clear national security strategy that does not endanger American lives. https://image.nostr.build/939fea0bb5c69f171a3da1073e197edcff23a600430b3bc455f6d41bc8a0319f.jpg Although not stated explicitly, I believe this third viewpoint is the one Kiron Skinner desires, as she considers American intervention important but advocates for balancing the costs of the war with its partners in the European Union and NATO. https://image.nostr.build/d1d0c7fb27bfc5dd14b8dde459b98ed6b7ca2706473b2580e0fbf5383f5a9c10.jpg 🇰🇵 North Korea: North Korea must be deterred from any military conflict and cannot be allowed to remain a de facto nuclear power. "The U.S. cannot allow North Korea to remain a de facto nuclear power with the capability to threaten the U.S. or its allies" (Skinner). https://image.nostr.build/95febb04f6d2e0575974a5e645fc7b5ec3b826b8828237ccc1f49b11d11d6bce.jpg Detailed Policy Proposals Refugee Admissions: The Biden administration has caused a collapse in border security and internal immigration enforcement, according to Skinner. She argues that the U.S. Refugee Admissions Program (USRAP) should be resized. "The federal government should redirect screening and verification resources to the border crisis, indefinitely reducing the number of USRAP refugee admissions until the crisis can be contained" (Skinner). https://image.nostr.build/a5740b33842e47b9a1ab58c7b72bd6514f9b6ffbb18706deed1445c59236bc0d.jpg Corporate Collaboration with China: Skinner criticizes the collaboration of companies like BlackRock and Disney with the Chinese regime, noting that "many are invested in an unwavering faith in the international system and global norms," refusing to acknowledge Beijing's malign activities. She emphasizes that the real issue is the communist dictatorship that oppresses the Chinese people, not the Chinese citizens themselves (Skinner). https://image.nostr.build/05a3c787f144c4519c2ee8a4b22e64b8729842819ace4b439c849ef70ecd60b4.jpg Fentanyl and Mexico: The trafficking of fentanyl, facilitated by Mexican cartels in collaboration with Chinese precursor chemical manufacturers, is a critical problem. "Mexican cartels, working closely with Chinese manufacturers of fentanyl precursor chemicals, are sending this drug to the U.S., causing an unprecedented lethal impact" (Skinner). The next administration should adopt a firm stance to halt this public health crisis. https://image.nostr.build/59e32aeef5dabab3344a94a3e415d57fed91fece8bc3c5f068e9f6f7d71f99bd.jpg Re-hemispherization of Manufacturing: Kiron proposes that the U.S. promote the relocation of manufacturing to partner countries such as Mexico and Canada. "The U.S. should do everything possible to shift global manufacturing to Central and South American countries, especially to move it away from China" (Skinner). This would improve the supply chain and represent a significant economic boost for the region. https://image.nostr.build/5d5d7d792f1c94eb6e2bd7a4b86c43236765719e183be8ba8e00ed7dd07eca66.jpg Abraham Accords and a New “Quad”: Skinner suggests that the next administration should expand the Abraham Accords to include countries like Saudi Arabia and form a new security pact in the Middle East that includes Israel, Egypt, Gulf states, and possibly India. "Protecting the freedom of navigation in the Gulf and the Red Sea/Suez Canal is vital for the global economy and, therefore, for U.S. prosperity" (Skinner). https://image.nostr.build/c87cd99cb3ea2bef40e9d1f1fea48b0c9f9f031f3077fff658f15f850e7b8589.jpg Policy for Africa: The U.S. strategy for Africa should shift focus from humanitarian assistance to economic growth and countering China’s malign activities. "Development assistance should focus on fostering free market systems and involving the U.S. private sector" (Skinner). She also highlights that African nations are opposed to the imposition of policies such as abortion and LGBT lobbying. https://image.nostr.build/44df42f32e61c14786ac46c231d368b14df4dc18124a0da458e8506f917302f2.jpg Relations with Europe and Asia Europe: The U.S. should demand that NATO countries increase their contributions to defense. "The U.S. cannot be expected to provide a defense umbrella for countries that do not contribute adequately" (Skinner). Additionally, urgent trade agreements should be pursued with the post-Brexit United Kingdom. https://image.nostr.build/6c013bacfa9e6505ad717104d9a6065f27664a321dd2c3d41fd7635258042d2f.jpg Asia: The withdrawal of U.S. troops from Afghanistan was humiliating and created new challenges. Skinner emphasizes the importance of India as a critical partner to counterbalance the Chinese threat and promote a free and open Indo-Pacific. Cooperation within the Quad, which includes the U.S., India, Japan, and Australia, is essential to this strategy. "The priority is to advance U.S.-India cooperation as a pillar of the Quad" (Skinner). https://image.nostr.build/1cc988b2f70d855c9676d7e38ffdb23564d04ad6333a8d256698f416a1c6704e.jpg International Organizations Skinner criticizes the corruption and failure of the World Health Organization (WHO) during the Covid-19 pandemic. "The next administration should end blind support for international organizations and direct the Secretary of State to initiate a cost-benefit analysis of U.S. participation in all international organizations" (Skinner). She also supports the “Geneva Consensus Declaration on Women’s Health and Protection of the Family,” which is against abortion, and believes that the U.S. government should not fund international organizations that promote abortion (Skinner). https://image.nostr.build/0b583511fef16d68736804fae2f15850eb5c803af01f006a3fe10cdbc583f48c.jpg Conclusion Skinner’s document provides a detailed vision for reorienting U.S. foreign policy under a conservative administration, with an emphasis on ensuring that the State Department serves the national interests defined by the president. With these guidelines, the next administration has the opportunity to redefine the U.S. position on the global stage, promoting security, prosperity, and freedom. https://image.nostr.build/697522745c5947cd4384cdd302b531ee98ce5d59a5d72de0b4f3a52c9abd4821.jpg
-
 @ 129f5189:3a441803
2024-09-09 23:23:45
@ 129f5189:3a441803
2024-09-09 23:23:45Project 2025, outlined in the "Mandate for Leadership" document by the Heritage Foundation, is a crucial guide for the next Republican administration. Crafted by conservative intellectuals from major American think tanks, this plan promises to have significant influence on a potential Donald Trump administration, even if he does not formally acknowledge it as his government plan. https://image.nostr.build/443d69c16dc32659be2353ce48d170d397e0ee682ffc3c4108df3047fd54472d.jpg This document presents proposals to depoliticize government agencies, increase efficiency, and reduce costs, aiming to dismantle the Deep State and combat the Woke agenda associated with the Democratic Party. https://image.nostr.build/06de3f0de3d48e086f47d0418d30e32cbfe0d88f452a93706987b7394458952d.jpg Dissolution of the DHS and Redistribution of Functions The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) was established in 2002 in response to the September 11 attacks, with the goal of consolidating various agencies responsible for domestic security under a single command. The DHS includes agencies such as FEMA, TSA, ICE, and CISA. Project 2025's proposal to dissolve the DHS and redistribute its functions to other agencies aims to address excessive bureaucracy and a lack of cohesion, arguing that centralization has failed to effectively integrate its diverse missions. https://image.nostr.build/ffca8d274914b725183b8fb19162c1b63f4d987c24e598f2eca88901d4a1a43c.jpg Impact on the Democratic Deep State: The dissolution of the DHS would pose a significant threat to the Democratic Deep State, as it would redistribute the power concentrated in a single entity across multiple other agencies, making it more difficult to politicize and centralize control over domestic security operations. This decentralization would reduce the ability to use the DHS as a political tool against opponents. https://image.nostr.build/1597e3b88572fe8aae7ce67cdaf975a873cf8bc68f76d59cb4253ad1520fc7bc.jpg Primary Recommendations Combining Immigration Agencies: Merge U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), the Office of Refugee Resettlement (ORR) of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and the Executive Office for Immigration Review (EOIR) of the Department of Justice (DOJ) into a new autonomous border and immigration agency. https://image.nostr.build/58eef4f2eca0ed2400261ec878c1dba2ca4bca519a16751b1fb7abd45da2906b.jpg Privatization of the TSA: Privatize the Transportation Security Administration (TSA), drawing inspiration from Canadian and European models, to reduce costs and improve service for travelers. Division of the Secret Service (USSS): The U.S. Secret Service (USSS), responsible for protecting national leaders and investigating financial crimes, would be divided. The protective element would be transferred to the Department of Justice (DOJ), while the financial investigations element would be moved to the Department of the Treasury. https://image.nostr.build/0a065cdbf158db4bc17b9aacd4af5a94029004caaa152eebf2c557042b08a641.jpg Impact on the Democratic Deep State: The division of the USSS would significantly weaken centralized control over protection and financial investigations, making it more difficult to use these functions for political purposes. Transferring the protective element to the DOJ and the financial investigations element to the Treasury would complicate efforts for any group or party to manipulate these crucial government functions for partisan objectives. https://image.nostr.build/1597e3b88572fe8aae7ce67cdaf975a873cf8bc68f76d59cb4253ad1520fc7bc.jpg Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Established in 2018, CISA is a federal agency responsible for protecting the U.S. critical infrastructure from cyber threats. CISA's mandate includes ensuring cybersecurity for sectors such as energy, transportation, and healthcare, and it collaborates with public and private entities to strengthen the country’s cyber resilience. Criticisms and Restructuring Proposals: Project 2025 strongly criticizes CISA for deviating from its original mission and being used as a political tool for censoring speech and influencing elections. The proposal is to transfer CISA to the Department of Transportation (DOT) and return the agency to its statutory focus. https://image.nostr.build/8bfb4a45053de96a775f67e3e1b83a44d9a65fee4705e3b16d3359bd799b8af2.jpg Review of Executive Order 12333 Executive Order 12333, issued in 1981, sets guidelines for U.S. intelligence activities, including the collection, analysis, and dissemination of information. Project 2025 proposes a review of this order to ensure that intelligence agencies are not used for political purposes but are focused on protecting national security. Objectives of the Review: Prevent Abuse: Ensure that intelligence collection is conducted legally, without being used to target political opponents. Ensure Impartiality: Reaffirm that intelligence operations must be conducted impartially, with a sole focus on the country's security. https://image.nostr.build/90d31cb35a33048d311716df2fbc65c97bd4c1972977e266133654404393fca0.jpg Reforms in Public Service Facilitation of Public Employee Dismissal: Project 2025 emphasizes the need to simplify the process for dismissing public employees who do not perform their duties impartially or who promote specific political agendas. Performance Evaluations: The document highlights the importance of merit-based compensation, stating that performance evaluations are only effective when tied to real consequences. Research indicates that 90% of major private companies in the U.S. use a merit-based pay system linked to evaluations. However, in the federal government, compensation remains largely based on seniority, despite efforts to adopt merit-based pay. https://image.nostr.build/1b858fd7b2a23c3c65c0677d3e69c44976721bbdcbe7facf4682ba3371562cff.jpg Inclusion of Employees Aligned with Conservative Values: Aligned Hiring: Establish mechanisms to hire public employees who share conservative values, ensuring that the policies and practices of agencies are consistent with the principles endorsed by the administration. https://image.nostr.build/ddbf5c59e7bb479998433991347f9d301dd117fbca0edb0f94e98fcac90b2974.jpg Controversial Cases and Politicization: Hunter Biden Laptop Case: Project 2025 harshly criticizes the FBI and the Department of Justice, accusing them of acting in a biased and politically motivated manner. The authors suggest that the agency is intimidating parents who protest by labeling them as "domestic terrorists," while simultaneously suppressing politically unfavorable speech under the guise of combating "disinformation." Furthermore, the critique highlights that the FBI is alleged to be neglecting violent attacks on pregnancy centers and violations of laws prohibiting attempts to intimidate Supreme Court justices. The criticism intensifies with allegations that the FBI interfered in domestic elections and engaged in propaganda operations, specifically citing the purported Russian collusion conspiracy in 2016 and the suppression of the Hunter Biden laptop case in 2020, which is seen as a threat to the Republic. https://image.nostr.build/e4f571a14102a939164465498bef514379ec0443e71a58e12f50c518e00570c6.jpg Politicization of the FBI: Election Interference: Russia Hoax and Trump, Suppression of Hunter Biden’s Laptop, and Big Tech Collusion. Revelations about the FBI’s role in the 2016 "Russia Hoax" and the suppression of Hunter Biden’s laptop in 2020 suggest that the agency may have strayed from its impartial duties. These actions indicate concerning politicization, where the agency appears to have been used to influence the political landscape in favor of certain interests. This includes collaboration between the FBI and Big Tech companies to control discourse. https://image.nostr.build/5dcd45fcec939b782d29d8d2e3d3b45244c525b5dbd3240f1629a4632e390a86.jpg Comprehensive Review of FBI Investigations: It is crucial to conduct an immediate and thorough review of all significant investigations and activities within the FBI, terminating those that are illegal or contrary to national interests. This step is essential for restoring public trust in the FBI. A public report on the findings of this review could enhance transparency and confidence. https://image.nostr.build/df98e2c6aff123d806187eab13d24a3ebb30a87df1f44cf57be97dc5624fff88.jpg Structural Reorganization: Align the FBI within the Department of Justice (DOJ) according to its purposes of national security and law enforcement. The agency should be under the supervision of the Assistant Attorney General for the Criminal Division and the National Security Division, ensuring that the FBI does not operate as an independent entity but is instead subordinated to the DOJ’s directives. https://image.nostr.build/0d1c0015c6b67a8afc2dd1595357ea571fcd5a9d83829065f49f9b60cf553eb0.jpg Prohibition on Policing Speech: Prohibit the FBI from engaging in activities related to combating "disinformation" or "misinformation" disseminated by Americans who are not linked to plausible criminal activities. The Constitution, through the First Amendment, prohibits the government from policing speech, ensuring a healthy public debate without governmental intervention. All these measures represent a significant attack on the "Deep State" within American institutions. These public policies have been considered a dictatorial threat by many sectors of the American press. However, the real issue should be the politicization of unelected bureaucrats by a political faction. https://image.nostr.build/9a44b19d15d53314f89528c1d89e2f637030ea18d8907a6a8c4e27d07064b8ec.jpg Combating Woke Culture in the Intelligence Community Future leadership of the Intelligence Community (IC) needs to implement a plan to replace the "woke" culture and identity politics that have spread throughout the federal government. The goal is to restore traditional American values such as patriotism, racial impartiality, and job competence, which have been replaced by advocacy for "social justice" and identity politics. https://image.nostr.build/7929dca5e36273c8e751f36d6ca6229f362e30792bce735f10be7e5d8581af5f.jpg Final Considerations The Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025 is not merely an administrative reform plan; it is a manifesto of resistance against the Washington status quo. The proposals aim to dismantle established power structures, eliminate politicization, and combat the Woke agenda. If implemented, this plan would profoundly impact how the U.S. government operates, promoting a more efficient, limited government aligned with conservative principles. Threat to the Democratic Deep State: A potential new administration under Donald Trump represents an existential threat to the Democratic Deep State entrenched in American institutions. The dissolution of the DHS, depoliticization of intelligence agencies, division of the Secret Service, review of Executive Order 12333, privatization of the TSA, and the hiring of employees aligned with conservative values are all measures that would significantly weaken centralized control and the ability to use these institutions for political purposes. By dismantling concentrated power and promoting a more transparent and accountable government, Project 2025 aims to restore public trust and ensure that government agencies serve national interests rather than partisan ones. Of course, not all aspects of the plan may be implemented, but the prospect of several of these measures being enacted should be a cause for concern for the Democratic Deep State.
-
 @ 129f5189:3a441803
2024-09-09 23:11:19
@ 129f5189:3a441803
2024-09-09 23:11:19Precious metals have served as monetary backing for millennia, but this does not guarantee that gold is a safe investment or a good hedge against economic crises and monetary collapses. Since its last major rally in the 1980s, gold has been progressively demonetized. Those who acquired gold in the late 1980s will need to rely on a significant increase in demand or a supply shock for its price to rise by 561% and regain the purchasing power it had 40 years ago. https://image.nostr.build/dd5fec2b474ea34cd72ddf5781393b528e63a358d523c9428f3ba4649f4f42aa.jpg If you look at the purchasing power of $1 (green line), you'll see that the depreciation is even faster. This might create the impression that gold is a good store of value. But does the fact that something loses value more slowly amidst a general decline really make it a store of value? Unless the total demand for gold increases at the same rate as its supply has grown in recent years, the purchasing power of the metal is likely to decline. https://image.nostr.build/9f24f6cf37780fe851746057520064ed94acd96547be53bd341c9e15b8762773.jpg In other words, if you own an ounce of gold, that ounce will represent an increasingly smaller fraction of the total gold reserves, meaning you are being diluted. Additionally, one should also consider the cost and risk of storage, but that's another issue. If you don't want to compare the purchasing power of gold today with the 1980s, you can consider its value from 9 years ago. Between September 2011 and November 2015, the Fed printed approximately $2.8 trillion. This also provides a perspective on gold's depreciation relative to the significant monetary expansion during that period. https://image.nostr.build/822e0a861e16ca258e0427875a84b5c8e5420e51bcf65674b453b55ed78edefd.jpg In other words, the Fed expanded its monetary base by about 30% during that 4-year period. However, the price of an ounce of gold fell by 45% (from $1,900 to $1,057) over the same interval. A true store of value should protect against excessive money printing. In contrast, during that same period, Bitcoin appreciated by 8,500% (from $5 to $419). https://image.nostr.build/32a7ca39a6e69e2780f9ab49390c7b7380499fcfe54ae4ef693e6fc91686a41e.jpg Indeed, while it is interesting to note that this was the exact period when gold derivatives were launched on CME Group, it's important to remember that correlation does not imply causation. Many factors can influence the price of gold and Bitcoin, and establishing a direct causal relationship requires more detailed analysis. https://derivsource.com/2011/06/21/cme-group-announces-the-launch-of-three-new-short-term-gold-crude-oil-and-natural-gas-options-contracts/ In an asset where supply can only be physically verified, flooding the market with gold contracts could lead to significant issues. This might result in market manipulation, legal liabilities, fines, and potentially even imprisonment for those involved. Such actions can undermine the integrity of the market and lead to regulatory and legal consequences. https://www.cnbc.com/2018/11/06/ex-jp-morgan-trader-pleads-guilty-to-manipulating-metals-markets.html Over longer periods, gold has not functioned as a true "store of value" relative to the dollar for quite some time, despite recently returning to its price from 9 years ago. This suggests that, while gold may have periods of price recovery, it has struggled to maintain its value over extended horizons compared to fiat currencies. It's worth noting that before 1980, aluminum was valued higher than gold. This reflects how market dynamics and technological advancements can significantly impact the value of commodities over time. https://www.mgsrefining.com/blog/why-aluminum-is-no-longer-a-precious-metal/ While gold has been undergoing a gradual demonetization process since 1980, another asset appears to be experiencing the opposite—hyper-monetization. (See in red; don't be alarmed.) https://image.nostr.build/435a5369f778a7be727b50e4c6328cfc353240bf804e1ed69313b9a8e1233f7e.jpg With the advent of Bitcoin, you believe that gold will continue on the same path as silver since the end of the bimetallic standard in 1853: a prolonged process of demonetization, with increasing volatility and reduced liquidity. https://image.nostr.build/5b9c8bfdb09e51d639e380df160c98beb9ee1d917ea13d28ef67711cfa5f8086.jpg Since 1913, the dollar has lost 97% of its purchasing power. Over the same period, the gold supply has increased significantly. Since 1980, gold has lost about 82% of its purchasing power. Given that the dollar is used as the unit of account and gold's liquidity is measured in dollars, these changes reflect the complex interaction between the currency and the precious metal. The U.S. is by far the country with the largest gold reserves in the world and is also the fourth-largest miner of the metal. Additionally, the country controls and issues the currency that serves as the unit of account for gold and has the highest liquidity in global trade. Is gold easy to transport? Is it simple to verify its supply and authenticity? Is it practical to store? Is its industrial utility significant? Can it be disrupted? And what about the continuous increase in its supply? These are important questions to consider. In my humble opinion, it will not be the dollar or fiat currencies that will suffer the most from the existence of Bitcoin, but rather the market cap of gold. https://image.nostr.build/61dddefabc4b69f784631a3294bdd978e3411bba40fb52d585e13b48002389fe.jpg
-
 @ e83b66a8:b0526c2b
2024-09-09 20:30:30
@ e83b66a8:b0526c2b
2024-09-09 20:30:30We have a confession to make. NOSTR is not perfect, we are still building. No client you use does everything you want it to, and everything it does is imperfect.
Therefore, I strongly advise you to run multiple clients.
On iPhone, I run: Damus: https://nostrapps.com/damus Primal: https://primal.net/downloads Nostur: https://nostrapps.com/nostur
On Android I run: Primal: https://primal.net/downloads Amethyst: https://nostrapps.com/amethyst
On desktop I run: Primal: https://primal.net/downloads noStrudel: https://nostrapps.com/nostrudel
Also, because I run a node (Umbrel & Start9), I self host noStrudel on my own relay.
If you haven’t taken the plunge to run a node, now might be a good time to think about it.
There are many, many options for clients, the “Social” section of https://nostrapps.com/
lists 23 currently.
Play with them, see what they do, if you’re a developer, you could even consider building or forking your own.
Have fun and realise we are building freedom tech, not just running it.
-
 @ e83b66a8:b0526c2b
2024-09-09 20:27:41
@ e83b66a8:b0526c2b
2024-09-09 20:27:41First,
Key management.
When you “created” your NOSTR account, what you actually created was a cryptographic key pair. This consists of a private key, which starts “nsec” and a public key which starts with “npub”.
As the names suggest, your “nsec” key is private and you should never reveal it to anyone. Your “npub” key is your public key, feel free to share that everywhere.
Your “npub” key is used by others to verify your identity, through the signature added to your messages. It is also used by others to encrypt private messages to you.
We don’t have perfect key management yet and because of the limitation of smart phones and various eco systems, it often becomes necessary for you to copy and paste your private key into apps in order to use them. This is less than ideal, but until we have ubiquitous cross platform key management devices, this situation will remain necessary.
For the moment, consider using software key management options, some of which are listed under “signers” here: https://nostrapps.com/
N.B. We do have projects like Seedsigner that provide more secure hardware key management, but this isn’t for the faint hearted:
Secondly,
Lightning wallets.
It is common for most people to link a Bitcoin Lightning wallet to their NOSTR profile
N.B. Your profile is stored on relays and signed by your private key, which is verified by others through your public key.
You are not tied to any specific wallet for sending payments (called zaps), but you do provide a specific incoming LN address for receiving payments. This could be something like a wallet of Satoshi Address i.e. “randomname@walletofsatoshi.com” or could you be your own node with a connection to it via “Nostr Wallet Connect” a free plugin that connects a lightning wallet.
Enabling this allows people to “zap” any posts or content or even send you payments directly at any time or for any reason. N.B. It is called freedom money for a reason….
It also allows you to send small micropayments to posts or people you like.
Thirdly,
Paid Services
As you go deeper into the NOSTR ecosystem, you’ll notice there is no advertising being pushed at you and there are no algorithms manipulating the content you receive. This is because there is no company behind NOSTR, it is a protocol. Because of this, while all the ecosystem is free to use and will remain so for the foreseeable future, most of it is run by enthusiastic volunteers or developers and incurs a cost to them. For that reason many of us choose to support these #devs by paying for services. This can also enhance our experience, giving our “npub” greater reach and discoverability.
I, for example choose to pay for the following services:
https://nostr.wine/ - 120,000 Sats for 2 years relay https://relay.tools/ - My own relay - https://nortis.nostr1.com/ 12,000 Sats a month https://nostr.build/ - Media storage - 69,000 Sats for 1 year
Total: 22,750 Sats per month Approx $15 per month
This is not strictly necessary, but I decided to support the various developers behind these projects.
Do not feel any pressure at this early stage to pay for any service, but if you enjoy the freedom NOSTR brings, you may want to consider supporting the projects that become important to you going forward.
-
 @ c11cf5f8:4928464d
2024-09-09 18:45:16
@ c11cf5f8:4928464d
2024-09-09 18:45:16originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/678432